- How To Install yum4 on Ubuntu 22.04
- What is yum4
- Install yum4 Using apt-get
- Install yum4 Using apt
- Install yum4 Using aptitude
- How To Uninstall yum4 on Ubuntu 22.04
- Uninstall yum4 And Its Dependencies
- Remove yum4 Configurations and Data
- Remove yum4 configuration, data, and all of its dependencies
- References
- Summary
- Как установить yum (dnf) в Debian Linux
- Введение
- Установка yum с помощью apt-get
- Установите yum с помощью apt
- Установка yum с помощью aptitude
- Как удалить yum в Debian
- How to Install YUM on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8
- Software Requirements and Conventions Used
- How to Use YUM on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8
- What is YUM on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 Really
- Is there a Difference?
- Conclusion
- Related Linux Tutorials:
- Installation and Configuration of Yum in Red Hat Linux 8
- Installing Yum to RHEL 8
- Manually Configuration
- Using External Software
How To Install yum4 on Ubuntu 22.04
In this tutorial we learn how to install yum4 on Ubuntu 22.04.
What is yum4
This is a transitional package. It can safely be removed.
There are three ways to install yum4 on Ubuntu 22.04. We can use apt-get , apt and aptitude . In the following sections we will describe each method. You can choose one of them.
Install yum4 Using apt-get
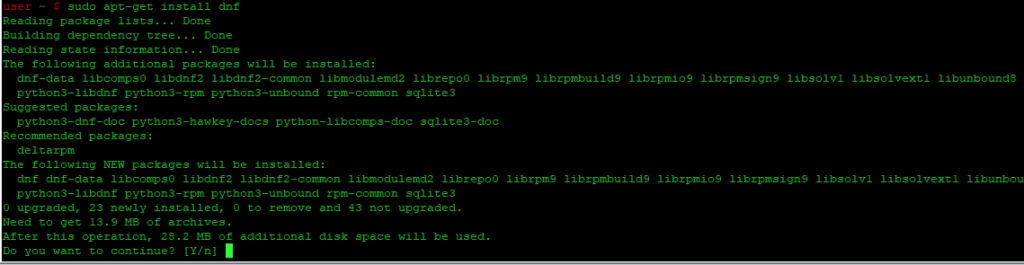
Update apt database with apt-get using the following command.
After updating apt database, We can install yum4 using apt-get by running the following command:
sudo apt-get -y install yum4 Install yum4 Using apt
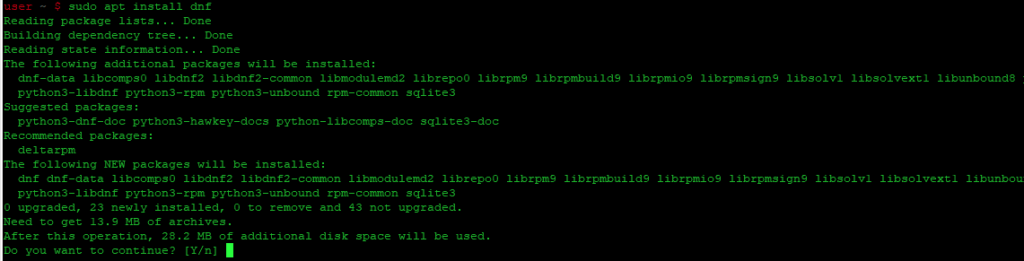
Update apt database with apt using the following command.
After updating apt database, We can install yum4 using apt by running the following command:
Install yum4 Using aptitude
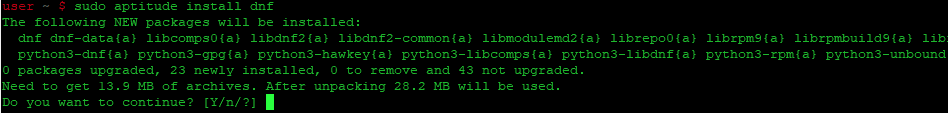
If you want to follow this method, you might need to install aptitude first since aptitude is usually not installed by default on Ubuntu. Update apt database with aptitude using the following command.
After updating apt database, We can install yum4 using aptitude by running the following command:
sudo aptitude -y install yum4 How To Uninstall yum4 on Ubuntu 22.04
To uninstall only the yum4 package we can use the following command:
Uninstall yum4 And Its Dependencies
To uninstall yum4 and its dependencies that are no longer needed by Ubuntu 22.04, we can use the command below:
sudo apt-get -y autoremove yum4 Remove yum4 Configurations and Data
To remove yum4 configuration and data from Ubuntu 22.04 we can use the following command:
Remove yum4 configuration, data, and all of its dependencies
We can use the following command to remove yum4 configurations, data and all of its dependencies, we can use the following command:
sudo apt-get -y autoremove --purge yum4 References
Summary
In this tutorial we learn how to install yum4 package on Ubuntu 22.04 using different package management tools: apt, apt-get and aptitude.
Как установить yum (dnf) в Debian Linux
yum — это расширенный интерфейс для rpm, в этом руководстве мы узнаем, как установить yum в Debian Linux.
Введение
Yum (Yellow dog Updater, Modified) — это автоматическая программа обновления и установки/удаления пакетов для систем rpm. Он автоматически вычисляет зависимости и определяет, что должно произойти для установки пакетов. Это облегчает обслуживание групп машин без необходимости вручную обновлять каждую из них с помощью rpm. .
- Множество репозиториев
- Простой конфигурационный файл
- Правильный расчет зависимостей
- Быстрая работа
- Поведение, совместимое с rpm
- Поддержка групп comps.xml, включая группы из нескольких репозиториев
- Простой интерфейс.
Есть три способа установить yum (dnf) на Debian. Мы можем использовать apt-get, apt и aptitude. В следующих разделах мы опишем каждый способ. Вы можете выбрать один из них.
Установка yum с помощью apt-get
Обновите базу данных apt с помощью apt-get, используя следующую команду.
После обновления базы данных apt мы можем установить yum с помощью apt-get, выполнив следующую команду:
Установите yum с помощью apt
Обновите базу данных apt с помощью apt, используя следующую команду.
После обновления базы данных apt мы можем установить yum с помощью apt, выполнив следующую команду:
Установка yum с помощью aptitude
Если вы хотите следовать этому методу, вам может потребоваться сначала установить aptitude, так как aptitude обычно не установлен по умолчанию в Debian. Обновите базу данных apt с помощью aptitude, используя следующую команду.
После обновления базы данных apt, мы можем установить yum с помощью aptitude, выполнив следующую команду:
sudo aptitude install dnf
Как удалить yum в Debian
Для удаления только пакета yum (dnf) мы можем использовать следующую команду:
Чтобы удалить yum и его зависимости, которые больше не нужны в Debian, мы можем использовать следующую команду:
sudo apt-get -y autoremove dnfЧтобы удалить конфигурацию и данные yum из Debian 10, мы можем использовать следующую команду:
Чтобы удалить конфигурацию yum, данные и все его зависимости, мы можем использовать следующую команду:
sudo apt-get -y autoremove --purge dnfHow to Install YUM on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8
Fedora made the change to DNF back with Fedora 22, but CentOS and RHEL have stayed with YUM, until now. RHEL has jumped to the next gen package manager, and that’s a good thing, but if you’re missing YUM or have scripts that rely on it, you’ll still have access to the old package manager. What’s even better, you don’t need to do anything extra.
In this tutorial you will learn:
- How to Use YUM on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8
- What is YUM on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8, Really
- Is there a Difference?
Software Requirements and Conventions Used
Software Requirements and Linux Command Line Conventions| Category | Requirements, Conventions or Software Version Used |
|---|---|
| System | RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 |
| Software | DNF/YUM |
| Other | Privileged access to your Linux system as root or via the sudo command. |
| Conventions | # – requires given linux commands to be executed with root privileges either directly as a root user or by use of sudo command $ – requires given linux commands to be executed as a regular non-privileged user |
How to Use YUM on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8
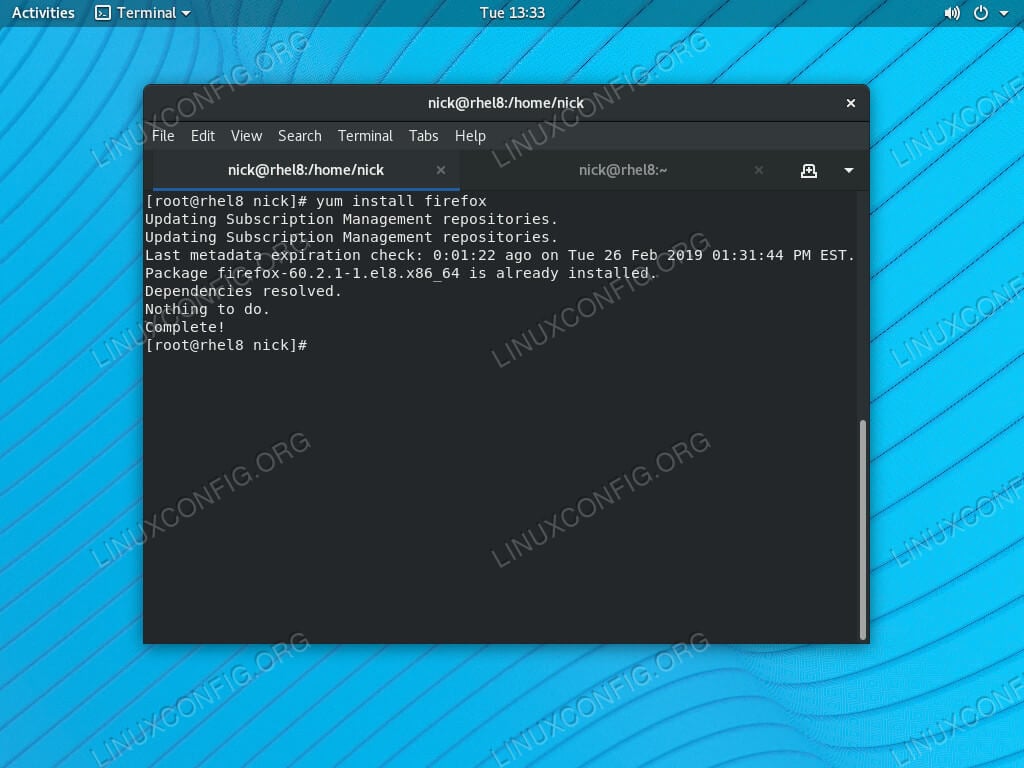
Open a terminal on your RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 system, and run the following command.
It worked, didn’t it? Try installing something with YUM, like you would on a RHEL 7 system.
It’s the same. Go ahead and try a few more commands. They should all behave exactly like on RHEL 7. Here’s the catch; YUM isn’t installed on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8. In fact, there isn’t even a package available for it. So, what’s going on?
What is YUM on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 Really
Red Hat have been making server operating systems long enough that change can go over like a lead balloon. So, they’ve done two things to ease the transition to DNF. First, they created a wrapper script to take the place of YUM and pass everything along to DNF. Take a look at the YUM executable to see what it’s about.
That’s all fairly straightforward, but why does it work so well? That has everything to do with DNF itself.
Is there a Difference?
The differences between DNF and YUM are mostly technical and exist below the surface. DNF was built to be backward compatible with YUM on the surface level. Syntactically, they’re nearly identical. In reality, DNF is just a new iteration of YUM with better dependency resolution, speed improvements, and better memory usage.
It’s entirely up to you. You can keep on using the yum command, or you can switch right over to dnf . There’s no need to change scripts right yet, and you can take your time acclimating.
Conclusion
There you have it! YUM already is installed on RHEL 8, sort of. You don’t need to do anything new, if you don’t want to. Switching to DNF to install packages is really simple, though, so try it out.
Related Linux Tutorials:
Installation and Configuration of Yum in Red Hat Linux 8
Yellowdog Updater Modifier sums as YUM and this is a PMT (Package Management Tool) for the RedHat Package Manager. YUM has been used for quite a long time. But, now in RHEL 8, we have a modest version of “yum” called “dnf” stands for Dandified YUM. Although both the commands work fine in Redhat 8 Linux but dnf is much faster, as some of the bugs have been removed.
Installing Yum to RHEL 8
Step 1: First move to the given location in RHEL 8 Linux CD or if you are using any virtual software then attach the iso or image file to the virtual machine and move to the location or folder below.
/run/media/root/RHEL-8-0-0-BaseOS-x86_64/BaseOS/Packages/
Step 2: Now open the terminal in the same folder where your rpm is present, and run the command given below.
Step 3: Here search for yum and you must get an rpm package, copy the name of the package.
rpm -i yum-4.0.9.2-5.el8.noarch.rpm # replace the name of yum to the copied name
Step 4: Now Type “yum” on the terminal and hit enter, if you see the output as below then yum has been installed.
Yum Can be Configured in 2 Ways 1. Manually 2. Using External Software/Program
Manually Configuration
Step 1: Go to
Here you will get some files with extension as .repo. You could edit these files or can create a file and add the repository URL to it. Step 2: Create a repository file
Step 3: Type the code and Save. Before this, you must check your BaseOS CD-ROM name and replace it by RHEL-8-0-0-BaseOs-x86_64 and do the rest of it the same.
[reponame1] # this is repository name baseurl=file:///run/media/root/RHEL-8-0-0-BaseOS-x86_64/AppStream #this is baseurl for the rhel 8 disk file gpgcheck=0 #this is to allow installation without any security check and delays. [reponame2] baseurl=file:///run/media/root/RHEL-8-0-0-BaseOS-x86_64/BaseOS gpgcheck=0
Using External Software
We can use external software or programs to configure yum for us. Two of these programs are epel and fusion. These create some repository files as we created manually and then add the baseurl for different software and programs for the respective version of Linux.
sudo dnf install --nogpgcheck https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/el/rpmfusion-free-release-8.noarch.rpm
installing fusion program
Configuring yum using external programs is the most suitable and used method in the community, as it has reduced the headache of dependencies( explained below). Why we really need YUM, DNF, APT-GET, and these kinds of software or programs? Let us take an example to understand this. Suppose a wedding is there and you are the person who has to organize everything in the marriage. There are lots of tasks like:
So all the work has to be done by you and only you, from invitation to decoration. If you want to send an invitation card then the first contact with the printing press and decide the color, shape, and all that, these things are called dependencies. To complete a task there is some more task to be done first. But what if, you hire someone to do this job. Then you just have to give the orders and the work will be done in no time, without worry. Similarly, yum, dnf and apt-get are hired software that does the work for the user, from installation to uninstalling the program and many more. This program has reduced the work of solving dependencies. Like if you want to install any software then these programs will install the most suitable software available according to your architecture. This is the big and short reason for the requirement of these kinds of programs.