- How can I open (launch) files using the terminal?
- 2 Answers 2
- Select the tool manually
- xdg-open
- How to open the file in bash
- Open file using Bash commands:
- Use of `cat` command:
- Use of `less` command:
- Use of `more` command:
- Open file using command-line editors:
- Use of vi editors:
- Use of nano editor:
- Open file using GUI text editor:
- Use of gedit editor:
- Use of geany editor:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- Fahmida Yesmin
- How to open a particular file from a terminal?
- 3 Answers 3
How can I open (launch) files using the terminal?
Objective: Open a text file and other types using the terminal. Let’s suppose I have a file named myFile.txt and I want to launch this file (open it, not sure how I’m supposed to say it), how can I do this? As I searched all I could find was articles about create and edit files or display the content in the terminal. Some of the failed attempts:
Hm, it’s not immediately obvious to me what you want to do with the file. If you don’t want to view or edit it, what exactly do you want to do with it? I’m only asking because your answer will help people recommend a particular program to you that will do what you want. (Typically, when one asks how to launch or open a file, they mean something like view or edit the contents.)
Alternatively, if the file is a program that you are trying to run or execute, you may be doing it correctly with ./myFile.txt , but you only need to set the file to be executable: chmod +x myFile.txt . Hope this helps.
Did you create myfile.txt in the first place or did something else create it? If you created it what program did you use to create it? This question might be an X-Y problem
2 Answers 2
xdg-open will try to guess your desktop environment and the file’s mime type and try to open it in the appropriate application:
Select the tool manually
Typically, when using the terminal window and command lines, you are expected to know which tool you want to use. I know that this can be difficult in the beginning, but there are several things you might want to do.
If you use a graphical file manager, there is
- a main tool (for the main task), that you start by left-double-clicking on the file’s icon.
- and often a few other tools (for other tasks), that you can select after right-clicking on the file’s icon.
The main tasks for a text file might be editing and viewing.
- In standard Ubuntu desktop there is gedit for these tasks.
- If you want only viewing in text mode, you can use less
- If you want to edit in text mode, you can use nano
So I suggest that you try
gedit file.txt less file.txt nano file.txt You mentioned some alternatives that do not work (because . )
This is typically used to run an executable file
This points to a file in the root directory /
cd myFile.txt cd ./myFile.txt cd /myFile.txt This changes the terminal window to the specified directory ( cd ‘change directory’ makes the terminal window look at the specified directory. You should specify a directory (not a file) after the cd command.)
eog «Eye of Gnome» is a viewer for picture files.
xdg-open
Until you know which tool to use, you can try with xdg-open . It will select a tool for you depending of the kind of file you are using. I would expect that it will select gedit for text files and eog for picture files (in standard Ubuntu desktop).
How to open the file in bash
The file is used to store the data permanently and use the data in any script when requires. A file can be opened for reading, writing, or appending. Many bash commands exist to open a file for reading or writing, such as `cat`, `less`, `more` etc. Any text editor can be used to open a file in bash. nano, vim, vi, etc., an editor is used to open a file from the terminal. Many GUI editors also exist in Linux to open a file, such as Gedit, Geany, etc. The file can be opened for reading or writing by using bash script also. The ways to open a file for various purposes have been shown in this tutorial.
Open file using Bash commands:
The uses of shell commands to open a file for creating or reading are shown in this tutorial. The uses of `cat`, `less`, and `more` commands have shown here.
Use of `cat` command:
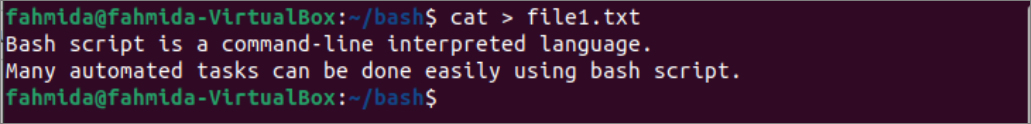
The `cat` is a very useful command of bash to create or display the file’s content. Any file type can be created easily and quickly by opening the file using the `cat` command with the ‘>’ symbol. Run the following `cat` command to open a file named file1.txt for writing. If the filename already exists, then the previous content of the file will be overwritten by the new content; otherwise, a new file will be created.
Add the following content to the file.
A bash script is a command-line interpreted language.
Many automated tasks can be done easily using a bash script.
Press Ctrl+D to finish the writing task. The following output will appear after creating the file.
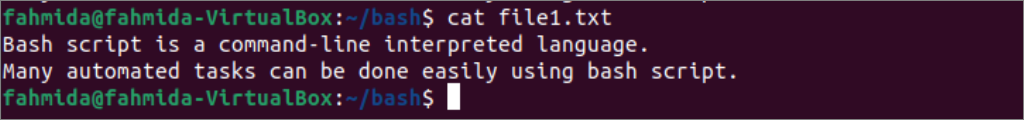
Now, run the following `cat` command to open the file.txt file for reading.
The following output will appear after executing the above command.
Use of `less` command:
The `less` command is used to open a file for reading only. It is mainly used to read the content of the large file. The user can move backward or forward through the file by using this command. It works faster than other text editors.
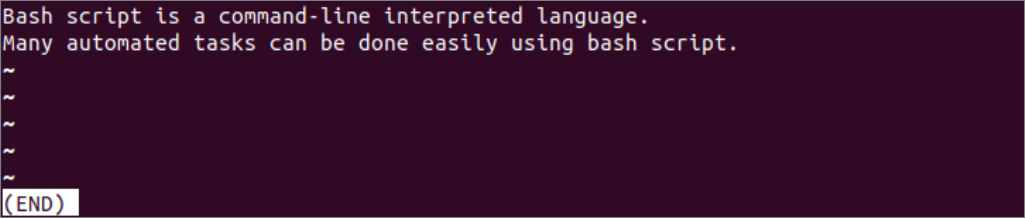
Run the following command to open the file1.txt file for reading. Here, the content of the file is very small. So when the user presses the enter key, then the content will go upward. Press the character ‘q’ to return to the command prompt.
The following output will appear after opening the file using the `less` command and pressing the enter key.
Use of `more` command:
Like the `less` command, the `more` command is used to open a large file for reading only. This command is mainly used to read a file’s large content in multiple pages to help the readers read long files.
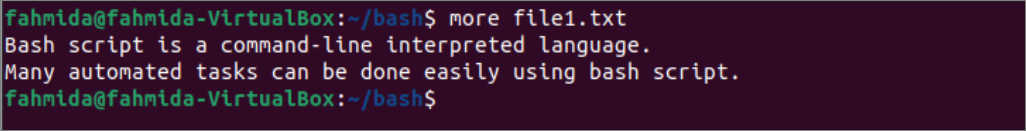
Run the following command to open the file1.txt file for reading by using the `more` command. It is a small file. So all content of the file has displayed on one page.
The following output will appear after opening the file using the `more` command.
Open file using command-line editors:
The uses of vi and nano command-line editors for opening the file to create and read have been shown in this part of this tutorial.
Use of vi editors:
One of the popular text editors of Linux is vi editors. It is installed on Ubuntu by default. The user can easily create, edit, and view any file by using this text editor. The advanced version of vi editors is called vim editor, which is not installed by default. This part of the tutorial shows how to use vi editor to open a file for creating and reading. Run the following command to open the file2.txt file for writing.
You have to press the character ‘i’ to start writing into the vi editor. Add the following content to the file.
Writing a file using vi editors.
You can do any of the following tasks after writing the content of the file.
- Type :wq to quit the editor after saving the file.
- Type :w to keep the file open in the editor after saving.
- Type :q to quit the editor without saving the file.
The following output shows that ‘:wq’ has been typed to quit the editor after saving the file.
Run the following command to open the file2.txt file and check the content exists or not that was added in the file.
The following output shows that the file contains the data that was added before. Here,’:’ has typed to quit the editor.
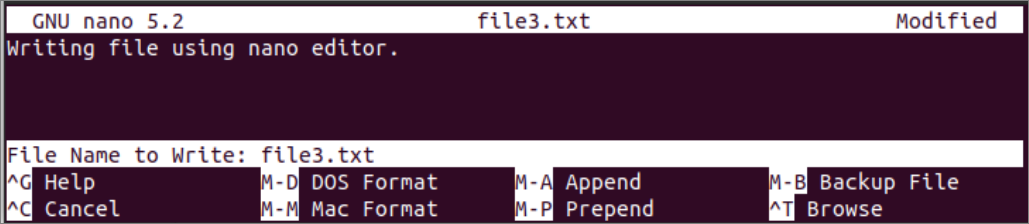
Use of nano editor:
Another useful and popular editor of Linux is the nano editor that is used to open a file for writing and reading. It is easier to use than the vi editor and more user-friendly than other command-line editors. Run the following command to open the file3.txt file for writing using nano editor.
Add the following content to the file.
Writing a file using nano editor.
If you type Ctrl+X after adding the content to the file, it will ask you to save the file. The following output will appear if you press the character, ‘y’. Now, press the enter to quit the editor after saving the file.
Open file using GUI text editor:
The ways to use gedit and geany GUI-based text editor have shown in the part of this tutorial.
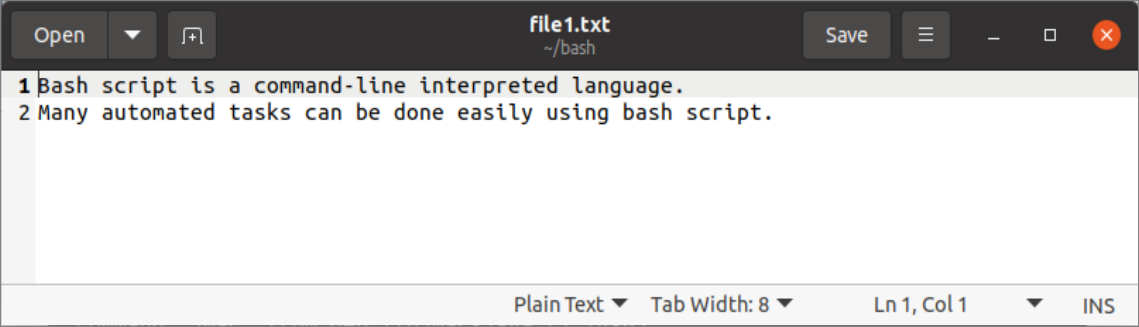
Use of gedit editor:
The gedit is mostly used GUI-based text editor that is installed by default on maximum Linux distributions. Multiple files can be opened by using this editor. Run the following command the open the existing file1.txt file using gedit editor.
The following output will appear after executing the command.
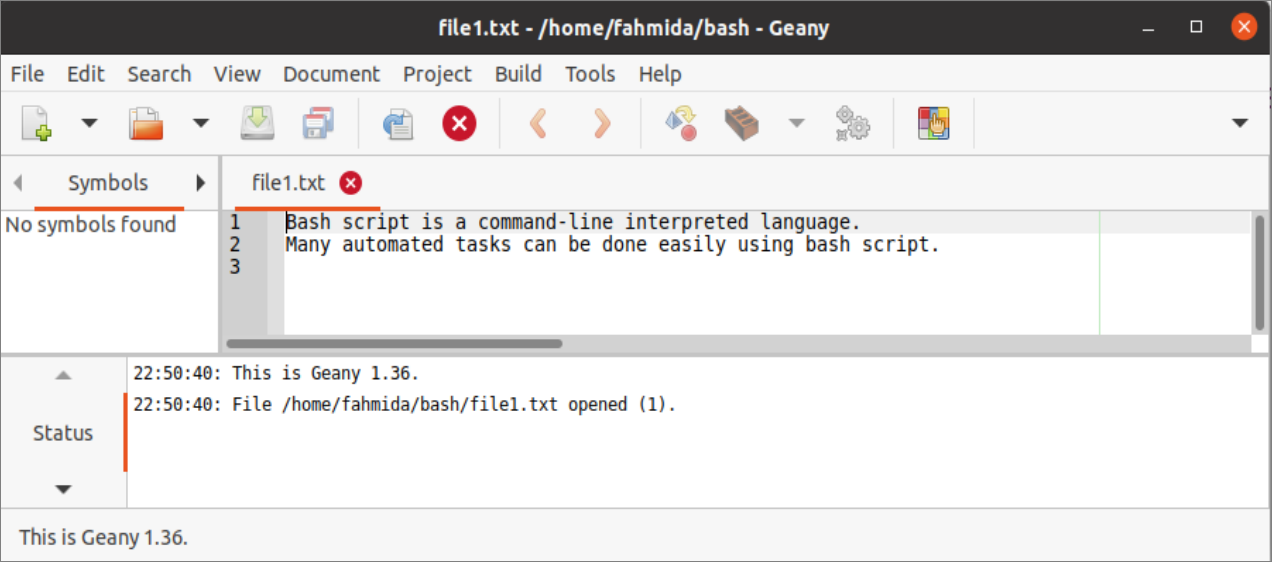
Use of geany editor:
Geany is a more powerful GUI-based editor than the gedit editor, and you have to install it to use it. It can be used to write code for many types of programming languages. Run the following command to install the geany editor.
After installing the editor, run the following command to open the file1.txt file.
The following output will appear after executing the command.
Conclusion:
Many ways to open a file for reading or writing have been shown in this tutorial by using bash command, command-line editors, and GUI-based editors. The Linux users can select any of the ways mention here to open a file in bash.
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.
How to open a particular file from a terminal?
Sounds like you’re coming from a Mac, where open does the same as double-clicking would in the Desktop.
3 Answers 3
You can use xdg-open to open files in a terminal.
From the man-page of xdg-open :
xdg-open — opens a file or URL in the user’s preferred application
The command xdg-open _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt will open the text file in a text editor that is set to handle text files. The command will also work with other common file extensions, opening the file with the relevant application.
If you struggle to remember xdg-open like I often do, add alias open=xdg-open to your ~/.bashrc file. Then, run source ~/.bashrc and now you can use open instead of xdg-open .
You must use an editor to open a text file:
- vi _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt - vim _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt - emacs _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt - nano _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt - gedit _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt (gnome's default editor) - leafpad _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt (lxde's default editor) - kedit _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt (KDE's default editor) Or if you wanted to just view the file without modifying its contents: cat _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt
EDIT #1: I just noticed that the question is tagged fedora, which up until now is using gnome as its core graphical user interface, which comes with gedit preinstalled. So this is guaranteed to work: gedit _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt