How to Create a Disk Partitions in Linux
In order to effectively use storage devices such as hard drives and USB drives on your computer, you need to understand and know how to structure them before using in Linux. In most cases, big storage devices are split into separate portions called partitions.
Partitioning enables you to split your hard drive into multiple parts, where each part acts as its own hard drive and this is useful when you are installing multiple operating systems in the same machine.
In this article, we will explain how to partition a storage disk in Linux systems such as CentOS, RHEL, Fedora, Debian and Ubuntu distributions.
Creating a Disk Partition in Linux
In this section, we will explain how to partition a storage disk in Linux using the parted command.
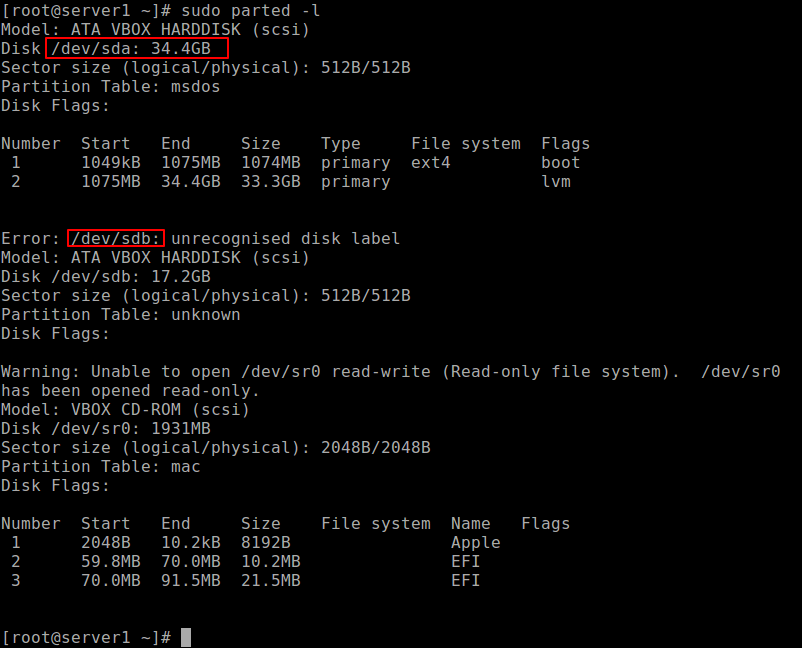
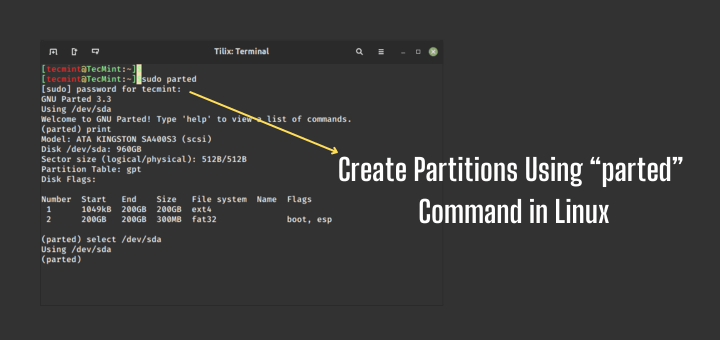
The first step is to view the partition table or layout on all block devices. This helps you identify the storage device you want to partition. You can do this using parted or fdisk command. We will use the former for purposes of demonstration, as follows, where the -l flag means list partition layout on all block devices.
From the output of the above command, there are two hard disks attached to the test system, the first is /dev/sda and the second is /dev/sdb .
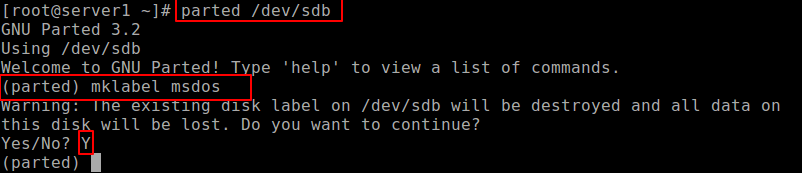
In this case, we want to partition hard disk /dev/sdb . To manipulate disk partitions, open the hard disk to start working on it, as shown.
At the parted prompt, make a partition table by running mklabel msdos or gpt, then enter Y/es to accept it.
Important: Make sure to specify the correct device for partition in the command. If you run parted command without a partition device name, it will randomly pick a storage device to modify.
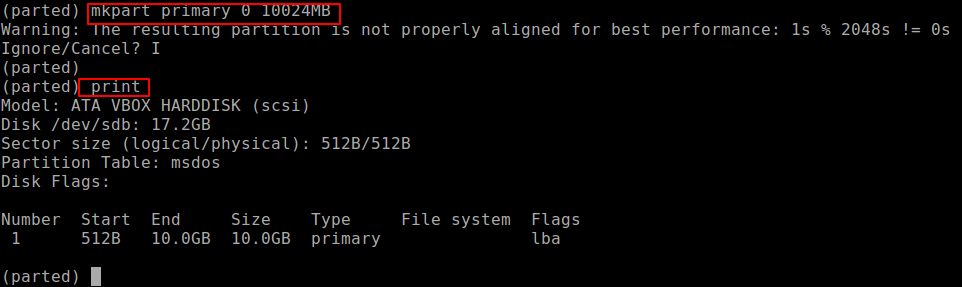
Next, create a new primary partition on the hard disk and print the partition table as shown.
(parted) mkpart primary ext4 0 10024MB (parted) print
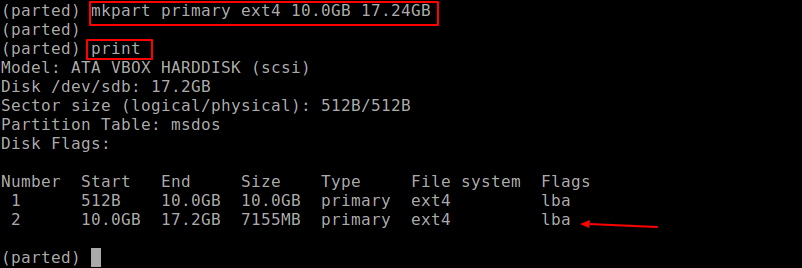
You can create another partition for the reaming space as shown.
(parted) mkpart primary ext4 10.0GB 17.24GB (parted) print
To quit, issue the quit command and all changes are automatically saved.
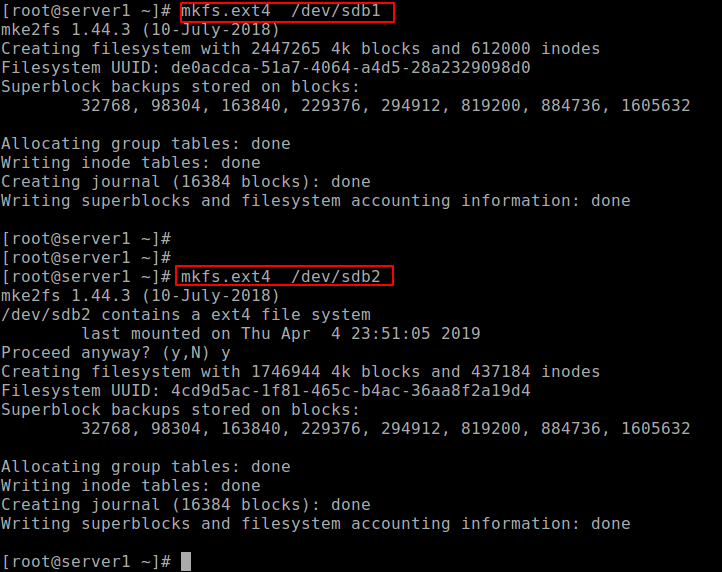
Next, create the file system type on each partition, you can use the mkfs utility (replace ext4 with the file system type you wish to use).
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1 # mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb2
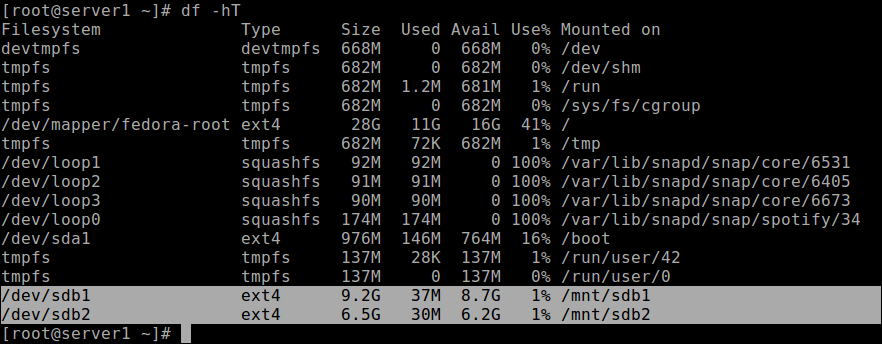
Last but not least, to access the storage space on the partitions, you need to mount them by creating the mount points and mount the partitions as follows.
# mkdir -p /mnt/sdb1 # mkdir -p /mnt/sdb2 # mount -t auto /dev/sdb1 /mnt/sdb1 # mount -t auto /dev/sdb2 /mnt/sdb2
To check if the partitions are actually mounted, run the df command to report file system disk space usage.
Important: You may need to update /etc/fstab file to mount newly created partitions automatically at boot time.
You might also like to read these following related articles:
That’s all! In this article, we have shown how to partition a storage disk, create a file system type on a partition and mount it in Linux systems. You can ask questions or share you thoughts with us via the comment form below.
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
Each tutorial at TecMint is created by a team of experienced Linux system administrators so that it meets our high-quality standards.
Related Posts
6 thoughts on “How to Create a Disk Partitions in Linux”
I successfully partitioned my drive for Linux and Windows. On boot up, I had set Linux as the default. This resulted in a screen giving me an option between OS choices. Then after a slight delay if nothing was selected the OS went to Linux. I was having a printer issue and changed the default to Windows. Now when I boot up the options screen does not show up and my system just goes straight into Windows. I would like to change the OS setting back to Linux as the default as I had before. Any help on getting a boot options screen in Windows would be greatly appreciated. Thanks Reply
@Jerry, Why not revert the changes you did and set Linux as the default option in your Boot settings? Reply
[[email protected] ahabab]# lsblk NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS sda 8:0 0 35G 0 disk ├─sda1 8:1 0 500M 0 part /boot/efi ├─sda2 8:2 0 2G 0 part [SWAP] ├─sda3 8:3 0 20G 0 part / ├─sda4 8:4 0 1G 0 part [SWAP] └─sda6 8:6 0 11.5G 0 part sr0 11:0 1 8G 0 rom /run/media/ahabab/RHEL-9-0-0-BaseOS-x86_64
[[email protected] ahabab]# df -HT | grep sda /dev/sda3 xfs 22G 5.3G 17G 25% / /dev/sda1 vfat 524M 7.4M 517M 2% /boot/efi
[[email protected] ahabab]# mount /dev/sda6 /testmount [[email protected] ahabab]# df -HT | grep sda /dev/sda3 xfs 22G 5.4G 17G 25% / /dev/sda1 vfat 524M 7.4M 517M 2% /boot/efi /dev/sda6 xfs 13G 120M 13G 1% /testmount
Before I started practicing according to your article, my machine’s partition system was as above. When I made the partition table by running “mklabel msdos“, then changed it to look like the below :
Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sda: 35 GiB, 37580963840 bytes, 73400320 sectors Disk model: VMware Virtual S Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disklabel type: dos Disk identifier: 0xc00800d1 Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type /dev/sda1 1 19578125 19578125 9.3G 83 Linux /dev/sda2 19578880 30064639 10485760 5G 83 Linux /dev/sda3 30064640 34258943 4194304 2G 83 Linux /dev/sda4 34258944 73400319 39141376 18.7G 5 Extended Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered. Failed to add partition 2 to system: Device or resource busy Failed to add partition 3 to system: Device or resource busy Failed to add partition 4 to system: Device or resource busy
The kernel still uses the old partitions. The new table will be used at the next reboot.
Syncing disks. What will happen after rebooting my laptop? Will I get my user login option ? will OS run in my computer ? Reply
Warning: The resulting partition is not properly aligned for best performance. what is this warning? Reply
Creating a disk partition in Linux
Creating and deleting partitions in Linux is a regular practice because storage devices (such as hard drives and USB drives) must be structured in some way before they can be used. In most cases, large storage devices are divided into separate sections called partitions. Partitioning also allows you to divide your hard drive into isolated sections, where each section behaves as its own hard drive. Partitioning is particularly useful if you run multiple operating systems.
Creating a Disk Partition in Linux
This procedure describes how to partition a storage disk in Linux using the parted command.
Procedure
- List the partitions using the parted -l command to identify the storage device you want to partition. Typically, the first hard disk ( /dev/sda or /dev/vda ) will contain the operating system, so look for another disk to find the one you want. For example:
sudo parted -l Model: ATA RevuAhn_850X1TU5 (scsi) Disk /dev/vdc: 512GB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: msdos Disk Flags: Number Start End Size Type File system Flags 1 1049kB 525MB 524MB primary ext4 boot 2 525MB 512GB 512GB primary lvm
sudo parted /dev/vdc GNU Parted 3.3 Using /dev/vdc Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands. (parted)
Be sure to indicate the specific device you want to partition. If you just enter parted without a device name, it will randomly select a storage device to modify.
(parted) mklabel gpt Warning: the existing disk label on /dev/vdc will be destroyed and all data on this disk will be lost. Do you want to continue? Yes/No? Yes
The mklabel and mktable commands are both used for making a partition table on a storage device. At the time of writing, the supported partition tables are: aix , amiga , bsd , dvh , gpt , mac , ms-dos , pc98 , sun , atari , and loop . Use help mklabel to get a list of supported partition tables. Remember mklabel will not make a partition, rather it will make a partition table.
(parted) print Model: Virtio Block Device (virtblk) Disk /dev/vdc: 1396MB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Disk Flags: Number Start End Size File system Name Flags
(parted) mkpart primary 0 1396MB Warning: The resulting partition is not properly aligned for best performance Ignore/Cancel? I (parted) print Model: Virtio Block Device (virtblk) Disk /dev/vdc: 1396MB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Disk Flags: Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 17.4kB 1396MB 1396MB primary
Providing a partition name under GPT is a must; in the above example, primary is the name, not the partition type. In a GPT partition table, the partition type is used as partition name.
(parted) quit Information: You may need to update /etc/fstab.
Help command for creating a new partition
To get help on how to make a new partition, type: help mkpart .
(parted) help mkpart mkpart PART-TYPE [FS-TYPE] START END make a partition PART-TYPE is one of: primary, logical, extended FS-TYPE is one of: udf, btrfs, nilfs2, ext4, ext3, ext2, fat32, fat16, hfsx, hfs+, hfs, jfs, swsusp, linux-swap(v1), linux-swap(v0), ntfs, reiserfs, hp-ufs, sun-ufs, xfs, apfs2, apfs1, asfs, amufs5, amufs4, amufs3, amufs2, amufs1, amufs0, amufs, affs7, affs6, affs5, affs4, affs3, affs2, affs1, affs0, linux-swap, linux-swap(new), linux-swap(old) START and END are disk locations, such as 4GB or 10%. Negative values count from the end of the disk. For example, -1s specifies exactly the last sector. 'mkpart' makes a partition without creating a new file system on the partition. FS-TYPE may be specified to set an appropriate partition ID.
- Setting filesystem type ( FS-TYPE ) will not create an ext4 filesystem on /dev/vdc1. You still have to create the ext4 filesystem with mkfs.ext4 .
- A DOS partition table’s partition types are primary, logical, and extended.
- Providing a partition name under GPT is a must. In a GPT partition table, the partition type is used as the partition name.
All Fedora Documentation content available under CC BY-SA 4.0 or, when specifically noted, under another accepted free and open content license.
Last build: 2023-07-13 00:51:09 UTC | Last content update: 2021-01-28