- How to Uninstall Python
- How to Uninstall Python in Linux
- Step A. First of all, check all the Python versions installed using the whereis command in Linux
- Misc A: Why it is not recommended to uninstall Python at /usr/bin
- Uninstall Python in Ubuntu 22.04
- Prerequisites
- Python Major Releases
- Method 1: Removing Python Using APT
- Step 2: Uninstalling Python
- Optional: Remove All Python Packages
- Method 2: Removing Python from the Source
- Method 3: Removing PyPy
- Bonus: Removing PIP
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Sidratul Muntaha
- Uninstall Python in Ubuntu
- Check if Python Installed in Your System
- Ways to Remove/Uninstall Python in Ubuntu
- Uninstall/Delete a Specific Version
- Remove Only the python3 Package
- Remove Packages With Their Dependencies
- Remove Settings, Configs, Datafiles Collectively
- Remove Configs, Data Files, and Dependencies of python3.5
- How to uninstall python in ubuntu completely and reinstalling it?
- 1 Answer 1
How to Uninstall Python
We may want to remove Python in our Linux or Windows systems for different reasons – conflicting packages and the need for a given Python version are some top reasons. Unlike in Windows, Python is a core program in most Linux distributions. In this case, uninstalling Python without utmost care may cause your Linux system to break. This article focuses on how we can safely remove Python from Windows and Linux systems.
How to Uninstall Python in Linux
Most Linux distros come with Python installed. In fact, in most cases, the default Python coming with the operating system is a core package for the system such that if it is removed, the graphical display manager breaks down, among other awful things. Other Python version(s) can also be installed alongside Linux-inbuilt Python (we will discuss how to do this later). We can safely remove the Python built from the source, but removing the Python that came with the distribution is not recommended.
To uninstall Python installed from the source, follow these steps:
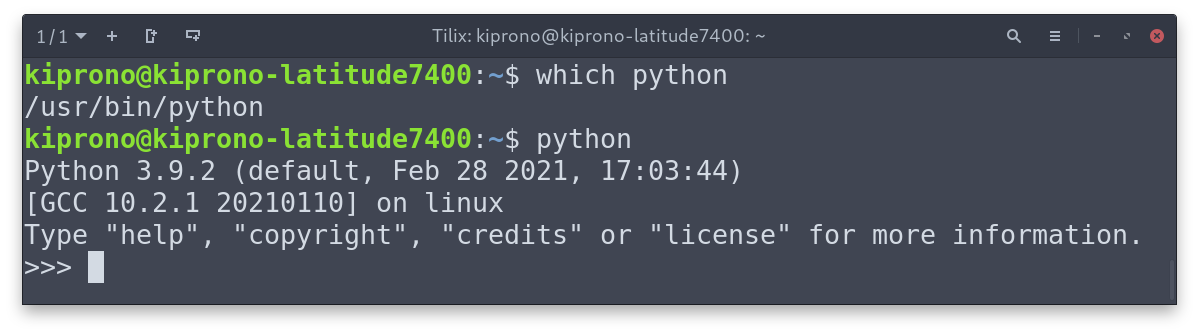
Step A. First of all, check all the Python versions installed using the whereis command in Linux
From Figure 1, what we are after are the binaries. They are located at bin/or local/bin. The inbuilt Python is in bin/, whereas the Python built from the source is mainly installed at the local/bin. In our case, we have Python3.9 (inbuilt – we don’t want to uninstall this) and Python3.6 located in local/bin directory, and we can safely remove it.
The following list can fully explain the Linux directories we are interested in:
- /bin – binary or executable programs.
- /lib – it contains kernel modules and a shared library.
- /usr – user-related programs.
- The /usr/local directory is where locally compiled applications are installed by default, preventing them from mucking up the rest of the system.
- /etc – system configuration files.
Misc A: Why it is not recommended to uninstall Python at /usr/bin
Many programs in most Linux distributions depend on pre-installed Python. You can identify the default Python by running python on the terminal. You can also find it by using which command.
If we take a closer look at the long listing of /usr/bin you will realize that Python and its dependencies are linked to other programs.
Uninstall Python in Ubuntu 22.04
Python is one of the most popular programming languages. It’s an interpreted general-purpose programming language with an emphasis on simplicity. Because of its versatility, Python is used for various purposes: web development, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and much more.
In this guide, we will have a look at uninstalling Python in Ubuntu 22.04.
Prerequisites
To follow this guide, you need the following components:
- A properly-configured Linux system. Learn more about setting up an Ubuntu virtual machine on VirtualBox.
- Access to a non-root user with sudo privilege. Check out the article on using sudoers to manage the sudo privilege.
Python Major Releases
As of now, the two major versions of Python are:
Python 2 received its last update (v2.7.18) on April 20, 2020. It’s been mostly phased out in favor of Python 3. This move, however, caused a major uproar in the community. Python 2 was so popular that the EOL had to be pushed multiple times into the future.
Although deprecated, you may still come across some Python 2 installations for compatibility reasons. By default, Ubuntu comes with installed Python 3.
Method 1: Removing Python Using APT
Step 1: Finding the Installed Python Package
Run the following commands:
- We ask the Python executable to print its version.
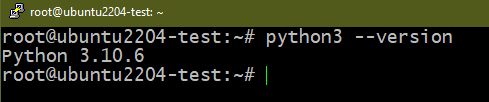
- Ubuntu 22.04 comes with pre-installed Python 3. So, the first command returns a version number.
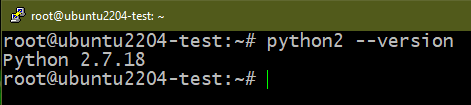
- Ubuntu 22.04 doesn’t come with pre-installed Python 2. So, the expected result is an error. However, if the command returns a version number, Python 2 is later installed.
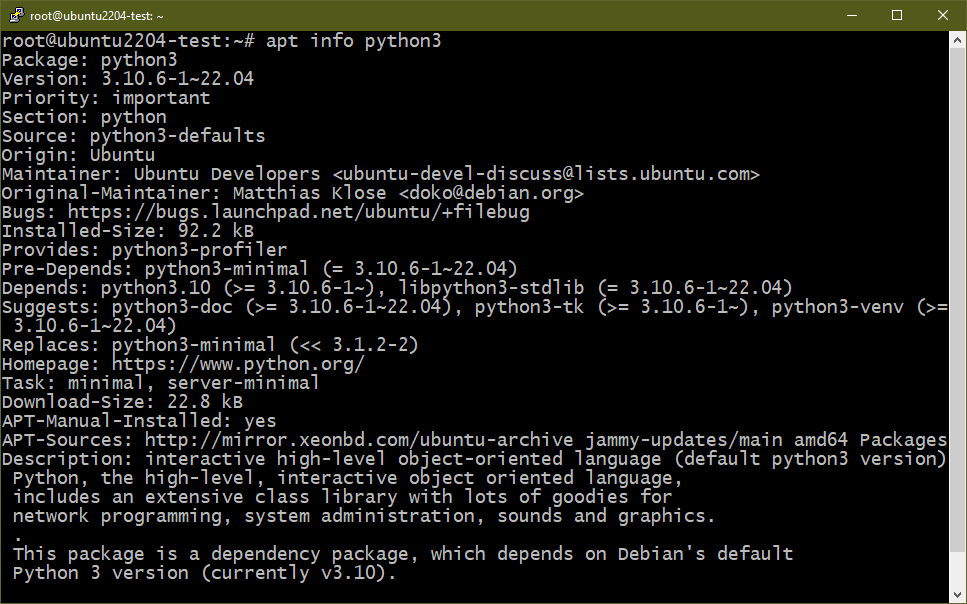
On Debian/Ubuntu, the core Python packages are as follows:
Step 2: Uninstalling Python
Now that we know what Python version is currently installed on the system, we can start to work on uninstalling them.
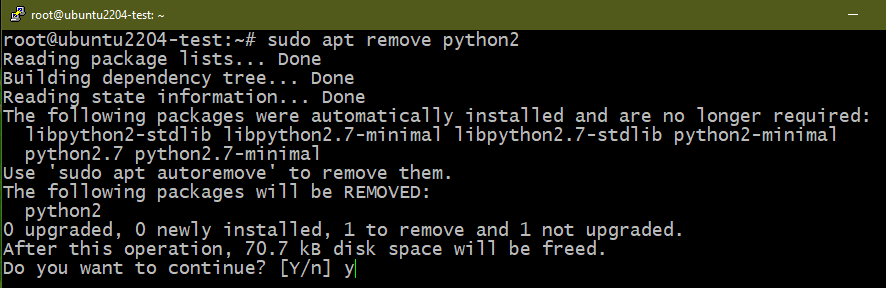
To remove Python 2, run the following command:
To remove Python 3, run the following command:
Optional: Remove All Python Packages
Removing all the Python-related packages is generally not recommended since various parts of the system depend on them. If you wish to proceed, ensure that you backed up all your important data.
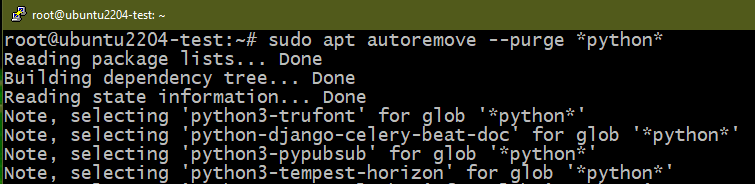
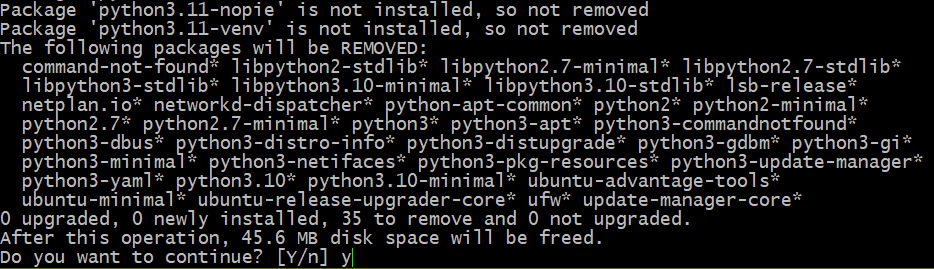
To remove all the Python packages from the system, run the following command:
- The APT package manager looks for packages that match the given regular expression (*python*). The matching packages are marked for removal.
- APT also marks the dependencies of those packages for removal.
Method 2: Removing Python from the Source
If Python was compiled and installed from its source code, APT won’t be able to recognize the installation. In that case, the uninstallation process will be different.
Assuming you still have the source directory which contains the compiled Python package, run the following commands:
If you removed the source directory, you could try removing the installed libraries and binaries manually:
Note that this is meant to be the last resort. It may lead to corrupted and broken configurations throughout the system.
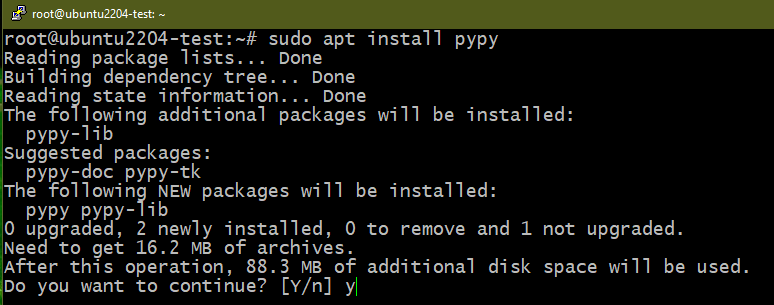
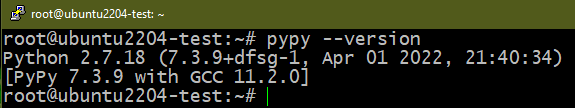
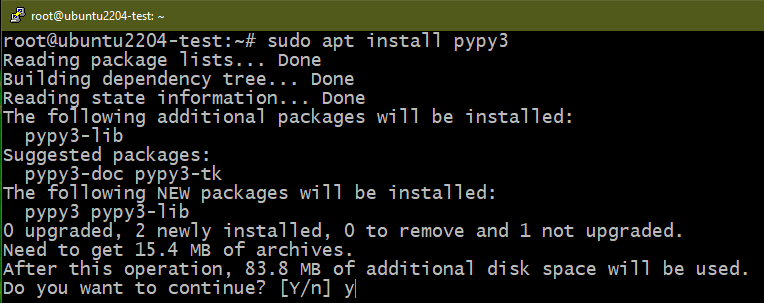
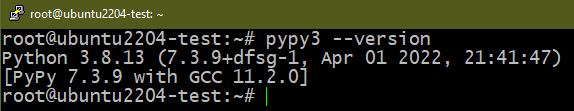
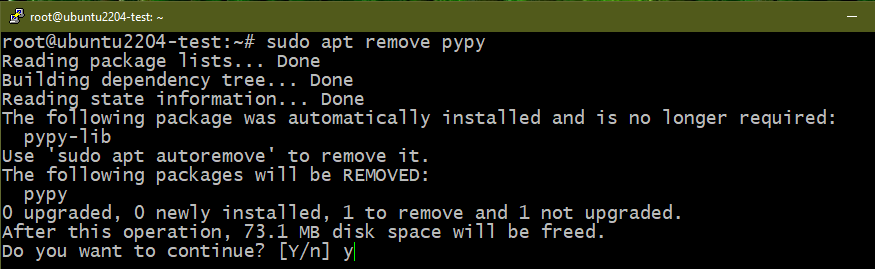
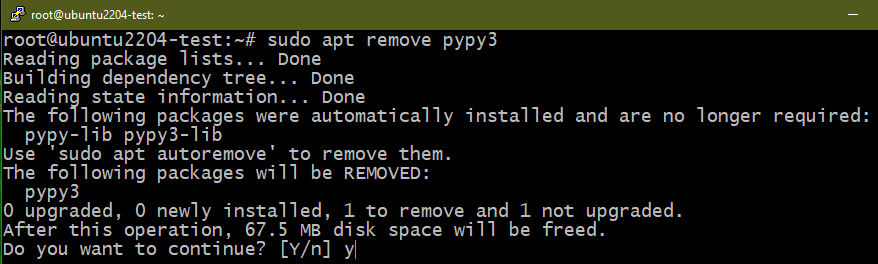
Method 3: Removing PyPy
PyPy aims to be a replacement for CPython (the default Python implementation). It’s built with RPython which was simultaneously developed with it. The key advantage to using PyPy other than CPython is performance. Although it’s an implementation of Python, certain differences can impact compatibility. Learn more about PyPy.
Similar to the classic Python, PyPy also has two major releases:
To install PyPy, run the following commands:
Similarly, to uninstall PyPy, run the following commands:
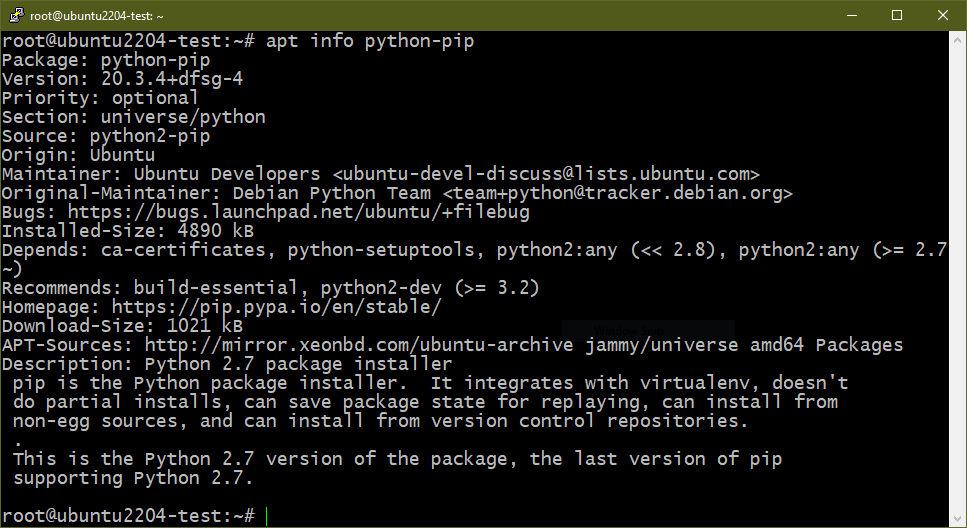
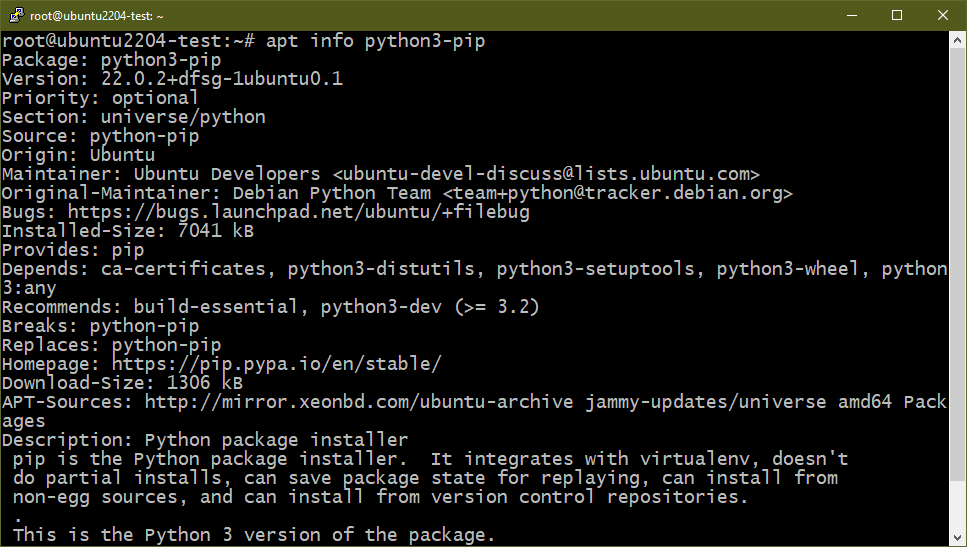
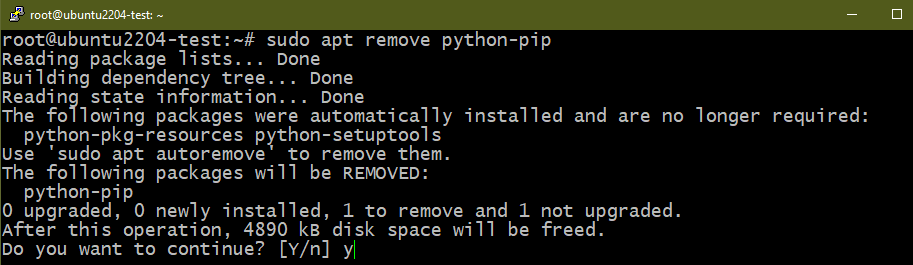
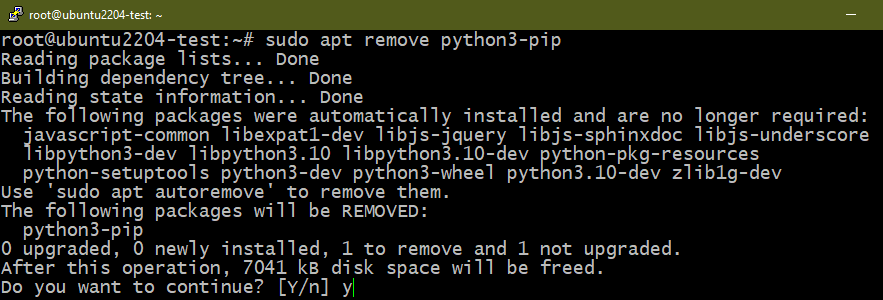
Bonus: Removing PIP
PIP is the de-facto standard package manager for Python packages/modules. By default, it’s configured to use the Python Package Index as the source of packages. Starting from Python 3 (v3.4 and later), PIP comes pre-installed with Python 3. The term “PIP” is a recursive acronym for “PIP Installs Packages”. Learn more about PIP.
Similar to the Python major releases, PIP has unique versions for both Python 2 (python-pip) and Python 3 (python3-pip).
If you removed all the Python packages, PIP is also uninstalled by default. However, if you desire to specifically uninstall PIP, run the following commands:
Conclusion
We demonstrated the multiple ways of removing Python from Ubuntu 22.04. We demonstrated uninstalling both CPython and PyPy from the system using APT. We also discussed uninstalling Python if it is installed from the source code.
Need to reinstall Python? Check out this guide on installing Python on Ubuntu 22.04. Interested in starting your journey with Python? The following guide features 30 example scripts to get started. The Python sub-category also contains numerous guides on various aspects of Python programming.
About the author
Sidratul Muntaha
Student of CSE. I love Linux and playing with tech and gadgets. I use both Ubuntu and Linux Mint.
Uninstall Python in Ubuntu
- Check if Python Installed in Your System
- Ways to Remove/Uninstall Python in Ubuntu
This article demonstrates how to delete or uninstall Python from Ubuntu.
Check if Python Installed in Your System
Open the Terminal using Ctrl + Alt + T .
After opening the terminal, check whether your system has python installed or not by using the command python3 —version .
If the command replies with the specific version of python, then leave it because you have already installed python on your pc/desktop.
If the command replies with Command not found , then to install python, write the command sudo apt install python3 .
There are many ways for its uninstallation depending upon a user’s needs. Different commands in the terminal do different tasks.
If there is only a need to delete specific dependencies related to a specific module of python or if there is a need to delete all the dependencies or to remove the Python3 package.
Depending upon the specific needs and requirements, the user can run the commands in the terminal for specific actions.
Ways to Remove/Uninstall Python in Ubuntu
Uninstall/Delete a Specific Version
Suppose a user wants to delete a specific version of Python installed on the Ubuntu machine. Run the below command and enter your user password. The version of Python will be removed from the machine.
sudo apt purge python-minimal Remove Only the python3 Package
If a user wants to remove the specific package of Python, i.e., python 3.5 , run the below command and select and remove the python3 packages.
sudo apt-get remove python3.5 Remove Packages With Their Dependencies
Suppose you want to remove a package and all the dependencies related to that package, run the below-mentioned command, enter your ubuntu password, and the package will be removed along with its dependencies.
sudo apt-get remove –auto-remove python3.5 Remove Settings, Configs, Datafiles Collectively
Suppose a user wants to remove all the configurations and settings or data files related to a python package. In that case, he should mention the below command in the terminal and enter the machine’s password to continue.
sudo apt-get purge python3.5 Remove Configs, Data Files, and Dependencies of python3.5
If a user wants to collectively remove any Python package’s configuration, files, and dependencies, then the user must use the below command.
sudo apt-get purge –auto-remove python sudo apt-get purge –auto-remove python3.5 Hello! I am Salman Bin Mehmood(Baum), a software developer and I help organizations, address complex problems. My expertise lies within back-end, data science and machine learning. I am a lifelong learner, currently working on metaverse, and enrolled in a course building an AI application with python. I love solving problems and developing bug-free software for people. I write content related to python and hot Technologies.
How to uninstall python in ubuntu completely and reinstalling it?
The default python version was 2.7.12 in ubuntu. I installed python2.7.13 using the below commands. Then download using the following command:
version=2.7.13 cd ~/Downloads/ wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/$version/Python-$version.tgz tar -xvf Python-$version.tgz cd Python-$version Now, install using the command you just tried, using checkinstall instead to make it easier to uninstall if needed:
./configure sudo make install Now there is some issue in pandas(giving no module named pandas when I try to import but if we try to install it shows required already satisfied) so I want to completely remove python 2.7.13 and reinstall python 2.7.12. How can I achieve this?
Don’t try to uninstall default python otherwise chances are many of your components of your ubuntu stop working. Just use virtual environments if you want to use different pythons.
1 Answer 1
My python was corrupted due to some module. So I planned to re-installed or remove the python completely from my Ubuntu 16.04 machine. But sudo apt-get install —reinstall python2.7 command was also failing and was throwing same error. So I finally Did few hacks and cracks. Here are the steps —
Removing all python version manually
- sudo rm -rf /usr/bin/python2.x as well as python3.x - sudo rm -rf /usr/lib/python2.x as well as python3.x - sudo rm -rf /usr/local/lib/python2.x as well as python 3.x In Between if you get this error The package needs to be reinstalled ubuntu Then Run following command
And delete all the lines from above file for the package which was expecting re-install and run sudo apt-get update again.
Now download a python tgz file from https://www.python.org/downloads/ and unzip it and CD into it
./configure make test sudo make install Python should be installed now. Check by running python