How to Rename a Directory in Linux Command Line
Renaming a directory is the same as renaming the files. You use the mv command.
When you are new to something, even the simplest of the tasks could be confusing.
Take renaming a directory in the Linux command line. There is a rmdir command but it is for removing directories, not renaming them.
In Linux, you can use the same command that you use for renaming files for renaming directories also:
Yes! That’s the move command and while its original purpose was to move (or cut-paste) a file from one location to another, it can be used to rename a file and directory.
All the files inside the directory remain as it is. They are not impacted.
Let’s take a deeper dive into this.
Rename directory using the mv command
When you rename an item, you erase the old item name and write a new name for it.
If you were to split the working of mv command, it acts in the following fashion (but obviously, this is done more efficiently). Assume that I want to rename ‘old_file’ file to ‘new_file’ file.
This is what a move operation is at its core — for a better or worse analogy.
This means that if you don’t change the directory of source and destination files, the only change will be in the filename.
Everything is a file in Linux. Even the directory is a special type of file that stores the index of files that are inside the folder.
This means that we can also rename a directory in the same fashion.
$ ls -l total 4 drwxrwxr-x 2 team team 4096 Feb 16 15:34 old_dir $ mv -v old_dir new_name renamed 'old_dir' -> 'new_name' $ ls -l total 4 drwxrwxr-x 2 team team 4096 Feb 16 15:34 new_nameAs you can see, the directory has been renamed from ‘old_dir’ to ‘new_name’.
This will not negatively affect any files that are inside the directory. The only change which will occur is the rename operation on the directory name.
The rename operation is just a move operation and that is what we do. There is no ‘rn’ command in GNU coreutils. Though there is a rename command-line utility that is specifically used for batch renaming files but it doesn’t come preinstalled on most distributions.
How to Rename a Directory in Linux
In Linux and Unix-like systems, we are always amazed to see several ways for a single operation. Whether to install something or to perform through the command-line, you will get multiple utilities and commands.
Even if you want to move, copy or rename a directory, it is quite handy to perform these functions with commands; you don’t need to install any specific tool.
In Linux distributions, everything is in the form of directories. So, it is good to keep all of them in a structured way. Sometimes, we need to create temporary folders to save data and later on, to keep them permanently, we have to rename those directories.
There are no traditional commands to rename a folder/directory; it can be done using several ways. We will discuss in this guide how to change the directory name using the “mv” command and “rename” command. It might shock you that this operation can be performed using the “mv” command. The “mv” command is not only used to move one directory to another; it is a multi-purpose command which helps to rename a directory as well.
So, let’s check how we can do use the “mv” command and “rename” command:
How to Rename a Folder Through “mv” Command
To rename a folder through the “mv” command is the simplest way you have ever seen.
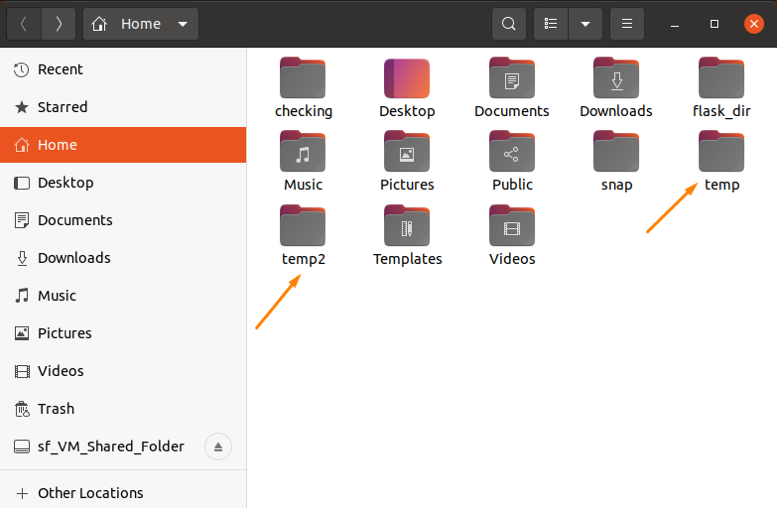
Create a directory in the terminal named “temp”:
To move the “temp” directory, make another directory with the name “temp 2”:
You can see in the home directory, two directories with the given names are created:
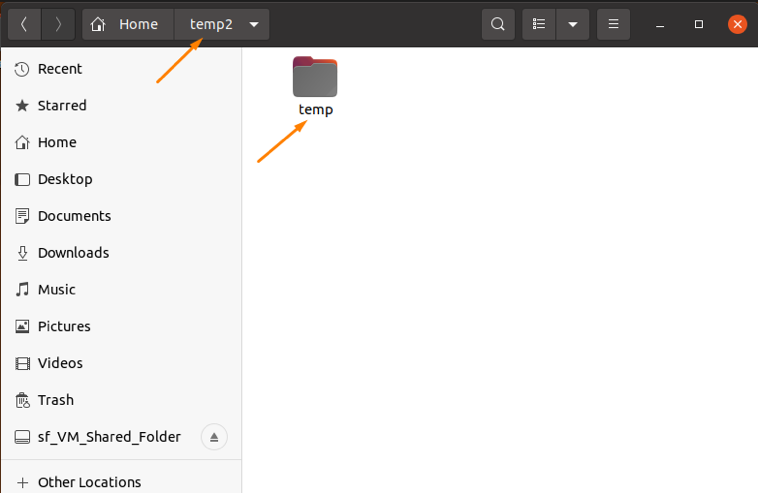
Now, move the “temp” to the “temp2” directory using the “mv” command:
Open the “temp 2” directory to check if the “temp” directory is successfully moved:
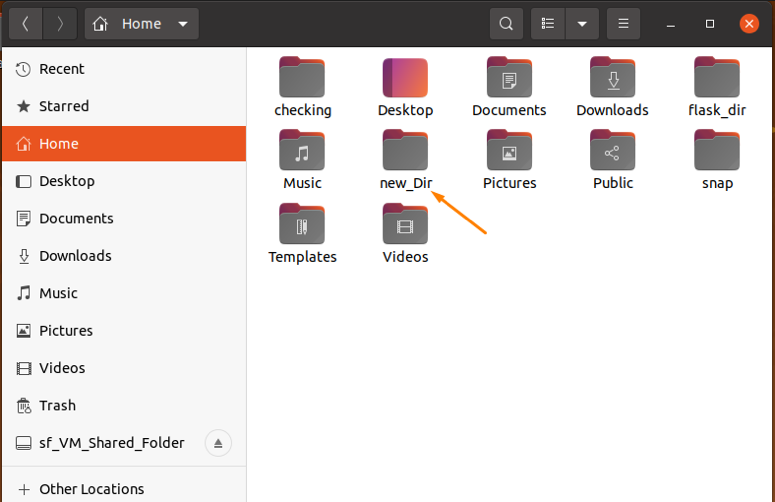
After moving, use the “mv” command again to rename a “temp2” directory:
So, the temp2 directory has been renamed successfully to the “new_Dir” directory:
You can also confirm it using a terminal to active a “new_Dir” directory in it, and check if the “temp” directory (we created first and moved to temp2 folder is present in the “new_Dir” directory or not):
To activate a “new_Dir” folder in the terminal, use the “cd” command:
Now, to display the list of files present in the “new_Dir” folder, type the “ls” command:
How to Rename a Folder Through “rename” Command
The “rename” command is a built-in tool in most Linux distributions that helps to rename folders and directories. It uses regular expressions to perform functions.
If it is not present in your system. Use the following command:
The syntax used for the “rename” command is:
Consider the given examples to check if it’s working:
Example 1:
To rename the directories from lowercase to uppercase, run the ls command to display directories in the desktop directory:
Use the rename command with the following expressions to change letter case:
To confirm it, type “ls” again:
Example 2:
To rename the text files present in the desktop directory as pdf files, run the command:
Type the “ls” command to display the output:
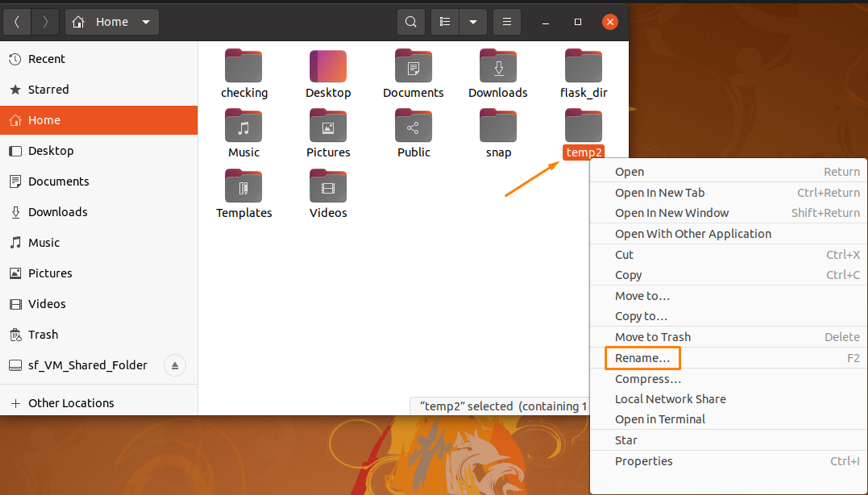
You can also rename a directory through GUI by simply right click on the desired folder and navigate to the “rename” option:
Click on the “rename” option, type the name you want to update, and click to the “rename” button:
And the directory name will be changed:
Conclusion
In this write-up, we have seen how to rename a directory in Linux operating system. There are multiple ways to do it, but why choose a difficult way when the simplest approach is available.
We have learned from this guide to rename directories using the “mv” command and “rename” command. The “mv” command is considered a multi-tasking command tool whereas, using the “rename” command directories can be changed through regular expressions. We have also checked it through the GUI approach.
About the author
Syeda Wardah Batool
I am a Software Engineer Graduate and Self Motivated Linux writer. I also love to read latest Linux books. Moreover, in my free time, i love to read books on Personal development.
Rename Directory/Folder in Linux
Renaming or moving folder and directories can be complicated if those folders and directories have some subfolders.
There’s absolutely not any rename function in Ubuntu Linux.
Rather, you merely move the document, giving it a new name. If you do not really mv it to a different directory, then you’ve effectively renamed it:
Renaming directories on Linux isn’t done with a specific “rename” or “ren” etc. command but with a command which serves multiple functions: the “mv” command.
The mv is the brief form for the “move”. We can simply rename by providing the current directory and folder name and destination folder or directory name. If the origin or directory has files we will need to rename by using the recursive move command. This is only going to change the given folder or directory name but transfer all subfolder and files.
Rename Directories on Linux with mv
To rename a directory on Linux, use the “mv” command and specify the directory to be renamed in addition to the destination for your directory. The general syntax of mv command is:
An example command of renaming folder
In this case, we’ll rename the directory called curr_data into new_data.
Rename Directories using the find command
In some instances, you might not know exactly where your directories can be found on your system that you want to rename.
Fortunately for you, there’s a command that can help you find the directories on a Linux system.
This is called the “find” command.
So as to locate and rename directories on Linux, use the “find” command with the “type” option so as to search for directories. After that, you can eliminate your directories by implementing the “mv” command with the“-execdir” alternative.
The general way of using the find command is:
An example of find command to rename
For this example, suppose that you need to rename a directory starting with “data” in your filesystem to “backupData”.
The first part of the command will find where your directory is located.
Now you know where your directory is, you can rename it by using the “execdir” option and the “mv” command.
$ find . -depth -type d -name temp -execdir mv <> backupData \;
Overwrite Forcibly If Exists
In some instances, there may be an existing directory or folder with the new name. We will need to confirm the overwrite. But this may be a daunting task if there’s a great deal of them. We can overwrite existing files and folder with -f option automatically. -f means by force.
Rename Directories using rename
Rather than using the “mv” command, you may use a dedicated built-in command, however this command might not be directly available in your distribution.
So as to rename directories on Linux, use “rename” with how you want the files to be renamed in addition to the target directory.
The general way of using rename command is:
The example command below shows how to rename all directories that have names in uppercase letters to lowercase letters: