- Как переименовать файл Linux
- Как переименовать файл в Linux с помощью mv
- Переименование файлов Linux с помощью rename
- Переименование файлов в pyRenamer
- Выводы
- How Do I Rename a File in the Ubuntu Terminal?
- Renaming Files in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS System Using Terminal
- Rename File in Ubuntu Using the mv Command
- Example
- How to Use the mv Command to Rename Multiple Files?
- How to Use the Rename Command to Rename Files in Ubuntu?
- Syntax of Rename Command
- Example
- Example
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Samreena Aslam
- How to Rename Files in Linux and MacOS Terminal
- Linux Commands
- Renaming files with the mv Command
- Renaming multiple files
- More Tips and Tricks for Linux
Как переименовать файл Linux
Переименование файла linux — очень простая операция, но для новичков в Linux эта задача может оказаться сложной. Также здесь есть несколько нюансов и возможностей, которые желательно знать уже опытным пользователям, например, массовое переименование. В графическом интерфейсе все делается очень просто, но настоящую гибкость дает терминал.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим как переименовать файл в Linux с помощью терминала, рассмотрим такие возможности, как массовое пакетное переименование файлов, а также регулярные выражения.
Как переименовать файл в Linux с помощью mv
В Linux существует замечательная стандартная утилита mv, которая предназначена для перемещения файлов. Но по своей сути перемещение — это то же самое, что и переименование файла linux, если выполняется в одной папке. Давайте сначала рассмотрим синтаксис этой команды:
$ mv опции файл-источник файл-приемник
Теперь рассмотрим основные опции утилиты, которые могут вам понадобиться:
- -f — заменять файл, если он уже существует;
- -i — спрашивать, нужно ли заменять существующие файлы;
- -n — не заменять существующие файлы;
- -u — заменять файл только если он был изменен;
- -v — вывести список обработанных файлов;
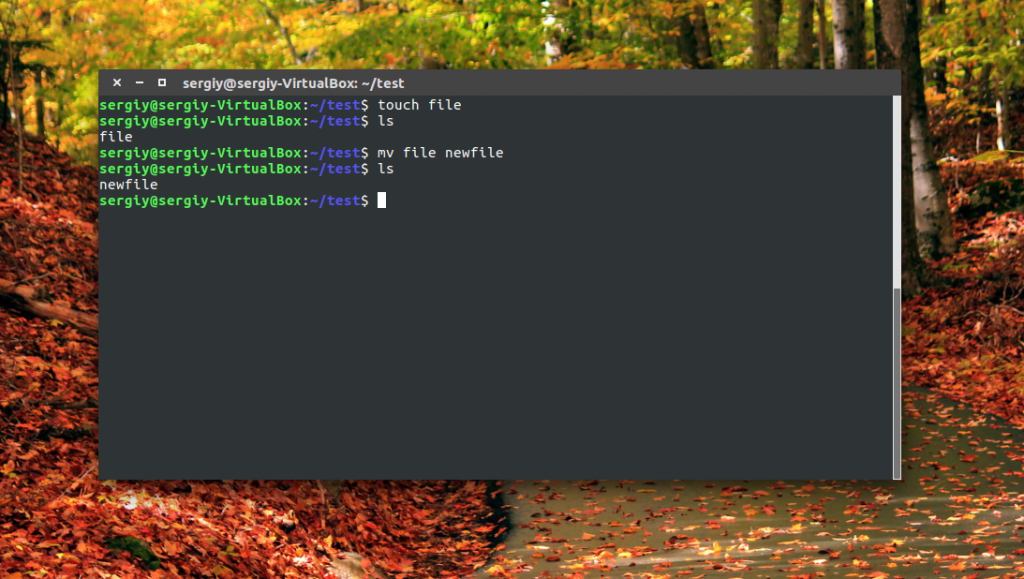
Чтобы переименовать файл linux достаточно вызвать утилиту без дополнительных опций. Просто передав ей имя нужного файла и новое имя:
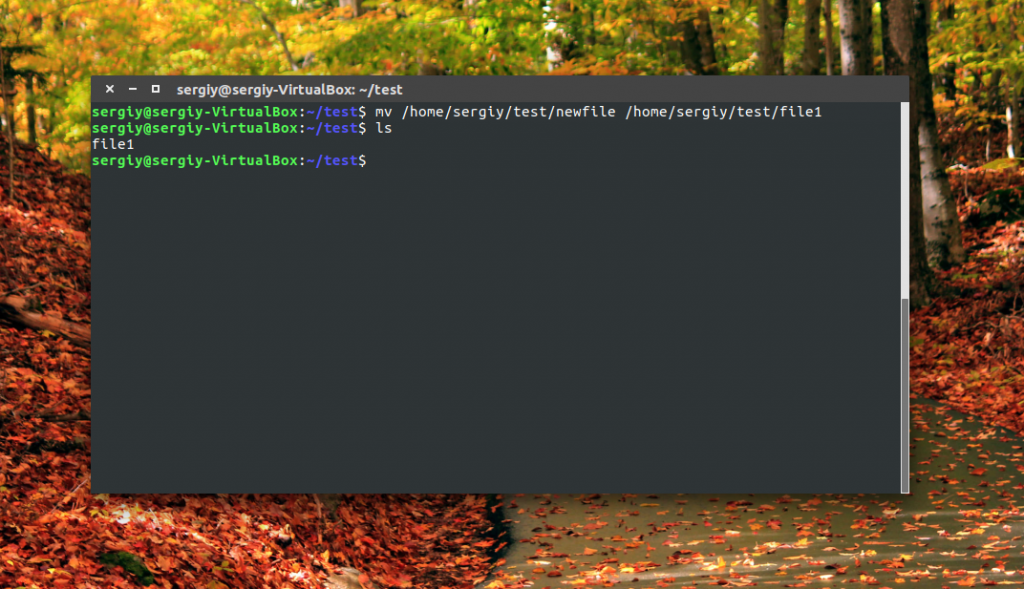
Как видите, файл был переименован. Вы также можете использовать полный путь к файлу или переместить его в другую папку:
mv /home/sergiy/test/newfile /home/sergiy/test/file1
Обратите внимание, что у вас должны быть права на запись в ту папку, в которой вы собираетесь переименовывать файлы. Если папка принадлежит другому пользователю, возможно, нужно будет запускать программу через sudo. Но в таком случае лучше запускать с опцией -i, чтобы случайно ничего не удалить.
Переименование файлов Linux с помощью rename
В Linux есть еще одна команда, которая позволяет переименовать файл. Это rename. Она специально разработана для этой задачи, поэтому поддерживает такие вещи, как массовое переименование файлов linux и использование регулярных выражений. Синтаксис утилиты тоже сложнее:
$ rename опции ‘s/ старое_имя / новое_имя ‘ файлы
$ rename опции старое_имя новое_имя файлы
В качестве старого имени указывается регулярное выражение или часть имени которую нужно изменить, новое имя указывает на что нужно заменить. Файлы — те, которые нужно обработать, для выбора файлов можно использовать символы подставки, такие как * или ?.
- -v — вывести список обработанных файлов;
- -n — тестовый режим, на самом деле никакие действия выполнены не будут;
- -f — принудительно перезаписывать существующие файлы;
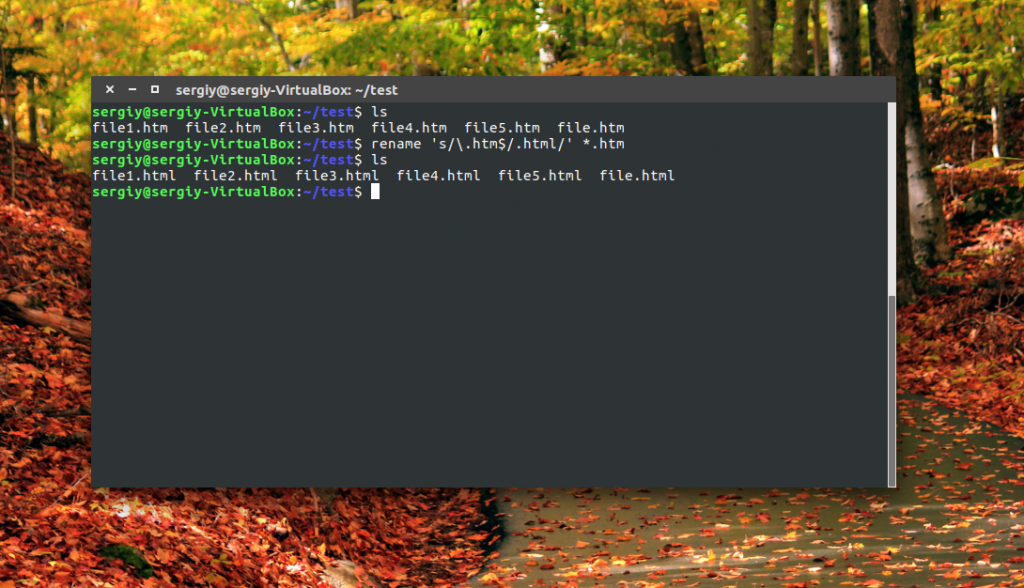
Например, переименуем все htm файлы из текущей папки в .html:
Символ звездочки означает, что переименование файлов linux будет выполнено для всех файлов в папке. В регулярных выражениях могут применяться дополнительные модификаторы:
- g (Global) — применять ко всем найденным вхождениям;
- i (Case Censitive) — не учитывать регистр.
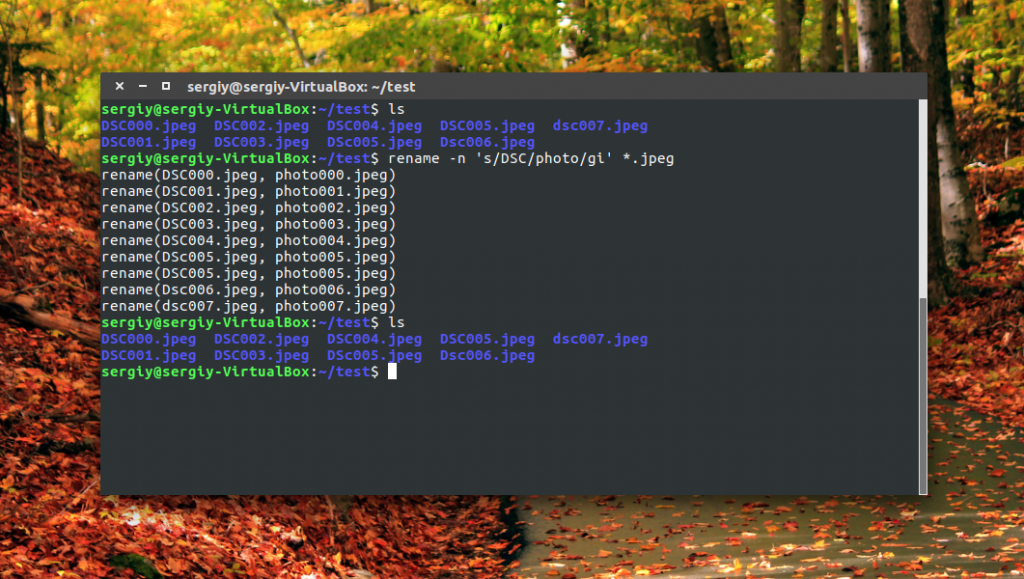
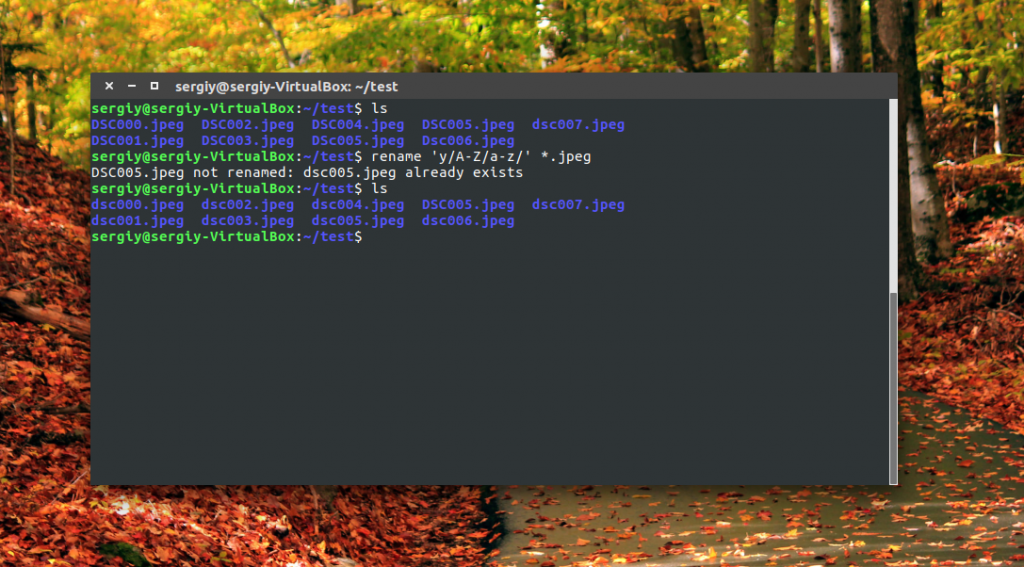
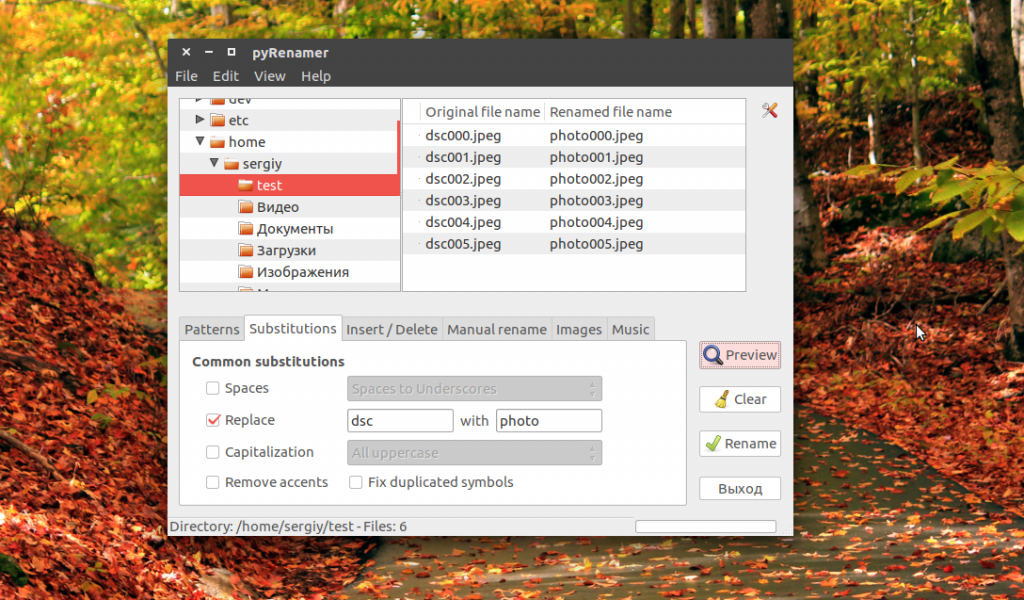
Модификаторы размещаются в конце регулярного выражения, перед закрывающей кавычкой. Перед тем, как использовать такую конструкцию, желательно ее проверить, чтобы убедиться, что вы не допустили нигде ошибок, тут на помощь приходит опция -n. Заменим все вхождения DSC на photo в именах наших фотографий:
rename -n ‘s/DSC/photo/gi’ *.jpeg
Будут обработаны DSC, DsC и даже dsc, все варианты. Поскольку использовалась опция -n, то утилита только выведет имена изображений, которые будут изменены.
Можно использовать не только обычную замену, но и полноценные регулярные выражения чтобы выполнить пакетное переименование файлов linux, например, переделаем все имена в нижний регистр:
Из этого примера мы видим, что даже если такой файл уже существует, то он перезаписан по умолчанию не будет. Не забывайте использовать опцию -n чтобы ничего случайно не повредить.
Переименование файлов в pyRenamer
Если вы не любите использовать терминал, но вам нужно массовое переименование файлов Linux, то вам понравится утилита pyrenamer. Это графическая программа и все действия здесь выполняются в несколько щелчков мыши. Вы можете установить ее из официальных репозиториев:
sudo apt install pyrenamer
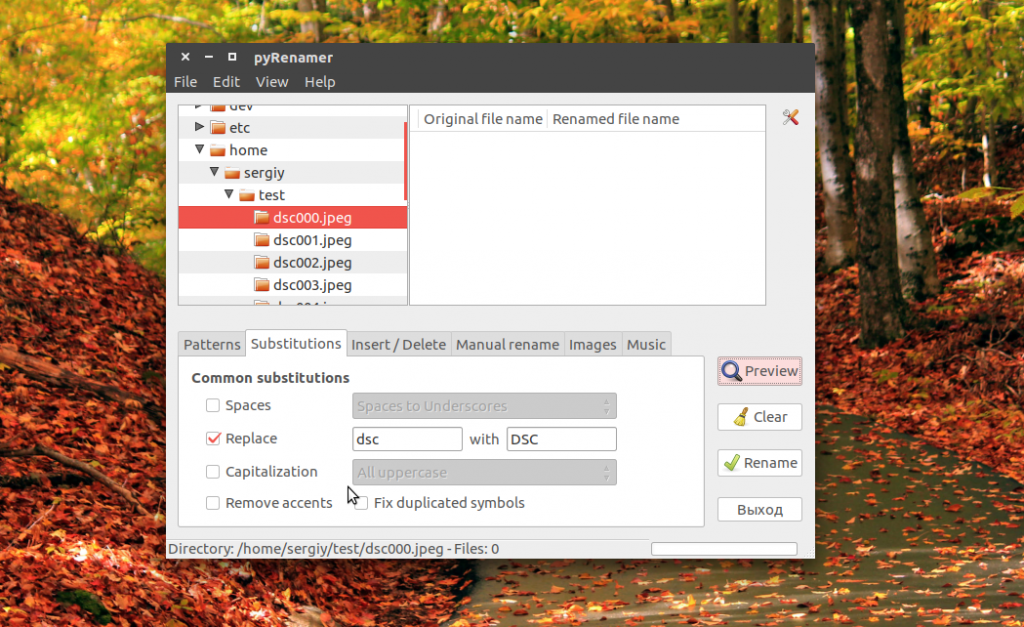
В окне программы вы можете видеть дерево файловой системы, центральную часть окна, где отображаются файлы, которые будут изменены, а также панель для указания параметров переименования.
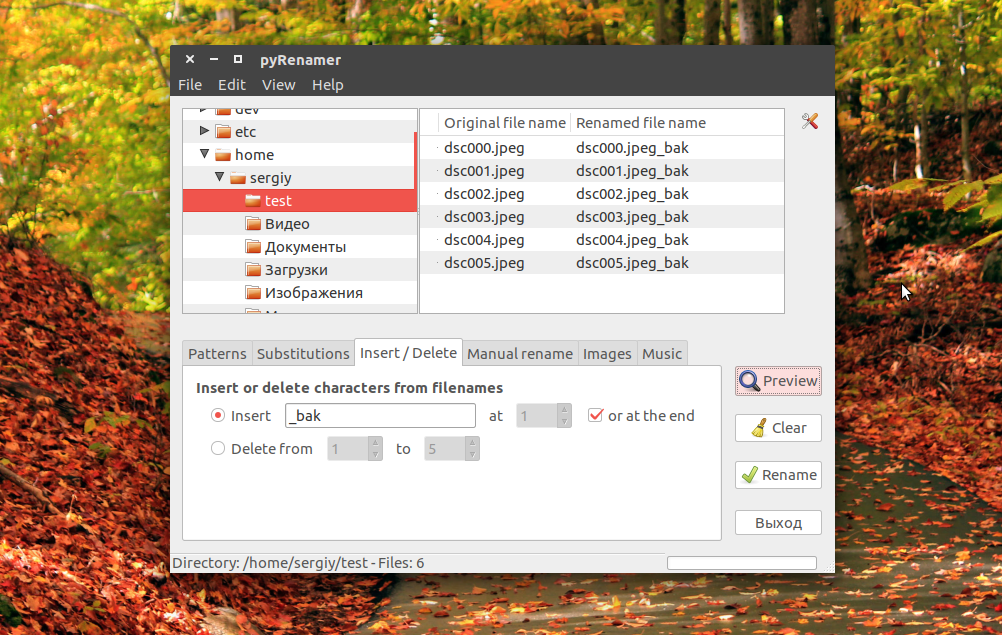
Вы можете удалять или добавлять символы, переводить регистр, автоматически удалять пробелы и подчеркивания. У программы есть подсказки, чтобы сделать ее еще проще:
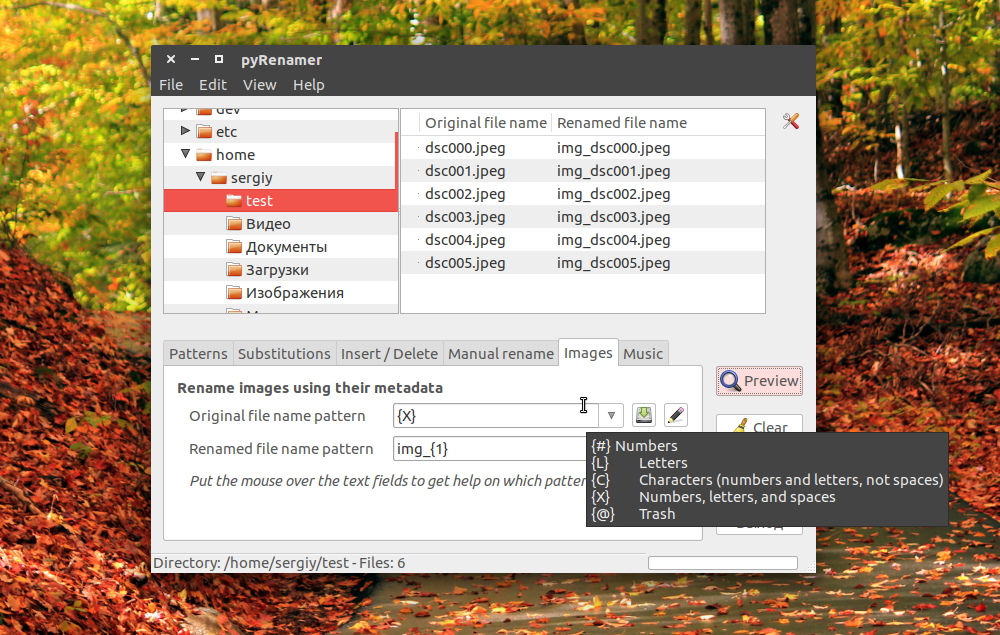
Опытным пользователям понравится возможность pyRenamer для переименования мультимедийных файлов из их метаданных. Кроме того, вы можете переименовать один файл если это нужно. Эта утилита полностью реализует функциональность mv и remove в графическом интерфейсе.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели как переименовать файл в консоли linux. Конечно, есть и другие способы, например, написать скрипт, или использовать файловые менеджеры. А как вы выполняете сложные операции по переименованию? Напишите в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How Do I Rename a File in the Ubuntu Terminal?
Renaming an existing file is a basic operation that usually does not require a specialized tool in any operating system. Renaming a single file in Linux is quite a simple task but renaming more than one or multiple files via terminal is a more challenging job for new Linux users. In all Linux distributions, the terminal is an essential command-line application for administering the Linux systems.
However, to use effectively this CLI application, you should have strong knowledge about basic Linux commands and fundamentals such as create, delete and renaming an existing file. Different commands are available in the Ubuntu Linux system to rename a file that we will explore in this article.
We will provide comprehensive details in this tutorial on how you can rename a file in Ubuntu using the command-line application Terminal. All commands have implemented for the demonstration on the Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system.
Renaming Files in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS System Using Terminal
The two different commands ‘mv’ and ‘rename’ are available in the Ubuntu Linux system to rename a file via terminal or command-line approach. Let us discuss each command in detail.
Rename File in Ubuntu Using the mv Command
Before using the ‘mv’ command, you should know how it works on your system. The basic syntax of the ‘mv’ command is given below:
The most popular ‘mv’ command options are provided below:
-f – Displays no message or alerts before overwriting a file name.
-i – Displays prompt confirmation or warning messages before renaming a file.
-u – It moves a file if the file does not exist on the specified destination or in case of a new file.
The file source can be the destination of one or more files. The destination only represents a single file.
Example
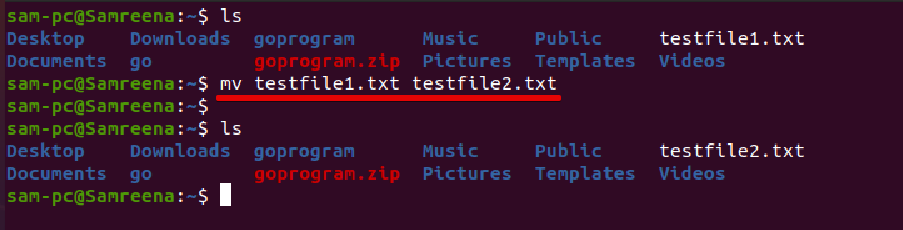
For example, to rename the file ‘testfile1.txt’ to ‘testfile2.txt, you need to run the following command:
How to Use the mv Command to Rename Multiple Files?
Usually, you can only rename a single file using the move command. To rename multiple files using the mv command, you can use the mv command to combine with different commands. Let us say, mv command can be used along with for loop, while loop, and find command.
Let us explain with the help of an example. Here, we want to rename all .txt extension files of the current directory replaced with another .html extension. In this case, the following code will help us:
The above code will iterate using for loop through the files list having the .txt extension. After that, in the second line, it will replace each file extension .txt with .html. In the end, ‘done’ indicated the end of the for loop segment.
How to Use the Rename Command to Rename Files in Ubuntu?
Using the rename command, you can rename multiple files of a current directly at once. This command contains more advance features as compared to the ‘mv’ command. For renaming files using the rename command, you should have basic knowledge about regular expressions usage.
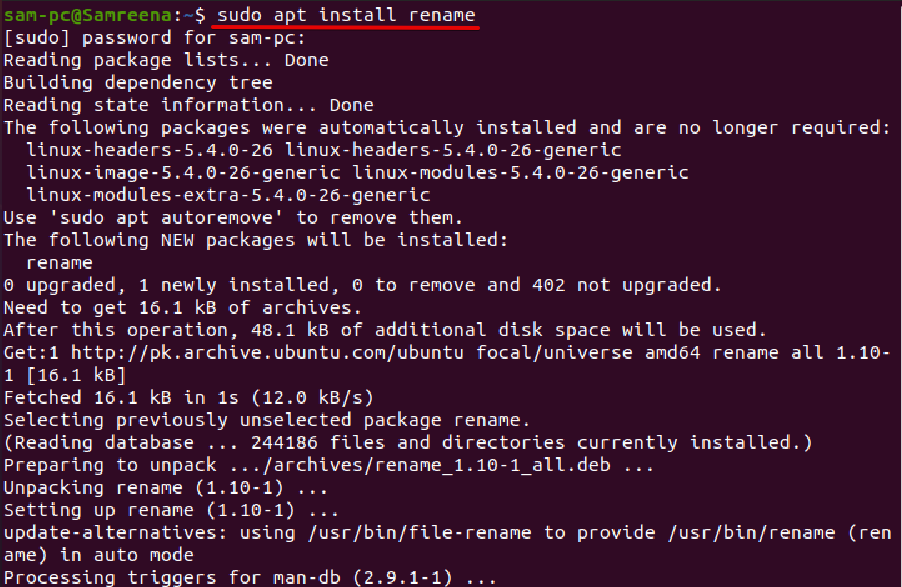
In most Linux distributions, the ‘rename’ command is installed by default. However, if you have not installed the rename command on your Ubuntu system then, it can be easily installed on Ubuntu and its derivatives by running the following command:
Syntax of Rename Command
Using the following syntax, you can use the rename command:
The rename command will rename files according to the specific regular Perl expressions.
Example
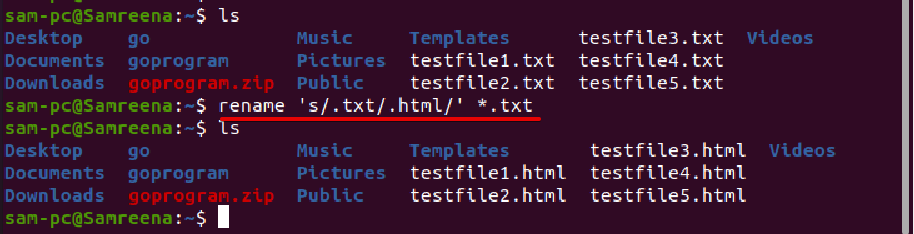
In the following example, we want to change the extension of all text files. So, we will change or replace all files with extension .txt to .html by executing the following command:
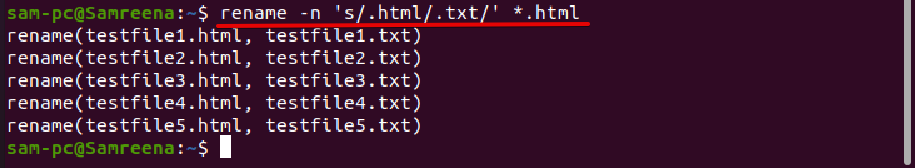
When you use the rename command followed by option ‘-n’, it also displays the file names to be renamed and renaming them as follows:
The above command displays the following result on the terminal window:
By default, the rename command does not overwrite an existing file. However, if you pass option -f along with the rename command then, it will help you to overwrite the existing files. Execute the following command to use the rename command followed by the -f option:
To change or rename the file name using rename command use the following command:
Example
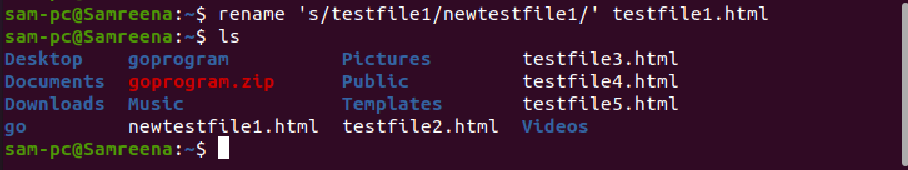
For example, we want to rename a single file with the name ‘testfile.txt’ to newtestfile.txt. In this case, the above command will be modified into the following form:
To see more usage of rename command, let us try the following examples:
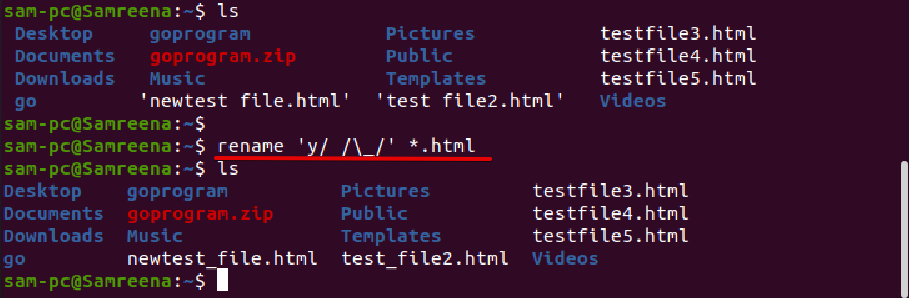
For example, to rename all those files, which contain spaces in file name and you want to replace it with underscores. In this case, the rename command will help you in the following way:
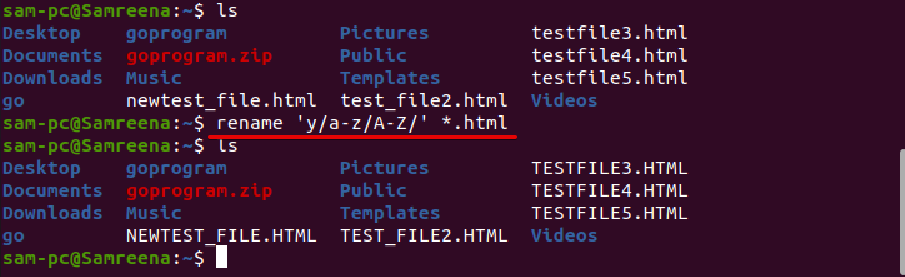
Using rename command, you can convert the file name in all lowercase letters as follows:
Similarly, to convert the file name to all uppercase letters, use the following command:
To explore more options and uses of rename command, type the following terminal command:
Conclusion
We discussed in this article how to rename files in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS distribution using the terminal application. Moreover, we explored the working and uses of the ‘mv’ and ‘rename’ commands for renaming a file. From the above discussion, we concluded mv command is useful for renaming a file but, rename command offers more advanced options for file renaming in the Ubuntu system.
About the author
Samreena Aslam
Samreena Aslam holds a master’s degree in Software Engineering. Currently, she’s working as a Freelancer & Technical writer. She’s a Linux enthusiast and has written various articles on Computer programming, different Linux flavors including Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and Mint.
How to Rename Files in Linux and MacOS Terminal
Renaming files is something that occurs frequently, and in Linux on terminal, there are many ways to rename files. Let’s look at some of the main ways you can rename your files on Linux and other Unix based systems like MacOS.
Linux Commands
Renaming files with the mv Command
The mv command moves a file to another place. It can also be used to move a file to the same location, and simply change it’s name. For example, if you wanted to rename a file called file-1.txt to file-2.txt , you would first cd into that directory, and run the following:
This technically “moves” the file, but in reality the end result is that the file is renamed and in the same location.
Renaming multiple files
If you want to rename more than one file at once, we can’t just use the mv command. For that, we need to loop through each file we want to rename. We can use this in conjunction with the find command to find all the files that fit our criteria easily. For example, the below will find all .txt, .csv and .html files, and turn them into .js files:
for f in $(find . -name '*.txt' -or -name '*.csv' -or -name '*.html'); do mv $f $.js done Let’s look at how this works in a little more detail:
- We run a for loop, for f in $() . This will find all files, where it matches what is inside $() . In this example, it finds anything with the file type .txt, .csv, or .html. You can learn more about find here.
- For each of the matching files, we run the mv command. We run mv $f $.js .
- $f is the current matching file we are looping through.
- $.html is saying rename any file with any extenstion ( could be , , etc), and change its name to the file name with our new extension, .js .
After that, you’ll have successfully moved all files.