- How to resize active root partition in Linux
- What is Gparted?
- Checking disk space usage in Linux
- Checking disk partition in Linux
- 1) Downloading GParted live ISO image
- 2) Booting the system with GParted live media
- 3) Keyboard selection
- 4) Language selection
- 5) Mode selection (GUI or Command-Line)
- 6) Loaded GParted live screen
- 7) Resizing the active root partition in Linux
- 8) Checking free disk space in the partition
- Расширение диска или раздела Linux
- Шаг 1. Расширение раздела
- Обычные тома (part)
- 1. С помощью утилиты growpart (без отмонтирования раздела)
- 2. С помощью утилиты fdisk/parted (требуется отмонтировать раздел)
- LVM
- Шаг 2. Изменение размера для файловой системы
- Увеличение разделов с Gparted
How to resize active root partition in Linux
Have you ever had the opportunity to resize an active root partition in Linux? If not, don’t worry, today, we will be discussing it. Disk partitioning is one of the best topics in Linux.
In this article, we will teach you how to resize the active root partition in Linux using the ‘GParted’ tool. Let’s assume you only have 30GB disk and you have configured the entire disk as a single partition while installing the Ubuntu operating system.
Now, you want to create a separate partition from that root partition for another purpose. If yes, you need to resize it. This is not limited to the root partition, and you can resize any partition available in the system.
If you have LVM configured on your system, you do not need to worry about file system resizing, as LVM allows you to resize the file system whenever you need it.
Resizing an active root partition is not a good idea, as it can lead to system crashes if you make a mistake. However, we are going to do this because there is no way to free up the file system.
Note: Make sure you back up important data before performing this operation, as your data can be easily retained in the event of a failure such as a power outage or a system restart during operation.
What is Gparted?
GParted is a free partition manager that enables you to resize, copy, and move partitions without data loss. All features of the GParted application can be used by using the GParted Live bootable image. GParted Live is a cross-platform tool that can be used on Linux, Windows and Mac OS X.
Checking disk space usage in Linux
Active partitions can be found in the Linux system using the df command. The following output clearly shows that we have only one partition with 30GB of space.
$ df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda1 30G 3.4G 26.2G 16% / none 4.0K 0 4.0K 0% /sys/fs/cgroup udev 487M 4.0K 487M 1% /dev tmpfs 100M 844K 99M 1% /run none 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock none 498M 152K 497M 1% /run/shm none 100M 52K 100M 1% /run/user
Checking disk partition in Linux
Disk partitions in Linux system can be verified in many ways, we will use ‘fdisk’ command to check the disk partitions in the system.
$ sudo fdisk -l [sudo] password for daygeek: Disk /dev/sda: 33.1 GB, 33129218048 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 4027 cylinders, total 64705504 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x000473a3 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sda1 * 2048 62609407 31303680 83 Linux /dev/sda2 62611454 64704511 1046529 5 Extended /dev/sda5 62611456 64704511 1046528 82 Linux swap / Solaris 1) Downloading GParted live ISO image
Make sure to copy the latest GParted ISO image from their download page then use the wget command to download it.
$ wget https://downloads.sourceforge.net/gparted/gparted-live-1.2.0-1-amd64.iso
2) Booting the system with GParted live media
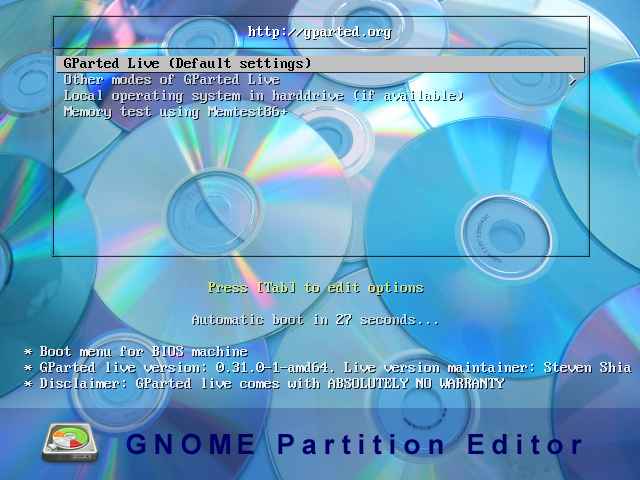
Boot your system with a GParted live installation media such as a burned CD/DVD or USB or ISO image. When you boot the system with GParted live media you will get an output similar to the below screen. Choose GParted Live (Default settings) and press Enter .
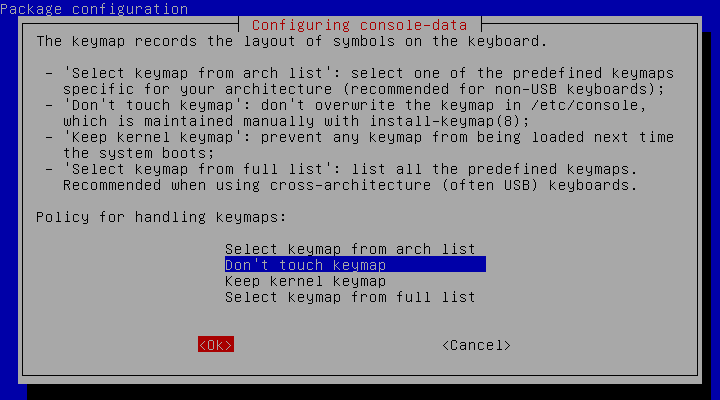
3) Keyboard selection
By default it chooses the second option, and press Ok to proceed:
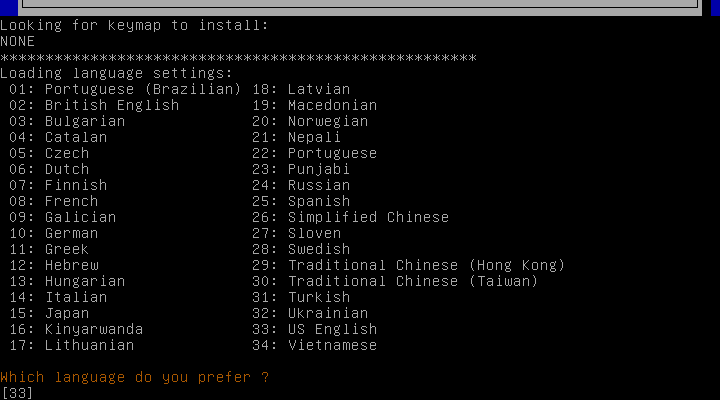
4) Language selection
By default, it chooses 33 for language that represents ‘US English’, and press Enter to proceed:
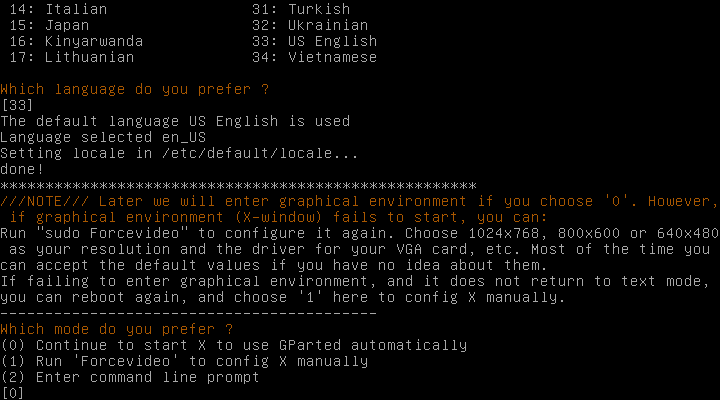
5) Mode selection (GUI or Command-Line)
By default, it selects 0 indicating GUI mode, and press Enter to proceed:
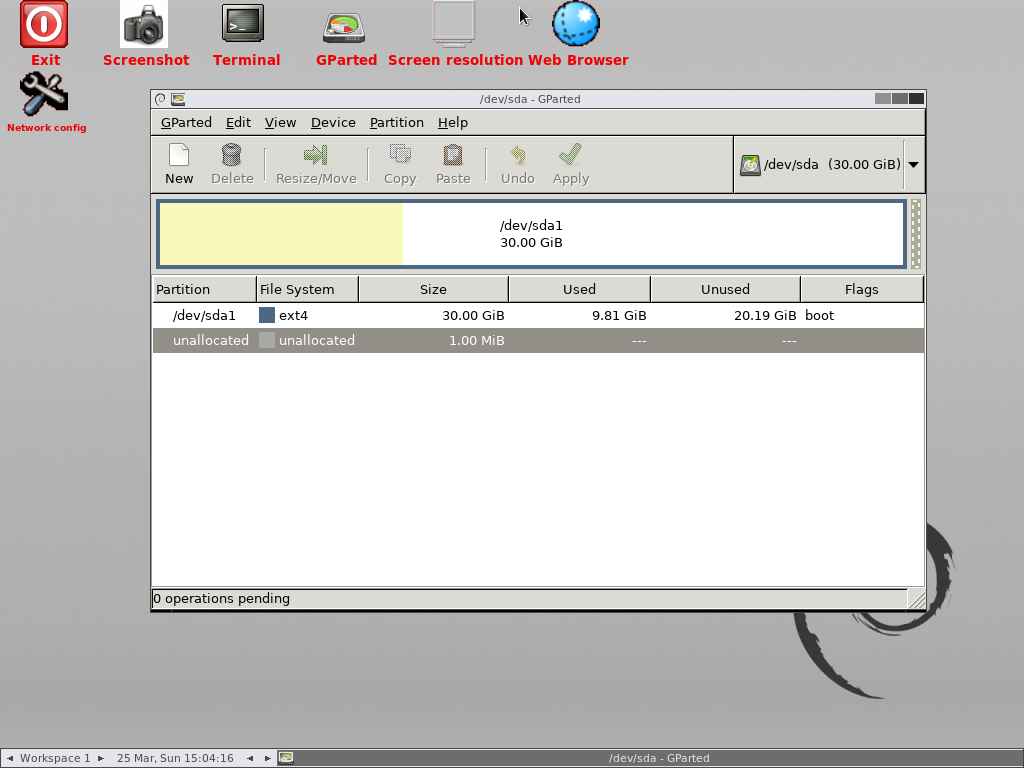
6) Loaded GParted live screen
Now, the GParted live screen is successfully loaded, and it displays the active partitions in the system:
7) Resizing the active root partition in Linux
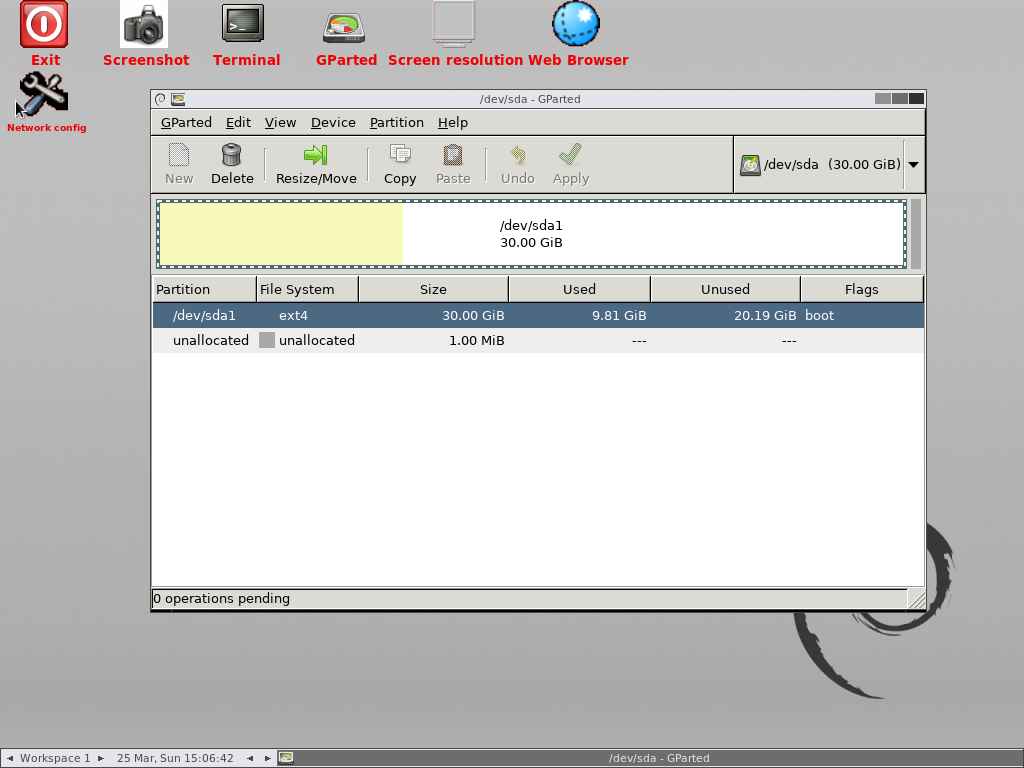
Select the root partition you want to resize. In this case, we only have one partition that belongs to the root partition, so we choose to resize it.
Press the Resize/Move button to resize the selected partition.
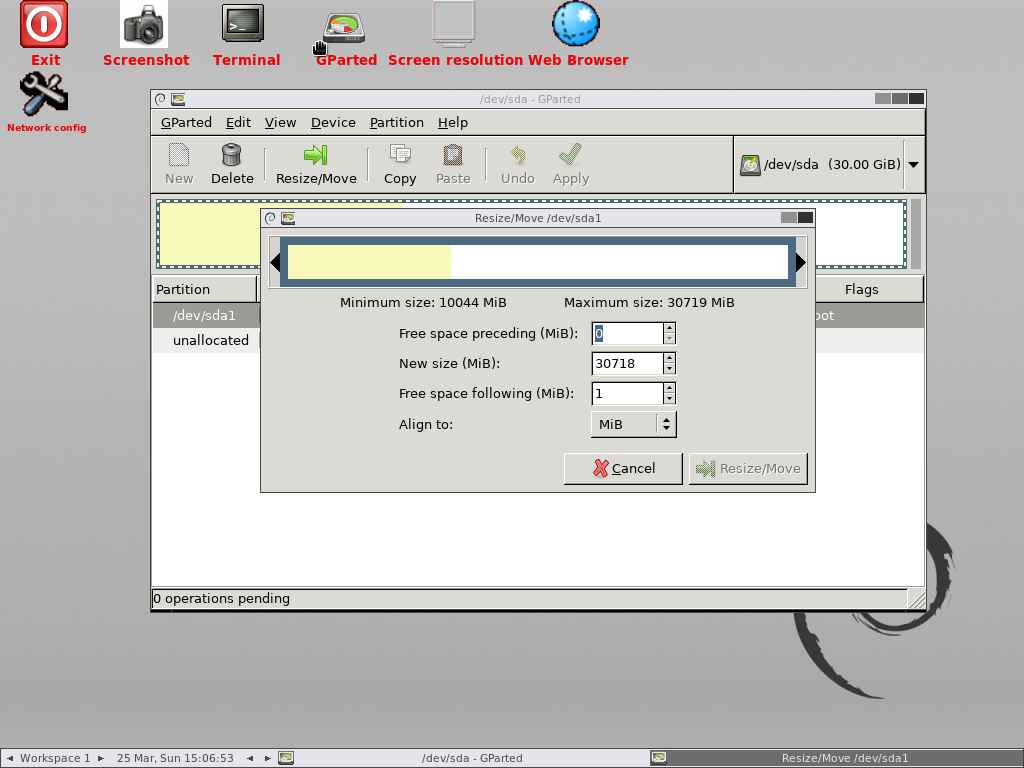
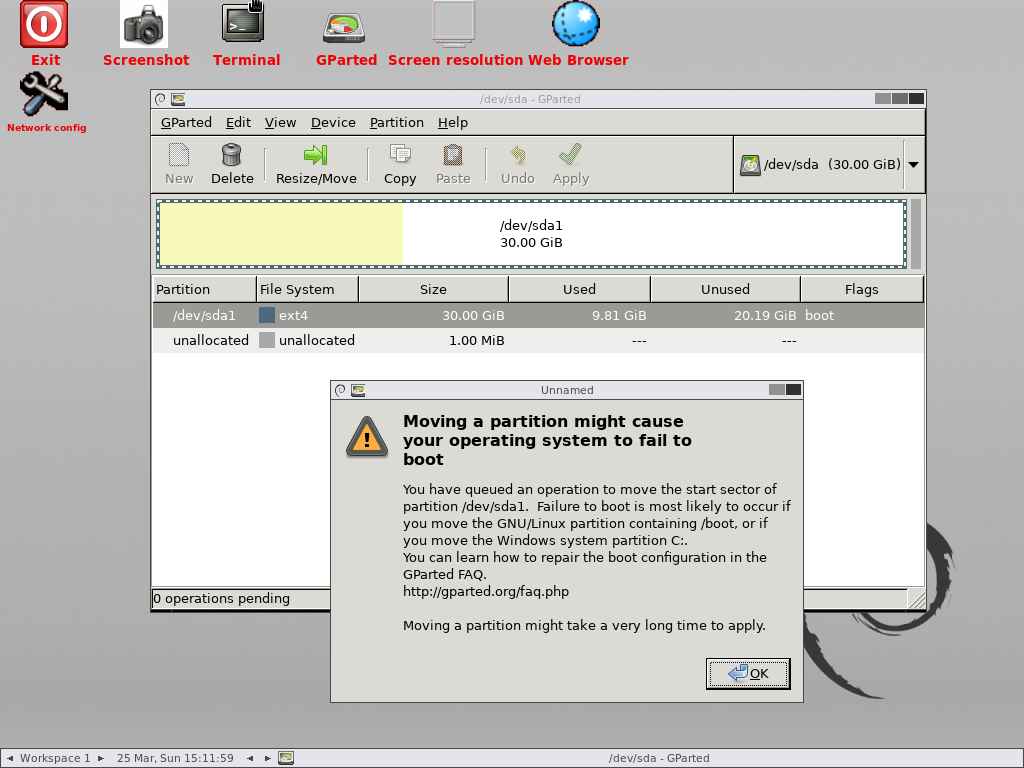
Enter the size that you want to take out from this partition in the first box. If you want to claim 10GB then add 10240MB in the first text box and leave the rest of the boxes as is, and press ‘Resize/Move’ button to proceed.
This will prompt you to confirm that the partition will be resized because you are editing the live system partition. Press the ok button to continue:
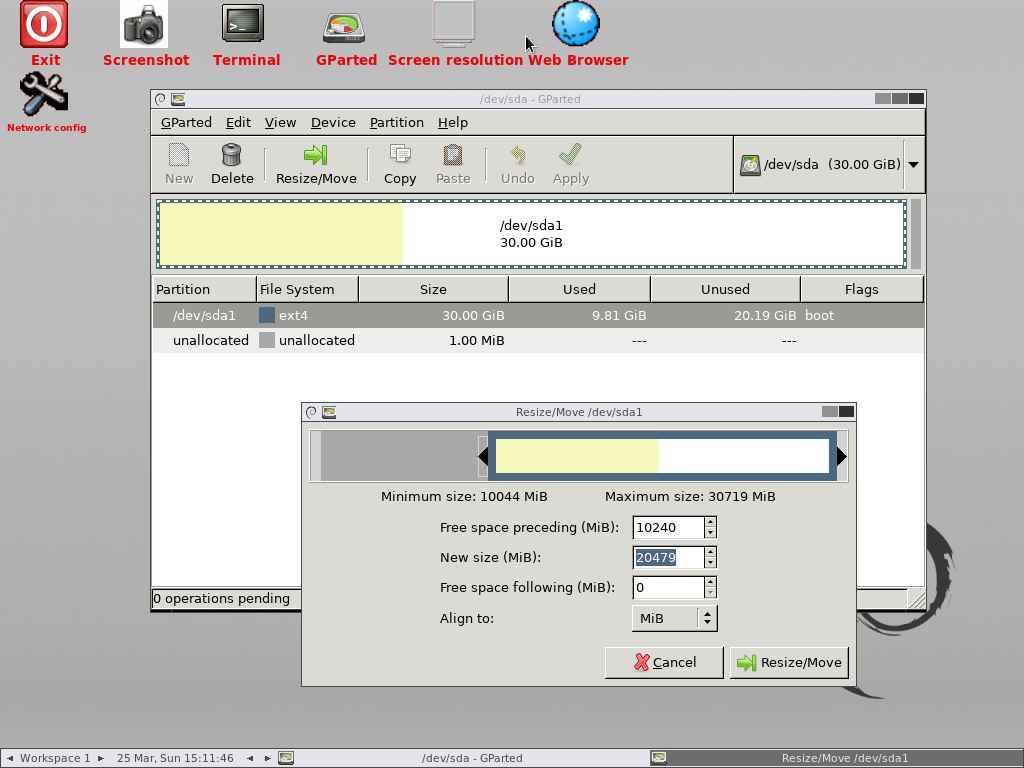
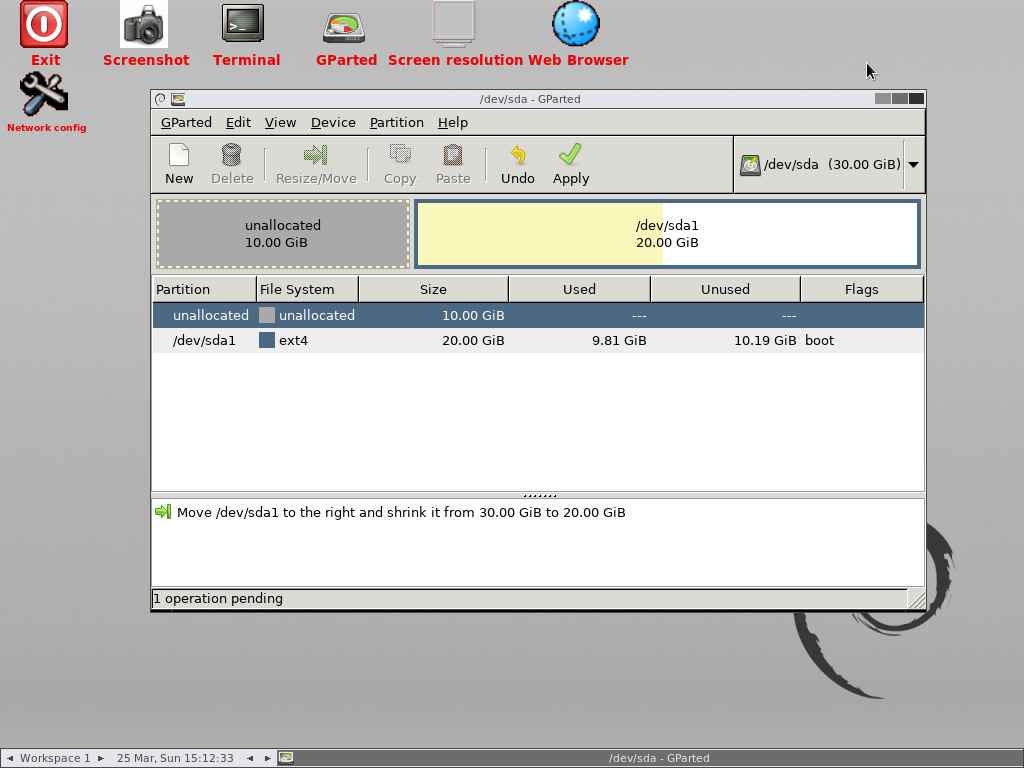
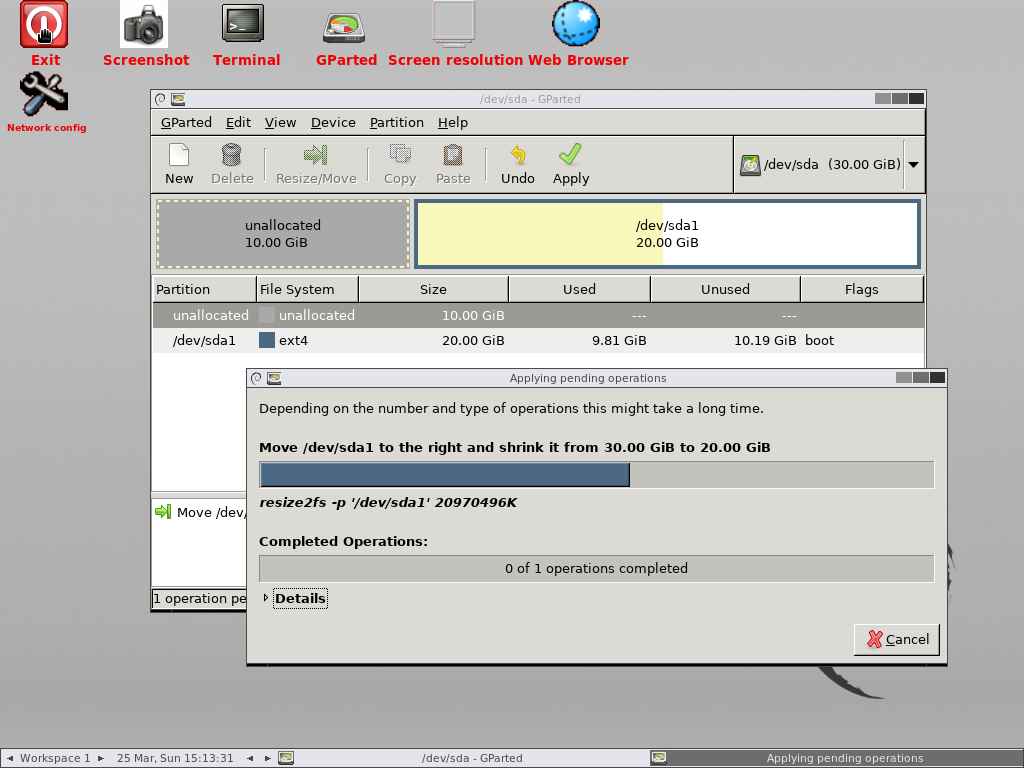
It has successfully compressed the partition from 30GB to 20GB and also shows 10GB of unallocated disk space:
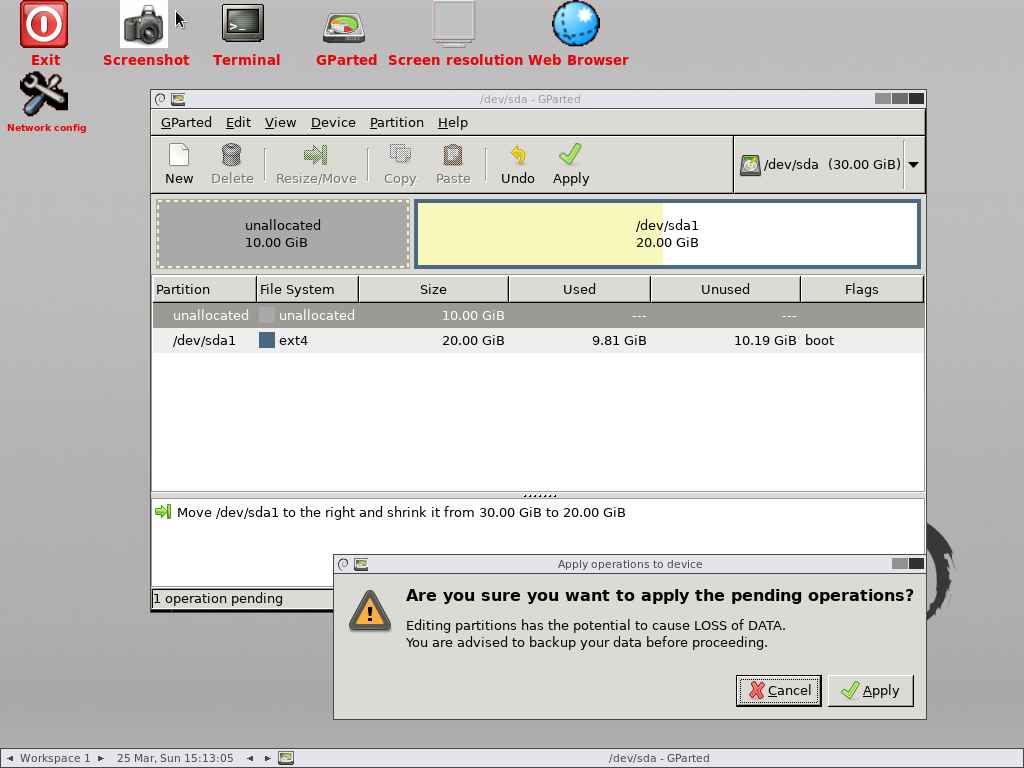
Finally, click Apply button to perform the remaining operations.
- e2fsck e2fsck is a file system check utility that automatically repair the file system for bad sectors, and I/O errors related to HDD.
- resize2fs The resize2fs program will resize ext2, ext3, or ext4 file systems. It can be used to enlarge or shrink an unmounted file system located on device.
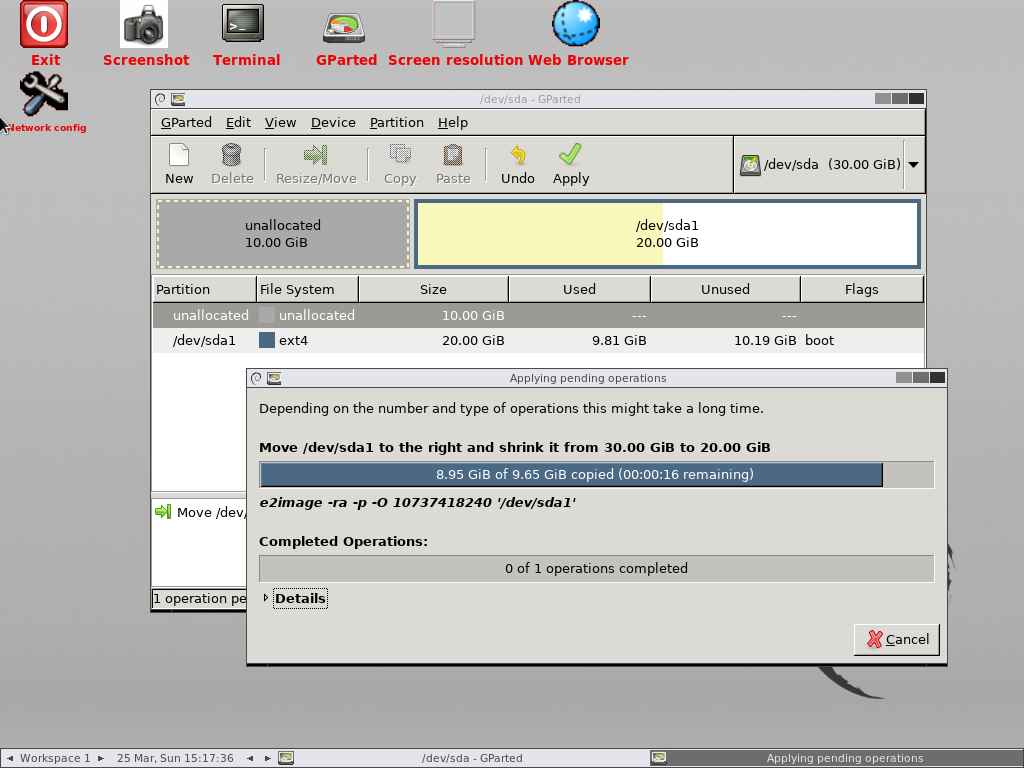
- e2image The e2image program will save critical ext2, ext3, or ext4 filesystem metadata located on device to a file specified by image-file.
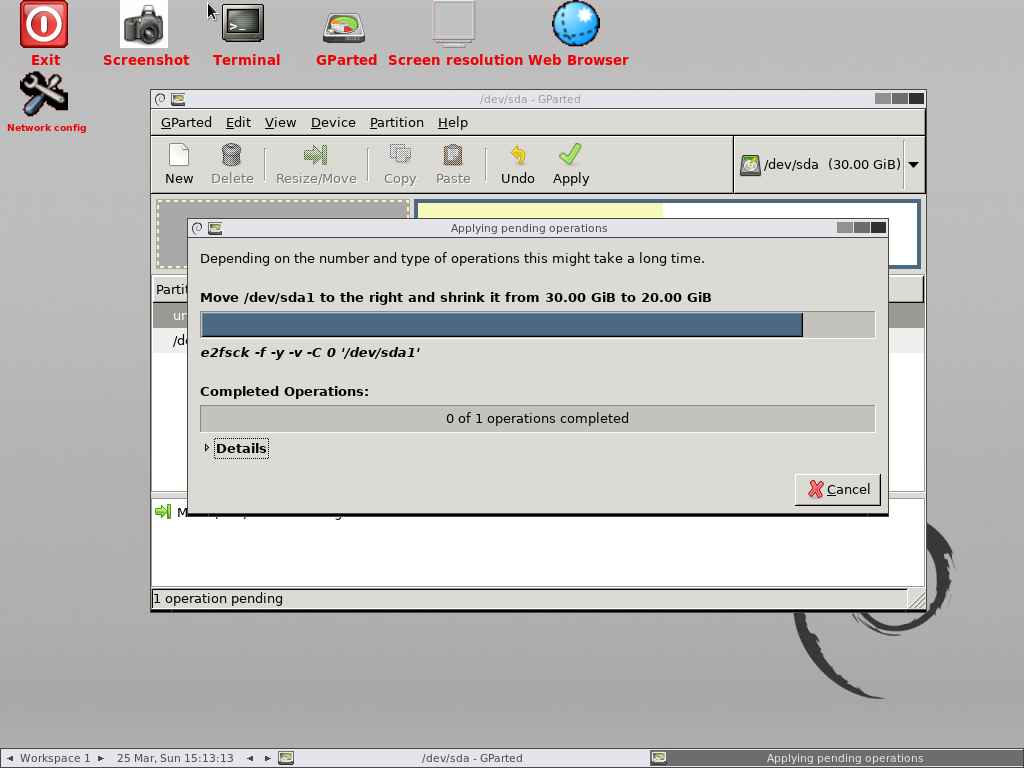
e2fsck : The e2fsck is a file system check utility that automatically repairs the file system for bad sectors, and I/O errors related to HDD:
resize2fs: The resize2fs program will resize ext2, ext3, or ext4 file systems. It can be used to enlarge or shrink an unmounted file system located on the device:
e2image : The e2image program will save critical ext2, ext3, or ext4 filesystem metadata located on the device to a file specified by image-file:
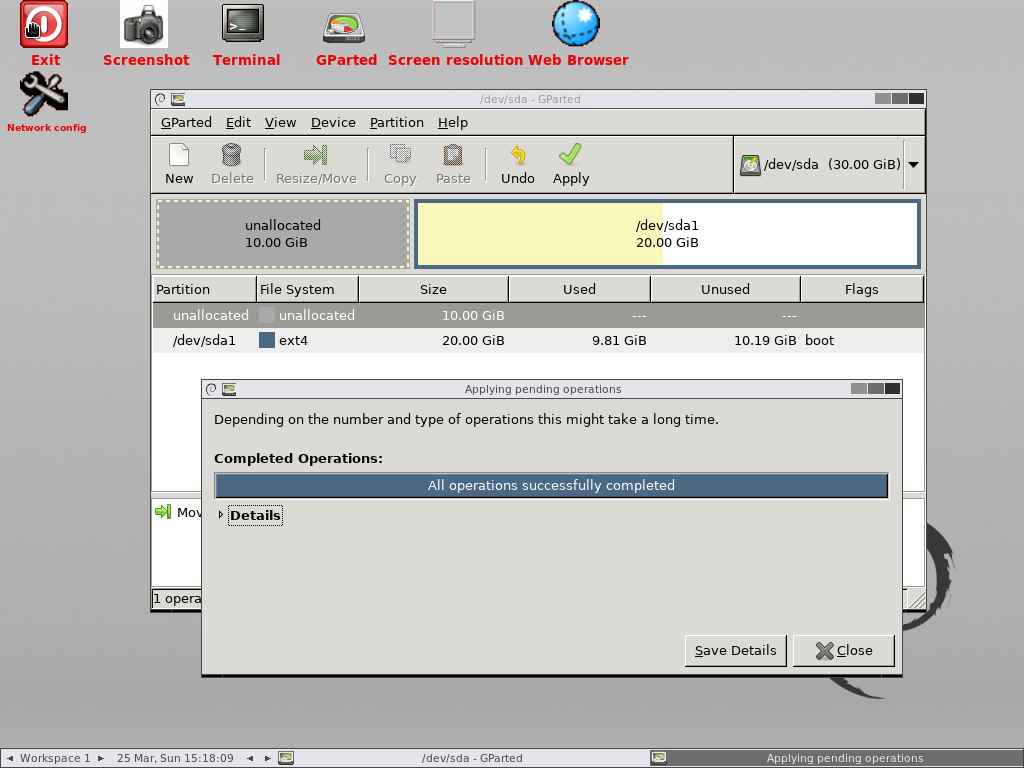
All the operations are now successfully completed. Now click close button to close the dialog box:
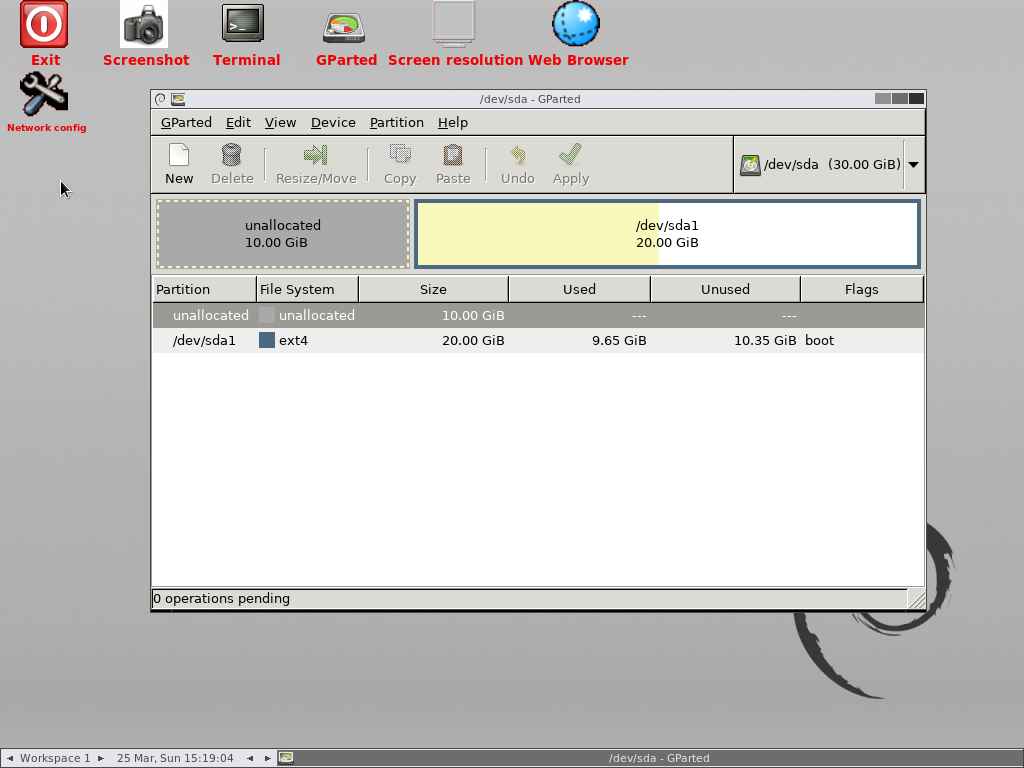
Now, I’m able to see 10GB of Unallocated disk partition as shown below:
Reboot the system to check this:
8) Checking free disk space in the partition
Login again and use the fdisk command to find the free space available in the given partition. And you should be able to see the 10GB of unallocated disk space in this partition as shown below:
$ sudo parted /dev/sda print free [sudo] password for daygeek: Model: ATA VBOX HARDDISK (scsi) Disk /dev/sda: 32.2GB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: msdos Disk Flags: Number Start End Size Type File system Flags 32.3kB 10.7GB 10.7GB Free Space 1 10.7GB 32.2GB 21.5GB primary ext4 boot Расширение диска или раздела Linux
Обновлено: 04.04.2023 Опубликовано: 22.06.2017
В зависимости от типа раздела и файловой системы, действия различаются.
Любая работа с диском несет риск потери информации. Перед началом работ убедитесь в наличие резервных копий ценных данных.
Шаг 1. Расширение раздела
Мы рассмотрим варианты работы с обычными томами (разделами) и томами LVM. Проверить, какой тип раздела у нас используется можно командой:
Нам интересны варианты part и lvm.
Обычные тома (part)
Допустим, есть диск /dev/sdb и раздел /dev/sdb2, который нужно увеличить. Разберем два подхода, сделать это.
1. С помощью утилиты growpart (без отмонтирования раздела)
Данная утилита позволяет увиличить размер слайса без необходимости его отмонтировать. Это очень удобно для работы с корневыми разделами. Данная утилита не установлена в системе. В зависимости от последней наши действия будут различаться.
а) Для систем DEB:
apt install cloud-guest-utils
б) Для систем RPM:
yum install cloud-utils-growpart
Если наш диск имеет разметку GPT, то потребуется установить также утилиту gdisk.
а) Для DEB:
Установка growpart завершена. Идем дальше.
Для расширения раздела /dev/sdb2 вводим команду:
Мы должны увидеть что-то на подобие:
CHANGED: partition=2 start=4096 old: size=20965376 end=20969472 new: size=41938910 end=41943006
2. С помощью утилиты fdisk/parted (требуется отмонтировать раздел)
Данный способ удобнее тем, что не нужно устанавливать дополнительных утилит, но он потребует отмонтирование раздела. Это можно сделать командой:
В случае работы с корневой директорией, отмонтировать ее не получиться. В таком случае необходимо загрузить компьютер с Windows LiveCD или GParted Live.
Подключаемся утилитой fdisk к /dev/sdb:
Если мы работаем с разделом более чем 2Тб, используем утилиту parted.
Удаляем раздел (не переживайте — все данные сохраняются):
* в моем примере, раздел для удаления на второй позиции.
На запрос начального и конечного секторов просто нажимаем Enter.
Если раздел был загрузочный, добавляем соответствующий флаг:
Еще раз проверяем, что получилось:
LVM
LVM-тома расширяются на лету, даже для корневых разделов. В данном примере, работаем с /dev/sda.
Подробнее о работе с LVM читайте в инструкции Как работать с LVM.
Открываем диск утилитой fdisk:
* напомню, что при работе с диском 2Тб и более, следует использовать утилиту parted.
Номер раздела оставляем тот, который предлагает система (просто нажимаем Enter).
Первый и последний сектора также оставляем по умолчанию для использования всего дискового пространства (еще два раза Enter).
Выбираем номер раздела (в моем примере создавался раздел 3):
Командой L можно посмотреть список всех типов, но нас интересует конкретный — LVM (8e):
Проинформируем систему, что в таблице разделов произошли изменения:
Создаем физический том из нового раздела:
Смотрим наши Volume Group и для нужного добавляем созданный том:
vgextend vg_centos /dev/sda3
* в моем примере группа томов LVM называется vg_centos
Смотрим LVM-разделы и расширяем пространства для нужного:
lvextend -l +100%FREE /dev/vg_centos/lv_root
* данная команда расширяем LVM-раздел /dev/vg_centos/lv_root, используя все свободное пространство (100%FREE).
Шаг 2. Изменение размера для файловой системы
После того, как на предыдущем шаге мы расширили раздел, система по-прежнему будет видеть старый по объему диск. Чтобы это исправить, необходимо выполнить команду по изменению размера файловой системы. В зависимости от последней, команды различаются.
Посмотреть файловую систему:
ext2/ext3/ext4:
* обратите внимание, что в данных примерах используются различные устройства.
Если раздел был отмонтирован, монтируем его, например:
Проверяем, что настройки применились:
Увеличение разделов с Gparted
Если работы выполняются на системе с графическим интерфейсом или есть возможность перезагрузить сервер и загрузиться с LiveCD, можно воспользоваться простым средством — утилитой Gparted, которая позволяем менять размер разделов мышкой.
Запускаем утилиту — выбираем диск, с которым будем работать — кликаем правой кнопкой по разделу, который хотим увеличить и выбираем Resize/Move:
В открывшемся окне с помощью мышки или форм меняем размер раздела:
Нажимаем кнопку Resize/Move.
Проверяем изменения в окне программы и сохраняем настройки кнопкой «Apply All Operations»: