- How to Start, Stop, and Restart MySQL Server
- How to Start, Stop, and Restart MySQL Server in Linux
- How to Start, Stop, and Restart MySQL Server in Windows
- How to Restart MySQL in Ubuntu
- How to validate the installation of MySQL in Ubuntu
- How to restart MySQL using the systemctl command in Ubuntu
- How to restart MySQL using the service command in Ubuntu
- How to restart MySQL through init.d process in Ubuntu
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Hammad Zahid
- Перезапуск MySQL
- Перезапуск MySQL или MariaDB
- Автоматический перезапуск MySQL
- Выводы
- How do I start/stop mysql server?
- 11 Answers 11
How to Start, Stop, and Restart MySQL Server
When using MySQL, there are times when it’s important to know how to start, stop, or restart your MySQL server. Luckily, there are multiple, easy ways to do this. Which methods are available to you however, will depend on the operating system your running.
Read on to learn how to start, stop, and restart MySQL server in both Linux and Windows.
How to Start, Stop, and Restart MySQL Server in Linux
If you need to stop or restart your MySQL server on a Linux system, there are three different commands that can be used:
- Depending on your Linux distribution, you can change the state of MySQL using the service command.
- To start MySQL server:
sudo service mysqld start
- To stop MySQL server:
sudo service mysqld stop
- To restart MySQL server:
sudo service mysqld restart
- To start MySQL server:
- If you don’t have the service command available or would prefer to make changes to MySQL using a different method, you can also use the init.d command to start/stop your MySQL server.
- To start MySQL server:
sudo /etc/init.d/mysqld start
- To stop MySQL server:
sudo /etc/init.d/mysqld stop
- To restart MySQL server:
sudo /etc/init.d/mysqld restart
- To start MySQL server:
- Lastly, you can also use the systemctl command to start, stop, and restart applications on Linux, including MySQL.
- To start MySQL server:
sudo systemctl start mysqld
- To stop MySQL server:
sudo systemctl stop mysqld
- To restart MySQL server:
sudo systemctl restart mysqld
- To start MySQL server:
How to Start, Stop, and Restart MySQL Server in Windows
If you’re trying to start, stop, or restart your MySQL server on a Windows-based system, you can do so easily from the command line. Just follow these 3 steps:
- To start, you’ll first need to open a terminal window. If you don’t have this somewhere easily accessible, you can find it quickly using the Windows’ Run dialog. To open the Run dialog, just press the Windows Key + R .
- Next, type in “ cmd ” and press the Enter key. This will open a new terminal window.
- Once you’ve opened a terminal window, just type the following commands to start or stop MySQL server:
- To start MySQL server:
mysqld start
- To stop MySQL server:
mysqld stop
- To start MySQL server:
*Note: depending on which version of Windows you are running, you may need the specific name of the MySQL version number you are running in order to start or stop the service. To find this, go to the start menu and search for Services . Locate the version of MySQL you are using and try the following commands, replacing “##” with your version number:
net start MySQL##
net stop MySQL##
For instance, if you’re running MySQL 8.0, replace “MySQL##” with “MySQL80”.
And there you have it! You now have several different methods for starting, stopping, and restarting MySQL server as needed.
Looking for more information on MySQL ? Search our Knowledge Base !
Interested in more articles about Databases ? Navigate to our Categories page using the bar on the left or check out these popular articles:
Popular tags within this category include: MySQL , MSSQL , phpMyAdmin , PostgreSQL , and more.
Don’t see what you’re looking for? Use the search bar at the top to search our entire Knowledge Base.
The Hivelocity Difference
Seeking a better Dedicated Server solution? In the market for Private Cloud or Colocation services? Check out Hivelocity’s extensive list of products for great deals and offers.
With best-in-class customer service, affordable pricing, a wide-range of fully-customizable options, and a network like no other, Hivelocity is the hosting solution you’ve been waiting for.
Unsure which of our services is best for your particular needs? Call or live chat with one of our sales agents today and see the difference Hivelocity can make for you.
How to Restart MySQL in Ubuntu
MySQL is an RDMS (Relational Database Management System), which is used in the back-end development of any website, to store its data and the data is stored in the form of rows and columns, which are combined to form tables. With the help of MySQL, one can not only store data, but also can insert it, delete it, or modify it in tables, and to improve the performance of the system MySQL needs to be restarted. In this article, we will learn how to restart MySQL in Ubuntu by running simple commands.
How to validate the installation of MySQL in Ubuntu
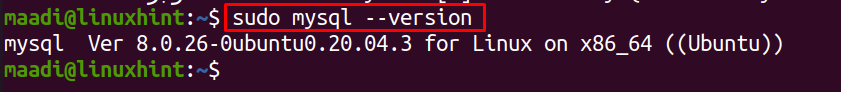
Before restarting, MySQL first confirmed that MySQL is installed in Ubuntu or not. To verify this, we will run the command to check the version of MySQL:
The output is displaying the version details of MySQL which mean MySQL has been installed in Ubuntu.
How to restart MySQL using the systemctl command in Ubuntu
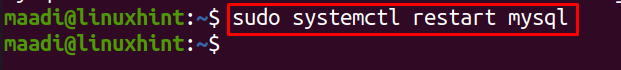
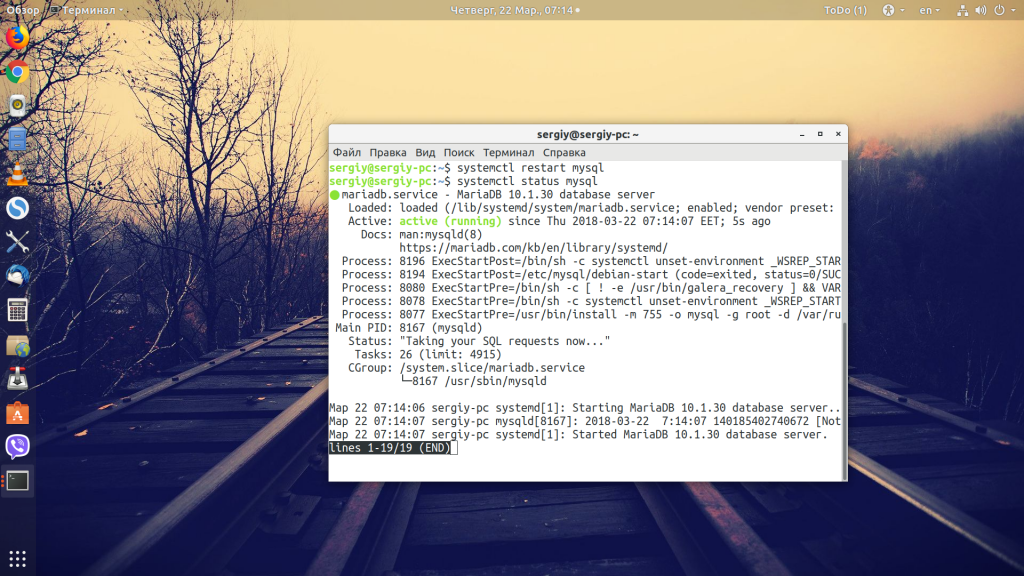
The systemctl command is used to start, restart, and stop the applications in Ubuntu and it is also used to check the status of applications. To restart MySQL, using the systemctl command:
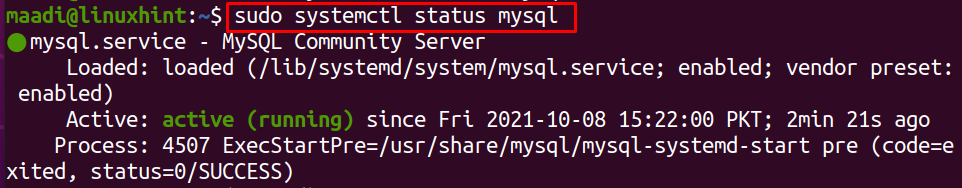
Though successful execution of the above command without generating any error is the indication that MySQL has been restarted, we can confirm it by checking its status again using the systemctl command:
How to restart MySQL using the service command in Ubuntu
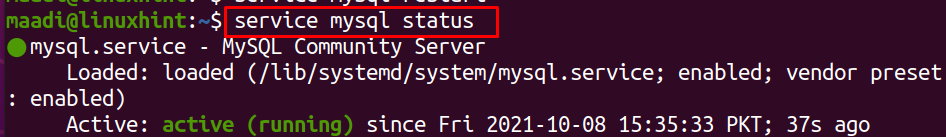
Likewise the systemctl command, the service command can also be used to manage the different applications to start, stop and restart. To restart MySQL in Ubuntu using the service command:
Once the command is executed, it will ask for the password for authentication purposes:
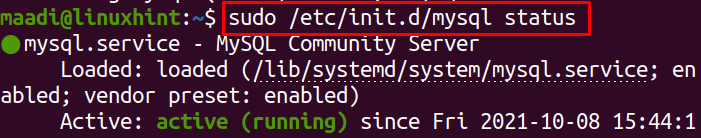
Type password, and click on Authenticate to proceed with the command. To confirm the successful execution of the above command, check the status of MySQL using the service command:
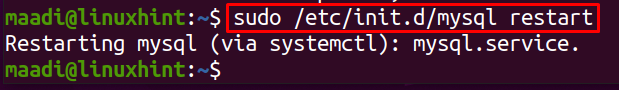
How to restart MySQL through init.d process in Ubuntu
Similar to the service and systemctl command, we can start, stop, and restart the applications by using the init.d command with the path of MySQL in Ubuntu. Before restarting the MySQL let us understand what is init.d?
There are many other services like ssh, MongoDB, etc whose scripts are located in this directory. When Linux is started, it’s the first process that initialized in Ubuntu is init.d, later on, other services start using init.d Now using the extension of “.d” with the path of a directory, which is stands for daemon, we can run these services and also supervise the processes. To restart MySQL in Ubuntu using the init.d:
Though from the output, it is being obvious the MySQL has been restarted but to confirm this by checking its status, run the command:
Conclusion
In MySQL after making changes in any configuration file, it is recommended to restart the MySQL, so modified changes can be implemented. To restart the MySQL in Ubuntu is not very tough, one has to simply run some simple commands in the terminal.
This article is related to the methods of the restart of MySQL in Ubuntu, three methods are discussed by using the systemctl command, by using the service command, or by using the init.d command. It is not recommended to restart the MySQL regularly because it removes the cache memory while restarting, and also engines have to wait until it starts again, as a result, it decreases the performance.
About the author
Hammad Zahid
I’m an Engineering graduate and my passion for IT has brought me to Linux. Now here I’m learning and sharing my knowledge with the world.
Перезапуск MySQL
MySQL — это самая популярная система баз данных, которая используется для обеспечения работы большинства сайтов. Пока вы размещаете свой сайт на хостинге, вам нет необходимости думать о её настройке или своевременной перезагрузке, потому что этим занимаются системные администраторы хостинга. Но когда вы переберётесь на VPS, это всё будет уже в зоне вашей ответственности.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как выполняется перезапуск MySQL в разных дистрибутивах Linux, а также как сделать, чтобы MySQL перезапускалась автоматически после падения.
Перезапуск MySQL или MariaDB
В большинстве современных дистрибутивов, а особенно тех, что используются для работы серверов, для управления службами применяют Systemd. Именно с её помощью мы будем перезапускать движок баз данных. Ещё один момент, с которым нужно определиться, — это название юнит-файла MySQL. В зависимости от версии и дистрибутива оно может отличаться:
- mysql-server;
- mariadb-server;
- mysql;
- mariadb;
- mariadbd
- mysqld;
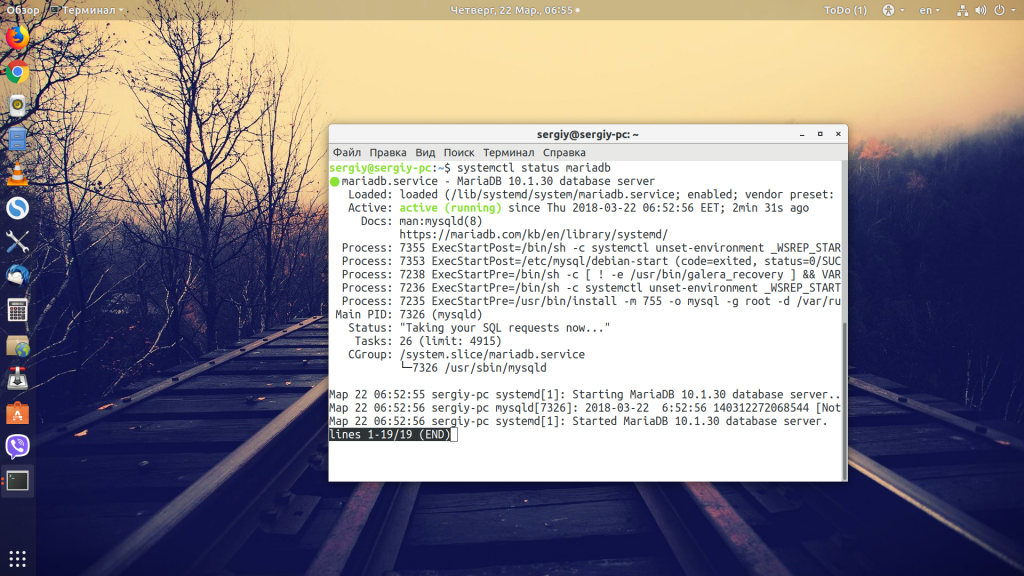
Вы можете попробовать использовать эти варианты, чтобы найти тот, что используется в вашей системе; последние версии Ubuntu понимают несколько имен MySQL. Таким образом, для MariaDB и выше перезапуск MySQL Сentos и Ubuntu не отличается. Просто попробуйте узнать состояние сервиса, если вы выбрали правильное название, то увидите что-то вроде этого:
Выполнить частичную перезагрузку только с обновлением конфигурации, так как это делалось в Apache и Nginx вы не сможете. Здесь необходимо полностью перезагружать сервис:
sudo systemctl restart mysql
В некоторых случаях необходимо полностью остановить работающий сервис, а потом запустить его заново. Для этого используем команду stop, затем start:
sudo systemctl stop mysql
sudo systemctl start mysql
Автоматический перезапуск MySQL
Из-за проблем с памятью на сервере или других ошибок MySQL может завершить свою работу. Это очень неприятное обстоятельство, поскольку вы не можете всегда следить за сервером, а когда такое случиться, ваш сайт будет недоступен для пользователей на протяжении долгого времени.
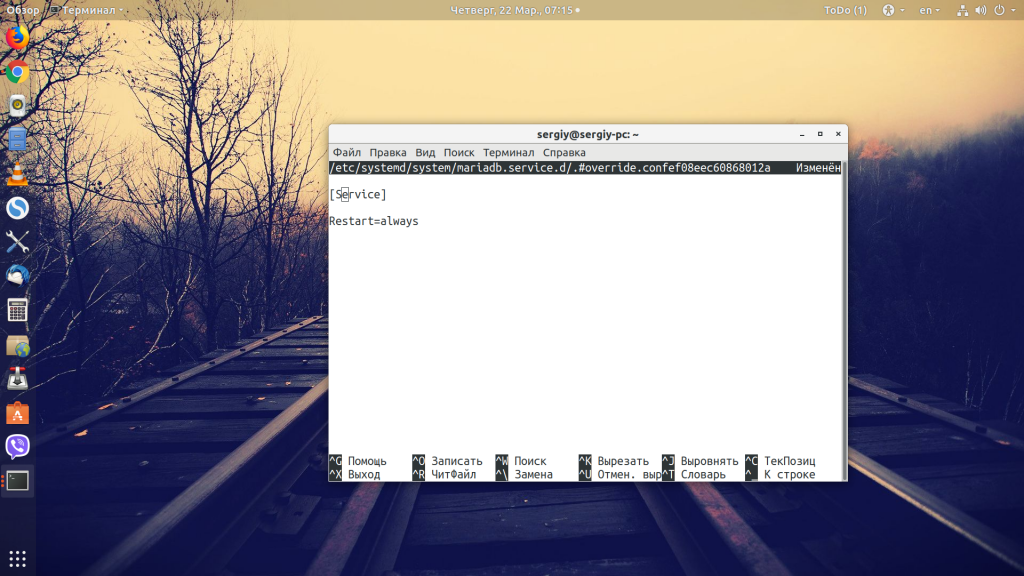
В systemd есть возможность, которая позволяет делать рестарт MySQL сразу же после того, как он неожиданно завершился. Для этого необходимо добавить такую строчку в конфигурацию юнит-файла MySQL:
Но обратите внимание, что редактировать файлы юнитов в папке /usr нельзя, потому что во время обновления они могут быть перезаписаны, можно только в /etc, и желательно создавать отдельный файл. Можно поступить проще: используйте команду systemctl edit:
sudo systemctl edit mariadb
Сохраните изменения. Эти строки будут записаны в виде отдельного файла, который автоматически подключается к основному.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели, как перезапустить MySQL для обновления конфигурации, а также как настроить автоматический перезапуск службы после возникновения ошибок. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!

Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How do I start/stop mysql server?
I tried to find in some articles describing how to correctly start & stop mysql server. I found this link: How to start/stop MySql server on Ubuntu 8.04 | Abhi’s Blogging World I ran this command:
ERROR 1045 (28000) Access denied for user. sudo /etc/init.d/mysql - root -p start ERROR 1049 (42000) Unknown database 'start'. MySQL server success started. Cool! So, what’s wrong with the other commands? Why do they result in error?
In fact, even with sudo it didn’t work for me, but then I found in the script the following hint: Rather than invoking init scripts through /etc/init.d, use the service(8) and it was ok
Generally you can use sudo -l to see what your specific user on your specific system is allowed to do with sudo. (Your permissions are configured in /etc/sudoers.) However I don’t know for sure if it would help in this particular case. EDIT: Wait, never mind, the access denied error looks like it is coming from MySQL or something, not sudo.
11 Answers 11
Your first two commands weren’t run as root so that is expected behaviour. You need to be root to stop/start mysql.
should work. Indeed it does, for me:
kojan:~> sudo /etc/init.d/mysql restart [sudo] password for chris: Stopping MySQL database server: mysqld. Starting MySQL database server: mysqld. Checking for corrupt, not cleanly closed and upgrade needing tables.. I used restart rather than start, since it was already running, but the effect is the same. Are you sure you entered your password correctly? 🙂 Have you edited your sudo config at all which would stop this working?
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql - root -p start The arguments are wrong. an init.d script only takes start or stop or restart — just one word telling it what to do. You cannot give it multiple arguments as you were trying to do.
Anyway, the short answer is the one you actually got to work, is the recommended way. service is replacing all the init.d scripts over time, so you should get into the habit of using service . The page you link to was written in 2008, so has to be taken with some salt 🙂