- 4 Ways to Transfer Files Between Remote and Local Systems Over SSH
- Method 1: Use scp command to copy files over SSH
- Copy files from the remote machine to your local machine
- Copy files from your local machine to the remote machine
- You can copy directories too
- Method 2: Use rsync to copy files and directories over SSH
- Copy files from the remote machine to your local machine
- Copy files from your local machine to the remote machine
- How about copying directories with rsync?
- Method 3: Using SSHFS to access files from remote system over SSH
- Method 4: Use a GUI-based SFTP client for transferring files between remote systems
- Which method do you prefer?
- Передача файлов между серверами Linux с использованием SCP и FTP
- Что такое FTP?
- Синтаксис FTP
- Команды FTP
- Как передавать файлы через FTP
- Шаг 1 — установка FTP-соединения
- Шаг 2 — выбор режима передачи
- Шаг 3 — передача файла
- Шаг 4 — завершение сессии
- Как передать несколько файлов через FTP
- Что такое SCP?
- Синтаксис SCP
- Как передать файлы по SCP с локальной машины на удаленный хост
- Как передать файлы по SCP с удаленного хоста на локальную машину
- Итоги
4 Ways to Transfer Files Between Remote and Local Systems Over SSH
From legacy scp to modern rsync. From the unconventional sshfs to the GUI convenience of FileZilla. Learn different ways for copying files over SSH.
Sooner or later, you’ll find yourself in a situation where you have to upload the file to the remote server over SSH or copy a file from it.
There are various ways you can transfer files over SSH. I am going to discuss the following methods here:
- scp: Legacy command which is being deprecated
- rsync: Popular command for file synchronization
- sshfs: Mounting remote directory over SSH
- sftp clients: GUI tool for accessing file over SFTP
For a successful file transfer over SSH, you need to
- have SSH access between the two machines
- know the username and password on the remote machine
- know the IP address or hostname (on the same subnet) of the remote machine
With that aside, let’s see the methods for copying files between remote systems via SSH.
Method 1: Use scp command to copy files over SSH
I have read that scp is going to be deprecated. Still, it is my favorite tool for transferring files between systems over SSH. Why? Because its syntax is similar to the cp command.
Let’s see how to use the scp command.
Copy files from the remote machine to your local machine
Here’s the scenario. You want to copy files from the remote Linux system to the currently logged in system.
Here’s a generic syntax that copies the file from the home directory of the user on the remote system to the current directory of your locally logged in system.
scp [email protected]_address:/home/username/filename .Do you see the similarity with the cp command? It’s almost the same except that you have to specify username and ip address with colon (:).
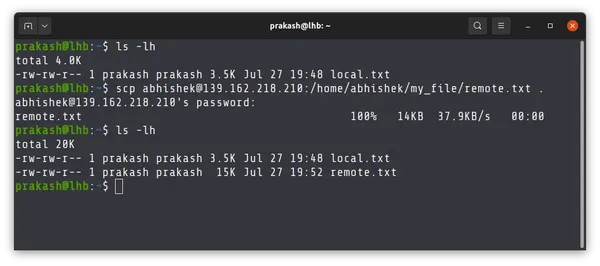
Now, let me show you a real-world example of this command.
In the example above, I copied the file remote.txt from the /home/abhishek/my_file directory on the remote system to the current directory of the local machine.
This should give you a hint that you should know the exact location of the file on the remote system. The tab completion does not work on remote systems.
Copy files from your local machine to the remote machine
The scenario is slightly changed here. In this one, you are sending a local file to the remote system over SSH using scp.
This is a generic syntax which will copy the filename to the home directory of username on the remote system.
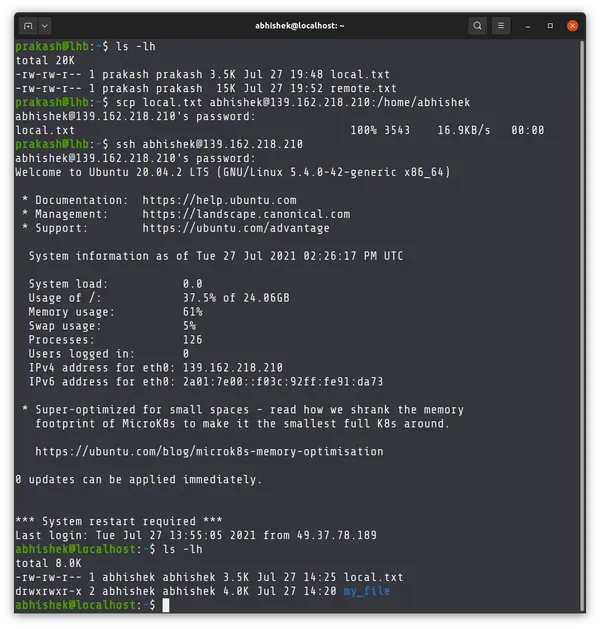
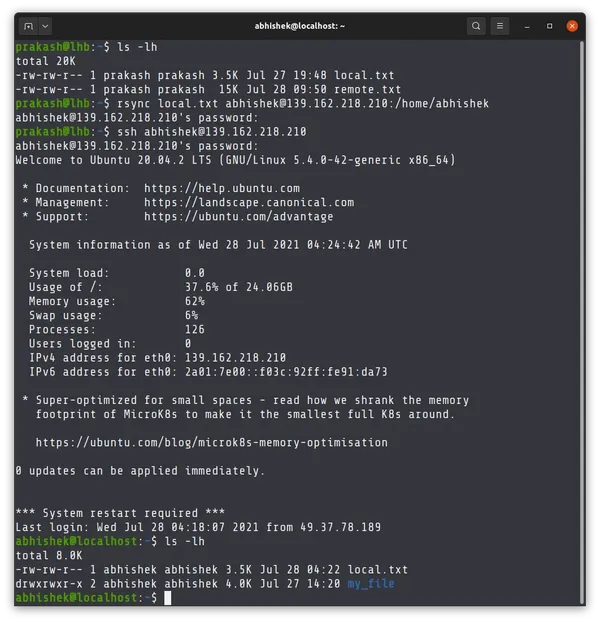
In the above example, I copied local.txt file from the current directory to the home directory of the user abhishek on the remote system.
Then I logged into the remote system to show that the file has actually been copied.
You can copy directories too
Remember I told you I like scp because of its similarity with the cp command?
Like cp command, you can also use scp to copy directory over SSH. The syntax is similar to the cp command too. You just have to use the -r option.
scp -r source_dir [email protected]_address:/home/username/target_dirYou can do a lot more with it. Read some more examples of scp command in this tutorial:
Method 2: Use rsync to copy files and directories over SSH
Since scp is being deprecated, rsync is the next best tool for copying files between remote system over SSH. Actually, it is better than scp in many terms.
The command syntax is the same as scp. Older versions of rsync had to use rsync -e ssh but that’s not the case anymore.
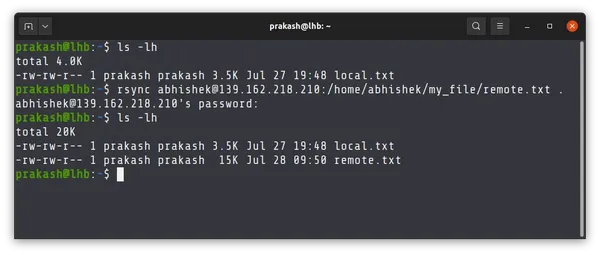
Copy files from the remote machine to your local machine
Let’s say you want to copy a file from the home directory of the user on the remote system to the current directory of your locally logged in system.
rsync [email protected]_address:/home/username/filename .Let’s take the same example you saw with scp. I am copying the file remote.txt from the /home/abhishek/my_file directory on the remote system to the current directory of the local machine.
Copy files from your local machine to the remote machine
Here is a generic syntax which will copy the file to the home directory of username on the remote system.
Time to see the real world example. I am copying local.txt file from the current directory to the home directory of the user abhishek on the remote system.
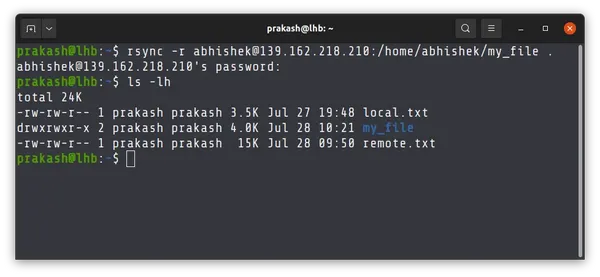
How about copying directories with rsync?
It’s the same. Just use -r option with rsync to copy entire directory over SSH between remote systems.
rsync -r source_dir [email protected]_address:/home/username/target_dirTake a look at this example. I copy the entire my_file directory from the remote system to the local system.
rsync is a versatile tool. It is essentially a tool for ‘recursively syncing’ the contents between two directories and quite popular for making automated backups.
Method 3: Using SSHFS to access files from remote system over SSH
There is also SSHFS (SSH Filesystem) that can be used to access remote files and directories. However, this is not very convenient just for copying files.
In this method, you mount the remote directory on your local system. Once mounted, you can copy files between the mounted directory and the local system.
You may need to install sshfs on your local system first using your distribution’s package manager.
On Debian and Ubuntu, you may use the following command:
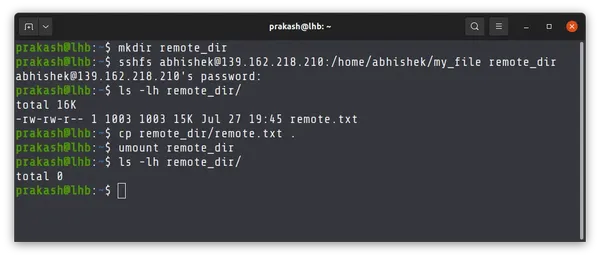
Once you have sshfs installed on your system, you can use it to mount the remote directory. It would be better to create a dedicated directory for the mount point.
Now mount the desired directory on the remote machine in this fashion:
sshfs [email protected]_address:path_to_dir mount_dirOnce it is mounted, you can copy files into this directory or from this directory as if it is on your local machine itself.
Remember that you have mounted this file. Once your work is done, you should also unmount it:
Here’s an example where I mounted the my_file directory from the remote system to the remote_dir directory on the local system. I copied the remote.txt file to the local system and then unmounted the directory.
Method 4: Use a GUI-based SFTP client for transferring files between remote systems
As the last resort, you can use an FTP client for transferring files between remote and local systems.
FileZilla is one of the most popular cross-platform FTP client. You can easily install on your local system.
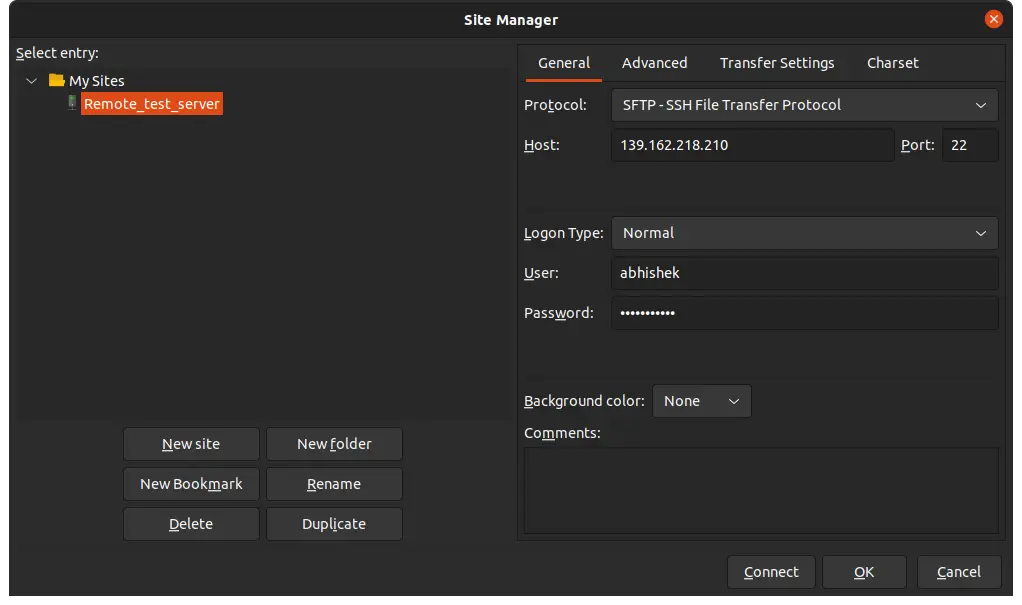
Once installed, go to File->Site Manager and add the remote system details like IP address, SSH port number, username and password.
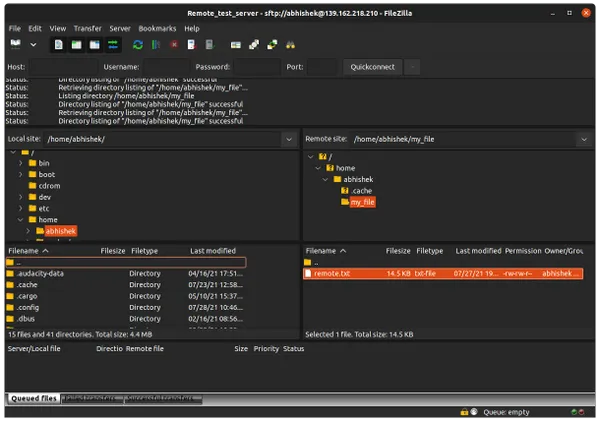
Once you connect, you can see a split window view that shows the local filesystem on the left and the remote filesystem on the right.
To transfer the file, drag and drop files from left to right or right to left. A progress bar appears at the bottom.
Which method do you prefer?
Alright! I showed various command line and GUI methods that can be used for copying files over SSH.
Now it is up to you to decide which method to use here. Do comment your preferred method for transferring files over SSH.
Передача файлов между серверами Linux с использованием SCP и FTP
Передача файлов между машинами — очень распространенная задача, с которой вы как разработчик будете сталкиваться постоянно.
Для передачи файлов в Linux есть специальные утилиты. В этой статье мы рассмотрим FTP и SCP. Они широко используются в скриптах автоматизации.
Что такое FTP?
FTP — это сетевой протокол, применяемый для обмена файлами по сети. Он использует порт 21. FTP позволяет вам подключаться к удаленной системе для обмена файлами при помощи команды ftp .
Синтаксис FTP
FTP-синтаксис довольно прост:
Здесь host может быть как именем, так и IP-адресом удаленного хоста, к которому вы хотите подключиться.
Команды FTP
FTP-команды напоминают команды Linux. Вот некоторые из них:
| Команда | Использование |
|---|---|
| open | Открывает удаленное соединение с другим компьютером. |
| get | Копирует файл из удаленной системы в локальную. |
| put | Копирует файл из локальной системы в директорию удаленной. |
| mget | Передача нескольких файлов из удаленной системы в текущую директорию локальной. |
| mput | Передача нескольких файлов из локальной системы в директорию удаленной. |
| bye/quit | Подготовка к выходу из FTP-окружения. |
| close | Закрывает FTP-соединение. |
| ascii | Включает ASCII-режим передачи файлов. |
| binary | Включает бинарный режим передачи файлов. |
Как передавать файлы через FTP
FTP предлагает два режима передачи файлов: ASCII и бинарный.
- ASCII расшифровывается как American Standard Code for Information Interchange («Американский стандартный код для обмена информацией»). Используется для передачи простых файлов, например, текстовых.
- Бинарный режим используется для передачи нетекстовых файлов, например, изображений.
По умолчанию FTP использует режим передачи ASCII.
Шаг 1 — установка FTP-соединения
В этом примере hostA — удаленный хост. После ввода команды вам будет предложено ввести имя пользователя и пароль.
$ ftp hostA Connected to hostA. 220 hostA FTP server ready. Name (hostA:user): user 331 Password required for user. Password: password 230 User user logged in. Remote system type is LINUX.
Когда соединение будет успешно установлено, вы заметите символы ftp> в начале строки. Это значит, что теперь вы можете вводить FTP-команды.
Шаг 2 — выбор режима передачи
Вы можете выбрать режим передачи файлов (бинарный или ASCII) в зависимости от их типа.
ftp> ascii 200 Type set to A.
Шаг 3 — передача файла
Здесь мы использовали команду get для передачи файла sample.txt с удаленного FTP-сервера на локальную машину.
ftp> get sample.txt 200 PORT command successful. 150 Opening ASCII mode data connection for sample.txt (22 bytes). 226 Transfer complete. local: sample.txt remote: sample.txt 22 bytes received in 0.012 seconds (1.54 Kbytes/s)
Шаг 4 — завершение сессии
ftp> bye 221-You have transferred 22 bytes in 1 files. 221-Total traffic for this session was 126 bytes in 2 transfers. 221-Thank you for using the FTP service on hostA. 221 Goodbye.
Как передать несколько файлов через FTP
Для передачи нескольких файлов одновременно используются две команды: mget и mput .
mget используется для скачивания файлов с сервера, а mput — для заливки на сервер.
ftp> mget sample_file.1 sample_file.2
Здесь мы скачиваем файлы с удаленного хоста на локальную машину.
ftp> mput sample_file.1 sample_file.2
А здесь — наоборот: заливаем с локальной машины на удаленный хост.
Все команды, описанные в этом разделе, можно поместить в исполняемый файл и запускать по расписанию.
От редакции Techrocks. К сожалению, автор не раскрыла тему защищенной передачи файлов по FTPS, SFTP и FTP через SSH.
Что такое SCP?
SCP расшифровывается как Secure Copy («защищенное копирование»). Для этого копирования используется протокол SSH и порт 22. Данные, передаваемые по SCP, шифруются, и злоумышленники не смогут получить к ним доступ. Это делает передачу файлов по SCP очень безопасной.
С помощью SCP можно передавать файлы как с локальной машины на удаленный хост, так и обратно.
Синтаксис SCP
Давайте рассмотрим SCP-синтаксис.
scp [FLAG] [user@]SOURCE_HOST:]/path/to/file1 [user@]DESTINATION_HOST:]/path/to/file2
[FLAG]. Здесь могут стоять различные опции — флаги. Вот некоторые из них:
| Флаг | Описание |
|---|---|
| -r | Рекурсивное копирование директорий. |
| -q | Используется, чтобы спрятать показатель прогресса копирования и всю другую информацию, кроме сообщений об ошибках. |
| -C | Сжатие данных при передаче. |
| -P | Указание SSH-порта на машине, куда пересылаются файлы. |
| -p | Сохраняет начальное время модификации файла. |
[user@]SOURCE_HOST. Имя пользователя и машина, с которой отправляется файл.
[user@]DESTINATION_HOST:]. Имя пользователя и машина, куда отправляется файл.
Примечание. Для передачи файлов по SCP нужно знать логин и пароль соответствующего пользователя на удаленной машине, а также иметь права на запись файлов.
Как передать файлы по SCP с локальной машины на удаленный хост
Для передачи файлов на удаленный хост введите следующую команду:
scp source_file.txt remote_username@10.13.13.11:/path/to/remote/directory
Здесь source_file.txt — файл, который нужно скопировать. Remote_username — имя пользователя на удаленном хосте 10.13.13.11. После двоеточия указывается путь на удаленной машине, куда нужно поместить файл.
remote_username@10.13.13.11's password: source_file.txt 100% 0 0.0KB/s 00:00
Теперь файл source_file.txt находится на удаленной машине, в директории по адресу /path/to/remote/directory.
Для копирования директорий используется флаг -r , как показано ниже.
scp -r /local/directory remote_username@10.13.13.11:/path/to/remote/directory
Как передать файлы по SCP с удаленного хоста на локальную машину
Для копирования файлов с удаленного хоста используется следующий формат команды:
scp remote_username@10.13.13.11:/remote/source_file.txt /path/to/local/directory
По сути, здесь все так же, как в предыдущем примере, просто исходный адрес и адрес назначения меняются местами.
При передаче файлов будьте предельно внимательны! SCP перезаписывает уже существующие файлы.
Итоги
Из этого руководства вы узнали, как передавать файлы и директории в командной строке, с использованием FTP и SCP.
При использовании в скриптах автоматизации эти команды очень полезны для сохранения, архивирования и пакетной обработки файлов.