- How to Update Git to a Newest Version on Linux(Ubuntu 20.04 LTS)
- How to Update Git to a Newest Version on Linux(Ubuntu 20.04 LTS)
- Step 1: Prerequisites
- Step 2: Check Current Version
- Step 3: Remove Older Version(Optional)
- Step 4: Add PPA Repository
- Step 5: Update Your System
- Step 6: Install Git
- Step 7: Check Version
- How to Update Git
- How to Check the Current Git Version?
- How to Update Git
- Update Git on Linux
- Update Git on Windows
- Update Git on Mac
How to Update Git to a Newest Version on Linux(Ubuntu 20.04 LTS)
In this article, I will take you through the steps to update Git to a newest version on Linux. If you have Git application installed on your System from default ubuntu repo then you might have noticed that you have installed the older version instead of installing the latest one. This might create problem for you as lot of application like Bitbucket which has dependency on Git might not install and work correctly as those application requires a specific git version, most of the time the latest one. So to deal with this problem, the easy solution is to update git to the newest version by following some simple steps explained in below section.
How to Update Git to a Newest Version on Linux(Ubuntu 20.04 LTS)
Step 1: Prerequisites
a) You should have a running Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Server.
b) You should have sudo or root access to run privileged commands.
c) You should have apt or apt-get package manager available in your system.
Step 2: Check Current Version
To check and verify the current git version, you can use git —version command as shown below. As you can see the latest package version available from default Ubuntu repo is 2.25.1 .
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ git --version git version 2.25.1
Step 3: Remove Older Version(Optional)
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt remove git Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. Done The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required: git-man liberror-perl linux-headers-5.13.0-44-generic linux-hwe-5.13-headers-5.13.0-44 linux-image-5.13.0-44-generic linux-modules-5.13.0-44-generic linux-modules-extra-5.13.0-44-generic Use 'sudo apt autoremove' to remove them. The following packages will be REMOVED: git 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 1 to remove and 0 not upgraded. After this operation, 36.5 MB disk space will be freed. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y (Reading database . 233292 files and directories currently installed.) Removing git (1:2.25.1-1ubuntu3.4) .
Step 4: Add PPA Repository
Since we are going to download and install the git package from Git maintainers repository, we need to first add this repo by using sudo add-apt-repository ppa:git-core/ppa -y command as shown below.
Please note that if you are also getting below gpg key timed out error then you don’t need to worry about that. You can safely ignore that error for now.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:git-core/ppa -y Error: retrieving gpg key timed out. Step 5: Update Your System
Next step is to update the package cache with all the package information from newly added repo by using sudo apt-get update command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get update [sudo] password for cyberithub: Hit:1 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal InRelease Hit:2 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates InRelease Hit:3 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-backports InRelease Ign:4 https://repo.vivaldi.com/stable/deb stable InRelease Hit:5 https://repo.vivaldi.com/stable/deb stable Release Hit:6 https://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb stable InRelease Hit:7 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security InRelease Get:8 http://ppa.launchpad.net/git-core/ppa/ubuntu focal InRelease [23.8 kB] Get:10 http://ppa.launchpad.net/git-core/ppa/ubuntu focal/main i386 Packages [3,020 B] Get:11 http://ppa.launchpad.net/git-core/ppa/ubuntu focal/main amd64 Packages [3,028 B] Get:12 http://ppa.launchpad.net/git-core/ppa/ubuntu focal/main Translation-en [2,252 B] Fetched 32.1 kB in 2s (13.5 kB/s) Reading package lists. Done
Step 6: Install Git
Once the repo information is updated, you can download and install the latest git package along with its dependencies by using sudo apt-get install git -y command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get install git -y Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. Done The following additional packages will be installed: git-man Suggested packages: git-daemon-run | git-daemon-sysvinit git-doc git-email git-gui gitk gitweb git-cvs git-mediawiki git-svn The following NEW packages will be installed: git The following packages will be upgraded: git-man 1 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Need to get 8,223 kB of archives. After this operation, 40.4 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://ppa.launchpad.net/git-core/ppa/ubuntu focal/main amd64 git-man all 1:2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1 [1,956 kB] Get:2 http://ppa.launchpad.net/git-core/ppa/ubuntu focal/main amd64 git amd64 1:2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1 [6,267 kB] Fetched 8,223 kB in 4s (2,213 kB/s) (Reading database . 197553 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack . /git-man_1%3a2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1_all.deb . Unpacking git-man (1:2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1) over (1:2.25.1-1ubuntu3.4) . Selecting previously unselected package git. Preparing to unpack . /git_1%3a2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1_amd64.deb . Unpacking git (1:2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1) . Setting up git-man (1:2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1) . Setting up git (1:2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1) . Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.1-1) .
Alternatively, if you have the older git version already installed and you would like to upgrade it without removing the older one, then all you need to do is to run the same sudo apt-get install git command as shown below. Here as you notice on the output, no new git package is getting installed but the older one is getting upgraded. So depending on your situation, you can choose either way.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get install git Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. Done The following additional packages will be installed: git-man Suggested packages: git-daemon-run | git-daemon-sysvinit git-doc git-email git-gui gitk gitweb git-cvs git-mediawiki git-svn The following packages will be upgraded: git git-man 2 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 5 not upgraded. Need to get 0 B/8,223 kB of archives. After this operation, 3,805 kB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y (Reading database . 199485 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack . /git_1%3a2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1_amd64.deb . Unpacking git (1:2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1) over (1:2.25.1-1ubuntu3.4) . Preparing to unpack . /git-man_1%3a2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1_all.deb . Unpacking git-man (1:2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1) over (1:2.25.1-1ubuntu3.4) . Setting up git-man (1:2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1) . Setting up git (1:2.37.0-0ppa1~ubuntu20.04.1) . Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.1-1) .
Step 7: Check Version
After successful installation, if you now check the current installed version by using git —version command then you will see that this time we have the newest version 2.37.0 available(At the time of writing this article, 2.37.0 is the newest version).
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ git --version git version 2.37.0 How to Update Git
Git is a version control system that allows multiple developers to work on the same project while tracking changes and revisions. Keeping Git up to date brings you the latest features and usability improvements.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to update to the latest version of Git on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
- A system running Linux, Windows, or macOS
- An installed version of Git
- Access to the terminal window (Linux, macOS) or command prompt (Windows)
- An account with administrator-level privileges
How to Check the Current Git Version?
To check the current version of Git, use the following command:
This command works on all operating systems. This example uses Windows:
How to Update Git
Below, we list different ways you can update your version of Git, depending on the operating system you are using. Skip to the section applicable for your machine.
Update Git on Linux
Note: To update Git on a Linux machine, use the appropriate package manager. When working with Git on CentOS, use a package manager such as yum or pacman .
This example shows how to update Git on Ubuntu.
Start by updating the system packages with the following command:
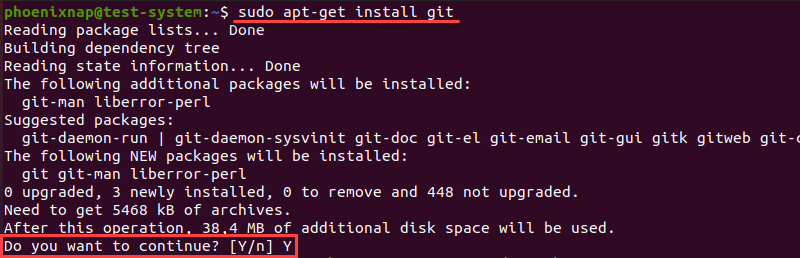
When prompted, type Y and press Enter to confirm the installation.
To verify the installation has completed, check the Git version one more time:
Another way to update Git on Linux is to install it from scratch using the original source code. Check out our guide to installing Git on Ubuntu for details.
Update Git on Windows
The method you use to update Git on Windows depends on the version of Git you are currently running.
For versions prior to 2.14.1, uninstall Git from your system and install a copy of the latest version from scratch. Check out our guide to installing Git on Windows for more details.
For versions from 2.14.2 to 2.16.1, use the following command in your command prompt:
For versions 2.16.1 on, update Git with:
The output above appears when you are running the latest Git version.
Update Git on Mac
The easiest way to update Git on Mac is to use the official installer. Download the installation file from the Git website. Run the installation and follow the install wizard to update Git to the latest version.
Note: Using the install wizard to update Git overwrites the current installation.
Another method is to update Git using Homebrew. If you don’t have Homebrew already, install it by using:
/usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"Update Homebrew to make sure you have the latest installation packages:
Install the latest version of Git with Homebrew:
If you already have Git installed using Homebrew, update to the latest version with:
Check the current Git version to confirm the update:
Note: If checking the Git version after updating results in an output that includes (Apple Git-101) , your system is still running the default Apple version of Git instead of the official one. Change your local path to the Homebrew version of Git to fix this issue:
export PATH=/usr/local/bin:$PATH
After following this tutorial, you should have a fully updated version of Git installed on a Linux, Windows, or macOS machine.
Take a look at our Git Commands Cheat Sheet for a comprehensive primer on working with Git. If you come across a Git merge conflict, make sure to read our article How to Resolve Merge Conflicts in Git.