I2C Device Interface¶
Usually, i2c devices are controlled by a kernel driver. But it is also possible to access all devices on an adapter from userspace, through the /dev interface. You need to load module i2c-dev for this.
Each registered i2c adapter gets a number, counting from 0. You can examine /sys/class/i2c-dev/ to see what number corresponds to which adapter. Alternatively, you can run “i2cdetect -l” to obtain a formatted list of all i2c adapters present on your system at a given time. i2cdetect is part of the i2c-tools package.
I2C device files are character device files with major device number 89 and a minor device number corresponding to the number assigned as explained above. They should be called “i2c-%d” (i2c-0, i2c-1, …, i2c-10, …). All 256 minor device numbers are reserved for i2c.
C example¶
So let’s say you want to access an i2c adapter from a C program. First, you need to include these two headers:
Now, you have to decide which adapter you want to access. You should inspect /sys/class/i2c-dev/ or run “i2cdetect -l” to decide this. Adapter numbers are assigned somewhat dynamically, so you can not assume much about them. They can even change from one boot to the next.
Next thing, open the device file, as follows:
int file; int adapter_nr = 2; /* probably dynamically determined */ char filename[20]; snprintf(filename, 19, "/dev/i2c-%d", adapter_nr); file = open(filename, O_RDWR); if (file < 0) < /* ERROR HANDLING; you can check errno to see what went wrong */ exit(1); >
When you have opened the device, you must specify with what device address you want to communicate:
int addr = 0x40; /* The I2C address */ if (ioctl(file, I2C_SLAVE, addr) < 0) < /* ERROR HANDLING; you can check errno to see what went wrong */ exit(1); >
Well, you are all set up now. You can now use SMBus commands or plain I2C to communicate with your device. SMBus commands are preferred if the device supports them. Both are illustrated below:
__u8 reg = 0x10; /* Device register to access */ __s32 res; char buf[10]; /* Using SMBus commands */ res = i2c_smbus_read_word_data(file, reg); if (res < 0) < /* ERROR HANDLING: i2c transaction failed */ >else < /* res contains the read word */ >/* * Using I2C Write, equivalent of * i2c_smbus_write_word_data(file, reg, 0x6543) */ buf[0] = reg; buf[1] = 0x43; buf[2] = 0x65; if (write(file, buf, 3) != 3) < /* ERROR HANDLING: i2c transaction failed */ >/* Using I2C Read, equivalent of i2c_smbus_read_byte(file) */ if (read(file, buf, 1) != 1) < /* ERROR HANDLING: i2c transaction failed */ >else < /* buf[0] contains the read byte */ >
Note that only a subset of the I2C and SMBus protocols can be achieved by the means of read() and write() calls. In particular, so-called combined transactions (mixing read and write messages in the same transaction) aren’t supported. For this reason, this interface is almost never used by user-space programs.
IMPORTANT: because of the use of inline functions, you have to use ‘-O’ or some variation when you compile your program!
Full interface description¶
The following IOCTLs are defined:
ioctl(file, I2C_SLAVE, long addr) Change slave address. The address is passed in the 7 lower bits of the argument (except for 10 bit addresses, passed in the 10 lower bits in this case). ioctl(file, I2C_TENBIT, long select) Selects ten bit addresses if select not equals 0, selects normal 7 bit addresses if select equals 0. Default 0. This request is only valid if the adapter has I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR. ioctl(file, I2C_PEC, long select) Selects SMBus PEC (packet error checking) generation and verification if select not equals 0, disables if select equals 0. Default 0. Used only for SMBus transactions. This request only has an effect if the the adapter has I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_PEC; it is still safe if not, it just doesn’t have any effect. ioctl(file, I2C_FUNCS, unsigned long *funcs) Gets the adapter functionality and puts it in *funcs . ioctl(file, I2C_RDWR, struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data *msgset)
Do combined read/write transaction without stop in between. Only valid if the adapter has I2C_FUNC_I2C. The argument is a pointer to a:
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data < struct i2c_msg *msgs; /* ptr to array of simple messages */ int nmsgs; /* number of messages to exchange */ >
The msgs[] themselves contain further pointers into data buffers. The function will write or read data to or from that buffers depending on whether the I2C_M_RD flag is set in a particular message or not. The slave address and whether to use ten bit address mode has to be set in each message, overriding the values set with the above ioctl’s.
ioctl(file, I2C_SMBUS, struct i2c_smbus_ioctl_data *args) If possible, use the provided i2c_smbus_* methods described below instead of issuing direct ioctls.
You can do plain i2c transactions by using read(2) and write(2) calls. You do not need to pass the address byte; instead, set it through ioctl I2C_SLAVE before you try to access the device.
You can do SMBus level transactions (see documentation file smbus-protocol for details) through the following functions:
__s32 i2c_smbus_write_quick(int file, __u8 value); __s32 i2c_smbus_read_byte(int file); __s32 i2c_smbus_write_byte(int file, __u8 value); __s32 i2c_smbus_read_byte_data(int file, __u8 command); __s32 i2c_smbus_write_byte_data(int file, __u8 command, __u8 value); __s32 i2c_smbus_read_word_data(int file, __u8 command); __s32 i2c_smbus_write_word_data(int file, __u8 command, __u16 value); __s32 i2c_smbus_process_call(int file, __u8 command, __u16 value); __s32 i2c_smbus_read_block_data(int file, __u8 command, __u8 *values); __s32 i2c_smbus_write_block_data(int file, __u8 command, __u8 length, __u8 *values);
All these transactions return -1 on failure; you can read errno to see what happened. The ‘write’ transactions return 0 on success; the ‘read’ transactions return the read value, except for read_block, which returns the number of values read. The block buffers need not be longer than 32 bytes.
The above functions are made available by linking against the libi2c library, which is provided by the i2c-tools project. See: https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/utils/i2c-tools/i2c-tools.git/.
Implementation details¶
For the interested, here’s the code flow which happens inside the kernel when you use the /dev interface to I2C:
- Your program opens /dev/i2c-N and calls ioctl() on it, as described in section “C example” above.
- These open() and ioctl() calls are handled by the i2c-dev kernel driver: see i2c-dev.c:i2cdev_open() and i2c-dev.c:i2cdev_ioctl(), respectively. You can think of i2c-dev as a generic I2C chip driver that can be programmed from user-space.
- Some ioctl() calls are for administrative tasks and are handled by i2c-dev directly. Examples include I2C_SLAVE (set the address of the device you want to access) and I2C_PEC (enable or disable SMBus error checking on future transactions.)
- Other ioctl() calls are converted to in-kernel function calls by i2c-dev. Examples include I2C_FUNCS, which queries the I2C adapter functionality using i2c.h:i2c_get_functionality(), and I2C_SMBUS, which performs an SMBus transaction using i2c-core-smbus.c: i2c_smbus_xfer() . The i2c-dev driver is responsible for checking all the parameters that come from user-space for validity. After this point, there is no difference between these calls that came from user-space through i2c-dev and calls that would have been performed by kernel I2C chip drivers directly. This means that I2C bus drivers don’t need to implement anything special to support access from user-space.
- These i2c.h functions are wrappers to the actual implementation of your I2C bus driver. Each adapter must declare callback functions implementing these standard calls. i2c.h:i2c_get_functionality() calls i2c_adapter.algo->functionality(), while i2c-core-smbus.c: i2c_smbus_xfer() calls either adapter.algo->smbus_xfer() if it is implemented, or if not, i2c-core-smbus.c:i2c_smbus_xfer_emulated() which in turn calls i2c_adapter.algo->master_xfer().
After your I2C bus driver has processed these requests, execution runs up the call chain, with almost no processing done, except by i2c-dev to package the returned data, if any, in suitable format for the ioctl.
© Copyright The kernel development community
I2c в Linux из пространства пользователя
Наконец дошли руки до i2c в raspberry pi. Шина i2c в Linux доступна из ядра и из пространства пользователя благодаря модулю i2c-dev.
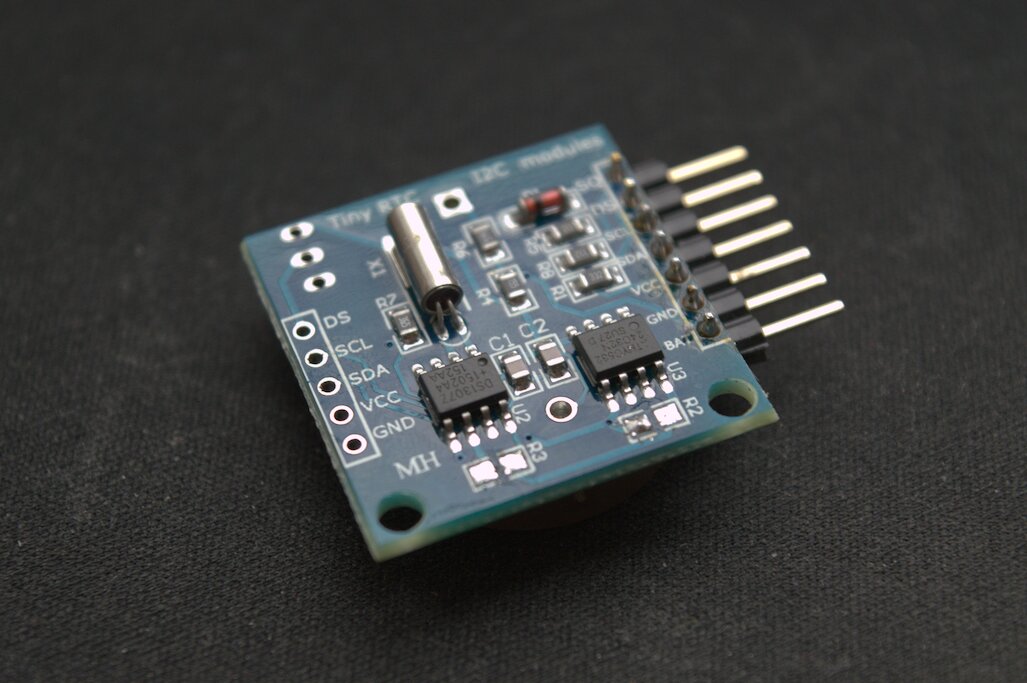
Как работать с i2c устройствами в linux рассмотрим на примере часов реального времени DS1307.
У меня модуль Tiny I2C Clock.
Стоит модуль копейки, но мне с ним очень не фортануло. Получил бракованную плату. Под батарейкой 3 закороченные дорожки.
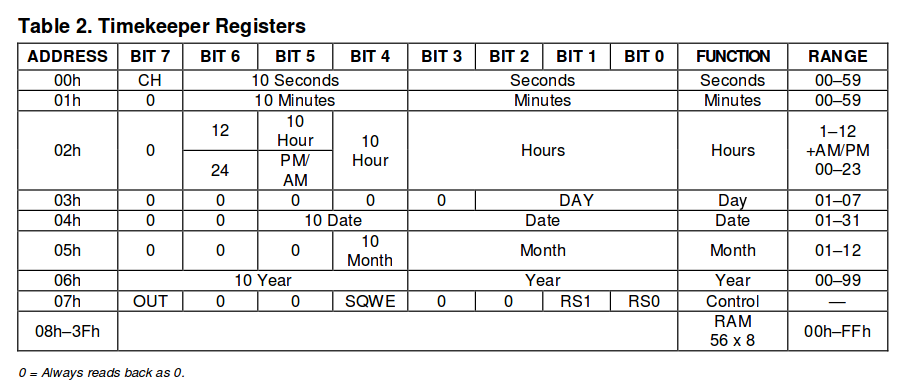
У часов есть такие регистры:
Дальше в памяти расположен RAM, который можно использовать под собственные нужды.
Не забываем включить i2c на raspberry. Для этого в файле /boot/config.txt раскоментируйте строки:
dtparam=i2c_arm=on dtparam=i2c=on
Для работы с i2c уже есть специальные утилиты i2c-tools.
Для установки на raspberry pi:
sudo apt-get install i2c-tools
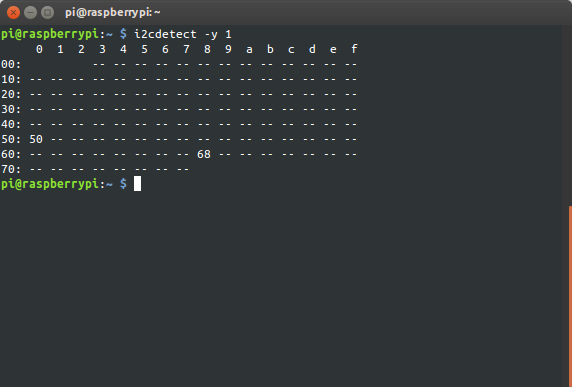
Теперь можно найти все устройства на шине 1:
Обнаружены часы и модуль eeprom памяти с той же платы.
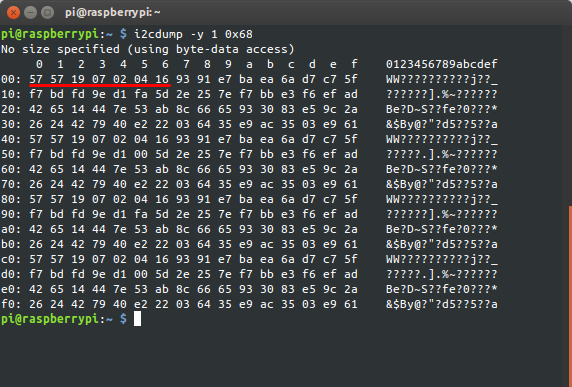
Сосредоточимся на часах. Согласно карте регистров выше видим, что нас интерисуют 6 первых регистров.
Вычитаем данные устройства с адресом 0x68:
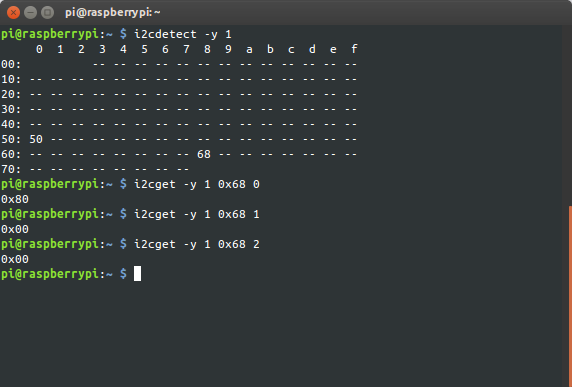
Также в наличии команда i2cget. Вычитаем 0 байт.
Это все очень весело и интересно, но мы же и сами программы писать умеем.
Почитаем 6 байт из i2c устройства.
Для этого открываем файл /dev/i2c-1 (или 0, если у вас старая малина).
Указываем адрес устройства (у меня 0x68)
Дабы установить указатель чтения в начало, нужно записать 0.
Читаем данные.
#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #define DEV_ADDRESS 0x68 #define DEV_REGISTERS_NUM 6 int main() < char i; char buf[10]; const char * devName = "/dev/i2c-1"; // Open up the I2C bus int file = open(devName, O_RDWR); if (file == -1) < perror(devName); exit(1); >// Specify the address of the slave device. if (ioctl(file, I2C_SLAVE, DEV_ADDRESS) < 0) < perror("Failed to acquire bus access and/or talk to slave"); exit(1); >// Write a byte to the slave. buf[0] = 0; if (write(file, buf, 1) != 1) < perror("Failed to write to the i2c bus"); exit(1); >// Read a byte from the slave. if (read(file,buf,DEV_REGISTERS_NUM) != DEV_REGISTERS_NUM) < perror("Failed to read from the i2c bus"); exit(1); >for(i=0;i
gcc i2c_example.c -o i2c_example
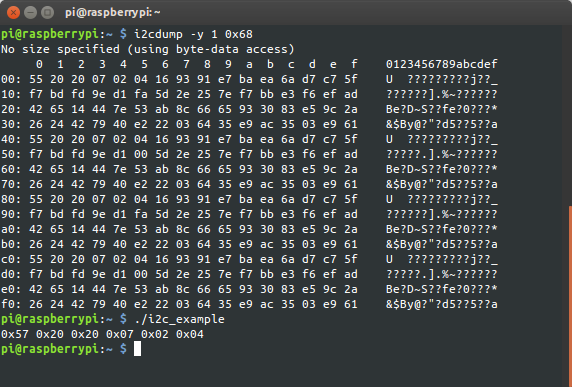
В первом байте хранятся секунды, так-что не обращайте внимание, что он отличается.
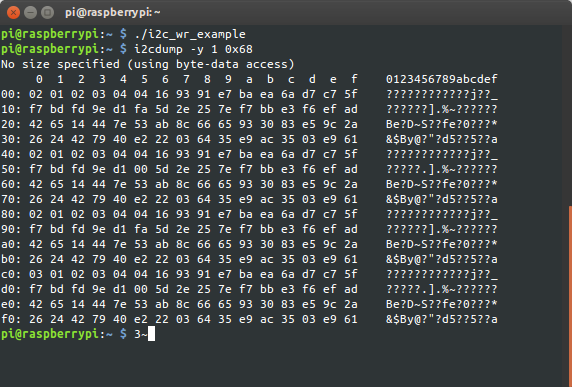
Вот так можно читать.
Как же записать данные в часы?
Все еще проще, вместо записи нуля, пишем 0 (это адрес регистра, если что), а затем данные.
#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #define DEV_ADDRESS 0x68 #define DEV_REGISTERS_NUM 6 int main() < char i; char buf[10]; const char * devName = "/dev/i2c-1"; // Open up the I2C bus int file = open(devName, O_RDWR); if (file == -1) < perror(devName); exit(1); >// Specify the address of the slave device. if (ioctl(file, I2C_SLAVE, DEV_ADDRESS) < 0) < perror("Failed to acquire bus access and/or talk to slave"); exit(1); >// Write a byte to the slave. buf[0] = 0; buf[1] = 0x00; buf[2] = 0x01; buf[3] = 0x02; buf[4] = 0x03; buf[5] = 0x04; buf[6] = 0x05; if (write(file, buf, DEV_REGISTERS_NUM) != DEV_REGISTERS_NUM) < perror("Failed to write to the i2c bus"); exit(1); >return 0; > Готово.
Помните, что работа с большинством i2c устройств таким образом — сущий изврат! В linux уже есть готовые драйвера для большинства устройств. И вам не нужно изобретать велосипед. Но об этом в следующей статье. Там мы посмотрим как скормить эти часы linux ядру и драйверу ds1307.