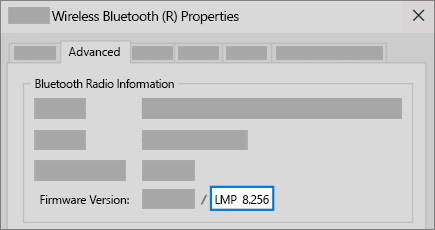
- What Bluetooth version is on my PC?
- To see which Bluetooth version is on your PC
- Need more help?
- Want more options?
- What Is Bluetooth? The Ultimate Guide
- In This Article
- Bluetooth Technology
- Connecting With Bluetooth
- Bluetooth Limitations
- How Secure Is Bluetooth?
- How to get Technical Information of a Bluetooth Device
What Bluetooth version is on my PC?
Bluetooth accessories sometimes require a minimum Bluetooth specification (version) in order to work with full functionality.
To see which Bluetooth version is on your PC
- In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager, then select it from the results.
- Select the arrow next to Bluetooth to expand it.
- Select the Bluetooth radio listing (yours might simply be listed as a wireless device).
- Select the Advanced tab, then look for the LMP (Link Manager Protocol) listing in the Firmware or Firmware version area. That number tells you what LMP version you have on your device.
Find your version number on the table below to map your LMP version to its Bluetooth Core Specification number. That’s the highest core specification your device fully supports. Accessories with higher specifications may still work, but with reduced functionality.
Link Manager Protocol Version (LMP)
Bluetooth Core Specification
Bluetooth Core Specification 1.0b (withdrawn)
Bluetooth Core Specification 1.1 (withdrawn)
Bluetooth Core Specification 1.2 (withdrawn)
Bluetooth Core Specification 2.0 + EDR (withdrawn)
Bluetooth Core Specification 2.1 + EDR (deprecated, to be withdrawn)
Bluetooth Core Specification 3.0 + HS (deprecated, to be withdrawn)
Bluetooth Core Specification 4.0
Bluetooth Core Specification 4.1
Bluetooth Core Specification 4.2
Bluetooth Core Specification 5.0
Bluetooth Core Specification 5.1
Bluetooth Core Specification 5.2


Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
What Is Bluetooth? The Ultimate Guide
Former Lifewire writer Melanie Uy has 5+ years’ experience writing about consumer-oriented technology and is an expert telecommuter.
Ryan Perian is a certified IT specialist who holds numerous IT certifications and has 12+ years’ experience working in the IT industry support and management positions.
In This Article
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless communication technology that allows devices such as mobile phones, computers, and peripherals to transmit data or voice wirelessly over a short distance. The purpose of Bluetooth is to replace the cables that normally connect devices, while still keeping the communications between them secure.
The «Bluetooth» name is taken from a 10th-century Danish king named Harald Bluetooth, who was said to unite disparate, warring regional factions. Like its namesake, Bluetooth technology brings together a broad range of devices across many different industries through a unifying communication standard.
Bluetooth Technology
Developed in 1994, Bluetooth was intended as a wireless replacement for cables. It uses the same 2.4GHz frequency as some other wireless technologies in the home or office, such as cordless phones and WiFi routers. It creates a 10-meter (33-foot) radius wireless network, called a personal area network (PAN) or piconet, which can network between two and eight devices. This short-range network allows you to send a page to your printer in another room, for example, without having to run an unsightly cable.
Bluetooth uses less power and costs less to implement than Wi-Fi. Its lower power also makes it far less prone to suffering from or causing interference with other wireless devices in the same 2.4GHz radio band.
Bluetooth range and transmission speeds are typically lower than Wi-Fi (the wireless local area network that you may have in your home). Bluetooth v3.0 + HS — Bluetooth high-speed technology — devices can deliver up to 24 Mbps of data, which is faster than the 802.11b WiFi standard, but slower than wireless-a or wireless-g standards. As technology has evolved, however, Bluetooth speeds have increased.
The Bluetooth 4.0 specification was officially adopted on July 6, 2010. Bluetooth version 4.0 features include low energy consumption, low cost, multivendor interoperability, and enhanced range.
The hallmark feature enhancement to the Bluetooth 4.0 spec is its lower power requirements; devices using Bluetooth v4.0 are optimized for low battery operation and can run off of small coin-cell batteries, opening up new opportunities for wireless technology. Instead of fearing that leaving Bluetooth on will drain your cell phone’s battery, for example, you can leave a Bluetooth v4.0 mobile phone connected all the time to your other Bluetooth accessories.
Connecting With Bluetooth
Many mobile devices have Bluetooth radios embedded in them. PCs and some other devices that do not have built-in radios can be Bluetooth-enabled by adding a Bluetooth dongle, for example.
The process of connecting two Bluetooth devices is called «pairing.» Generally, devices broadcast their presence to one another, and the user selects the Bluetooth device they want to connect to when its name or ID appears on their device. As Bluetooth-enabled devices proliferate, it becomes important that you know when and to which device you’re connecting, so there may be a code to enter that helps ensure you’re connecting to the correct device.
This pairing process can vary depending on the devices involved. For example, connecting a Bluetooth device to your iPad can involve different steps from those to pair a Bluetooth device to your car.
Bluetooth Limitations
There are some downsides to Bluetooth. The first is that it can be a drain on battery power for mobile wireless devices like smartphones, though as the technology (and battery technology) has improved, this problem is less significant than it used to be.
Also, the range is fairly limited, usually extending only about 30 feet, and as with all wireless technologies, obstacles such as walls, floors, or ceilings can reduce this range further.
The pairing process may also be difficult, often depending on the devices involved, the manufacturers, and other factors that all can result in frustration when attempting to connect.
How Secure Is Bluetooth?
Bluetooth is considered a reasonably secure wireless technology when used with precautions. Connections are encrypted, preventing casual eavesdropping from other devices nearby. Bluetooth devices also shift radio frequencies often while paired, which prevents an easy invasion.
Devices also offer a variety of settings that allow the user to limit Bluetooth connections. The device-level security of «trusting» a Bluetooth device restricts connections to only that specific device. With service-level security settings, you can also restrict the kinds of activities your device is permitted to engage in while on a Bluetooth connection.
As with any wireless technology, however, there is always some security risk involved. Hackers have devised a variety of malicious attacks that use Bluetooth networking. For example, «bluesnarfing» refers to a hacker gaining authorized access to information on a device through Bluetooth; «bluebugging» is when an attacker takes over your mobile phone and all its functions.
For the average person, Bluetooth doesn’t present a grave security risk when used with safety in mind (e.g., not connecting to unknown Bluetooth devices). For maximum security, while in public and not using Bluetooth, you can disable it completely.
Bluetooth 5.0 is the newest version of the wireless standard. Devices began supporting Bluetooth in mid-2017, and it’s now implemented in many compatible Bluetooth devices. Bluetooth 5.0 offers four times the range, twice the speed, and improved bandwidth over Bluetooth 4.0.
Bluetooth tethering is when Bluetooth pairs two devices in the same Personal Area Network (PAN), and the internet connection of one device can be shared with the second device.
Bluetooth powers smart speakers such as the Amazon Echo and Google Home devices and wireless portable speakers designed for indoor, outdoor, and beach use.
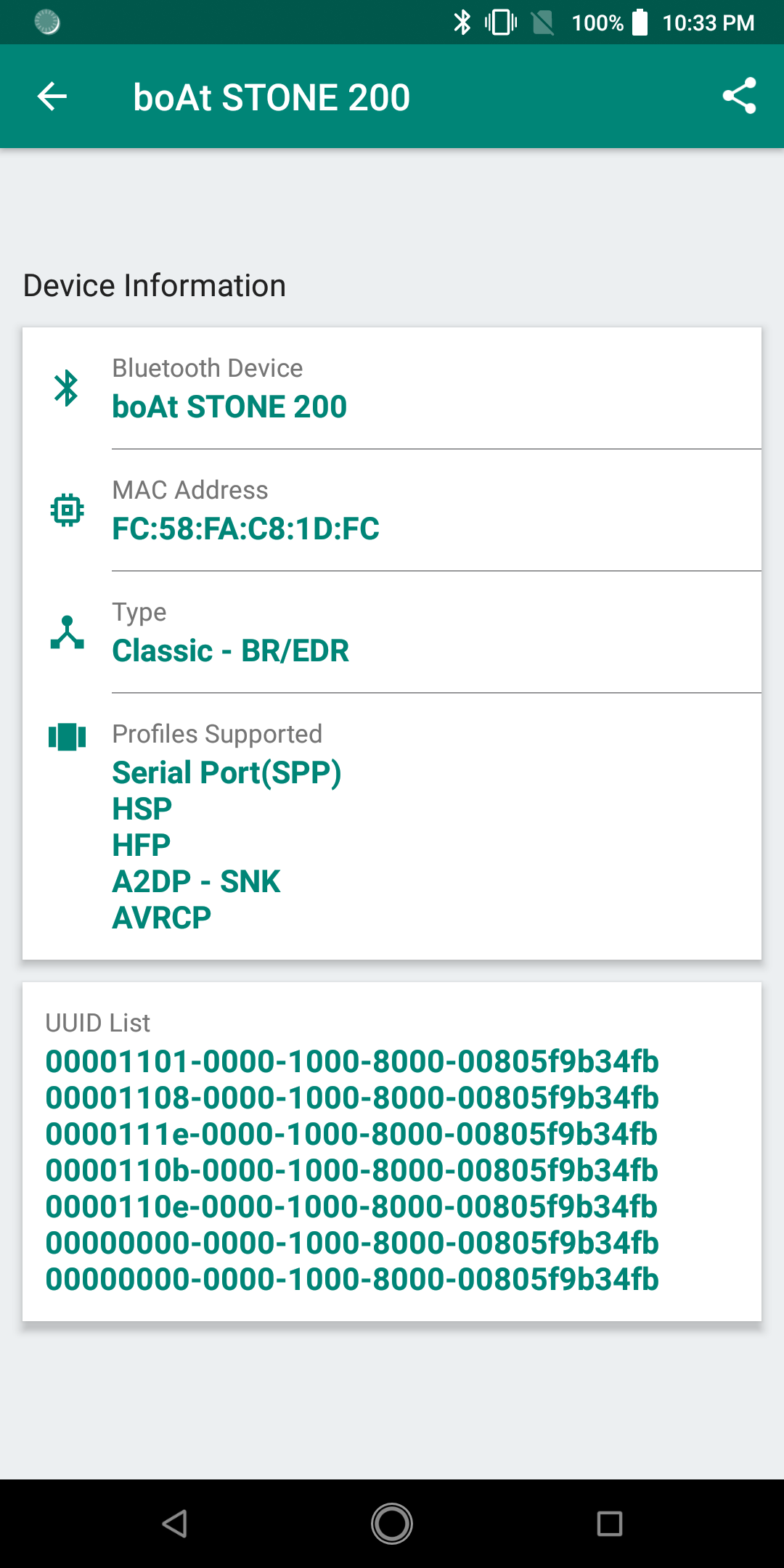
How to get Technical Information of a Bluetooth Device
Bluetooth devices have become an integral part of our day to day life. We are using Bluetooth devices like Speaker, Headset, Home Theatre, Keyboard, Mouse in our day to day activities. We started to love Bluetooth devices as it avoids messy physical wires.
Each Bluetooth device has technical information like MAC Address, Profiles supported, UUID. Bluetooth Device’s technical information can be grabbed using an Android Application – Bluetooth Devices Info in Google Play Store.

The Android Application provides essential technical information of a Bluetooth Device like
- Bluetooth Device Name
- MAC Address
- Bluetooth Device Type
- List of Bluetooth Profiles supported by the Bluetooth Device.
- List of UUIDs.
Screenshot of the Android application displaying technical details of Boat Stone 200.
- Bluetooth Device Name
Name assigned to the Bluetooth device by Manufacturer. - MAC Address
MAC Address is a unique 48-bit address assigned to Bluetooth Device. It is usually represented as a 6-byte hexadecimal address separated by a colon. The first three bytes of MAC address is Organizationally Unique Identifier(OUI) which represents the manufacturer of the Bluetooth Device and the second three bytes of MAC address is assigned by the manufacturer to the Bluetooth Device.
Instructions for using the Android Application – Bluetooth Devices Info.
- Download and install Bluetooth Devices Info from Google Play Store from this link
- Pair and connect the Bluetooth device to the smartphone.
- Open the Bluetooth Devices Info Android application.
- Select the Bluetooth device from the list of paired Bluetooth devices.
- Technical Information on the Bluetooth device is displayed.
- Make use of the share button to share the technical information.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Bluetooth-57faff6d5f9b586c357f82bd.jpg)