- Input Output Redirection in Linux/Unix with Examples
- Output Redirection
- Input Redirection
- File Descriptors (FD)
- What are File Descriptors?
- Error Redirection
- Why Error Redirection Occurs?
- Summary
- Input Output Redirection in Linux/Unix Examples
- Output Redirection
- Input redirection
- File Descriptors (FD)
- Error Redirection
- Why Error Redirection?
- Summary
Input Output Redirection in Linux/Unix with Examples
Redirection is the process of changing the input or output of commands given for execution in Linux/Unix. By redirection, you are going to change the execution of commands as standard input/output.
The basic workflow of Linux is that it takes input and after processing show the output. As we all know the standard input device (stdin) is keyboard and the standard output device (stdout) is screen. Usually Linux operates on this basic system of input/output. With redirection, we can change the standard input and output.
So, in this tutorial, we will learn.
Output Redirection
Output redirection is represented by a sign “>” The “>” symbol is used for output (STDOUT).
First, we will see with examples that how can we take output in Linux rather than having it on our screen we will see it in the Terminal.
Here’s the output of the given command ls-al is redirected to the file “output” rather than displaying on the screen.
Note: Double check the file name and make sure you are using correct file name while redirecting the output to the file. If you have already file with the same name and you again type the same file name all data on the file will be deleted and new output will be written to that file.
If you want to add some more information to previously output file, you can use the “>>” sign to add more output value to it.
You can also redirect standard output to devices. For instance you want to add some audio outputs to the other device you can do this so. It means we can apply standard output to files as well as devices.
The cat command reads the file song.mp3 and sends the output to the device /dev/audio which will play the music of that file.
Note: Make sure your audio systems are properly working and configuration of sound is working.
Input Redirection
Input redirection is represented by a sign “ .
We will see with examples that how we can use mail system to send mail as an input from our Terminal.
We can type the contents of the mail, we want to send to our Friends, Family or anyone. With the help of input redirection, we can add files to our mails by just typing a command in Terminal.
This will read the file name, attach it to the mail recipient and finally send it to the recipient.
The above example described is sample, now we will move towards the advanced redirection techniques which will make use of advanced redirection techniques like File Descriptors (FD).
File Descriptors (FD)
What are File Descriptors?
In Linux/Unix everything is a file. This includes your regular files, folders, and even your devices are also files. These files are specified against specific numbers. These numbers are called File Descriptor (FD).
Your Screen is also assigned a file descriptor. When you execute a command or give instructions to show some results, the output is sent to the file descriptor of the screen which will show the results on your screen. Similarly, your printer also assigned a specific number which will be called when you require for printing some documents or anything else.
Error Redirection
In Linux/Unix, when we run a program or execute a command 3 files are open always.
These files are open whenever you run a program. As we discuss earlier that these files are associated with the specific descriptor number.
Standard Input STDIN
Standard Output STDOUT
And Standard Error STDERR
File Descriptor
Normally the error stream is displayed on the screen but error redirection routs the errors to the files other than your screen.
Why Error Redirection Occurs?
Error-redirection is the most popular and common feature of Linux/Unix .
Frequent Unix users faces that many command return them a large amount of errors. Let’s see some examples.
- First, suppose you are looking for a file and you do not have specific permissions to read or write or even find that file, you will redirect to error. These errors show permission denied error and do not allow you to find a specific file.
- Similarly, in executing shell scripts, you do not find the exact output you are looking for due to some errors.
So, the only solution is to redirect the error to a specific file
In above example, we are executing a program name “myfile”.
The file descriptor for error redirection is 2. By using “2>” output would not be cluttered with errors.
Summary
- So, Each file in Linux/Unix including any files, folders or devices is assigned with the descriptor numbers.
- The keyboard is referred to as the basic and standard input device and the screen is standard output device in Linux/Unix.
- The symbol “>” shows the output redirection and the symbol “ shows the input redirection while the symbol “>>” appends the output to the existing file(only in case if you retype the filename that existed before)
- “>&” symbol redirects the output of one file to the other one.
- Finally, you can redirect error redirection in accordance with the corresponding descriptor number.
You can also learn about the Tar command in our post.
Please share this post and join our Telegram Channel.
Input Output Redirection in Linux/Unix Examples
Redirection is a feature in Linux such that when executing a command, you can change the standard input/output devices. The basic workflow of any Linux command is that it takes an input and give an output.
- The standard input (stdin) device is the keyboard.
- The standard output (stdout) device is the screen.
With redirection, the above standard input/output can be changed.
In this tutorial, we will learn-

Click here if the video is not accessible
Output Redirection
The ‘>‘ symbol is used for output (STDOUT) redirection.
Here the output of command ls -al is re-directed to file “listings” instead of your screen.
Note: Use the correct file name while redirecting command output to a file. If there is an existing file with the same name, the redirected command will delete the contents of that file and then it may be overwritten.”
If you do not want a file to be overwritten but want to add more content to an existing file, then you should use ‘>>‘ operator.
You can redirect standard output, to not just files, but also devices!
The cat command reads the file music.mp3 and sends the output to /dev/audio which is the audio device. If the sound configurations in your PC are correct, this command will play the file music.mp3
Input redirection
Example: The mail program in Linux can help you send emails from the Terminal.
You can type the contents of the email using the standard device keyboard. But if you want to attach a File to email you can use the input re-direction operator in the following format.
This would attach the file with the email, and it would be sent to the recipient.
The above examples were simple. Let’s look at some advance re-direction techniques which make use of File Descriptors.
File Descriptors (FD)
In Linux/Unix, everything is a file. Regular file, Directories, and even Devices are files. Every File has an associated number called File Descriptor (FD).
Your screen also has a File Descriptor. When a program is executed the output is sent to File Descriptor of the screen, and you see program output on your monitor. If the output is sent to File Descriptor of the printer, the program output would have been printed.
Error Redirection
Whenever you execute a program/command at the terminal, 3 files are always open, viz., standard input, standard output, standard error.
These files are always present whenever a program is run. As explained before a file descriptor, is associated with each of these files.
| File | File Descriptor |
|---|---|
| Standard Input STDIN | 0 |
| Standard Output STDOUT | 1 |
| Standard Error STDERR | 2 |
By default, error stream is displayed on the screen. Error redirection is routing the errors to a file other than the screen.
Why Error Redirection?
Error re-direction is one of the very popular features of Unix/Linux.
Frequent UNIX users will reckon that many commands give you massive amounts of errors.
- For instance, while searching for files, one typically gets permission denied errors. These errors usually do not help the person searching for a particular file.
- While executing shell scripts, you often do NOT want error messages cluttering up the normal program output.
The solution is to re-direct the error messages to a file.
Above we are executing a program names myprogram.
The file descriptor for standard error is 2.
Using “2>” we re-direct the error output to a file named “errorfile”
Thus, program output is not cluttered with errors.
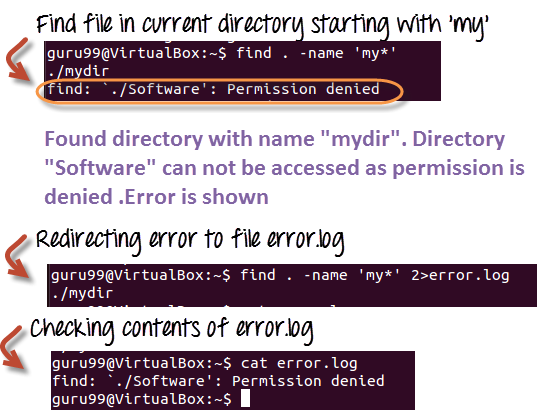
Here is another example which uses find statement –
Using the “find” command, we are searching the “.” current directory for a file with “name” starting with “my”
Example 3: Let’s see a more complex example,
Server Administrators frequently, list directories and store both error and standard output into a file, which can be processed later. Here is the command.
ls Documents ABC> dirlist 2>&1
- which writes the output from one file to the input of another file. 2>&1 means that STDERR redirects to the target of STDOUT (which is the file dirlist)
- We are redirecting error output to standard output which in turn is being re-directed to file dirlist. Hence, both the output is written to file dirlist
Summary
- Each file in Linux has a corresponding File Descriptor associated with it
- The keyboard is the standard input device while your screen is the standard output device
- “>” is the output redirection operator. “>>” appends output to an existing file
- “
- “>&”re-directs output of one file to another.
- You can re-direct error using its corresponding File Descriptor 2.







.png)