- 3 Command Line Tools to Install Deb Packages in Ubuntu
- 1. Install .deb Package Using dpkg Command
- Remove Deb Packages Using dpkg Command
- 2. Install .deb Package Using Apt Command
- Remove Deb Packages using apt Command
- 3. Install .deb Package Using Gdebi Command
- Install .deb Packages Using Gdebi GUI
- How to Install Deb Files in Ubuntu, Mint and Debian
- Installing Deb Package on Ubuntu, Mint, and Debian
- 1. Using the ‘dpkg’ Command
- 2. Using the apt Command
- 3. Using a Graphical Package Manager
- Remove Deb Packages in Ubuntu, Mint, and Debian
- Remove Deb File with Configuration Files
- Remove Deb File without Configuration Files
- How to install DEB packages on Linux Mint?
3 Command Line Tools to Install Deb Packages in Ubuntu
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install local software packages (.DEB) in Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint using three different command line tools and they are dpkg, apt, and gdebi.
This is useful to those new users who have migrated from Windows to Ubuntu or Linux Mint. The very basic problem they face is installing local software on the system.
However, Ubuntu and Linux Mint have their own Graphical Software Center for easy software installation, but we will be looking forward to installing deb packages through the terminal way.
1. Install .deb Package Using dpkg Command
Dpkg is a package manager for Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint. It is used to install, build, remove, and manage .deb packages. but unlike other Linux package management systems, it cannot automatically download and install packages with their dependencies.
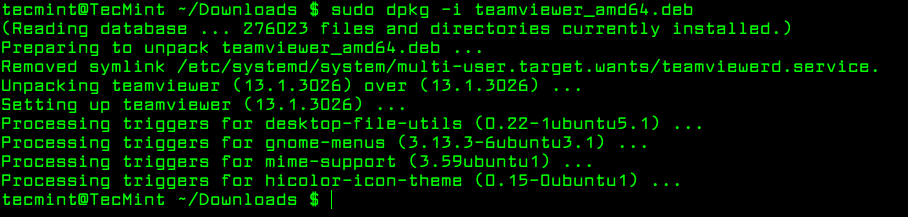
To install a .deb package, use the dpkg command with the -i flag along with the package name as shown.
$ sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_amd64.deb
If you get any dependency errors while installing or after installing and launching a program, you can use the following apt command to resolve and install dependencies using the -f flag, which tells the program to fix broken dependencies.
Remove Deb Packages Using dpkg Command
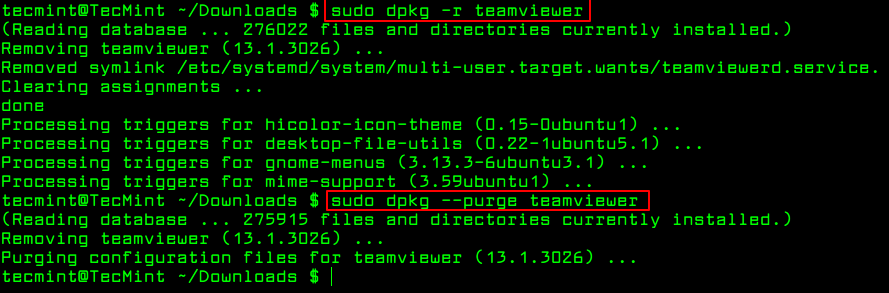
To remove a .deb package use the -r option or if you want to remove all its files including configuration files, you can purge it using the —purge option as shown.
$ sudo dpkg -r teamviewer [Remove Package] $ sudo dpkg --purge teamviewer [Remove Package with Configuration Files]
To know more about installed packages, read our article that shows how to list all files installed from a .deb package.
2. Install .deb Package Using Apt Command
The apt command is an advanced command-line tool, which offers new software package installation, existing software package upgradation, updating of the package list index, and even upgrading the whole Ubuntu or Linux Mint system.
It also offers apt-get and apt-cache command-line tools for managing packages more interactively on Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint systems.
Essentially, apt-get or apt do not understand .deb files, they are designed to primarily handle package names (for example teamviewer, apache2, mariadb, etc..) and they retrieve and install .deb archives associated with a package name, from a source specified in the /etc/apt/sources.list file.
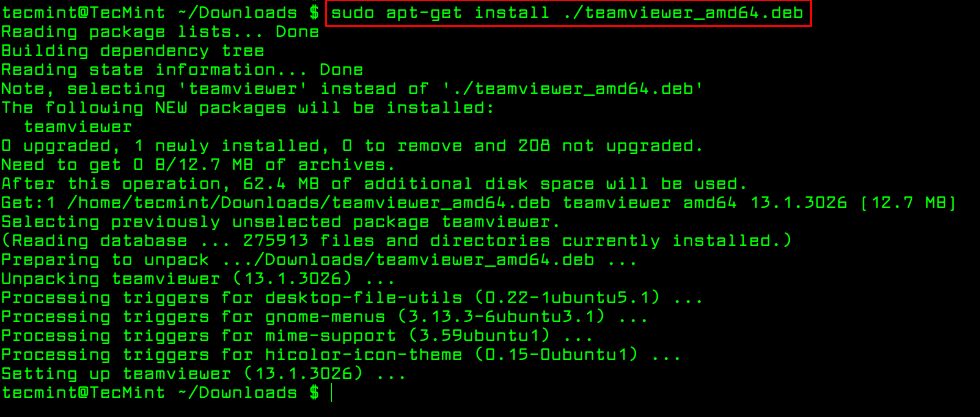
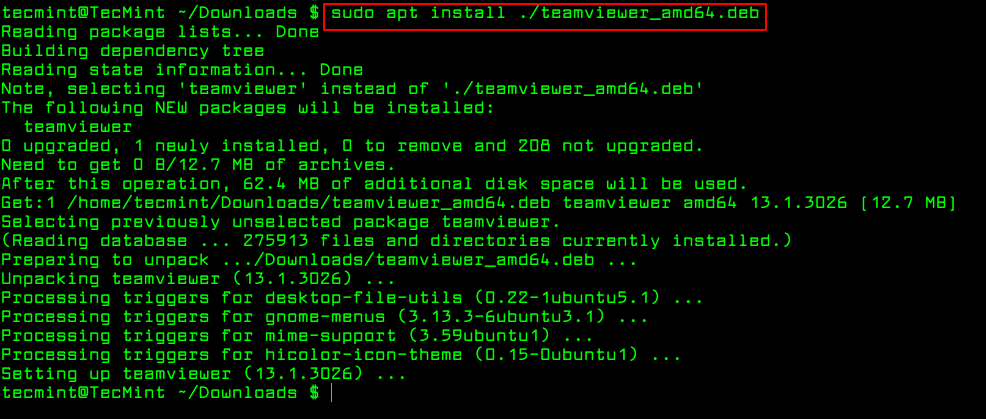
The only trick to installing a .deb Debian package using apt-get or apt is by specifying a local relative or absolute path ( ./ if in current dir) to the package, otherwise it will try to retrieve the package from remote sources and the operation will fail.
$ sudo apt install ./teamviewer_amd64.deb $ sudo apt-get install ./teamviewer_amd64.deb
Remove Deb Packages using apt Command
To remove a .deb package use the remove option or if you want to remove all its files including configuration files, you can purge it using the purge option as shown.
$ sudo apt-get remove teamviewer $ sudo apt-get purge teamviewer OR $ sudo apt remove teamviewer $ sudo apt purge teamviewer
3. Install .deb Package Using Gdebi Command
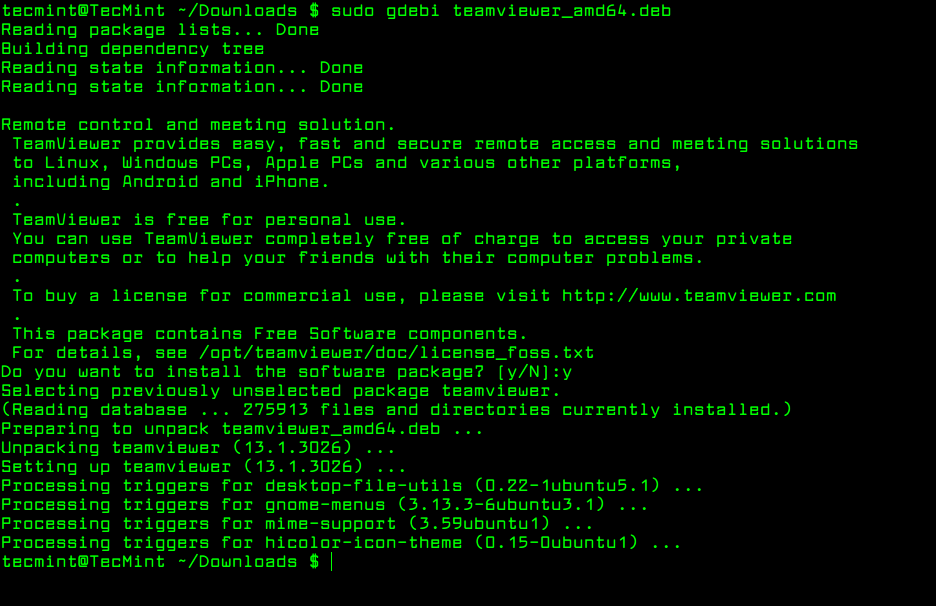
gdebi is a tiny command line and GUI tool for installing local deb packages. It resolves and installs package dependencies on the fly. To install a package, use the following command.
$ sudo gdebi teamviewer_13.1.3026_amd64.deb
To remove a .deb package installed from gdebi, you can use apt, apt-get or dpkg commands using purge option as shown.
$ sudo apt purge teamviewer OR $ sudo apt-get purge teamviewer OR $ sudo dpkg --purge teamviewer
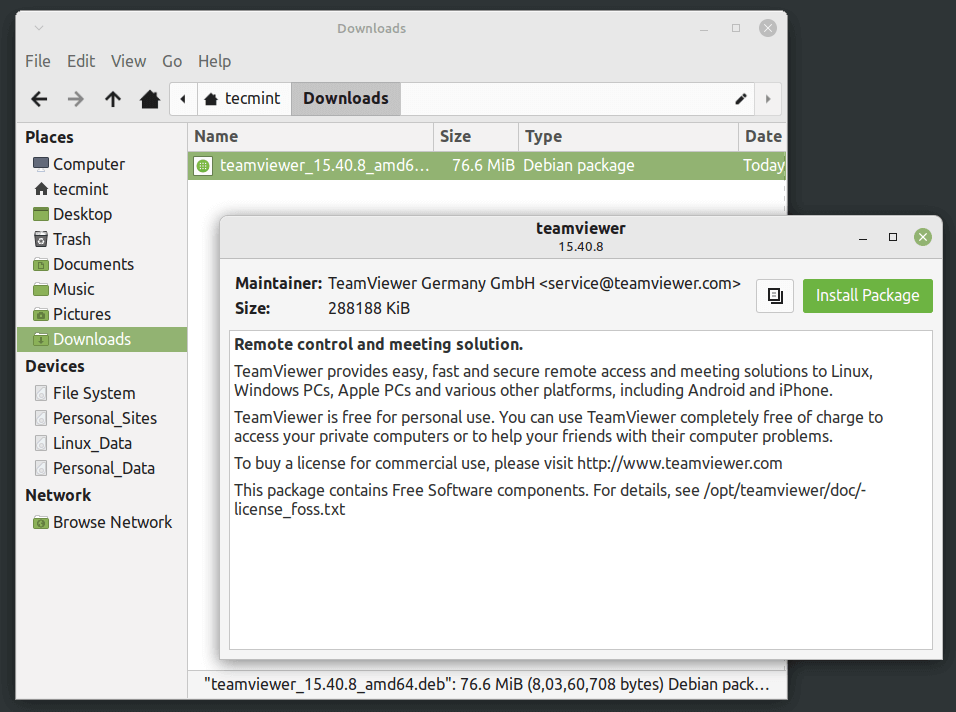
Install .deb Packages Using Gdebi GUI
The most recommended way for beginners to installing .deb files is through the Gdebi GUI installer. Simply, go to the directory where you have downloaded the file and double-click to install it as shown.
That’s It! In this tutorial, we have explained three different command line tools for installing or removing .deb Debian packages in Ubuntu and Linux Mint.
If you know any other way of installing local packages, do share with us using our comment section below.
How to Install Deb Files in Ubuntu, Mint and Debian
Before we look at the different approaches to installing deb files on Ubuntu or Debian-based Linux distributions, we first need to understand them.
Debian, Ubuntu, and Linux Mint distributions support the use of a package file with a ‘.deb’ file extension, which contains the needed metadata, scripts, and files that are crucial in the installation and management of targeted Linux-supported software packages.
The Debian Project developed the ‘.deb’ file format as a standard software package distribution format. By conceptualizing a ‘control file‘, the targeted software package is enriched with metadata info like name, version, dependencies, and installation scripts associated with the software package in question.
Installing Deb Package on Ubuntu, Mint, and Debian
There is more than one approach to installing ‘.deb’ files on Ubuntu and Debian-based Linux distributions as explained in the following steps.
1. Using the ‘dpkg’ Command
The dpkg command is used to install, manage, and remove ‘.deb’ software packages along with their dependencies if any as shown.
The -i flag in the command above triggers the installation of the google-chrome .deb file.
Once installed, you can confirm the installed version of the ‘.deb’ software package using the dpkg-query command.
$ sudo dpkg-query -l google-chrome-stable
2. Using the apt Command
The apt command is effective in managing packages (install, upgrade, and remove) since it is the default package manager. This approach of installing a ‘.deb’ file automatically caters to the download and installation of missing dependencies. Also, ‘.deb’ packages installed via this approach are automatically upgraded during the next system update.
To install a ‘.deb’ file using ‘apt’, implement the following command:
Once installed, you can confirm the installed version of the ‘.deb’ software package using the apt command.
$ sudo apt list -a google-chrome-stable
3. Using a Graphical Package Manager
A Graphical Package Manager is an ideal alternative to install Deb files on Ubuntu and Debian-based systems. Their user-friendly interface makes it easy to install, manage, and upgrade packages as shown.
To install Deb packages via the default Graphical Package Manager, consider the following installation steps:
Right-click on the targeted ‘.deb’ file.
Select the ‘Open With Other Application‘ option and choose the ‘Software Install‘ option.
Next, click on the ‘Select‘ button and wait for the application details to load. You should see an ‘install‘ button for installing the selected software package.
Click on it and provide a Sudoer user password for the installation to proceed.
After a while, the software package should be installed.
Remove Deb Packages in Ubuntu, Mint, and Debian
Before uninstalling a ‘.deb’ file, we need to be certain of its exact program name. For instance, for Google Chrome, we will run the following command:
From the above output, we can use the exact program name for Google Chrome (google-chrome-stable) software to uninstall it if necessary.
Remove Deb File with Configuration Files
Fully uninstall a Deb file together with its configuration files using the dpkg or apt command.
$ sudo dpkg -P google-chrome-stable OR $ sudo apt purge google-chrome-stable
Remove Deb File without Configuration Files
To uninstall a Deb file without removing configuration files, use the dpkg or apt command.
$ sudo dpkg -r google-chrome-stable OR $ sudo apt remove google-chrome-stable
Conclusion
The ‘.deb’ file format plays a crucial role in Debian-based distributions such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint. For instance, its existence makes it convenient and efficient to distribute and install targeted software packages on these systems.
If you have any questions on how to install and remove Deb files on Debian-based distributions, feel free to leave a comment.
How to install DEB packages on Linux Mint?
The packages on Linux are compressed file that contains, in turn, a set of files such as sources or binaries and a set of instructions that indicate what to do with these.
Generally, packages contain instructions by which you can install applications using a package manager for the Linux distribution.
So generally, a package consists of:
- A Header that contains the instructions for the installation process and configuration of the contained files. Here are also the dependencies that the system has to meet in order for it to work.
- Data which are the binary files or sources that will execute an action in the system. Here, for example, you will find the binaries of the applications.
Many packages are dependent on each other. That is to say, they need each other to operate correctly. In addition to this, it is also possible that several packages share other packages as dependencies.
Installing a DEB package in Linux Mint
DEB is the standard Linux Mint package. And for this, you can do it using the terminal or the graphical interface. Keep in mind that it is always faster to do it using the terminal.
Using the terminal to install a DEB package
To install a DEB package using the terminal, we have two essential commands. The first one is dpkg and the second one is apt .
The dpkg command unpacks a package. Or in short, install it. In addition to that, dpkg also removes already installed packages.
To install a package with the dpkg command, you have to run the command together with the -i install option.
sudo dpkg -i [package-name].debThis will prepare the system for installation. You can also use relative and absolute paths. Remember that your user has to belong to the sudo group.
Another interesting command to perform DEB package installation in Linux Mint is apt .
APT is the Linux Mint package manager that will help to install and manage packages easily. Although APT is regularly used to install packages from the official repositories, you can also use it to install downloaded DEB packages.
To do this, we just need to use the install sub command and specify the file name. For example,
sudo apt install ./[package-name].debThis is how quick and easy it is to install DEB packages using the terminal.
Installing DEB packages using the Linux Mint graphical interface
As I said at the beginning, Linux Mint is a distribution that makes everything easy for the user. So, to install a DEB package, just double-click on it or right-click on it and select Open with GDebi Package Installer.
You will see a screen with the information provided by the package header and an installation button. Entering the password will start the process.
As you may have noticed in this post, you have several options for installing DEB packages in Linux Mint. Some users may feel better using the terminal because it is faster, or using the graphical interface if you wish.
The final recommendation is that you don’t install just any package, and make sure of its provenance.