- Установка программ и пакетов формата .deb
- Утилита APT
- Как установить deb-пакет на Ubuntu и Debian из официального репозитория
- How to Install Deb Files (Packages) on Ubuntu
- Install deb Files Using GUI
- Option 1: Software Center
- Option 2: GDebi GUI
- Install deb Files using the Terminal
- Option 1: dpkg Command
- Option 2: apt Package Manager
- Option 3: GDebi Package Installer
- How to Remove deb Packages
- Option 1: Software Center
- Option 2: GDebi GUI
- Option 3: dpkg Command
- Option 4: apt Package Manager
Установка программ и пакетов формата .deb
В этой статье мы расскажем, как проходит установка deb-пакета Ubuntu и Debian, установка приложений, и какие для этого нужны инструменты.
Для использования операционной системы мало просто установить её. В процессе работы могут понадобиться дополнительные программы, которые нужно загружать отдельно.
Для установочных пакетов Debian (и производных дистрибутивов — Linux Mint, Kali Linux, Ubuntu) было разработано расширение .deb. Где можно найти debian-пакеты? Создать deb-пакет может любой разработчик, поэтому найти этот формат можно на любом сайте или в официальных репозиториях Debian и Ubuntu.
Для поиска, установки, обновления и удаления пакетов программ в Debian (и других основанных на нём ОС, в частности, Ubuntu) используется APT.
Утилита APT
APT (Advanced Packaging Tool) ― это инструмент командной строки, который помогает взаимодействовать с программами. Этот пакетный менеджер был разработан для Debian, однако позже стал использоваться и в других дистрибутивах, основанных на нём.
Обратите внимание! Раньше использовалась команда apt-get. В последних версиях Debian произошло обновление и есть возможность использовать просто apt. Инструмент apt совмещает функциональность apt-get и apt-cache. Старый вариант команды работает в современных системах. Для использования сложных сценариев всё ещё предпочтительнее использовать apt-get. Однако в своей инструкции мы будем использовать новый вариант, так как в этом случае он подходит лучше.
Синтаксис для работы с утилитой:
sudo apt опции команда имя_пакетаКоманды apt для управления пакетами:
- download ― скачать, но не устанавливать пакет;
- update ― обновление информации о списках пакетов в репозиториях,
- upgrade ― обновление системы без удаления пакетов,
- full-upgrade ― полное обновление системы с удалением конфликтующих зависимостей,
- install ― установка пакета,
- remove ― удаление пакета, но без удаления конфигурационных файлов,
- purge ― полное удаление пакета,
- autoremove ― автоматическое удаление ненужных пакетов,
- search ― поиск пакета в локальной базе данных,
- show ― узнать информацию о пакете.
- c ― сторонний конфигурационный файл,
- o ― строка конфигурации,
- t ― версия релиза, для которой устанавливать пакет,
- f ― выполнить операцию принудительно.
Как установить deb-пакет на Ubuntu и Debian из официального репозитория
Установка программ в Debian и Ubuntu происходит одинаково.
How to Install Deb Files (Packages) on Ubuntu
A deb package (.deb file) is a software package in a specific format designed for Debian-based distributions recognized by the .deb extension. Deb packages allow installing local software on an Ubuntu system.
This article shows several ways to install and remove deb packages on Ubuntu.
- A system running Ubuntu.
- Access to terminal window/command line.
- User with root/sudo privileges.
Install deb Files Using GUI
Installing deb files through the GUI is straightforward and convenient. Below are the two most common options that allow installing deb packages through the user interface.
Option 1: Software Center
To install a deb package with the Software Center (Ubuntu Software), follow the simple steps below:
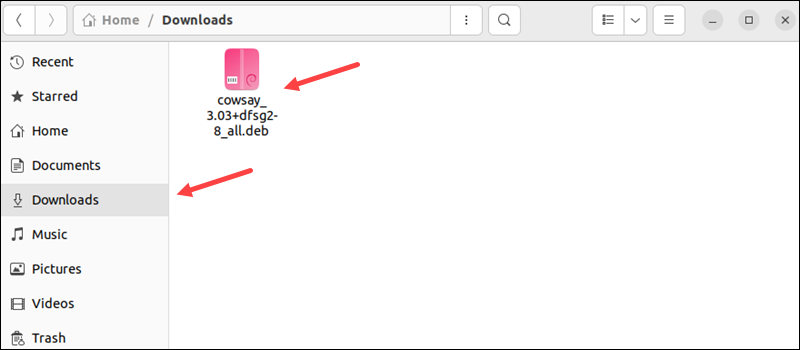
1. Locate the downloaded deb package. By default, the system stores downloaded files in the Downloads directory.
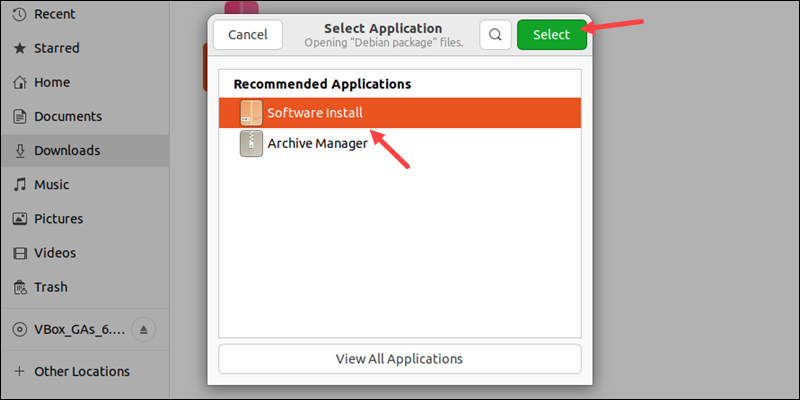
2. Right-click the deb file and choose Open with Another Application.
3. Select Software Install from the program list.
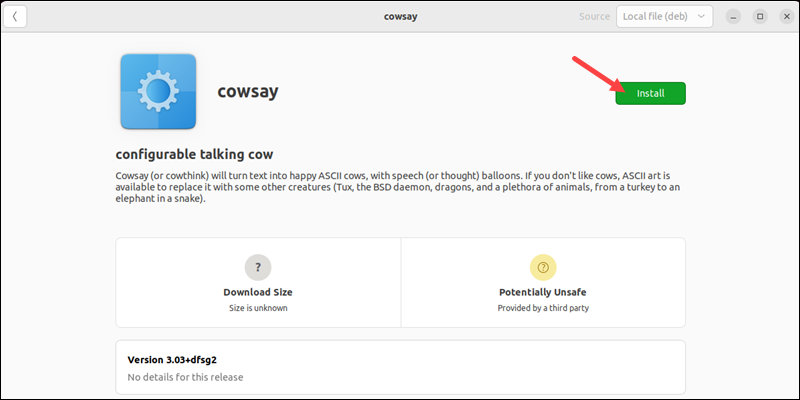
A new dialogue box opens with details about the software.
4. Click on the Install button to proceed.
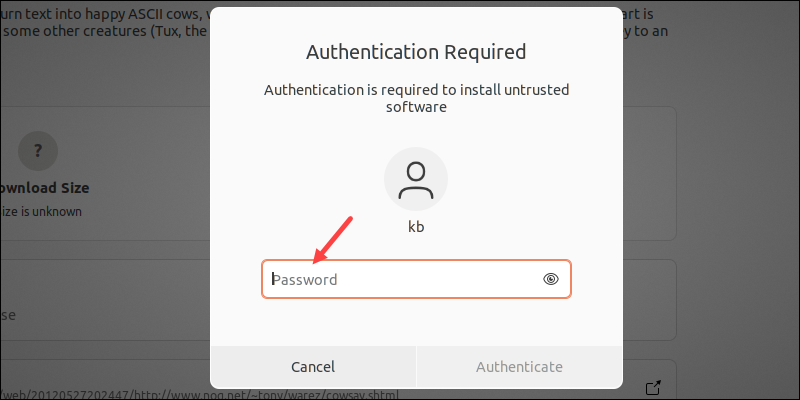
5. Enter the user’s password when prompted and press Enter to authenticate.
6. Wait for the installation to complete. When finished, the software is ready to use.
Option 2: GDebi GUI
GDebi is a simple tool for installing local deb packages. The program also identifies all the required dependencies and automatically downloads and installs them using the apt package manager. GDebi is available both as a command-line and GUI tool.
Note: GDebi does not come on Ubuntu by default. To install it, use the following command:
To install a deb package using the GDebi GUI, follow these steps:
1. Open the file manager and locate the deb file.
2. Right-click on the deb file and choose Open With Other Application.
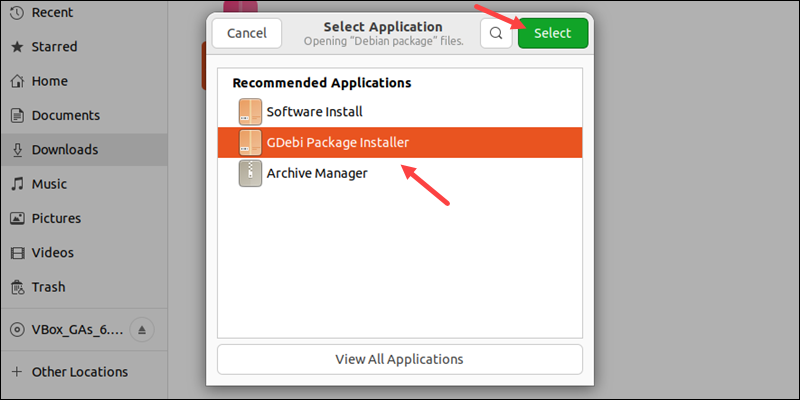
3. Mark the GDebi Package Installer and click Select.
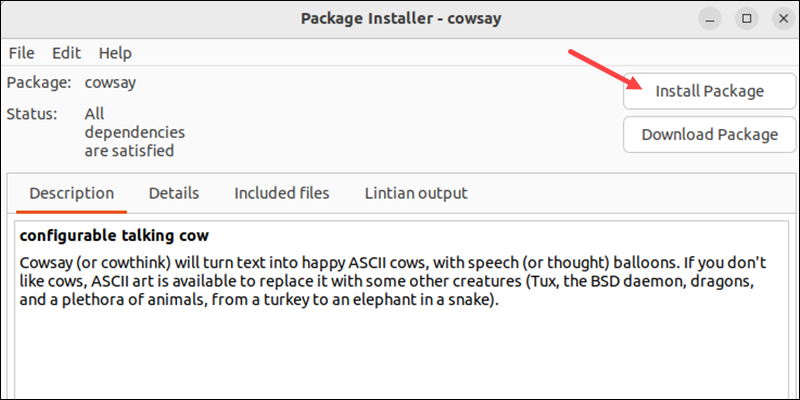
4. The installer loads the deb package and shows the software description. Click Install Package to start the installation.
5. Provide the user password when prompted and press Enter.
6. Wait for the installation to complete. Once done, the software is ready to use.
Install deb Files using the Terminal
The Ubuntu terminal enables installing packages using different package managers and commands. Below are a few options to install deb packages using terminal commands.
Option 1: dpkg Command
The dpkg command a is a package manager for installing, removing, and building packages.
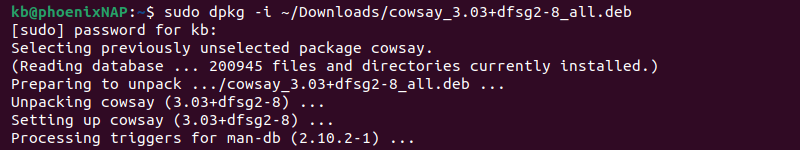
To install a deb package using the dpkg command, run the following command:
Provide the user’s password and wait for the installation to complete. If a package relies on unavailable dependencies, the dpkg command returns an error. Download any dependencies manually.
Option 2: apt Package Manager
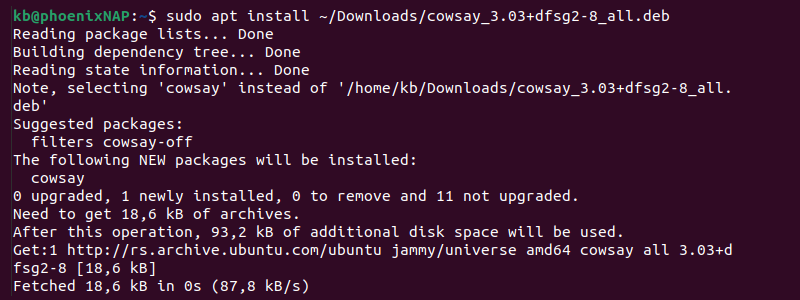
The apt command runs the apt package manager software. To install a deb package using the apt command, run:
Provide the user’s password if prompted. The package manager also locates and installs any dependencies automatically.
Option 3: GDebi Package Installer
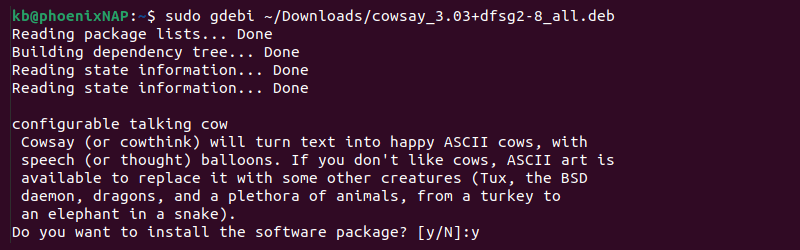
The GDebi tool also works as a command-line tool for package installation. To install a deb package with GDebi in the command line, run the following in the terminal:
Press Y to confirm the installation and enter the user’s password.
How to Remove deb Packages
There are several different ways to remove a previously installed deb package. The removal method depends on how the package was initially installed.
Below are examples of several options to remove deb packages from the system.
Option 1: Software Center
To remove a deb package using the software center, do the following:
1. Open the Ubuntu Software application.
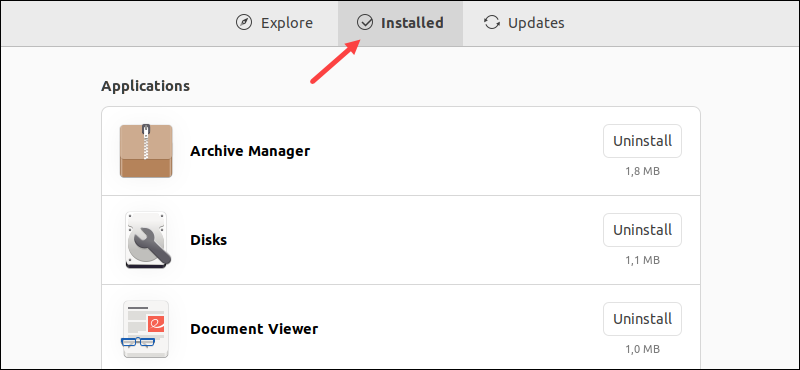
2. Navigate to the Installed tab.
3. Locate the software you want to remove. Click Uninstall to remove the application.
4. Confirm the uninstallation and provide the user’s password to complete the software removal.
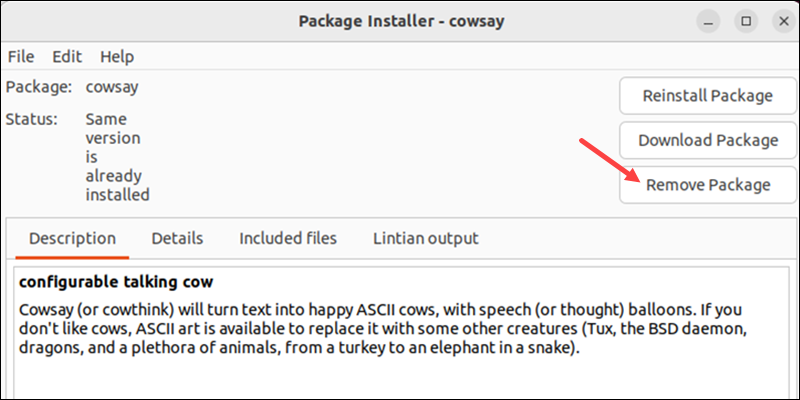
Option 2: GDebi GUI
To uninstall software with Gdebi, do the following:
1. Locate the .deb package file on the system.
2. Right-click the file and select Open With Other Application.
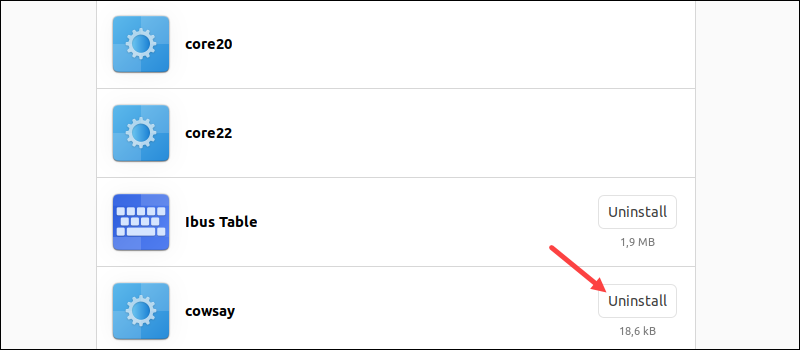
3. Choose GDebi Package Installer from the list.
4. Click Remove Package to uninstall the software.
5. Provide the user’s password and wait for the uninstall process to complete.
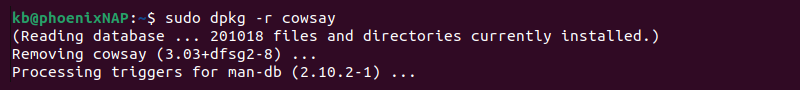
Option 3: dpkg Command
To remove packages installed with dpkg, use the following command in the terminal:
Use the official package name (not the .deb file name) in the command.
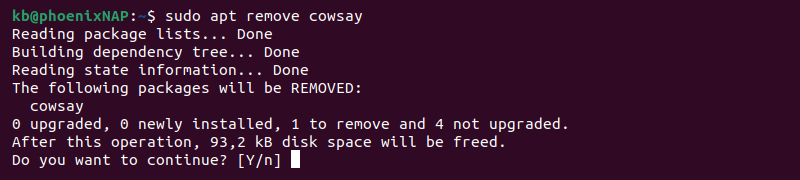
Option 4: apt Package Manager
To uninstall a package using the apt command, run the following:
Press Y to confirm the removal.
The method works if the initial installation was through the Ubuntu software center or the apt package manager.
You now know several ways to install and remove local software packages (.deb) on Ubuntu. Next, see different ways to list installed packages on Ubuntu.
Milica Dancuk is a technical writer at phoenixNAP who is passionate about programming. Her background in Electrical Engineering and Computing combined with her teaching experience give her the ability to easily explain complex technical concepts through her content.
This guide will walk you through several methods for removing old or unwanted software from an Ubuntu Linux.
RPM is a package format used by Red Hat based derivatives like CentOS, RHEL or Fedora. It gets its name from.