- 3 Ways to Install Deb Files on Ubuntu [& How to Remove Them Later]
- Installing .deb files on Ubuntu and Debian-based Linux Distributions
- Method 1: Use the default Software Center
- Troubleshoot: Double-clicking deb file doesn’t open in the software center in Ubuntu 20.04
- Method 2: Use Gdebi application for installing deb packages with dependencies
- Method 3: Install .deb files in the command line
- How to remove deb packages
- Method 1: Remove deb packages using apt command
- Method 2: Remove deb packages using dpkg command
- What about updating the deb packages?
- 3 Command Line Tools to Install Deb Packages in Ubuntu
- 1. Install .deb Package Using dpkg Command
- Remove Deb Packages Using dpkg Command
- 2. Install .deb Package Using Apt Command
- Remove Deb Packages using apt Command
- 3. Install .deb Package Using Gdebi Command
- Install .deb Packages Using Gdebi GUI
- Установка программ и пакетов формата .deb
- Утилита APT
- Как установить deb-пакет на Ubuntu и Debian из официального репозитория
3 Ways to Install Deb Files on Ubuntu [& How to Remove Them Later]
This beginner article explains how to install deb packages on Ubuntu. It also shows you how to remove those deb packages afterward.
This is another article in our Ubuntu beginner series. If you’re completely new to Ubuntu, you might wonder how to install applications. The easiest way is to use the Ubuntu Software Center. Search for an application by name and install it from there. Life would be too simple if you could find all the applications in the Software Center. That’s not the case, unfortunately. Some applications are available via ‘deb’ packages. These are archived files that end with the .deb extension. You can think of .deb files as .exe files in Windows. You double-click on the .exe file and it starts the installation procedure in Windows. Deb packages are pretty much the same. You can find these deb packages in the download section of a software provider’s website. For example, if you want to install Google Chrome on Ubuntu, you can download the Chrome deb package from its website. Now the question arises, how do you install deb files? There are multiple ways of installing deb packages on Ubuntu. I’ll show them to you one by one in this tutorial.
Installing .deb files on Ubuntu and Debian-based Linux Distributions
You can choose a GUI or command-line tool for installing a deb package. The choice is yours. Let’s go on and see how to install deb files.
Method 1: Use the default Software Center
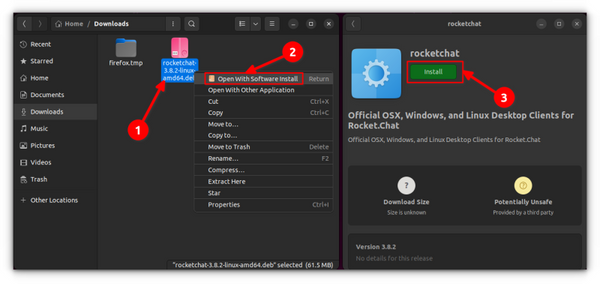
The simplest method is to use the default software center in Ubuntu. There’s nothing special to do here. Simply go to the folder where you downloaded the .deb file (usually the Downloads folder) and double-click on the file. It will open the software center, where you should see the option to install the software. All you have to do is to hit the install button and enter your login password. See, it’s even simpler than installing from a .exe file on Windows, isn’t it?
Troubleshoot: Double-clicking deb file doesn’t open in the software center in Ubuntu 20.04
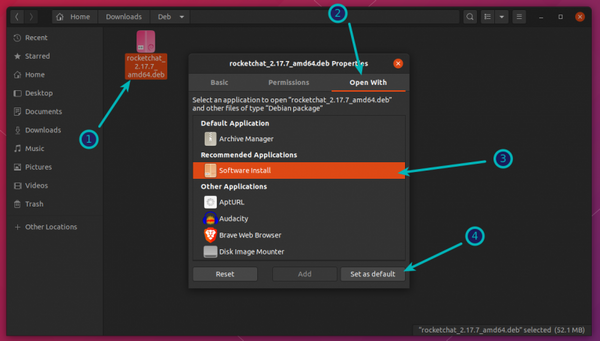
Double-clicking the deb file in Ubuntu 20.04 opens the file in archive manager instead of software center. This is weird but can easily be fixed. All you have to do is right-click on the deb file and go for the Open With option. Here, choose open with Software Install as the default choice.
Method 2: Use Gdebi application for installing deb packages with dependencies
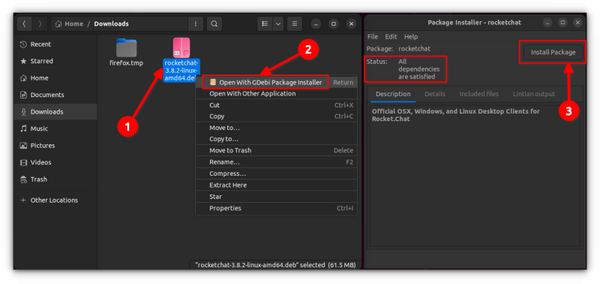
Again, life would be a lot simpler if things always went smoothly. But that’s not life as we know it. Now that you know .deb files can be easily installed via the Software Center, let me tell you about the dependency error that you may encounter with some packages. What happens is that a program may be dependent on another piece of software (such as libraries). When the developer is preparing the deb package for you, he/she may assume that your system already has that piece of software. But if that’s not the case and your system doesn’t have those required pieces of software, you’ll encounter the infamous ‘dependency error’. The Software Center cannot handle such errors on its own so you have to use another tool called gdebi. gdebi is a lightweight GUI application solely to install deb packages. It identifies the dependencies and tries to install these along with the .deb files. Personally, I prefer gdebi over the software center for installing deb files. It is a lightweight application so the installation seems quicker. You can read in detail about using gDebi and making it the default for installing DEB packages. You can install gdebi deb package installer from the software center or using the command below:
Method 3: Install .deb files in the command line
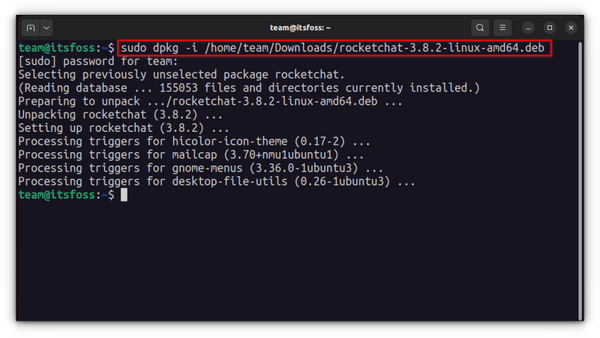
If you want to install deb packages in the command line, you can use either the apt command or the dpkg command. The apt command uses the dpkg command underneath it, but apt is more popular and easier to use. If you want to use the apt command for deb files, use it like this:
sudo apt install path_to_deb_filesudo apt install ./deb_filesudo dpkg -i path_to_deb_fileIn both commands, you should replace path_to_deb_file with the path and name of the deb file you’ve downloaded. If you get a dependency error while installing the deb packages, you can use the following command to fix it:
How to remove deb packages
Removing a deb package isn’t a big deal, either. And no, you don’t need the original deb file you used to install the program.
Method 1: Remove deb packages using apt command
All you need is the name of the program you’ve installed and then you can use apt or dpkg to remove that program.
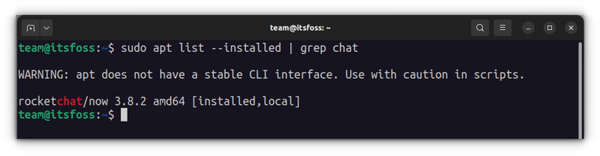
sudo apt remove program_nameNow, how do you find the exact program name you need to use in the remove command? The apt command has a solution for that as well. You can find the list of all installed files with the apt command, but manually going through this will be a pain. So you can use the grep command to search for your package. For example, I installed the RocketChat application in the previous section but if I want to find out the exact program name, I can use something like this:
sudo apt list --installed | grep chatThis will give me all the packages that have ‘chat’ in their name, and I can get the exact program name from there. As you can see, a program called ‘rocketchat’ is installed. Now you can use this program name with the apt remove command.
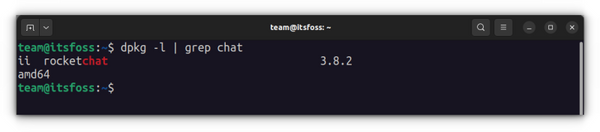
Method 2: Remove deb packages using dpkg command
The output will give all the packages installed that have ‘chat’ in their names. ii in the above command output means that the package has been correctly installed. Now that you have the program name, you can use the dpkg command to remove it:
What about updating the deb packages?
Some deb packages (like Chrome) provide updates through system updates, but for most other software you’ll have to remove the existing program and install the newer version. I hope this beginner’s guide helped you install deb packages on Ubuntu. I added the removal part so that you can have better control over your installed programs.
3 Command Line Tools to Install Deb Packages in Ubuntu
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install local software packages (.DEB) in Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint using three different command line tools and they are dpkg, apt, and gdebi.
This is useful to those new users who have migrated from Windows to Ubuntu or Linux Mint. The very basic problem they face is installing local software on the system.
However, Ubuntu and Linux Mint have their own Graphical Software Center for easy software installation, but we will be looking forward to installing deb packages through the terminal way.
1. Install .deb Package Using dpkg Command
Dpkg is a package manager for Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint. It is used to install, build, remove, and manage .deb packages. but unlike other Linux package management systems, it cannot automatically download and install packages with their dependencies.
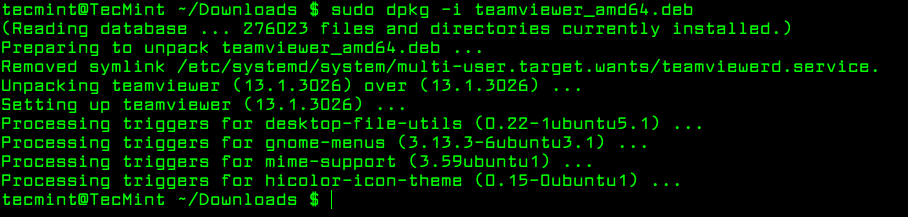
To install a .deb package, use the dpkg command with the -i flag along with the package name as shown.
$ sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_amd64.deb
If you get any dependency errors while installing or after installing and launching a program, you can use the following apt command to resolve and install dependencies using the -f flag, which tells the program to fix broken dependencies.
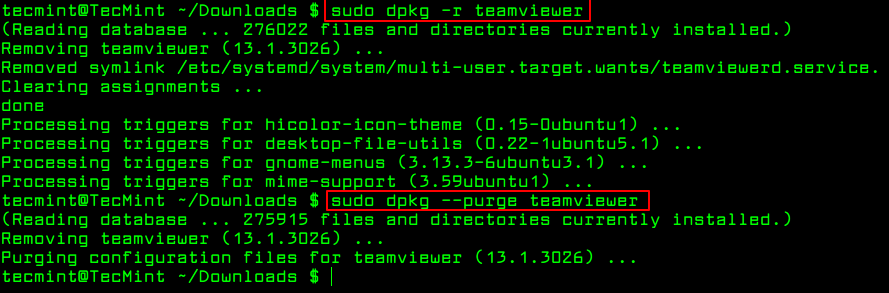
Remove Deb Packages Using dpkg Command
To remove a .deb package use the -r option or if you want to remove all its files including configuration files, you can purge it using the —purge option as shown.
$ sudo dpkg -r teamviewer [Remove Package] $ sudo dpkg --purge teamviewer [Remove Package with Configuration Files]
To know more about installed packages, read our article that shows how to list all files installed from a .deb package.
2. Install .deb Package Using Apt Command
The apt command is an advanced command-line tool, which offers new software package installation, existing software package upgradation, updating of the package list index, and even upgrading the whole Ubuntu or Linux Mint system.
It also offers apt-get and apt-cache command-line tools for managing packages more interactively on Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint systems.
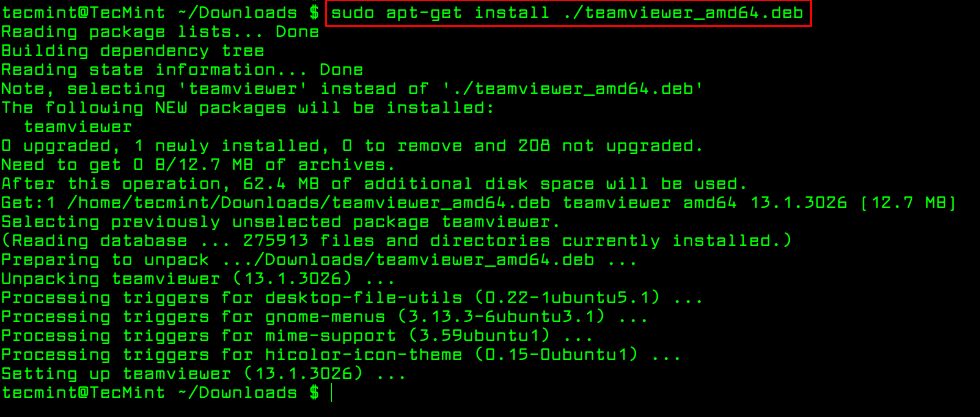
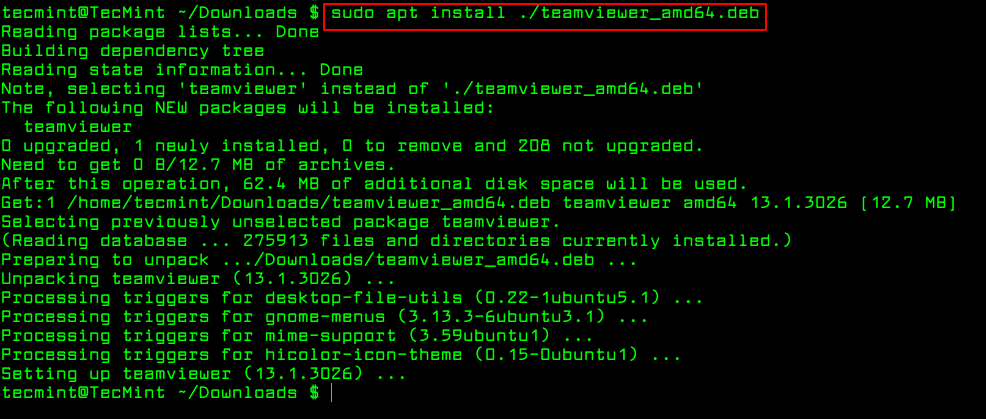
Essentially, apt-get or apt do not understand .deb files, they are designed to primarily handle package names (for example teamviewer, apache2, mariadb, etc..) and they retrieve and install .deb archives associated with a package name, from a source specified in the /etc/apt/sources.list file.
The only trick to installing a .deb Debian package using apt-get or apt is by specifying a local relative or absolute path ( ./ if in current dir) to the package, otherwise it will try to retrieve the package from remote sources and the operation will fail.
$ sudo apt install ./teamviewer_amd64.deb $ sudo apt-get install ./teamviewer_amd64.deb
Remove Deb Packages using apt Command
To remove a .deb package use the remove option or if you want to remove all its files including configuration files, you can purge it using the purge option as shown.
$ sudo apt-get remove teamviewer $ sudo apt-get purge teamviewer OR $ sudo apt remove teamviewer $ sudo apt purge teamviewer
3. Install .deb Package Using Gdebi Command
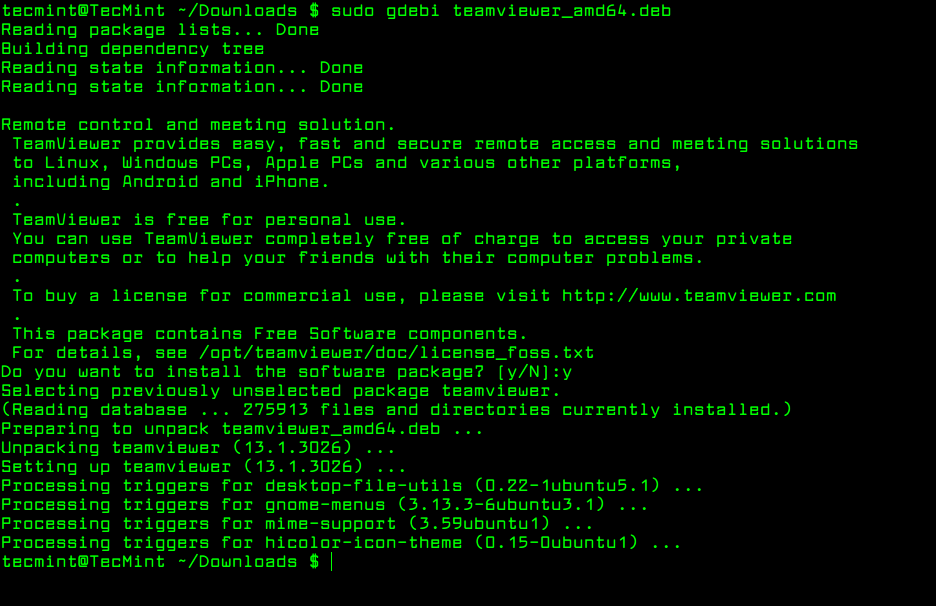
gdebi is a tiny command line and GUI tool for installing local deb packages. It resolves and installs package dependencies on the fly. To install a package, use the following command.
$ sudo gdebi teamviewer_13.1.3026_amd64.deb
To remove a .deb package installed from gdebi, you can use apt, apt-get or dpkg commands using purge option as shown.
$ sudo apt purge teamviewer OR $ sudo apt-get purge teamviewer OR $ sudo dpkg --purge teamviewer
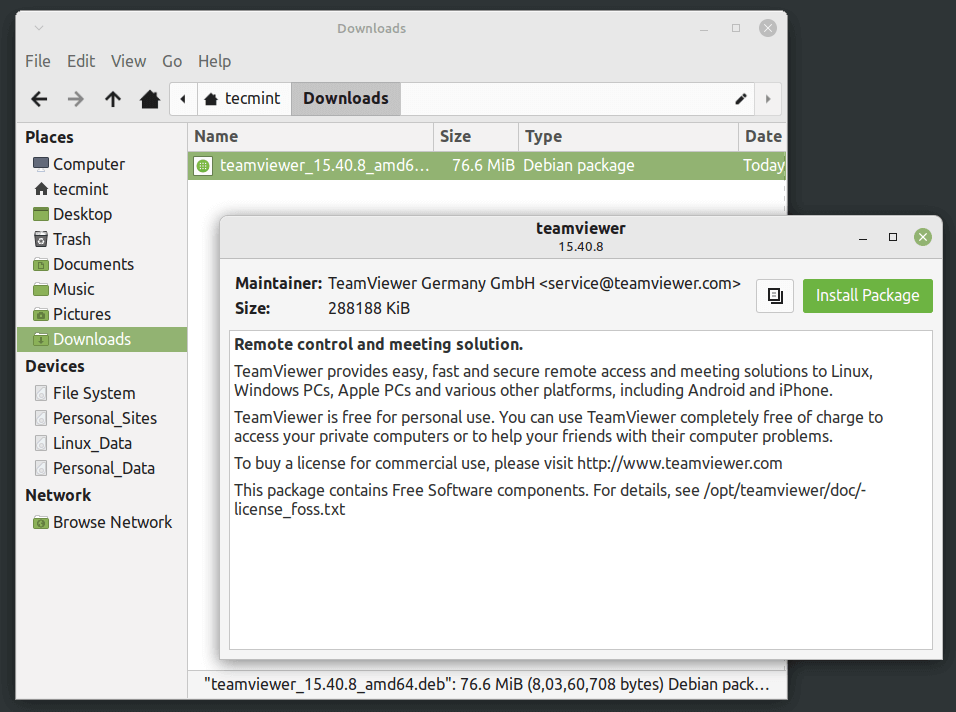
Install .deb Packages Using Gdebi GUI
The most recommended way for beginners to installing .deb files is through the Gdebi GUI installer. Simply, go to the directory where you have downloaded the file and double-click to install it as shown.
That’s It! In this tutorial, we have explained three different command line tools for installing or removing .deb Debian packages in Ubuntu and Linux Mint.
If you know any other way of installing local packages, do share with us using our comment section below.
Установка программ и пакетов формата .deb
В этой статье мы расскажем, как проходит установка deb-пакета Ubuntu и Debian, установка приложений, и какие для этого нужны инструменты.
Для использования операционной системы мало просто установить её. В процессе работы могут понадобиться дополнительные программы, которые нужно загружать отдельно.
Для установочных пакетов Debian (и производных дистрибутивов — Linux Mint, Kali Linux, Ubuntu) было разработано расширение .deb. Где можно найти debian-пакеты? Создать deb-пакет может любой разработчик, поэтому найти этот формат можно на любом сайте или в официальных репозиториях Debian и Ubuntu.
Для поиска, установки, обновления и удаления пакетов программ в Debian (и других основанных на нём ОС, в частности, Ubuntu) используется APT.
Утилита APT
APT (Advanced Packaging Tool) ― это инструмент командной строки, который помогает взаимодействовать с программами. Этот пакетный менеджер был разработан для Debian, однако позже стал использоваться и в других дистрибутивах, основанных на нём.
Обратите внимание! Раньше использовалась команда apt-get. В последних версиях Debian произошло обновление и есть возможность использовать просто apt. Инструмент apt совмещает функциональность apt-get и apt-cache. Старый вариант команды работает в современных системах. Для использования сложных сценариев всё ещё предпочтительнее использовать apt-get. Однако в своей инструкции мы будем использовать новый вариант, так как в этом случае он подходит лучше.
Синтаксис для работы с утилитой:
sudo apt опции команда имя_пакетаКоманды apt для управления пакетами:
- download ― скачать, но не устанавливать пакет;
- update ― обновление информации о списках пакетов в репозиториях,
- upgrade ― обновление системы без удаления пакетов,
- full-upgrade ― полное обновление системы с удалением конфликтующих зависимостей,
- install ― установка пакета,
- remove ― удаление пакета, но без удаления конфигурационных файлов,
- purge ― полное удаление пакета,
- autoremove ― автоматическое удаление ненужных пакетов,
- search ― поиск пакета в локальной базе данных,
- show ― узнать информацию о пакете.
- c ― сторонний конфигурационный файл,
- o ― строка конфигурации,
- t ― версия релиза, для которой устанавливать пакет,
- f ― выполнить операцию принудительно.
Как установить deb-пакет на Ubuntu и Debian из официального репозитория
Установка программ в Debian и Ubuntu происходит одинаково.