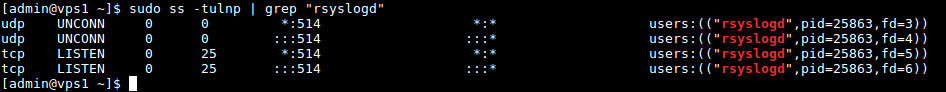- How to Setup Central Logging Server with Rsyslog in Linux
- Testing Environment
- How to Install and Configure Rsyslog Server
- How to Configure Rsyslog Client to Send Logs to Rsyslog Server
- How to Monitor Remote Logging on the Rsyslog Server
- How to install syslog on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8
- Software Requirements and Conventions Used
- How to install syslog on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 step by step instructions
- Related Linux Tutorials:
How to Setup Central Logging Server with Rsyslog in Linux
Logs are a critical component of any software or operating system. Logs usually record user’s actions, system events, network activity and so much more, depending on what they are intended for. One of the most widely used logging systems on Linux systems is rsyslog.
Rsyslog is a powerful, secure and high-performance log processing system which accepts data from different types of source (systems/applications) and outputs it into multiple formats.
It has evolved from a regular syslog daemon to a fully-featured, enterprise level logging system. It is designed in a client/server model, therefore it can be configured as a client and/or as a central logging server for other servers, network devices, and remote applications.
Testing Environment
For the purpose of this guide, we will use the following hosts:
How to Install and Configure Rsyslog Server
Most Linux distributions come with the rsyslog package preinstalled. In case it’s not installed, you can install it using your Linux package manager tool as shown.
$ sudo yum update && yum install rsyslog #CentOS 7 $ sudo apt update && apt install rsyslog #Ubuntu 16.04, 18.04
Once rsyslog installed, you need to start the service for now, enable it to auto-start at boot and check it’s status with the systemctl command.
$ sudo systemctl start rsyslog $ sudo systemctl enable rsyslog $ sudo systemctl status rsyslog
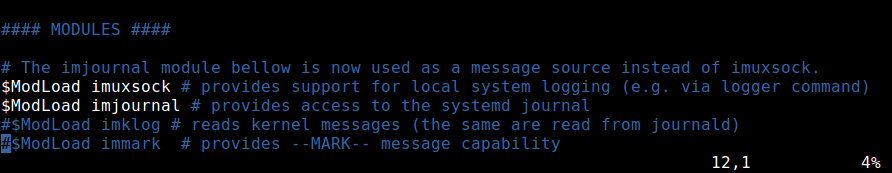
The main rsyslog configuration file is located at /etc/rsyslog.conf, which loads modules, defines the global directives, contains rules for processing log messages and it also includes all config files in /etc/rsyslog.d/ for various applications/services.
By default, rsyslog uses the imjournal and imusock modules for importing structured log messages from systemd journal and for accepting syslog messages from applications running on the local system via Unix sockets, respectively.
To configure rsyslog as a network/central logging server, you need to set the protocol (either UDP or TCP or both) it will use for remote syslog reception as well as the port it listens on.
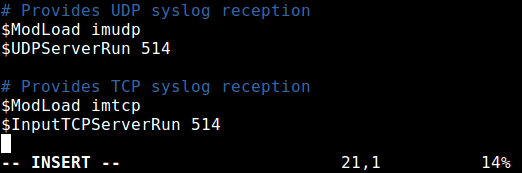
If you want to use a UDP connection, which is faster but unreliable, search and uncomment the lines below (replace 514 with the port you want it to listen on, this should match the port address that the clients send messages to, we will look at this more when configuring a rsyslog client).
$ModLoad imudp $UDPServerRun 514
To use TCP connection (which is slower but more reliable), search and uncomment the lines below.
$ModLoad imtcp $InputTCPServerRun 514
In this case, we want to use both UDP and TCP connections at the same time.
Next, you need to define the ruleset for processing remote logs in the following format.
facility.severity_level destination (where to store log)
- facility: is type of process/application generating message, they include auth, cron, daemon, kernel, local0..local7. Using * means all facilities.
- severity_level: is type of log message: emerg-0, alert-1, crit-2, err-3, warn-4, notice-5, info-6, debug-7. Using * means all severity levels and none implies no severity level.
- destination: is either local file or remote rsyslog server (defined in the form IP:port).
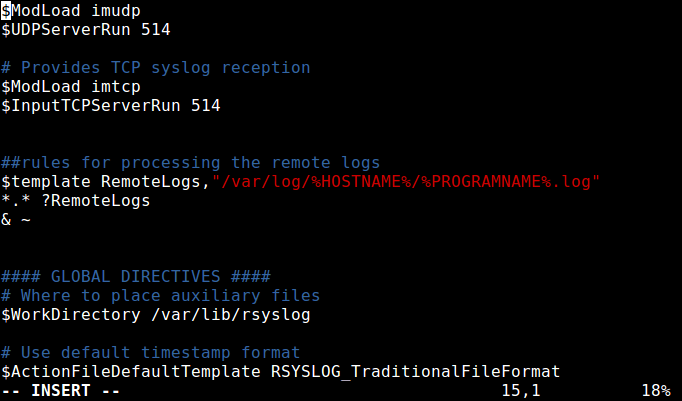
We will use the following ruleset for collecting logs from remote hosts, using the RemoteLogs template. Note that these rules must come before any rules for processing local messages, as shown in the screenshot.
$template RemoteLogs,"/var/log/%HOSTNAME%/%PROGRAMNAME%.log" *.* ?RemoteLogs & ~
Looking at the above ruleset, the first rule is “$template RemoteLogs,”/var/log/%HOSTNAME%/%PROGRAMNAME%.log””.
The directive $template tells rsyslog daemon to gather and write all of the received remote messages to distinct logs under /var/log, based on the hostname (client machine name) and remote client facility (program/application) that generated the messages as defined by the settings present in the template RemoteLogs.
The second line “*.* ?RemoteLogs” means record messages from all facilities at all severity levels using the RemoteLogs template configuration.
The final line “& ~” instructs rsyslog to stop processing the messages once it is written to a file. If you don’t include “& ~”, messages will instead be be written to the local files.
There are many other templates that you can use, for more information, see the rsyslog configuration man page (man rsyslog.conf) or refer to the Rsyslog online documentation.
That’s it with configuring the rsyslog server. Save and close the configuration file. To apply the recent changes, restart rsyslog daemon with the following command.
$ sudo systemctl restart rsyslog
Now verify the rsyslog network sockets. Use the ss command (or netstat with the same flags) command and pipe the output to grep to filter out rsyslogd connections.
$ sudo ss -tulnp | grep "rsyslog"
Next, on CentOS 7, if you have SELinux enabled, run the following commands to allow rsyslog traffic based on the network socket type.
$ sudo semanage -a -t syslogd_port_t -p udp 514 $ sudo semanage -a -t syslogd_port_t -p tcp 514
If the system has firewall enabled, you need to open port 514 to allow both UDP/TCP connections to the rsyslog server, by running.
------------- On CentOS ------------- $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=514/udp $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=514/tcp $ sudo firewall-cmd --reload ------------- On Ubuntu ------------- $ sudo ufw allow 514/udp $ sudo ufw allow 514/tcp $ sudo ufw reload
How to Configure Rsyslog Client to Send Logs to Rsyslog Server
Now on the client system, check if the rsyslog service is running or not with the following command.
$ sudo systemctl status rsyslog
If it’s not installed, install it and start the service as shown earlier on.
$ sudo yum update && yum install rsyslog #CentOS 7 $ sudo apt update && apt install rsyslog #Ubuntu 16.04, 18.04 $ sudo systemctl start rsyslog $ sudo systemctl enable rsyslog $ sudo systemctl status rsyslog
Once the rsyslog service is up and running, open the main configuration file where you will perform changes to the default configuration.
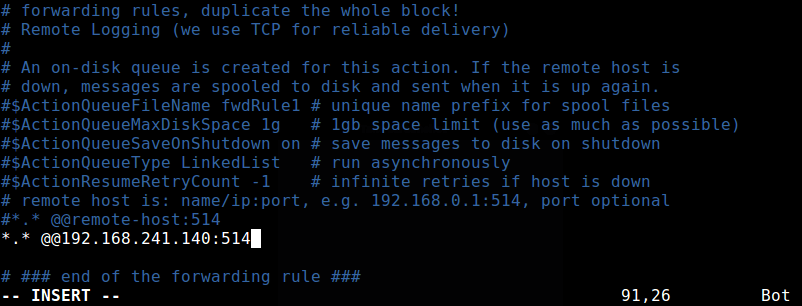
To force the rsyslog daemon to act as a log client and forward all locally generated log messages to the remote rsyslog server, add this forwarding rule, at the end of the file as shown in the following screenshot.
The above rule will send messages from all facilities and at all severity levels. To send messages from a specific facility for example auth, use the following rule.
Save the changes and close the configuration file. To apply the above settings, restart the rsyslog daemon.
$ sudo systemctl restart rsyslog
How to Monitor Remote Logging on the Rsyslog Server
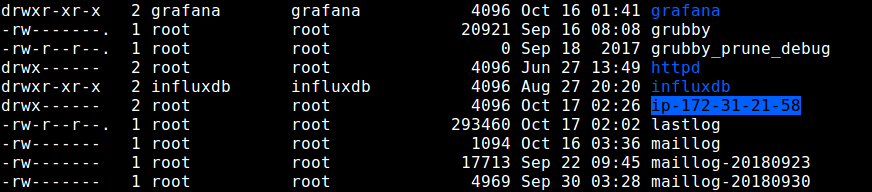
The final step is to verify if the rsyslog is actually receiving and logging messages from the client, under /var/log, in the form hostname/programname.log.
Run a ls command to long listing of the parent logs directory and check if there is a directory called ip-172.31.21.58 (or whatever your client machine’s hostname is).
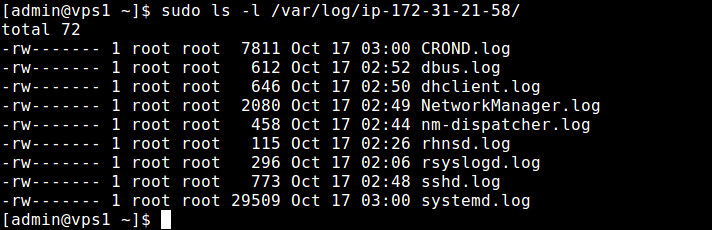
If the directory exists, check the log files inside it, by running.
$ sudo ls -l /var/log/ip-172-31-21-58/
Summary
Rsyslog is a high-performance log processing system, designed in a client/server architecture. We hope you are able to install and configure Rsyslog as a central/network logging server and as a client as demonstrated in this guide.
You may also want to refer to relevant rsyslog manual pages for more help. Feel free to give us any feedback or ask questions.
How to install syslog on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8
The syslog functionality is one of the main tools for a sysadmin. While writing logfiles with events of interest is a common feature of any application, having a system-wide logging functionality means all logs can be handled as one on the system. But syslog does not stop there. With these tool, a sysadmin can centralize log processing in the datacenter by forwarding the incoming events from applications to central logservers, where they can be processed at a large scale.
Centralized logging is an overkill on a home system with a few computers, but already have it’s benefits around a dozen machine. For example, a dozen desktops sending all their logfiles to a central logserver mean they don’t need to store them on the long run, the logs will occupy disk space in the logserver. The admin can check for problems in only one place (possibly by means of automated reports), the logs can be preserved in a safe way by the means of backups, stored more effective by means of heavy compressing, and will not be lost on a client’s failure or user error.
In this tutorial you will learn:
- How to install rsyslog package on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8.
- How to verify successful install.
- How to start, stop and autostart rsyslog service.
- How to test syslog functionality with logger.
Software Requirements and Conventions Used
| Category | Requirements, Conventions or Software Version Used |
|---|---|
| System | RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 |
| Software | rsyslog 8 |
| Other | Privileged access to your Linux system as root or via the sudo command. |
| Conventions | # – requires given linux commands to be executed with root privileges either directly as a root user or by use of sudo command $ – requires given linux commands to be executed as a regular non-privileged user |
How to install syslog on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 step by step instructions
On RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 rsyslog package should be installed and running by default. There may be cases where you need to install it anyway, for example package broken/deleted, reverting from another syslog service, etc.
- The rsyslog is reachable from the base repositories. You need to have Subscription Management repositories set up and reachable in order to install any packages. With that in place, install is only one dnf command away:
# rpm -q rsyslog rsyslog-8.37.0-6.el8.x86_64
# dnf info rsyslog --verbose [. ] Installed Packages Name : rsyslog Version : 8.37.0 Release : 6.el8 Arch : x86_64 Size : 2.2 M Source : rsyslog-8.37.0-6.el8.src.rpm Repo : @System [. ] Install time : Thu Dec 27 12:24:35 2018 Installed by : [. ]
And lastly, systemd should know about the service (not running), which means the service files are in place:
# systemctl status rsyslog.service ● rsyslog.service - System Logging Service Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/rsyslog.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: inactive (dead) Docs: man:rsyslogd(8) http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/
# systemctl start rsyslog.service
# systemctl stop rsyslog.service
The status showed that the service is enabled on installation, which means it will start automatically on startup of the operating system. We can disable this autostart feature with:
# systemctl disable rsyslog.service
# systemctl enable rsyslog.service
# echo "test message from user root" | logger
And see the message properly shipped into the main syslog file by checking the last lines of /var/log/messages :
# tail /var/log/messages [. ] Dec 27 12:39:46 rhel8 rsyslogd[2636]: [origin software="rsyslogd" swVersion="8.37.0-6.el8" x-pid="2636" x-info="http://www.rsyslog.com"] start Dec 27 12:39:46 rhel8 systemd[1]: Started System Logging Service. Dec 27 12:41:56 rhel8 testuser[2668]: test message from user root