- How to install «make» in ubuntu? [closed]
- How to install make on Ubuntu
- How to install the Make package on Ubuntu
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Taimoor Mohsin
- How to Install make command on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa)
- How to Install make command on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa)
- Step 1: Prerequisites
- Step 2: Update Your Server
- Step 3: Install make command
- Step 4: Verify Installation
- Step 5: Check Version
- Step 6: Using make command
- Step 7: Check all the Available Options
How to install «make» in ubuntu? [closed]
I’m trying to install «yum» or «apt-get» into my system «ubuntu centOS». I did download the binary files for these two programs from the internet using the command wget. but after decompressing the files using the command «tar -zxvf «filename» ,then configuring the file «./configuring», and then when I want to use the command «make» I get the following error «make: not found». I have searched for a method to download the «make» command but all the methods I found on the net use either the command «yum» or «apt-get» and I don’t have any of them.
You have this slightly wrong. Make is not a program you need to download. it’s a utility that comes integrated into nearly every distribution of linux.
Wait, what? «ubuntu centOS»? Those are two different flavors with their own (often radically different) ways of doing things. It’s almost certainly either one or the other, unless there’s some freakish mashup of the two i haven’t seen or heard of yet. Either way, this is a question about installing software, and seems more suited to Super User.
Just for future reference, there are a couple of major flavors of Linux. I personally count 4: Debian (which includes Ubuntu), RedHat (which includes CentOS), Slackware (including SuSE), and Gentoo. (Some would argue with Gentoo being «major», but IMO it’s popular enough to earn a place, and it’s definitely its own flavor.) Most of the big distros are derived (indirectly or indirectly) from one of those main lines; the ones that aren’t are typically specialized or indie-type stuff. And the main flavors are different enough that you’ll typically only derive from one of them.
How to install make on Ubuntu
The ”make” command in Linux is used to compile and manage a collection of applications and files from source code. It allows developers to use the terminal to install and collect a variety of programs. It also manages and reduces the amount of time that is required for the compilation. The make command’s primary goal is to break down a huge program into smaller pieces and assess whether or not it needs to be recompiled. It also gives the essential instructions for recompiling them.
The make command is used to execute the makefile which is a unique file that includes the shell commands we write to keep the project running. It includes executable targets and instructions and is not permitted to generate several makefiles. It’s best if you make a separate directory for it. It maintains track of recently updated files, so only update those that are needed. As a result, this article will show you how to install the make package on Ubuntu.
How to install the Make package on Ubuntu
Before installing the make package, it is better to update your already installed packages; otherwise, you may find compatibility issues with some software. You can do that by typing.
This command will provide you with the information of all outdated packages that can be upgraded to the newer version, so this is highly recommended before installing any new package. Make package comes in default in the Ubuntu OS, so you should verify if it is already installed before considering installing it. You can verify it by typing the below-mentioned command in the terminal.
If the make package is not installed in Ubuntu due to any reason, you will get the error as shown below.
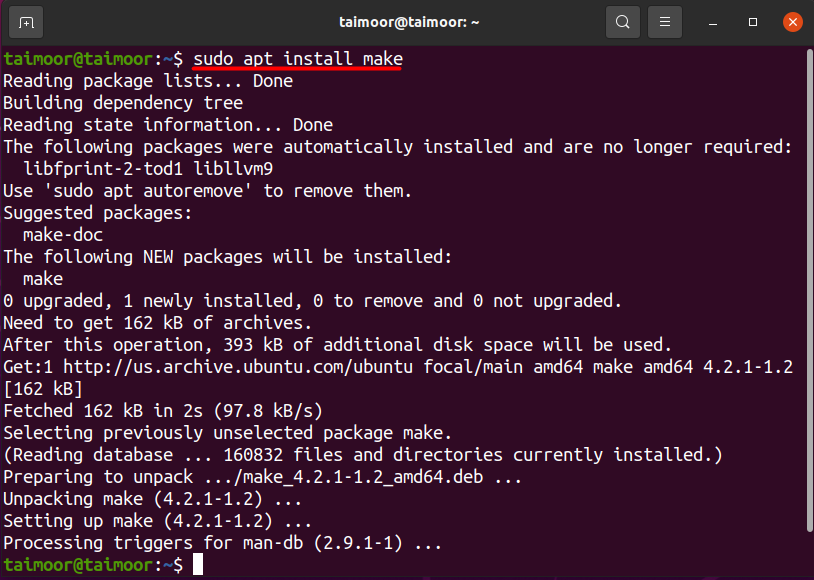
You can install the make package by typing.
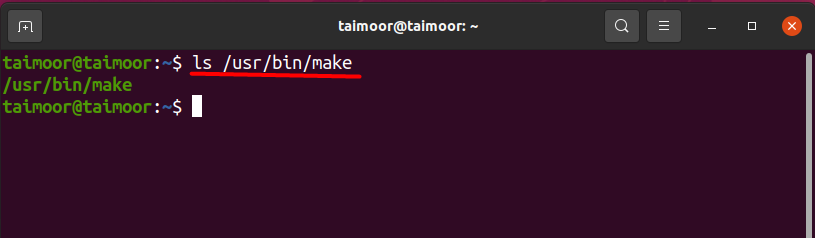
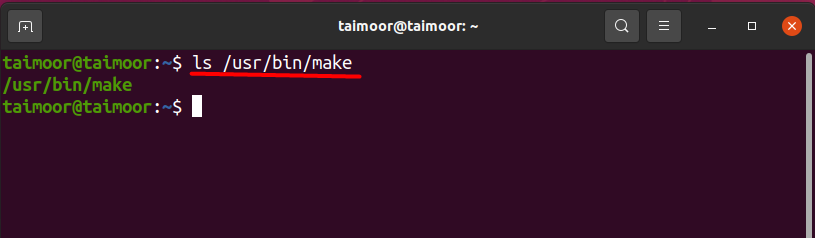
Your system should have a make directory; otherwise, you cannot use the make package. You can verify that by typing.
If the directory is available then you can use the “make” utility; if it displays an error as shown below then there is a way to solve this problem as well:
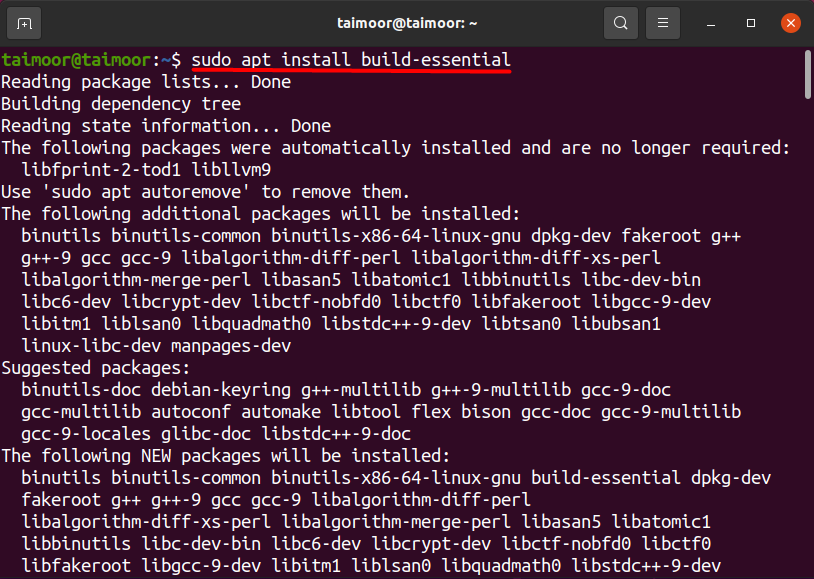
By installing the build-essential package you get rid of this error. It is also known as a meta-package, and you can use it to install a make package and several other packages as well. Many packages are dependent and linked with this package, and you can’t install them without installing the meta-package first. For its installation, you need to type the following command in the terminal.
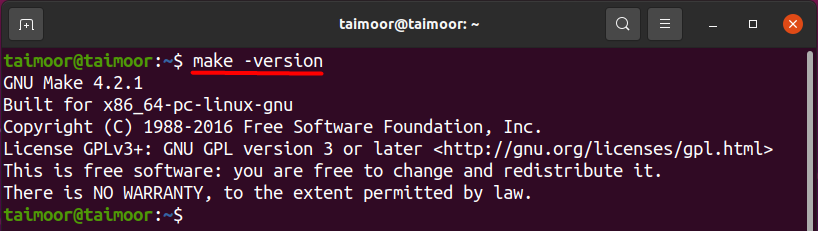
After its installation, you should check the make version to verify if it is properly installed or not. You can also verify the make directory that you won’t see if it is not working correctly before. You can check the version as discussed before by typing the command.
And you can check the make directory, use:
As of now, you can see both the version and the directory, the make package is now correctly installed, and you can use it as per your requirement.
Conclusion
The make command in Linux is used to compile and manage a collection of applications and files from source code. It allows developers to use the terminal to install and collect a variety of programs. It also manages and reduces the time that is required for the compilation process for large projects. In this article, we have shown you how you can install the make package, and some of the solutions have also been discussed if you are not able to install this package
About the author
Taimoor Mohsin
Hi there! I’m an avid writer who loves to help others in finding solutions by writing high-quality content about technology and gaming. In my spare time, I enjoy reading books and watching movies.
How to Install make command on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa)
In this article, I will take you through the steps to install make command on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS. GNU make is a free and open source utility to compile and link a program. It requires a Makefile to know how to compile and link a program. It is widely used by programmers and developers to compile their programs on Linux/Unix based systems across the globe.
make utility plays an important role when you have to compile a larger program which has number of source code files. Instead of compiling and linking every program manually, you can simply write a Makefile to compile and build the programs using make utility. It saves lot of time and effort. It is also very easy to install in almost all the famous Linux and Unix distributions. Here we will see the steps to install make utility on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS based systems.
How to Install make command on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa)
Step 1: Prerequisites
a) You should have a running Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Server.
b) You should have sudo or root access to run privileged commands.
c) You should have apt utility available in your System.
Step 2: Update Your Server
In the first step, you need to check for any latest available updates and then install it by using sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade Hit:1 https://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb stable InRelease Hit:2 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal InRelease Get:3 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security InRelease [114 kB] Hit:4 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates InRelease Hit:5 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-backports InRelease Fetched 114 kB in 2s (73.8 kB/s) Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. Done All packages are up to date. Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. Done Calculating upgrade. Done The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required: gir1.2-goa-1.0 libfwupdplugin1 libllvm11 libxmlb1 Use 'sudo apt autoremove' to remove them. 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Step 3: Install make command
In the next step you can install make utility from default Ubuntu repo by using sudo apt install make command as shown below. This will download and install the package along with all its dependencies.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt install make [sudo] password for cyberithub: Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. Done The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required: libfwupdplugin1 libllvm11 libxmlb1 Use 'sudo apt autoremove' to remove them. Suggested packages: make-doc The following NEW packages will be installed: make 0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Need to get 162 kB of archives. After this operation, 393 kB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/main amd64 make amd64 4.2.1-1.2 [162 kB] Fetched 162 kB in 1s (122 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package make. (Reading database . 196300 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack . /make_4.2.1-1.2_amd64.deb . Unpacking make (4.2.1-1.2) . Setting up make (4.2.1-1.2) . Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.1-1) .
Step 4: Verify Installation
After successful installation, you can verify the installed files path by using dpkg -L make command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ dpkg -L make /. /usr /usr/bin /usr/bin/make /usr/bin/make-first-existing-target /usr/include /usr/include/gnumake.h /usr/share /usr/share/doc /usr/share/doc/make /usr/share/doc/make/ABOUT-NLS.gz /usr/share/doc/make/AUTHORS /usr/share/doc/make/Explanations.gz /usr/share/doc/make/NEWS.Debian.gz /usr/share/doc/make/NEWS.gz /usr/share/doc/make/README.Debian-Source /usr/share/doc/make/README.customs.gz /usr/share/doc/make/README.gz /usr/share/doc/make/changelog.Debian.gz /usr/share/doc/make/copyright /usr/share/man /usr/share/man/man1 /usr/share/man/man1/make-first-existing-target.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/make.1.gz Step 5: Check Version
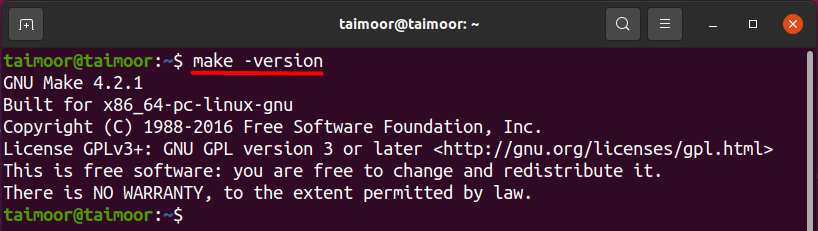
You can also verify the current installed version by using make —version command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ make --version GNU Make 4.2.1 Built for x86_64-pc-linux-gnu Copyright (C) 1988-2016 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Step 6: Using make command
Now that make command is successfully installed, you can test it by compiling any source code using the Makefile configuration as shown below. You just need to write or use correct Makefile to generate object files by running make command. Below is one of the example where I am compiling the rtl8821cu Wifi USB driver source code using make utility. Similarly, you can also check and verify the utility in your system as well.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~/brektrou/rtl8821CU$ make make ARCH=x86_64 CROSS_COMPILE= -C /lib/modules/5.15.0-58-generic/build M=/home/cyberithub/brektrou/rtl8821CU modules make[1]: Entering directory '/usr/src/linux-headers-5.15.0-58-generic' CC [M] /home/cyberithub/brektrou/rtl8821CU/core/rtw_cmd.o CC [M] /home/cyberithub/brektrou/rtl8821CU/core/rtw_security.o CC [M] /home/cyberithub/brektrou/rtl8821CU/core/rtw_debug.o CC [M] /home/cyberithub/brektrou/rtl8821CU/core/rtw_io.o CC [M] /home/cyberithub/brektrou/rtl8821CU/core/rtw_ioctl_query.o CC [M] /home/cyberithub/brektrou/rtl8821CU/core/rtw_ioctl_set.o CC [M] /home/cyberithub/brektrou/rtl8821CU/core/rtw_ieee80211.o CC [M] /home/cyberithub/brektrou/rtl8821CU/core/rtw_mlme.o CC [M] /home/cyberithub/brektrou/rtl8821CU/core/rtw_mlme_ext.o CC [M] /home/cyberithub/brektrou/rtl8821CU/core/rtw_mi.o CC [M] /home/cyberithub/brektrou/rtl8821CU/core/rtw_wlan_util.o . Step 7: Check all the Available Options
To check more options available with make command, you need to use make —help command as shown below.
cyberithub@ubuntu:~$ make --help Usage: make [options] [target] . Options: -b, -m Ignored for compatibility. -B, --always-make Unconditionally make all targets. -C DIRECTORY, --directory=DIRECTORY Change to DIRECTORY before doing anything. -d Print lots of debugging information. --debug[=FLAGS] Print various types of debugging information. -e, --environment-overrides Environment variables override makefiles. --eval=STRING Evaluate STRING as a makefile statement. -f FILE, --file=FILE, --makefile=FILE Read FILE as a makefile. -h, --help Print this message and exit. -i, --ignore-errors Ignore errors from recipes. .