- Installing Node.js via package manager
- Alpine Linux
- Android
- Arch Linux
- CentOS, Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Alternatives
- Debian and Ubuntu based Linux distributions
- Alternatives
- fnm
- FreeBSD
- Gentoo
- IBM i
- macOS
- Alternatives
- n
- NetBSD
- Nodenv
- nvm
- nvs
- Windows
- macOS,UnixLike
- Usage
- OpenBSD
- openSUSE and SLE
- SmartOS and illumos
- Snap
- Solus
- Void Linux
- Windows
- Alternatives
- z/OS
- Установка Node.js на CentOS 8
- Как установить Node.js в CentOS 8
- 1. Установка из официальных репозиториев
- 2. Установить Node.js через NVM
- Выводы
Installing Node.js via package manager
Note: The packages on this page are maintained and supported by their respective packagers, not the Node.js core team. Please report any issues you encounter to the package maintainer. If it turns out your issue is a bug in Node.js itself, the maintainer will report the issue upstream.
Alpine Linux
Node.js LTS and npm packages are available in the Main Repository.
Node.js Current can be installed from the Community Repository.
Android
Android support is still experimental in Node.js, so precompiled binaries are not yet provided by Node.js developers.
However, there are some third-party solutions. For example, Termux community provides terminal emulator and Linux environment for Android, as well as own package manager and extensive collection of many precompiled applications. This command in Termux app will install the last available Node.js version:
Currently, Termux Node.js binaries are linked against system-icu (depending on libicu package).
Arch Linux
Node.js and npm packages are available in the Community Repository.
CentOS, Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Node.js is available as a module called nodejs in CentOS/RHEL 8 and Fedora.
dnf module install nodejs:
where corresponds to the major version of Node.js. To see a list of available streams:
For example, to install Node.js 18:
dnf module install nodejs:18/common Alternatives
These resources provide packages compatible with CentOS, Fedora, and RHEL.
Debian and Ubuntu based Linux distributions
Alternatives
Packages compatible with Debian and Ubuntu based Linux distributions are available via Node.js snaps.
fnm
Fast and simple Node.js version manager built in Rust used to manage multiple released Node.js versions. It allows you to perform operations like install, uninstall, switch Node versions automatically based on the current directory, etc. To install fnm, use this install script.
fnm has cross-platform support (macOS, Windows, Linux) & all popular shells (Bash, Zsh, Fish, PowerShell, Windows Command Line Prompt). fnm is built with speed in mind and compatibility support for .node-version and .nvmrc files.
FreeBSD
The most recent release of Node.js is available via the www/node port.
Install a binary package via pkg:
Or compile it on your own using ports:
cd /usr/ports/www/node && make install Gentoo
Node.js is available in the portage tree.
IBM i
LTS versions of Node.js are available from IBM, and are available via the ‘yum’ package manager. The package name is nodejs followed by the major version number (for instance, nodejs12 , nodejs14 etc)
To install Node.js 14.x from the command line, run the following as a user with *ALLOBJ special authority:
Node.js can also be installed with the IBM i Access Client Solutions product. See this support document for more details
macOS
Download the macOS Installer directly from the nodejs.org web site.
If you want to download the package with bash:
curl "https://nodejs.org/dist/latest/node-$node-(.*)\.pkg.*|\1|p')>.pkg" > "$HOME/Downloads/node-latest.pkg" && sudo installer -store -pkg "$HOME/Downloads/node-latest.pkg" -target "/" Alternatives
port install nodejs # Example port install nodejs7 Install the binary package:
Or build manually from pkgsrc:
cd pkgsrc/lang/nodejs && bmake install n
n is a simple to use Node.js version manager for Mac and Linux. Specify the target version to install using a rich syntax, or select from a menu of previously downloaded versions. The versions are installed system-wide or user-wide, and for more targeted use you can run a version directly from the cached downloads.
See the homepage for install methods (bootstrap, npm, Homebrew, third-party), and all the usage details.
If you already have npm then installing n and then the newest LTS node version is as simple as:
NetBSD
Node.js is available in the pkgsrc tree:
cd /usr/pkgsrc/lang/nodejs && make install Or install a binary package (if available for your platform) using pkgin:
Nodenv
nodenv is a lightweight node version manager, similar to nvm . It’s simple and predictable. A rich plugin ecosystem lets you tailor it to suit your needs. Use nodenv to pick a Node version for your application and guarantee that your development environment matches production.
Nodenv installation instructions are maintained on its Github page. Please visit that page to ensure you’re following the latest version of the installation steps.
nvm
Node Version Manager is a bash script used to manage multiple released Node.js versions. It allows you to perform operations like install, uninstall, switch version, etc. To install nvm, use this install script.
On Unix / OS X systems Node.js built from source can be installed using nvm by installing into the location that nvm expects:
env VERSION=`python tools/getnodeversion.py` make install DESTDIR=`nvm_version_path v$VERSION` PREFIX="" After this you can use nvm to switch between released versions and versions built from source. For example, if the version of Node.js is v8.0.0-pre:
Once the official release is out you will want to uninstall the version built from source:
nvs
Windows
The nvs version manager is cross-platform and can be used on Windows, macOS, and Unix-like systems
To install nvs on Windows go to the release page here and download the MSI installer file of the latest release.
You can also use chocolatey to install it:
macOS,UnixLike
You can find the documentation regarding the installation steps of nvs in macOS/Unix-like systems here
Usage
After this you can use nvs to switch between different versions of node.
To add the latest version of node:
Or to add the latest LTS version of node:
Then run the nvs use command to add a version of node to your PATH for the current shell:
$ nvs use lts PATH -= %LOCALAPPDATA%\nvs\default PATH += %LOCALAPPDATA%\nvs\node\14.17.0\x64 To add it to PATH permanently, use nvs link :
OpenBSD
Node.js is available through the ports system.
openSUSE and SLE
Node.js is available in the main repositories under the following packages:
- openSUSE Leap 15.2: nodejs10 , nodejs12 , nodejs14
- openSUSE Tumbleweed: nodejs16
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) 12: nodejs10 , nodejs12 , and nodejs14 (The «Web and Scripting Module» must be enabled.)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) 15 SP2: nodejs10 , nodejs12 , and nodejs14 (The «Web and Scripting Module» must be enabled.)
For example, to install Node.js 14.x on openSUSE Leap 15.2, run the following as root:
Different major versions of Node can be installed and used concurrently.
SmartOS and illumos
SmartOS images come with pkgsrc pre-installed. On other illumos distributions, first install pkgsrc, then you may install the binary package as normal:
Or build manually from pkgsrc:
cd pkgsrc/lang/nodejs && bmake install Snap
Node.js snaps are available as node on the Snap store.
Solus
Solus provides Node.js in its main repository.
sudo eopkg install nodejs Void Linux
Void Linux ships Node.js stable in the main repository.
Windows
Download the Windows Installer directly from the nodejs.org web site.
Alternatives
winget install OpenJS.NodeJS # or for LTS winget install OpenJS.NodeJS.LTS After running one of the two commands above, it may be necessary to restart the terminal emulator before the node CLI command becomes available.
cinst nodejs # or for full install with npm cinst nodejs.install scoop install nodejs # or for LTS scoop install nodejs-lts z/OS
IBM® SDK for Node.js — z/OS® is available in two installation formats, SMP/E and PAX. Select the installation format that applies to you:
Copyright OpenJS Foundation and Node.js contributors. All rights reserved. The OpenJS Foundation has registered trademarks and uses trademarks. For a list of trademarks of the OpenJS Foundation, please see our Trademark Policy and Trademark List. Trademarks and logos not indicated on the list of OpenJS Foundation trademarks are trademarks™ or registered® trademarks of their respective holders. Use of them does not imply any affiliation with or endorsement by them.
Установка Node.js на CentOS 8
Node.js — это кросс-платформенная, легкая и очень мощная среда выполнения Javascript с открытым исходным кодом для серверного программирования, построенная на движке V8 от Google и используемая для создания масштабируемых сетевых проектов и веб-приложений, требующих бэкенд-функциональности.
В этой статье мы расскажем вам о двух различных способах установки node.js на CentOS 8, после чего вы сможете начать разработку. Все команды необходимо выполнять от имени пользователя root с привилегиями sudo.
Как установить Node.js в CentOS 8
Сперва авторизуемся от имени пользователя root использовав команду:
1. Установка из официальных репозиториев
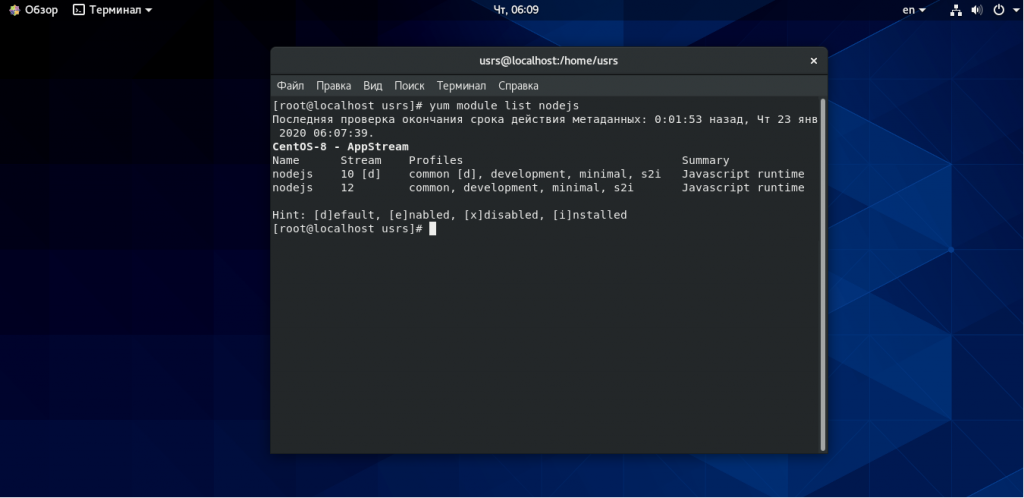
Первым способом установки о котором мы расскажем вам будет установка node js из официальных репозиториев CentOS. Перед установкой необходимо перечислить доступные для установки профили с помощью следующей команды:
На этом снимке видно, что доступны четыре различных профиля, но вам нужно установить только профиль по умолчанию, который выделен с помощью [d]. Теперь устанавливаем общий набор пакетов среды выполнения. Для этого выполните команду:
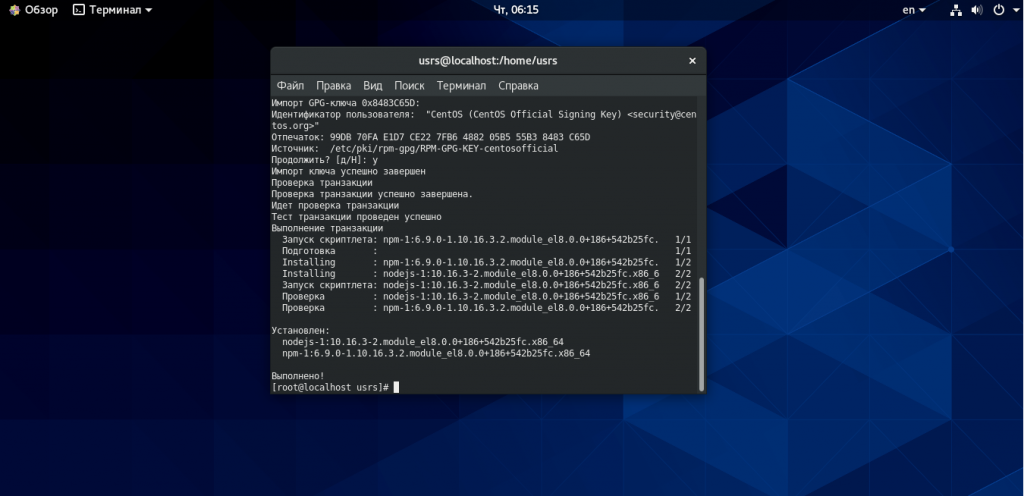
yum module install nodejs
На рисунке 4 приведен вывод команды установки.
Если вы разработчик, вы можете установить профиль разработки, который позволит добавить дополнительные библиотеки, требуемые для создания динамически загружаемых модулей, как показано на рисунке.
yum module install nodejs/development
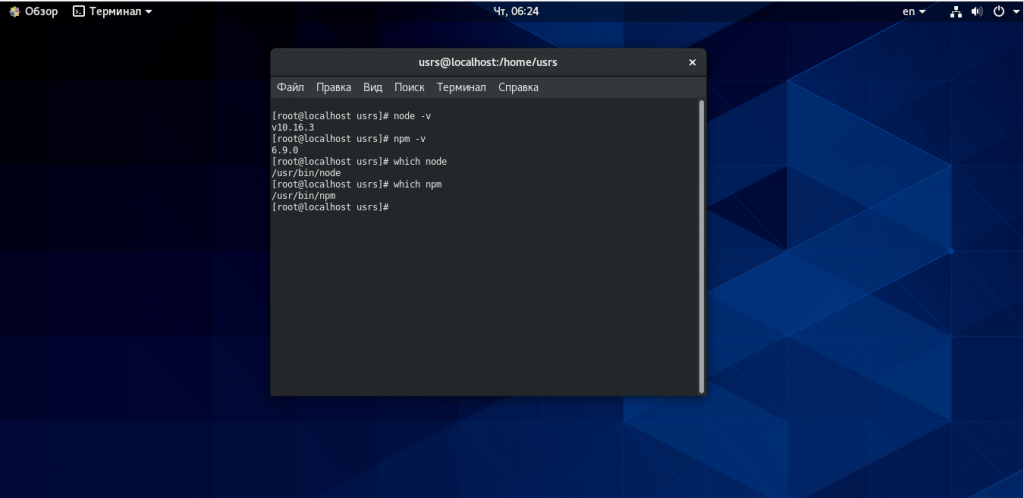
После установки пакетов node.js, вы можете проверить версию и расположение файлов, используя приведенные ниже команды:
node -v
npm -v
which node
which npm
Это был самый простой способ установки среды node. js на CentOS 8 Linux из репозиториев самой CentOS.
2. Установить Node.js через NVM
Ещё установка Node js CentOS 8 может быть выполнена с помощью NVM, Node Version Manager — это скрипта написанного на языке программирования bash, который позволяет устанавливать, удалять и обслуживать несколько версий node.js в системе.
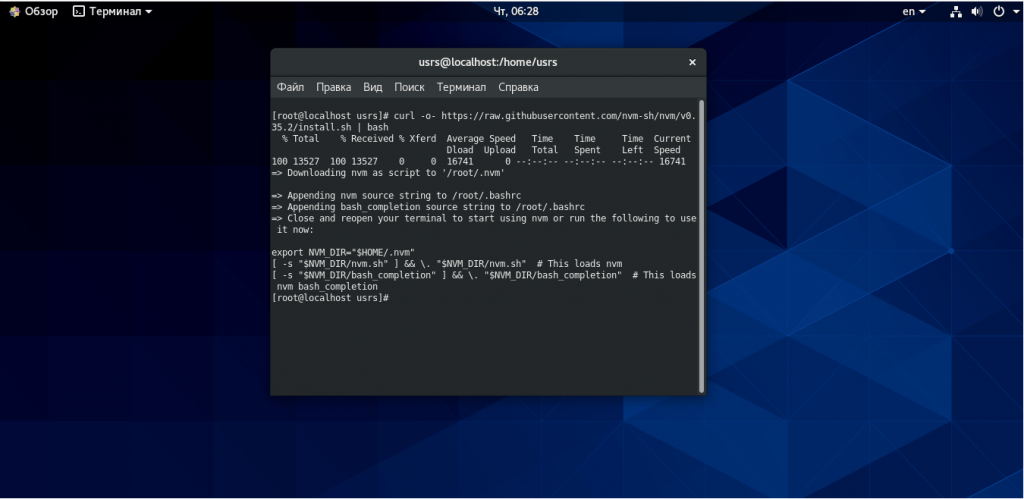
Чтобы установить или обновить NVM в CentOS 8, используйте одну из приведенных ниже команд curl или wget:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.35.2/install.sh | bash
wget -qO- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.35.2/install.sh | bash
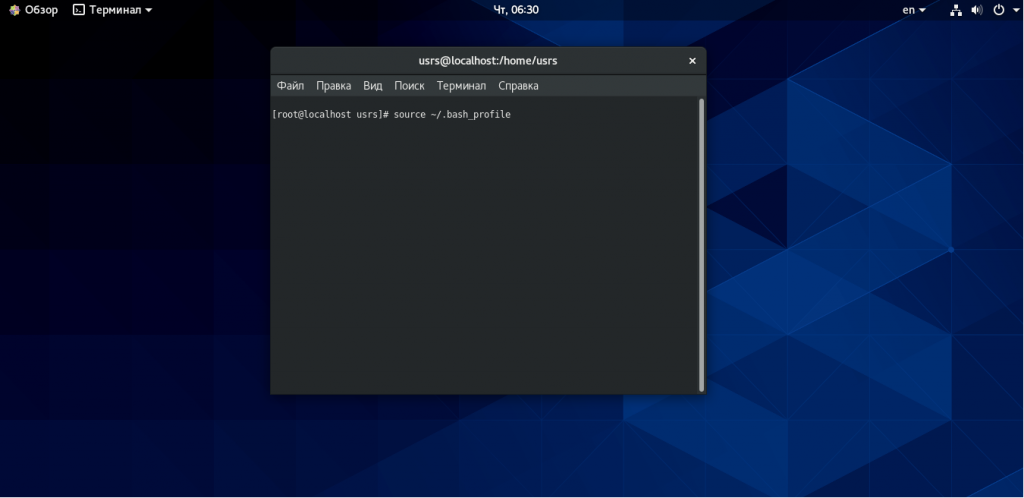
В приведенном выше сценарии происходит установка nvm centos в домашнюю папку вашего пользователя. Чтобы начать его использование, вам нужно обновить переменные окружения из .bash_profile.
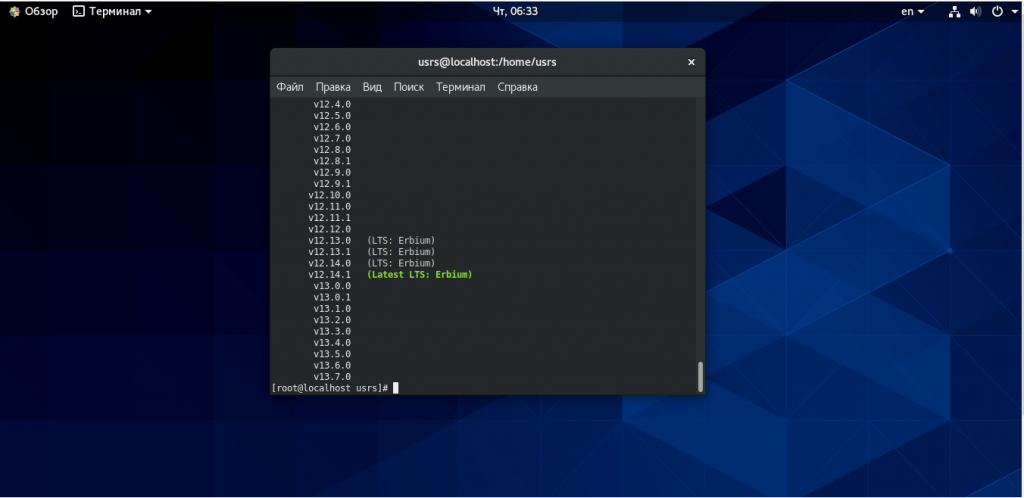
И после его создания вы можете просмотреть доступные версии node.js с помощью команды ls-remote:
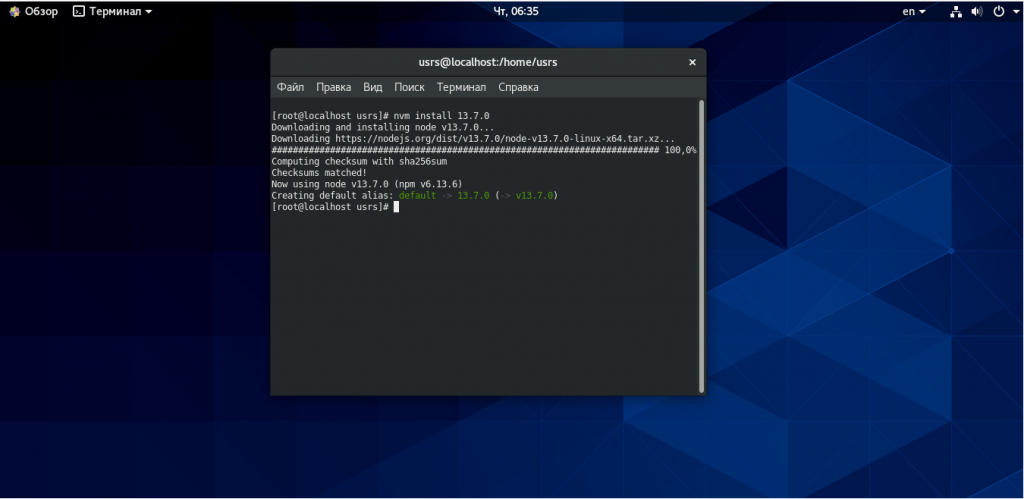
Теперь возможна установка Node.js CentOS 8 любой версии, которую вы видите в списке. Например, чтобы получить версию v13.7.0, вы можете ввести следующую команду:
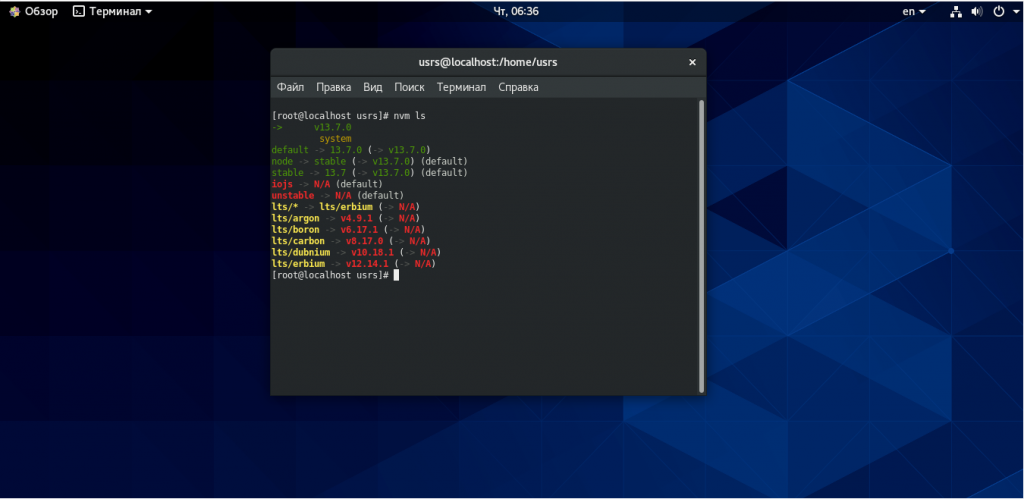
После завершения установки можно ввести список установленных в системе версий node.js:
Вы можете переключаться между установленными версиями Node командой nvm use, например, для версии v13.7.0:
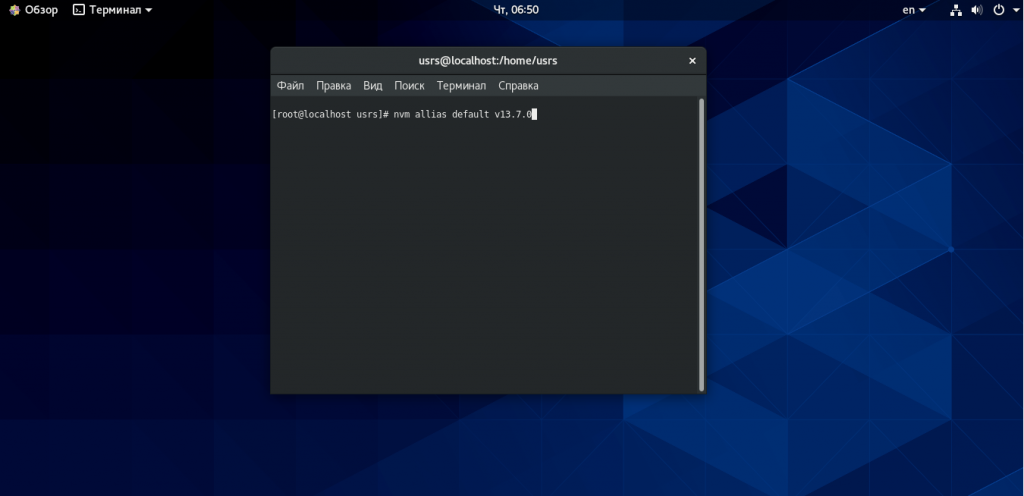
Вы также можете установить версию Node.js по умолчанию и проверить ее, запустив.
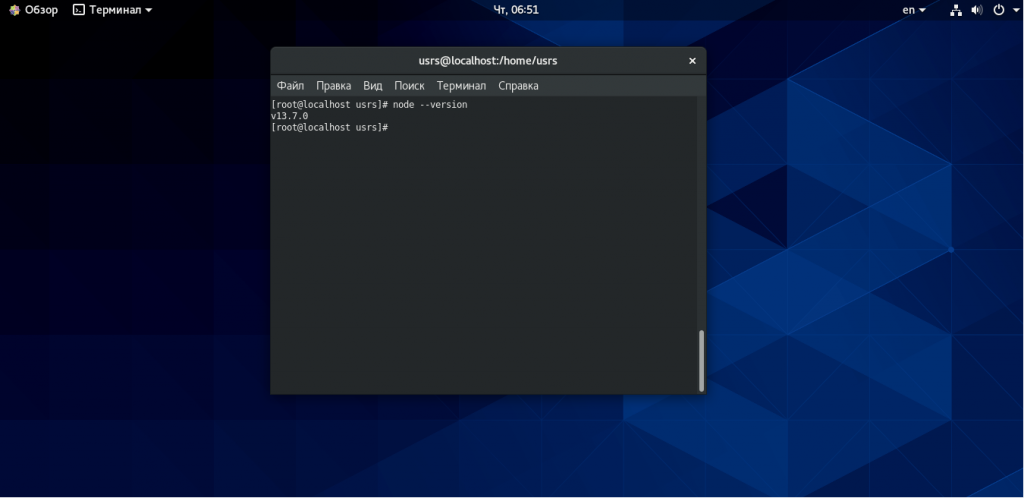
Проверить установленную версию node.js вы можете выполнив команду приведенную ниже:
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели как установить Node.js на CentOS 8 из официальных репозиториев или с помощью менеджера версий Node.js — NVM. Последний вариант позволяет получить самую свежую версию программы.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.