- How to Install PHP 8.0 on Ubuntu 20.04 / 18.04
- On this page
- Step 1: Add the Ondřej Surý PPA Repository
- Step 2: Install PHP 8.0 with Apache on Ubuntu
- Step 2: Install PHP 8.0 with Nginx on Ubuntu
- Step 4: Install PHP 8 Extensions in Ubuntu
- Step 5: Verify PHP 8 Installation in Ubuntu
- Install php linux apt get
- Использование APT
- Контроль конфигурации
- Стандартные проблемы
- User Contributed Notes 6 notes
- Установка разных версий PHP на Linux Ubuntu
- Установка PHP
- Установка базовой версии
- Установка определенной версии
- Выбор версии PHP по умолчанию
- Установка расширений
- Настройка PHP
How to Install PHP 8.0 on Ubuntu 20.04 / 18.04
PHP is arguably one of the most widely used server-side programming languages. It’s the language of choice when developing dynamic and responsive websites. In fact, popular CM platforms such as WordPress, Drupal, and Magento are based on PHP.
At the time of penning down this guide, the latest version of PHP is PHP 8.0. It was released on November 26, 2020. It boasts of new features and optimizations such as union types, named arguments, null safe operator, match expression, JIT, and improvements in error handling and consistency.
This tutorial walks you through the installation of PHP 8.0 on Ubuntu 20.04 / 18.04.
On this page
Step 1: Add the Ondřej Surý PPA Repository
PHP 7.4 is the default PHP version in Ubuntu 20.04 repositories at the time of writing this tutorial. To install the latest version of PHP, we are going to use the Ondrej PPA repositories. This repository contains multiple PHP versions and PHP extensions.
But first, let’s update your Ubuntu system packages and install some dependencies as shown.
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt upgrade $ sudo apt install ca-certificates apt-transport-https software-properties-common
Next, add the Ondrej PPA.
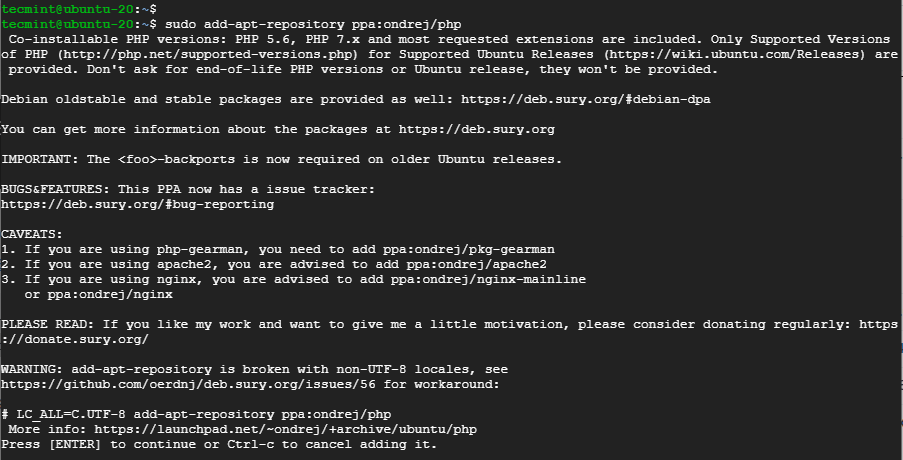
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php
When prompted, press ENTER to proceed with adding the repository.
Step 2: Install PHP 8.0 with Apache on Ubuntu
Next, update the system repositories to start using the PPA.
If you are running the Apache web server, install PHP 8.0 with the Apache module as shown.
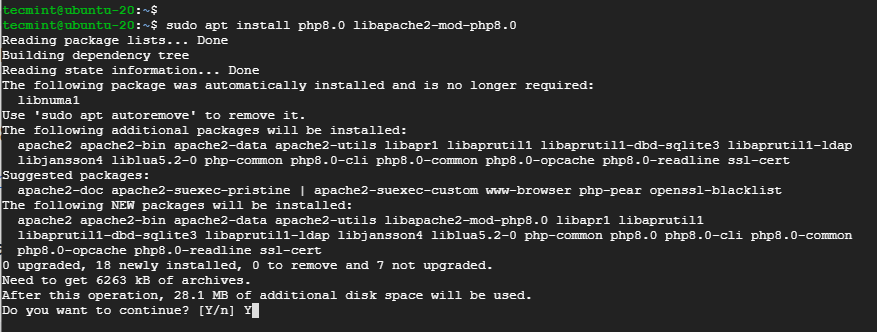
$ sudo apt install php8.0 libapache2-mod-php8.0
Next, restart the Apache webserver to enable the module.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
If you want to use Apache webserver with PHP-FPM, run the command below to install the required packages:
$ sudo apt install php8.0-fpm libapache2-mod-fcgid
Since PHP-FPM is not enabled by default, enable it by invoking the following commands:
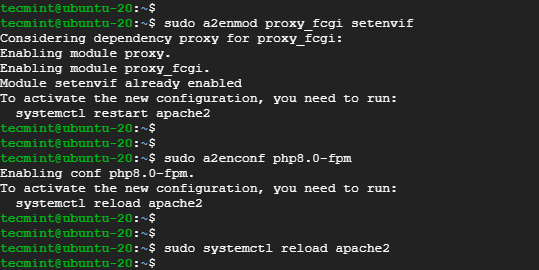
$ sudo a2enmod proxy_fcgi setenvif $ sudo a2enconf php8.0-fpm
Then restart the Apache webserver for the changes to come into effect.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Step 2: Install PHP 8.0 with Nginx on Ubuntu
If you choose to use PHP 8.0 with Nginx installation, the most recommended step to take is to install PHP-FPM to process PHP files.
Therefore, install PHP and PHP-FPM using the following command:
$ sudo apt install php8.0-fpm
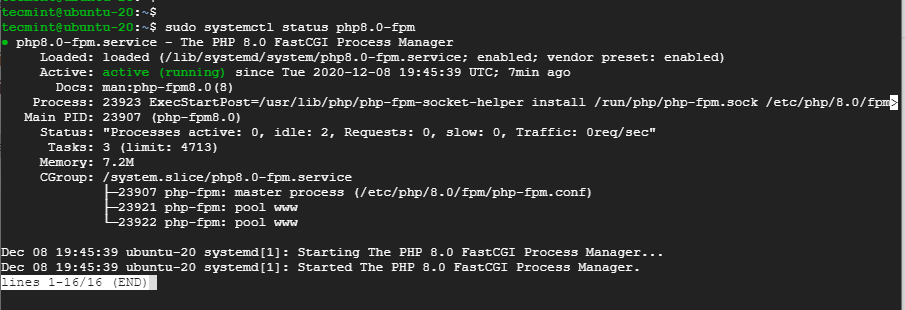
The PHP-FPM service should start automatically. You can verify this as shown:
$ sudo systemctl status php8.0-fpm
For Nginx to process PHP files, configure your Nginx server block by updating the server section as shown:
Finally, restart the Nginx web server for the changes to come into effect.
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Step 4: Install PHP 8 Extensions in Ubuntu
PHP extensions are libraries that extend the functionality of PHP. These extensions exist as packages and can be installed as follows:
$ sudo apt install php8.0-[extension-name]
For instance, the example below installs the SNMP, Memcached, and MySQL extensions.
$ sudo apt install php8.0-snmp php-memcached php8.0-mysql
Step 5: Verify PHP 8 Installation in Ubuntu
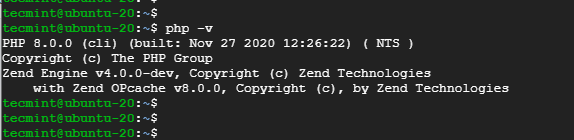
To confirm the version of PHP installed, run the command:
Additionally, you can create a sample php file at /var/www/html as shown:
$ sudo vim /var/www/html/info.php
Paste the following lines and save the file.
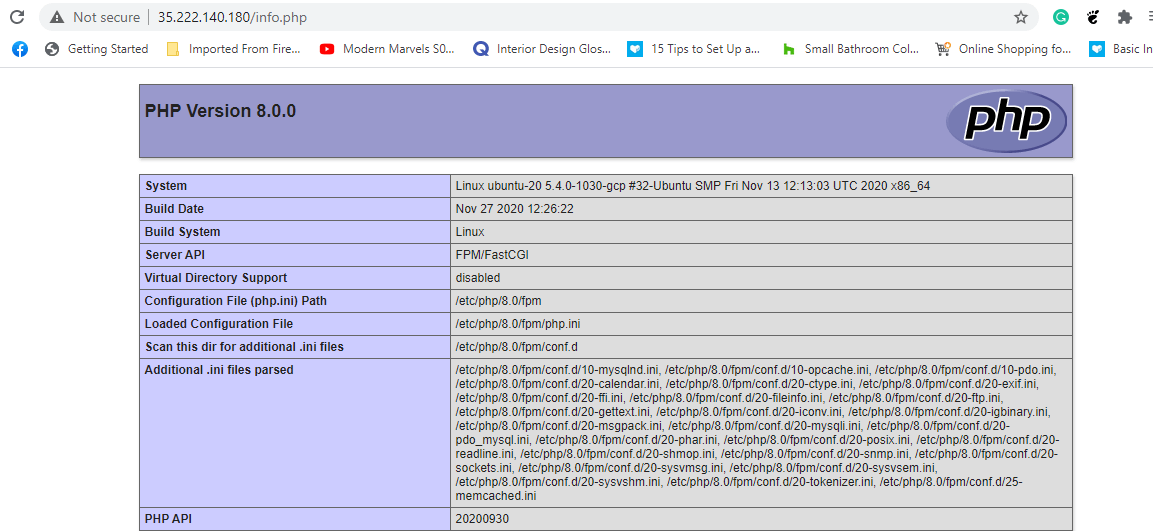
Finally, head over to your browser and browse the server’s IP address as shown.
You should get the webpage shown.
Conclusion
It’s our hope that you can now install PHP 8.0 and comfortably integrate it with either Apache or Nginx web servers. Your feedback is most welcome.
Install php linux apt get
Раздел содержит информацию и подсказки, относящиеся к установке PHP на » Debian GNU/Linux.
Неофициальные сборки от третьих лиц не поддерживаются. О любых ошибках следует сообщать разработчикам Debian, но перед этим стоит проверить, возможно они уже исправлены в новых релизах, которые можно скачать на » странице загрузки.
Хотя и существует универсальная инструкция по установке PHP на Unix/Linux, в этом разделе мы рассмотрим особенности специфичные для Debian, такие как использование команд apt или aptitude . В рамках этого руководства обе эти команды рассматриваются как взаимозаменяемые.
Использование APT
Во первых, обратите внимание на то, что некоторые пакеты связаны: libapache-mod-php нужен для интеграции с Apache 2, и php-pear с PEAR.
Во-вторых, перед установкой убедитесь, что список пакетов находится в актуальном состоянии. Как правило, это делается с помощью команды apt update.
Пример #1 Пример установки Apache 2 на Debian
# apt install php-common libapache2-mod-php php-cli
APT автоматически установит модуль PHP для Apache 2 и все их зависимости и, затем, активирует их. Apache должен быть перезапущен для того, чтобы изменения вступили в силу. Например:
Пример #2 Остановка и запуск Apache после установки PHP
# /etc/init.d/apache2 stop # /etc/init.d/apache2 start
Контроль конфигурации
Изначально, PHP устанавливается только с основными модулями ядра. Если вы хотите установить дополнительные модули, такие как MySQL, cURL, GD и т.д., это также можно сделать с помощью команды apt .
Пример #3 Способы получить список дополнительных пакетов PHP
# apt-cache search php # apt search php | grep -i mysql # aptitude search php
Будет выведен список большого числа пакетов, включая несколько специфичных, таких как php-cgi, php-cli and php-dev. Определите, какие вам нужны и установите с помощью apt-get или aptitude . И, так как Debian производит проверку зависимостей, вам будет выведен запрос на их установку.
Пример #4 Установка PHP с MySQL и cURL
# apt install php-mysql php-curl
APT автоматически добавит необходимые строки в соответствующие php.ini , /etc/php/7.4/php.ini , /etc/php/7.4/conf.d/*.ini , и т.д. В зависимости от модуля, будут внесены записи типа extension=foo.so . В любом случае, чтобы эти изменения вступили в силу, необходимо будет перезапустить сервер веб-сервер.
Стандартные проблемы
- Если скрипты PHP не разбираются веб-сервером, то скорее всего это означает, что PHP не был добавлен в конфигурацию веб-сервера. На Debian это обычно /etc/apache2/apache2.conf или похожий. Смотрите документацию Debian для выяснения подробностей.
- Модуль, по-видимому, установлен, а его функции всё равно не распознаются. В таком случае убедитесь, что соответствующий ini-файл был загружен и/или веб-сервер был перезагружен после установки модуля.
- Для установки пакетов в Debian существуют две основных команды (не считая стандартных вариантов Linux): apt и aptitude . Объяснения их синтаксиса, особенностей и отличий друг от друга выходит за рамки данного руководства.
User Contributed Notes 6 notes
To refresh this document, perhaps it would be worth mentioning more modern methods to serve php content under apache httpd.
Specifically, the preferred method is now fastcgi, using either of those recipes:
While the legacy mod_php approach is still applicable for some older installations, the fastcgi method is much faster, and require much less RAM to operate, based on similar traffic patterns.
Compiling PHP on Ubuntu boxes.
If you would like to compile PHP from source as opposed to relying on package maintainers, here’s a list of packages, and commands you can run
STEP 1:
sudo apt-get install autoconf build-essential curl libtool \
libssl-dev libcurl4-openssl-dev libxml2-dev libreadline7 \
libreadline-dev libzip-dev libzip4 nginx openssl \
pkg-config zlib1g-dev
So you don’t overwrite any existing PHP installs on your system, install PHP in your home directory. Create a directory for the PHP binaries to live
STEP 2:
# download the latest PHP tarball, decompress it, then cd to the new directory.
STEP 3:
Configure PHP. Remove any options you don’t need (like MySQL or Postgres (—with-pdo-pgsql))
./configure —prefix=$HOME/bin/php-latest \
—enable-mysqlnd \
—with-pdo-mysql \
—with-pdo-mysql=mysqlnd \
—with-pdo-pgsql=/usr/bin/pg_config \
—enable-bcmath \
—enable-fpm \
—with-fpm-user=www-data \
—with-fpm-group=www-data \
—enable-mbstring \
—enable-phpdbg \
—enable-shmop \
—enable-sockets \
—enable-sysvmsg \
—enable-sysvsem \
—enable-sysvshm \
—enable-zip \
—with-libzip=/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu \
—with-zlib \
—with-curl \
—with-pear \
—with-openssl \
—enable-pcntl \
—with-readline
STEP 4:
compile the binaries by typing: make
If no errors, install by typing: make install
STEP 5:
Copy the PHP.ini file to the install directory
cp php.ini-development ~/bin/php-latest/lib/
cd ~/bin/php-latest/etc;
mv php-fpm.conf.default php-fpm.conf
mv php-fpm.d/www.conf.default php-fpm.d/www.conf
STEP 7:
create symbolic links for your for your binary files
cd ~/bin
ln -s php-latest/bin/php php
ln -s php-latest/bin/php-cgi php-cgi
ln -s php-latest/bin/php-config php-config
ln -s php-latest/bin/phpize phpize
ln -s php-latest/bin/phar.phar phar
ln -s php-latest/bin/pear pear
ln -s php-latest/bin/phpdbg phpdbg
ln -s php-latest/sbin/php-fpm php-fpm
STEP 8: link your local PHP to the php command. You will need to logout then log back in for php to switch to the local version instead of the installed version
# add this to .bashrc
if [ -d «$HOME/bin» ] ; then
PATH=»$HOME/bin:$PATH»
fi
Установка разных версий PHP на Linux Ubuntu
Обновлено: 03.04.2023 Опубликовано: 06.11.2021
В Ubuntu можно легко управлять несколькими версиями PHP. Мы рассмотрим процесс установки разных версий PHP и жонглирования ими.
Установка PHP
В зависимости от необходимой версии PHP и версии Ubuntu, подход к установке может отличаться.
Установка базовой версии
Это самый простой способ. Каждая версия Ubuntu в своем репозитории содержит соответствующую версию PHP.
Посмотреть, какая версия будет установлена из репозитория системы можно командой:
apt search —names-only ‘^php[.0-9]$’
Установка выполняется одной командой:
Установка определенной версии
Если нам необходима версия PHP, которой нет в репозитории, выполняем установку дополнительного — для этого вводим две команды:
apt install software-properties-common
.
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: ‘gpg’
Устанавливаем gnupg-agent:
Теперь можно установить нужную версию интерпретатора:
Выбор версии PHP по умолчанию
Посмотреть текущую версию php, которая работает по умолчанию можно командой:
Сменить версию по умолчанию:
update-alternatives —config php
There are 2 choices for the alternative php (providing /usr/bin/php).
Selection Path Priority Status
————————————————————
* 0 /usr/bin/php8.0 80 auto mode
1 /usr/bin/php7.4 74 manual mode
2 /usr/bin/php8.0 80 manual mode
* в данном примере используется версия php8 как версия по умолчанию.
Для смены, система предложит нам выбрать версию из списка:
Press to keep the current choice[*], or type selection number: 1
* так мы переключимся на php7.4.
Установка расширений
Расширения устанавливаются с синтаксисом:
Для версии, которая идет по умолчанию в репозитории, установку можно выполнить так:
В остальных случаях обязательно указываем версию:
Настройка PHP
В Ubuntu настройки PHP находятся в разных файлах — для каждой версии и для каждой системы, которая обрабатывает запросы.
Например, для php версии 8.0, которая будет запускаться из командной строки, файл будет: