- How to get setuptools and easy_install?
- 9 Answers 9
- recompile python
- install from GitHub
- Installing pip/setuptools/wheel with Linux Package Managers¶
- Fedora¶
- CentOS/RHEL¶
- openSUSE¶
- Debian/Ubuntu and derivatives¶
- Arch Linux¶
- Table of Contents
- Previous topic
- Next topic
- Navigation
- How to Install setuptools in Python?
- How to Install setuptools on Windows?
- How to Install setuptools on Linux?
- How to Install setuptools on macOS?
- How to Install setuptools in PyCharm?
- How to Install setuptools in a Jupyter Notebook?
- How to Resolve ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘setuptools’?
- Improve Your Python Skills
How to get setuptools and easy_install?
I downloaded the ez_setup code from here: http://peak.telecommunity.com/dist/ez_setup.py and ran it, but i don’t think setuptools was properly installed. When i try to open an egg using easy_install i am getting a NameError. Any thoughts? Here is the specific error:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "C. setup.py", line 223, in easy_install eggsetup.py NameError: name 'easy_install' is not defined 9 Answers 9
For linux versions(ubuntu/linux mint), you can always type this in the command prompt:
sudo apt-get install python-setuptools
This will automatically install easy_install .
After doing this, another install which depends on setuptools still tells me that setuptools isn’t installed!
sudo apt-get install python3-setuptools please try to install the dependencie with pip, run this command:
sudo pip install -U setuptools 2021 update:
- easy_install no longer exists, it was replaced by pip install .
- setuptools is built-in with Python 3. It’s the package to read package files (wheels) and do things under the hood.
- pip is built-in with Python 3.
- venv is built-in with Python 3.
Some operating systems (Debian) like to split packages into smaller independent packages, you may have to sudo apt-get install python3 python3-pip python3-venv to get all the executables. Nonetheless, the tools are usually available even if the command isn’t exposed, try calling python3 -m pip install . .
apt-get install python-setuptools python-pip apt-get install python3-setuptools python3-pip you’d also want to install the python packages.
I’m assuming you’re on Windows (could be wrong) but if you click the green Downloads button, it should take you to a table where you can choose to download a .exe version of setuptools appropriate for your version of Python. All that eggsetup stuff should be taken care of in the executable file.
Let me know if you need more help.
On Ubuntu until python-distribute is something newer than 0.7 I’d recommend:
$ wget https://bitbucket.org/pypa/setuptools/raw/bootstrap/ez_setup.py -O - | sudo python yum install -y python-setuptools If you are installing from distro packages, then this probably doesn’t apply to your scenario.
recompile python
I have multiple versions of Python built from source installed, and I found I didn’t have setuptools for version 3.5. It seems like I was missing the zlib libraries when I compiled 3.5, which subsequently made the setuptools install fail quietly (to me at least). Recompiling with the zlib libs installed fixed this for me.
install from GitHub
If you are for some reason missing setuptools and have Python compiled with all the necessary libs, you should be able to install it from the GitHub repo like this:
git clone https://github.com/pypa/setuptools.git cd ./setuptools python3.5 bootstrap.py sudo python3.5 setup.py install Installing pip/setuptools/wheel with Linux Package Managers¶
This section covers how to install pip , setuptools , and wheel using Linux package managers.
If you’re using a Python that was downloaded from python.org, then this section does not apply. See the Requirements for Installing Packages section instead.
Note that it’s common for the versions of pip , setuptools , and wheel supported by a specific Linux Distribution to be outdated by the time it’s released to the public, and updates generally only occur for security reasons, not for feature updates. For certain Distributions, there are additional repositories that can be enabled to provide newer versions. The repositories we know about are explained below.
Also note that it’s somewhat common for Distributions to apply patches for the sake of security and normalization to their own standards. In some cases, this can lead to bugs or unexpected behaviors that vary from the original unpatched versions. When this is known, we will make note of it below.
Fedora¶
sudo dnf install python3-pip python3-wheel
To learn more about Python in Fedora, please visit the official Fedora docs, Python Classroom or Fedora Loves Python.
CentOS/RHEL¶
CentOS and RHEL don’t offer pip or wheel in their core repositories, although setuptools is installed by default.
To install pip and wheel for the system Python, there are two options:
- Enable the EPEL repository using these instructions. On EPEL 7, you can install pip and wheel like so:
sudo dnf install python3-pip python3-wheel
sudo dnf install python3-pip python3-wheel
sudo dnf upgrade python3-setuptools
To install pip, wheel, and setuptools, in a parallel, non-system environment (using yum) then there are two options:
- Use the “Software Collections” feature to enable a parallel collection that includes pip, setuptools, and wheel.
- For Redhat, see here: https://developers.redhat.com/products/softwarecollections/overview
- For CentOS, see here: https://github.com/sclorg
Be aware that collections may not contain the most recent versions.
sudo yum install python34u python34u-wheel
openSUSE¶
sudo zypper install python3-pip python3-setuptools python3-wheel
Debian/Ubuntu and derivatives¶
Firstly, update and refresh repository lists by running this command:
sudo apt update sudo apt install python3-venv python3-pip
Recent Debian/Ubuntu versions have modified pip to use the “User Scheme” by default, which is a significant behavior change that can be surprising to some users.
Arch Linux¶
Currently, there is no “copr” yum plugin available for CentOS/RHEL, so the only option is to manually place the repo files as described.
Table of Contents
- An Overview of Packaging for Python
- The Packaging Flow
- Tutorials
- Guides
- Installing packages using pip and virtual environments
- Installing stand alone command line tools
- Installing pip/setuptools/wheel with Linux Package Managers
- Installing scientific packages
- Package index mirrors and caches
- Hosting your own simple repository
- Packaging and distributing projects
- Including files in source distributions with MANIFEST.in
- Single-sourcing the package version
- Dropping support for older Python versions
- Packaging binary extensions
- Packaging namespace packages
- Creating and discovering plugins
- Using TestPyPI
- Making a PyPI-friendly README
- Publishing package distribution releases using GitHub Actions CI/CD workflows
- Tool recommendations
- Analyzing PyPI package downloads
Previous topic
Next topic
Navigation
© Copyright 2013–2020, PyPA.
This page is licensed under the Python Software Foundation License Version 2.
Examples, recipes, and other code in the documentation are additionally licensed under the Zero Clause BSD License.The Python Software Foundation is a non-profit corporation. Please donate.
Last updated on Jun 16, 2023. Found a bug?
Created using Sphinx 4.5.0.How to Install setuptools in Python?
The Python setuptools library is among the top 100 Python libraries, with more than 103,209,780 downloads. This article will show you everything you need to get this installed in your Python environment.
How to Install setuptools on Windows?
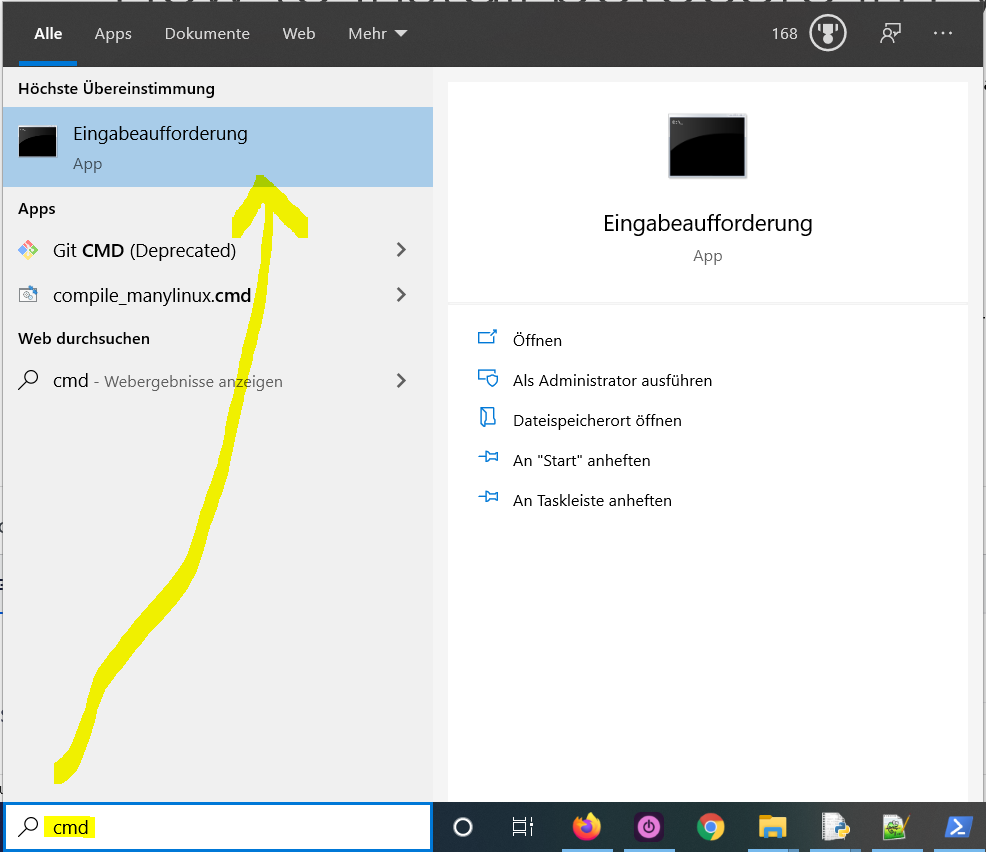
- Type «cmd» in the search bar and hit Enter to open the command line.
- Type “ pip install setuptools ” (without quotes) in the command line and hit Enter again. This installs setuptools for your default Python installation.
- The previous command may not work if you have both Python versions 2 and 3 on your computer. In this case, try «pip3 install setuptools» or “ python -m pip install setuptools “.
- Wait for the installation to terminate successfully. It is now installed on your Windows machine.
Here’s how to open the command line on a (German) Windows machine:
First, try the following command to install setuptools on your system:
Second, if this leads to an error message, try this command to install setuptools on your system:
Third, if both do not work, use the following long-form command:
python -m pip install setuptools
The difference between pip and pip3 is that pip3 is an updated version of pip for Python version 3. Depending on what’s first in the PATH variable, pip will refer to your Python 2 or Python 3 installation—and you cannot know which without checking the environment variables. To resolve this uncertainty, you can use pip3 , which will always refer to your default Python 3 installation.
How to Install setuptools on Linux?
You can install setuptools on Linux in four steps:
- Open your Linux terminal or shell
- Type “ pip install setuptools ” (without quotes), hit Enter.
- If it doesn’t work, try «pip3 install setuptools» or “ python -m pip install setuptools “.
- Wait for the installation to terminate successfully.
The package is now installed on your Linux operating system.
How to Install setuptools on macOS?
Similarly, you can install setuptools on macOS in four steps:
- Open your macOS terminal.
- Type “ pip install setuptools ” without quotes and hit Enter .
- If it doesn’t work, try «pip3 install setuptools» or “ python -m pip install setuptools “.
- Wait for the installation to terminate successfully.
The package is now installed on your macOS.
How to Install setuptools in PyCharm?
Given a PyCharm project. How to install the setuptools library in your project within a virtual environment or globally? Here’s a solution that always works:
- Open File > Settings > Project from the PyCharm menu.
- Select your current project.
- Click the Python Interpreter tab within your project tab.
- Click the small + symbol to add a new library to the project.
- Now type in the library to be installed, in your example «setuptools» without quotes, and click Install Package .
- Wait for the installation to terminate and close all pop-ups.
Here’s the general package installation process as a short animated video—it works analogously for setuptools if you type in “setuptools” in the search field instead:
Make sure to select only “setuptools” because there may be other packages that are not required but also contain the same term (false positives):
How to Install setuptools in a Jupyter Notebook?
To install any package in a Jupyter notebook, you can prefix the !pip install my_package statement with the exclamation mark «!» . This works for the setuptools library too:
This automatically installs the setuptools library when the cell is first executed.
How to Resolve ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘setuptools’?
Say you try to import the setuptools package into your Python script without installing it first:
import setuptools # . ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'setuptools'
Because you haven’t installed the package, Python raises a ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘setuptools’ .
To fix the error, install the setuptools library using “ pip install setuptools ” or “ pip3 install setuptools ” in your operating system’s shell or terminal first.
See above for the different ways to install setuptools in your environment.
Improve Your Python Skills
If you want to keep improving your Python skills and learn about new and exciting technologies such as Blockchain development, machine learning, and data science, check out the Finxter free email academy with cheat sheets, regular tutorials, and programming puzzles.
While working as a researcher in distributed systems, Dr. Christian Mayer found his love for teaching computer science students.
To help students reach higher levels of Python success, he founded the programming education website Finxter.com that has taught exponential skills to millions of coders worldwide. He’s the author of the best-selling programming books Python One-Liners (NoStarch 2020), The Art of Clean Code (NoStarch 2022), and The Book of Dash (NoStarch 2022). Chris also coauthored the Coffee Break Python series of self-published books. He’s a computer science enthusiast, freelancer, and owner of one of the top 10 largest Python blogs worldwide.
His passions are writing, reading, and coding. But his greatest passion is to serve aspiring coders through Finxter and help them to boost their skills. You can join his free email academy here.
Be on the Right Side of Change 🚀
- The world is changing exponentially. Disruptive technologies such as AI, crypto, and automation eliminate entire industries. 🤖
- Do you feel uncertain and afraid of being replaced by machines, leaving you without money, purpose, or value? Fear not! There a way to not merely survive but thrive in this new world!
- Finxter is here to help you stay ahead of the curve, so you can keep winning as paradigms shift.
Learning Resources 🧑💻
⭐ Boost your skills. Join our free email academy with daily emails teaching exponential with 1000+ tutorials on AI, data science, Python, freelancing, and Blockchain development!
Join the Finxter Academy and unlock access to premium courses 👑 to certify your skills in exponential technologies and programming.
New Finxter Tutorials:
Finxter Categories: