- Jswizzy / InstallingSwift.md
- 3. Extract the downloaded «tar» file
- 4. Move the extracted files
- Footer
- How to Use Swift Programming Language on Ubuntu
- Installing Swift on Ubuntu Linux
- Step 1: Install the dependencies
- Step 2: Download the files
- Step 3: Verify the Files
- Step 4: Extract the files
- Step 5: Set up environment variables
- Step 6: Verify the installation
- Writing programs in Swift on Linux
- Method 1. Using REPL
- Method 2. Creating a Swift package
- Building a sample Swift project automatically
- Building a sample Swift project manually
- Next Step
Jswizzy / InstallingSwift.md
“clang”[ˈklæŋ] is the compiler based on LLVM for C, C++, Objective-C, and Objective-C++. clang is needed to install in order to Swift. Run the following code in Ubuntu terminal.
Before installing swift “libpython2.7” and “libpython2.7-dev” are needed to get Swift running. Run the following code.
sudo apt install clang libpython2.7 libpython2.7-dev
2. Download Swift tar for Ubunutu 20.04
There is a source code in Swift documentation page. Swift.org — Download Swift
By using “wget” command, download the Swift tar file for Ubuntu20.04 from the above page. (Noted swift-5.3 is the newest version when this article is published.) Before running the below code, change to the directory which you want to download by using “cd” command. And then, run the following code.
wget https://swift.org/builds/swift-5.3-release/ubuntu2004/swift-5.3-RELEASE/swift-5.3-RELEASE-ubuntu20.04.tar.gz
3. Extract the downloaded «tar» file
By using “tar” command, expand the downloaded archive file.
x = extract/unzip z= gunzip format f= file
tar xzf swift-5.3-RELEASE-ubuntu20.04.tar.gz
4. Move the extracted files
Move the extracted file to the user’s “share” directory. A good place to put applications.
sudo mv swift-5.3-RELEASE-ubuntu20.04 /usr/share/swift
5. Add to system PATH enviroment variable
Set the Swift path on the system’s PATH environment variable.
note: If using bash change ~/.zshrc to ~/.bashrc
echo "export PATH=/usr/share/swift/usr/bin:$PATH" >> ~/.zshrc source ~/.zshrc
6. Check Install successful
if successful
Swift version 5.3 (swift-5.3-RELEASE) Target: x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu
run the REPL
if successful the swift REPL will run
to quit the REPL, run the «:exit» command
Thanks for the tutorial, I noticed some mistakes that can be correct this way :
3. Extract the downloaded «tar» file
.tar.gz at the end is missing and the name is ubunutu and not ubuntu
tar xzf swift-5.3-RELEASE-ubuntu20.04.tar.gz
4. Move the extracted files
a / is missing between share and swift and the name is again ubunutu
sudo mv swift-5.3-RELEASE-ubuntu20.04 /usr/share/swift
I created a Brazilian Portuguese version here. Also updated it for Ubuntu 22.04 LTS and Swift 5.7.1. Hope you don’t mind (credit at the very end).
https://gist.github.com/rafaelclaycon/276e3b70e3f265851a5ec695e0933e50
I would probably do sudo mv swift-5.3-RELEASE-ubuntu20.04 /usr/local/swift since most of the time, other packages would install the executables in /usr/local/ while putting related documentation, metadata and images into /usr/share .
Also echo «export PATH=/usr/local/swift/usr/bin:\$PATH» >> ~/.zshrc . Put an \ before the second PATH so it’s not expended when running this command.
I wish there was a way this would appear as a top search. Good stuff!
Easy to follow, thanks!
This guide worked great for me to install current Swift 5.7.3 to an Ubuntu 20.04.5 virtual machine using UTM on M2 MacBook Pro. I used the suggestions by @DeboBurro and the bash setup since I haven’t switched to zsh yet on the VM. I also needed to use swift repl to enter the REPL at the end to test. Here’s what my commands looked like:
sudo apt install clang libpython2.7 libpython2.7-dev wget https://download.swift.org/swift-5.7.3-release/ubuntu2004-aarch64/swift-5.7.3-RELEASE/swift-5.7.3-RELEASE-ubuntu20.04-aarch64.tar.gz tar xzf swift-5.7.3-RELEASE-ubuntu20.04-aarch64.tar.gz sudo mv swift-5.7.3-RELEASE-ubuntu20.04-aarch64 /usr/local/swift echo "export PATH=/usr/local/swift/usr/bin:\$PATH" >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc swift -v swift repl :exit
sudo apt install clang libpython2.7 libpython2.7-dev wget https://swift.org/builds/swift-5.8-release/ubuntu2004/swift-5.8-RELEASE/swift-5.8-RELEASE-ubuntu20.04.tar.gz tar xzf swift-5.8-RELEASE-ubuntu20.04.tar.gz sudo mv swift-5.8-RELEASE-ubuntu20.04 /usr/share/swift echo "export PATH=/usr/share/swift/usr/bin:$PATH" >> ~/.zshrc source ~/.zshrc Check if it worked with swift —version
Footer
You can’t perform that action at this time.
How to Use Swift Programming Language on Ubuntu
The open source programming language Swift by Apple is available on Linux. Learn how to install Swift on Ubuntu and run your first Swift program.
Installing Swift on Ubuntu Linux
To install Swift, you need to install a handful of dependencies first. The process may seem a bit complicated and requires that you are familiar with the basic Linux commands. An official Snap package would have made things a lot easier.
I am using Ubuntu 22.04 for this tutorial, but the steps for 20.04 and even 18.04 are similar, except for the package files.
Step 1: Install the dependencies
You’ll have to install a few dependencies to make Swift work in Linux. For Ubuntu 22.04, use the command below to install them. The download size is around 260 MB.
sudo apt-get install binutils \ git \ gnupg2 \ libc6-dev \ libcurl4-openssl-dev \ libedit2 \ libgcc-9-dev \ libpython3.8 \ libsqlite3-0 \ libstdc++-9-dev \ libxml2-dev \ libz3-dev \ pkg-config \ tzdata \ unzip \ zlib1g-devThe backslash \ at the end of the line escapes the new line character. Thus it allows displaying a long Linux command over a span of multiple lines so you can see them all at one glance.
For Ubuntu 20.04 and 18.04, use the following command to install the dependencies.
sudo apt-get install \ binutils \ git \ gnupg2 \ libc6-dev \ libcurl4 \ libedit2 \ libgcc-9-dev \ libpython2.7 \ libsqlite3-0 \ libstdc++-9-dev \ libxml2 \ libz3-dev \ pkg-config \ tzdata \ uuid-dev \ zlib1g-devStep 2: Download the files
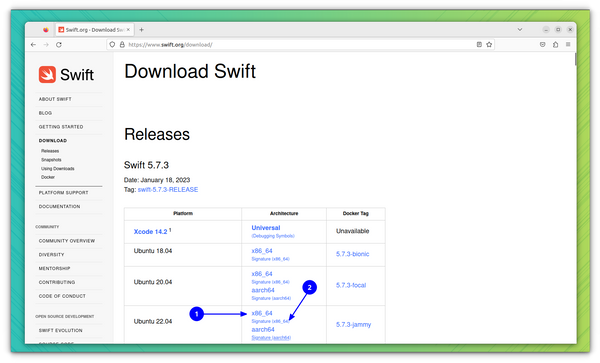
Apple has provided snapshots for various Ubuntu LTS releases, CentOS7, etc. You can download the files from the link below.
Files are around 500 MB in size. You need to download both the Swift release file and the signature file (for verification), as shown in the screenshot below.
Step 3: Verify the Files
If you are downloading Swift packages for the first time, import the PGP keys into your keyring. You can skip this step if you have already imported the keys in the past.
Go to the directory where you have downloaded the tar file and signature file; in my case, the ~/Downloads directory:
Now follow the below commands to verify your installation file.
wget -q -O - https://swift.org/keys/all-keys.asc | gpg --import -First, refresh the keys to download new key revocation certificates, if any are available:
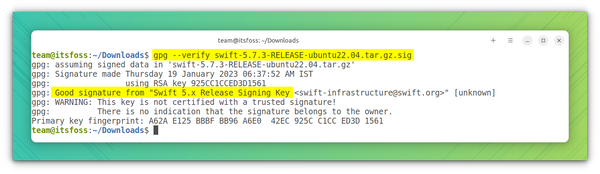
gpg --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com --refresh-keys SwiftThen, use the signature file to verify that the archive is intact:
This will give you a «Good Signature» and you can proceed to installation securely.
You can get the details of various signing keys from their official downloads page.
Step 4: Extract the files
Once you verify the integrity of your installation files, extract them to start the installation:
This will create a directory with a similar name to the archive in your ~/Downloads directory.
Step 5: Set up environment variables
Once you have extracted the files, it is time to set up the path to binaries so that you could execute the programs.
There is a usr/bin directory in your extracted directory. You need to add this path to the PATH environment variable.
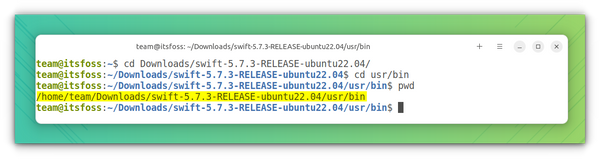
For this, you would need the absolute path to the extracted directory. Considering that you have followed the exact steps I mentioned, your extracted files would be in /home//Downloads location.
Just for the sake of beginners, I advise you to do this:
cd ~/Downloads/ cd usr/bin pwdThe result of pwd will give you the exact location that we will be using.
So, when you have the path to the bin directory, add them to the PATH variable like this. Do change the value of path_to_swift_usr_bin in the command below.
export PATH=path_to_swift_usr_bin:$PATHThis is for one shell instance and if you want it permanently, add it to your ~/.bashrc file with the following command:
echo 'export PATH=path_to_swift_usr_bin:$PATH' >> ~/.bashrcNow, restart your terminal session.
If you have Linux command line experience, you will find these instructions tedious, but it might help someone who is a noob to the command line in Linux.
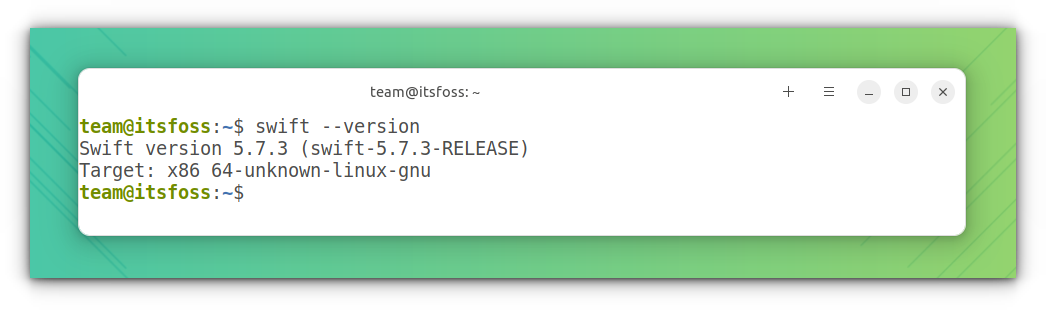
Step 6: Verify the installation
Use the command below to see if Swift is installed:
The result should be something like this:
Writing programs in Swift on Linux
Once you have everything ready, it’s time to write a simple program.
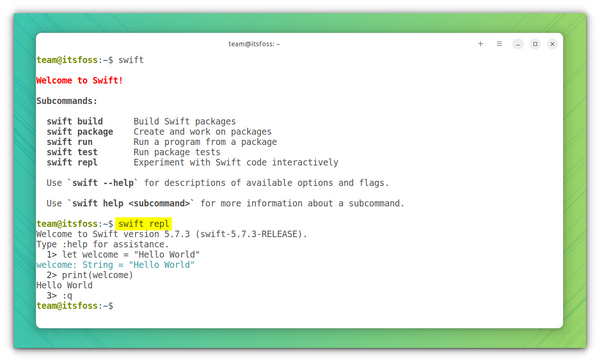
Method 1. Using REPL
Swift has its own interactive shell, REPL, where you can run a few commands. This is good if someone wants to verify Swift code quickly.
If you just run swift , it will output a small help section with some subcommands and their functions. Run swift repl to access the REPL and you can definitely print your “Hello World” here. Take a look at this screenshot for example:
You’ll have to use :q to get out of the shell.
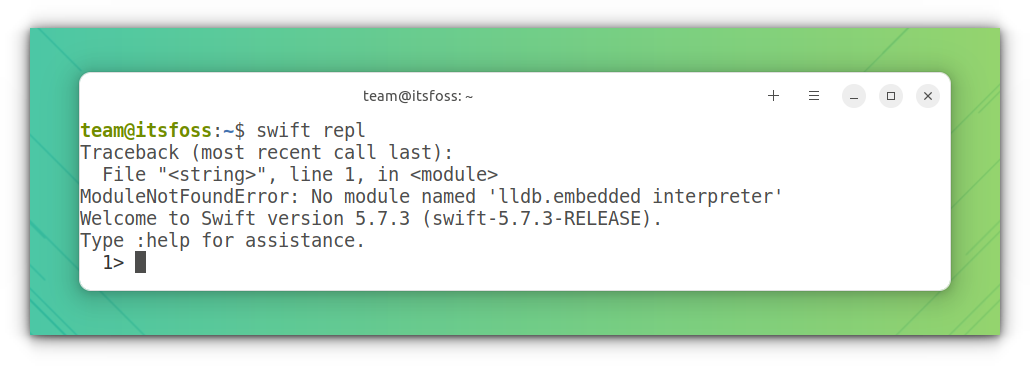
Troubleshoot: Module Not Found Error in Ubuntu 22.04
Sometimes, running swift repl will output a REPL with a ModuleNotFoundError.
In this particular case, open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo apt install python3-lldb-14 ln -s /usr/lib/llvm-14/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/lldb/* /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/lldb/This eliminated the error in the next run.
Anyway, this REPL shell is not enough to build applications. That’s a different procedure.
Method 2. Creating a Swift package
For all practical purposes, direct coding from REPL is not enough. We need to create executable packages. There is a couple of methods to do this from a beginner’s perspective.
- Building a sample Swift project automatically
- Building a sample Swift project manually
Building a sample Swift project automatically
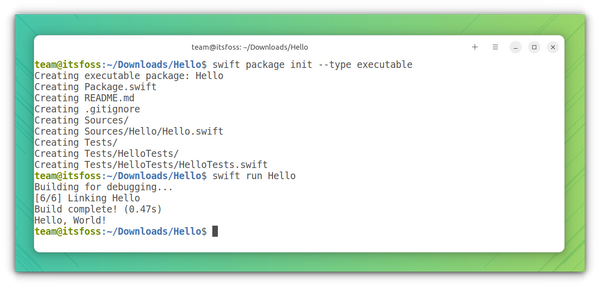
You can create a project simply by using the swift init commands. For this, first, create a directory for your project and enter inside that directory:
Inside this directory, run the below command:
swift package init --type executableThis will create an executable package, with all the required files. Now, you can run this by:
Or, first, compile it and run the executable file using the below commands one by one:
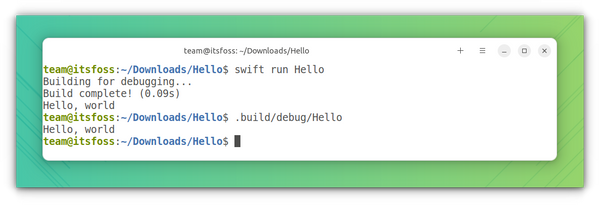
swift build .build/debug/HelloThis will create everything for you. If you want to actually know the inner working, refer to the next section, how to do this manually.
Building a sample Swift project manually
This part will show you how to make a Swift project that prints Hello World. In the directory of your choice, create a Hello directory and switch to it:
We have just created a Swift package named Hello. But it is not complete yet as there each package must have Package.swift file. Create this file using this command:
You need to have a Sources directory with a main.swift file in it.
mkdir Sources touch Sources/main.swiftNow, edit the Package.swift file using your favorite editor and add the below lines.
// swift-tools-version:5.7.3 import PackageDescription let package = Package( name: "Hello", dependencies: [], targets: [ .executableTarget( name: "Hello", dependencies: [], path: "Sources") ] )I am using Swift version 5.7.3, and all versions above 5.4, including 5.4 should use executableTarget() and versions below 5.4 should use target() .
Now, edit this main.swift file. You can use a graphical text editor or do it in the command line. All you need to put the following line in the file:
Now use the below command to compile it:
This will give you the executable program in .build/debug/Hello. You can either run swift run Hello directly without the above build command or run .build/debug/Hello to get the output printed on the terminal.
Next Step
Well, as I had said in the beginning, this tutorial is not going to teach you Swift programming. This is more of getting started with Swift in Linux with configuration and settings.
Unlike Xcode, you don’t get to use Playground to create iOS apps easily. There is no decent IDE for Swift in Linux yet.
Since you have just made your first program on Swift in Linux, I advise you to follow other tutorials and documentation on the official Swift website.