- How to Install Python Tkinter on Linux
- Prerequisites
- Install Tkinter in Linux
- Verify the Tkinter installation
- Running an Example with Tkinter
- How to install tkinter for python 3.8?
- 5 Answers 5
- What is Tkinter and How to Install it (Windows, macOS, Linux)
- What is Tkinter and Why Do You Need it?
- Installing Tkinter on Windows
- Installing Tkinter on macOS
- Installing Tkinter on Linux
- Overview of the Widgets Used to Create GUIs
- Conclusion
How to Install Python Tkinter on Linux
Tkinter is a Python library that is used to create graphical user interfaces (GUIs). It is a standard Python interface to the Tk GUI toolkit, which is widely used in the Linux operating system. In this tutorial, we will learn how to install Tkinter on a Linux system using either pip or apt-get.
Prerequisites
To install Python’s Tkinter module on a Linux system, you will need to have the following prerequisites installed:
- Python: Tkinter is a module for Python, so you will need to have Python installed on your system. Most Linux distributions come with Python pre-installed, but if you don’t have it installed you can use your distribution’s package manager to install it.
- Tcl/Tk: Tkinter is built on top of the Tcl/Tk libraries, so you will need to have these libraries installed in order to use Tkinter. Most Linux distributions come with Tcl/Tk pre-installed, but if you don’t have them installed you can use your distribution’s package manager to install them.
- A development environment: In order to install Tkinter, you will need to have a development environment set up on your system. This typically includes a compiler (such as GCC) and the make utility. If you don’t have these tools installed, you can use your distribution package manager to install them.
Install Tkinter in Linux
Python Tkinter library packages are available under the default package repositories. You can install it using the system’s package manager to install the Python Tkinter module based on the operating system.
- On Debian-based Linux (Ubuntu, Debian, Pop!_OS):
sudo apt-get install python3-tk sudo yum install -y tkinter tk-devel sudo dnf install python3-tkinter This will install the Tkinter module on your system.
Verify the Tkinter installation
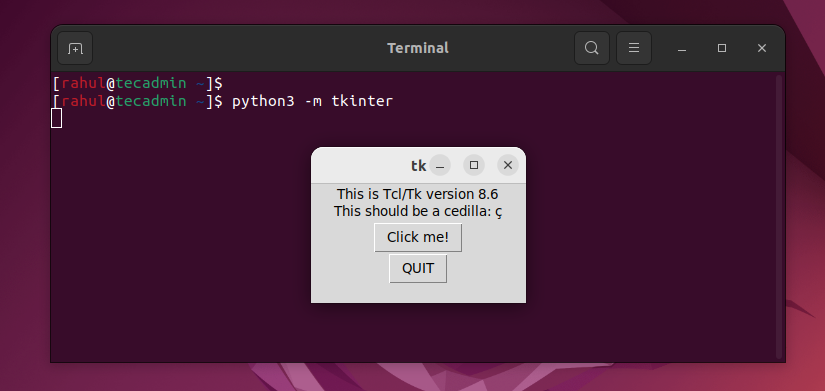
Once the Python Tkinter module is successfully installed on your system. The following command will show you the Tkinter versions.
The below screenshot shows that Python Tkinter 8.6 is installed.
Running an Example with Tkinter
Let’s make a sample Python program using the Tkinter module. Create a file `example.py` file with the following content.
How to install tkinter for python 3.8?
I have Python 3.8 on Ubuntu 16.04. I installed python3-tk (it is required for showing plots in matplotlib):
Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. Done python3-tk is already the newest version (3.5.1-1). 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 12 not upgraded. Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. Done python3.8-tk is already the newest version (3.8.2-1+xenial1). 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 12 not upgraded. $ python3.8 -m tkinter Traceback (most recent call last): File "/usr/local/lib/python3.8/runpy.py", line 184, in _run_module_as_main mod_name, mod_spec, code = _get_module_details(mod_name, _Error) File "/usr/local/lib/python3.8/runpy.py", line 143, in _get_module_details return _get_module_details(pkg_main_name, error) File "/usr/local/lib/python3.8/runpy.py", line 110, in _get_module_details __import__(pkg_name) File "/usr/local/lib/python3.8/tkinter/__init__.py", line 36, in import _tkinter # If this fails your Python may not be configured for Tk ModuleNotFoundError: No module named '_tkinter' 5 Answers 5
If you installed python3.8 using apt (via ppa:deadsnakes/ppa), it can be installed using apt too, the name of library is python3.8-tk .
sudo apt install python3.8-tk In my case, it solves the problem. For instance, now I can use matplotlib in python3.8 which requires tkinter.
Recompile and reinstall python3.8 specifying path to folders with tcl, tk includes and libraries.
sudo apt install build-essential zlib1g-dev libncurses5-dev libgdbm-dev libnss3-dev libssl-dev libreadline-dev libffi-dev python-tk python3-tk tk-dev cd ~/Downloads wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.8.2/Python-3.8.2.tgz tar -xvf Python-3.8.2.tgz cd Python-3.8.2 Edit ./configure file the next way: replace . for next lines:
--with-tcltk-includes='-I/usr/include' --with-tcltk-libs='-L/usr/lib' ./configure make -j2 # replace 2 by number of processor cores you have sudo make install $ python3.8 Python 3.8.2 (default, May 11 2020, 14:30:03) [GCC 5.4.0 20160609] on linux Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> import tkinter >>> Python 3.8 installed through apt and pyenv on 16.04 does not include tkinter, as I think or there’s a some bug that does not allow to import it. Only rebuilding helped. Previously I’ve used 20.04 with built in Python 3.8 version, which supports tkinter with only additional packages installing as it is for Python 3.5 on 16.04.
python3.8-tk installation as Ankur A Sharma said is also required. I’ve forget to mention it. But it is not sufficient for 16.04, at least in my case.
Additional requirement from OP’s comment:
sudo ./configure --with-tcltk-includes='-I/usr/include -I/usr/include/tcl' --with-tcltk-libs='-L/usr/lib -ltcl -ltk' --enable-optimizations What is Tkinter and How to Install it (Windows, macOS, Linux)
Python has a wide array of frameworks that are used for building GUI (Graphical User Interface) applications. However, the only framework that is included in the Python standard library is Tkinter .
So, since Tkinter is already part of the standard Python library, it typically comes included with installations of Python. However, if you’re yet to install Python or your version of Python doesn’t include Tkinter, don’t worry!
In this guide, we’ll go over how to install Tkinter on Windows, macOS, Linux , and also the visual elements that are included in Tkinter.
So, let’s jump right into it!
Table of Contents
What is Tkinter and Why Do You Need it?
Tkinter is the de-facto Python framework for building GUI applications, and with good reason.
Tkinter is widely used due to the fact that it’s cross-platform , has a native look and feel , and provides a lot of customizability . Additionally, Tkinter has also been praised for being easily understandable thanks to its smaller library size .
While having many advantages, Tkinter also has disadvantages . So, Tkinter has been said to have a UI that isn’t always reliable and it also doesn’t include advanced widgets . However, many people would argue that the advantages outweigh the disadvantages.
Overall, Tkinter is useful for many different people and needs, including those who want to get a working and native-feeling application that runs on multiple operating systems quickly and efficiently.
Now, that we have a basic understanding of what it is, let’s jump right into the steps to install it!
Installing Tkinter on Windows
If you would like to install Tkinter on a Windows machine:
- First, verify if python is installed on your system by opening the Command Prompt and entering python –version .
If python is installed on your system, the version will be displayed. Else, if you don’t have python installed, you can install it from here.
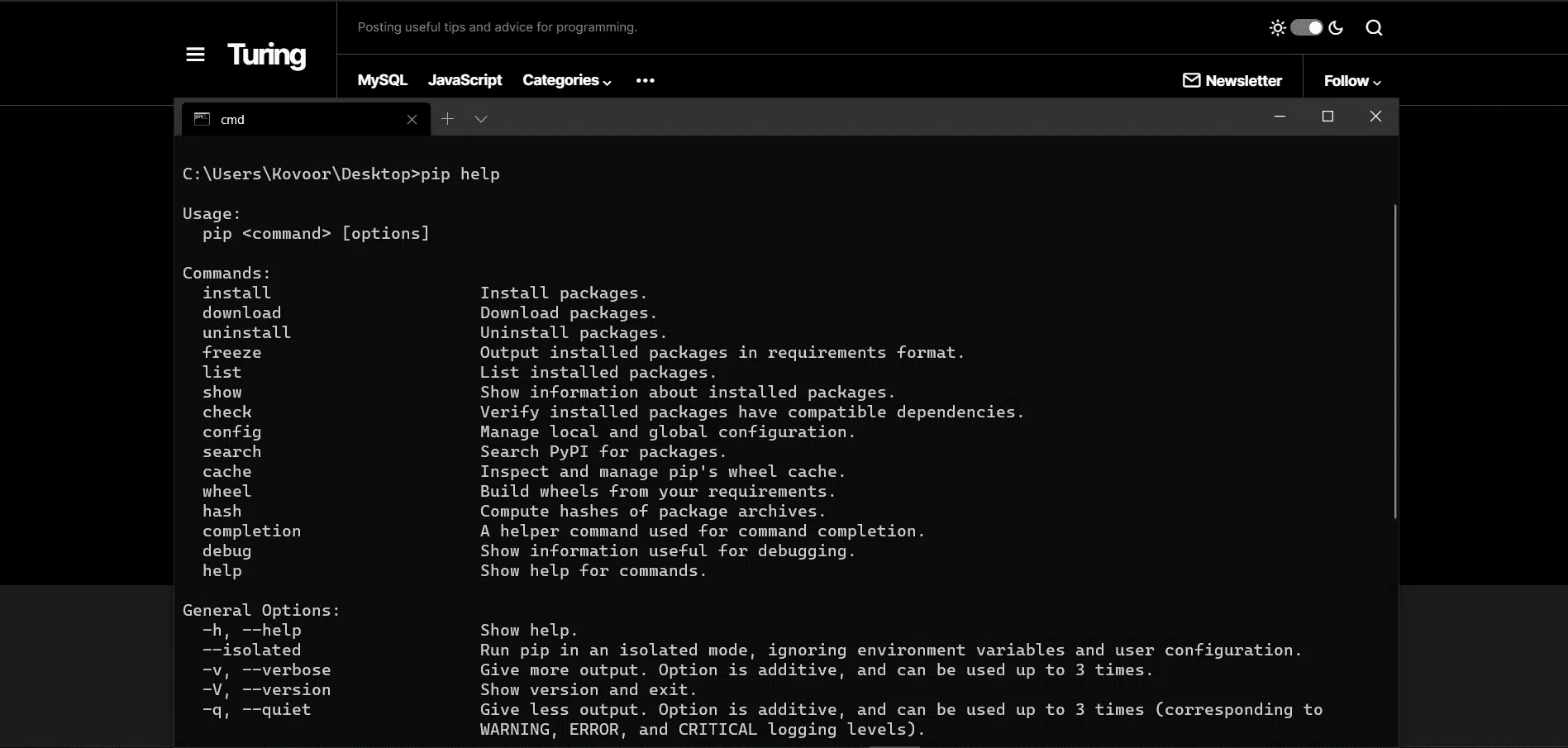
- Next, verify if pip is installed on your system as we will be using pip to install Tkinter. So, enter pip help in the command line.
Again, if pip is installed, the version will be displayed. Else if you don’t have pip installed, you can learn how to install it here .
- Third, install Tkinter by entering pip install tk in the command line. Once Tkinter has been installed, you will receive a confirmation message that looks like the following:
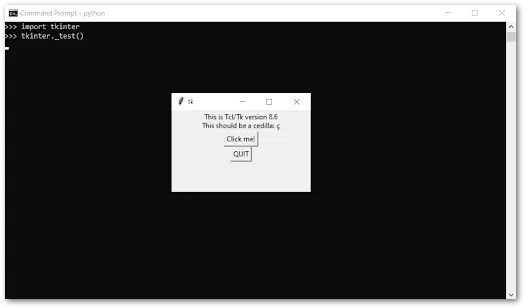
- Lastly, enter import tk in the Python Terminal once Tkinter has been installed to verify if it works. There should be no error message shown once imported. You can also enter tkinter._test() after importing, and a small GUI window should appear that looks like this.
Installing Tkinter on macOS
If you would like to install Tkinter on a macOS machine:
- First, verify if python is installed on your system by opening the Terminal and entering python3 –version .
If python is installed on your system, the version will be displayed. Else, if you don’t have python installed, you can install it from here.
- Second, verify if pip is installed on your system as we will be using pip to install Tkinter. So, enter pip3 –version or pip help in the Terminal.
If pip is installed, the version will be displayed. Else, if you don’t have pip installed, learn how to do it here .
- Third, install Tkinter by entering pip install tk in the Terminal. You will receive a confirmation message that looks similar to the one listed in the Windows section once Tkinter has been installed.
- Lastly, enter import tk in the Python Terminal once Tkinter has been installed to verify if it works. There should be no error message shown once imported.
Installing Tkinter on Linux
- First, verify if python is installed on your system by opening the Linux Terminal and entering python3 –version .
If python is installed on your system, the version will be displayed. Else, if you don’t have python installed, you can install it from here.
- Second, assuming you are using a Debian-based distribution of Linux, install Tkinter by entering sudo apt-get install python-tk in the Linux Terminal.
sudo apt-get install python-tk
- Then, enter your password if prompted and enter “y” to confirm the installation.
- Lastly, enter import tk in the Python Terminal once Tkinter has been installed to verify if it works. There should be no error message shown once imported.
Overview of the Widgets Used to Create GUIs
Widgets are basic elements and they are essential to the creation of GUIs using Tkinter. Without widgets, users wouldn’t be able to interact with and use an application properly.
Therefore, below are a few examples of common widgets used in the Tkinter library:
- Label
-
- A label is a one-line widget used to display text or an image on the screen.
- Frame
-
- A frame is a container widget used to group and organize widgets.
- Button
-
- A button is a widget that may contain text and when clicked, performs an action.
- Entry
-
- An entry is a one-line text field that is used to get input from the user.
- Text
-
- A text is a widget that allows users to input multi-line text.
- Canvas
-
- A canvas widget is used to draw in your GUI. You can create shapes, graphs, and more.
- Checkbutton
-
- A checkbutton widget is a button that is used to execute an on/off choice. A checkbutton is commonly used for customization purposes where users can choose whether they want to turn a setting on or off.
Conclusion
Learning how to develop a GUI application can be a very beneficial skill to add to your skillset.
There are many reasons why someone may want to develop a GUI application. These range from wanting to add on to their programming skills to develop a user-friendly version of their project that previously ran on the command line. The latter can be very helpful when it comes to getting a non-computer savvy person to use an application as navigating through a GUI is far easier than the command line.
That being said, in this article, we looked at how to install Tkinter on Windows , macOS , and Linux machines and verifying that it works. Additionally, we looked at the basic building blocks of GUIs on Tkinter, called widgets .
Having said that, we hope you’ve found this guide helpful when it comes to installing Tkinter and understanding the basics of widgets.
Feel free to share this post with your fellow coders to guide them through installing Tkinter!