- Утилиты Traceroute и Tracert
- Как работают Tracert и Traceroute
- Как использовать Traceroute и Tracert
- How to Install and run Traceroute on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
- Tutorial Install and run Traceroute on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
- Description of the traceroute tool
- Install Traceroute on Ubuntu 20.04 | Ubuntu 18.04
- How to Run Traceroute on Ubuntu 20.04
- Conclusion
- How to Install and Run Traceroute on Ubuntu 22.04?
- How to Install Traceroute on Ubuntu 22.04?
- How to Run Traceroute on Ubuntu 22.04?
- How Does Traceroute Command Work?
- How to Use Traceroute Command?
- How to Uninstall Traceroute on Ubuntu 22.04?
- Bonus Tip: How to Install Traceroute on Other Linux Distributions?
- Conclusion
Утилиты Traceroute и Tracert
Traceroute — это утилита, которая позволяет проследить маршрут следования данных до удалённого адресата в сетях TCP/IP. В Linux используется команда Traceroute, а в Windows — Tracert. При помощи этих команд можно увидеть путь пакета данных от вашего компьютера до целевого сервера или сайта.
Как работают Tracert и Traceroute
Когда вы пытаетесь открыть сайт, браузер отправляет сообщение (запрос) серверу, на котором этот сайт находится. Сообщение на своём пути проходит через маршрутизаторы. Они решают, куда дальше передать сообщение, чтобы гарантированно его доставить адресату. В трассировке маршрутизаторы ещё называют хопами (хоп — прыжок) или узлами. Количество узлов, через которые на своём пути пройдёт запрос, можно узнать при помощи утилит Tracert и Traceroute. Узлы, которые не являются целевыми для запроса, называют транзитными.
Утилита Traceroute формирует UDP-датаграмму (сообщение, которое нужно доставить целевому серверу), упаковывает её в IP-пакет и передаёт первому транзитному узлу. В заголовке такого IP-пакета есть поле TTL (Time To Live) — время жизни пакета. Оно определяет количество хопов, через которые пакет может пройти. На каждом узле TTL уменьшается на единицу. Если на пути к удалённому адресату время жизни пакета станет равно 0, маршрутизатор отбросит пакет и отправит источнику ICMP-сообщение об ошибке «Time Exceeded» (время истекло).
Этот принцип лежит в основе работы утилит Tracert и Traceroute, однако между ними есть отличия. Рассмотрим каждую утилиту отдельно.
Tracert отправляет на хост назначения ICPM-запрос «Echo Request» с TTL=1. Первый маршрутизатор, который получит запрос, проверяет, кому он предназначен. Если маршрутизатор не является целевым хостом, он уменьшает TTL на 1, отбрасывает пакет и отправляет ICMP-сообщение источнику, так как время жизни теперь равно 0. В этом сообщении маршрутизатор указывает информацию о себе и причину дропа пакета. Получив сообщение, Tracert запоминает этот маршрутизатор как первый хоп (прыжок) и отправляет следующий пакет, но уже с TTL=2. Первый хоп успешно обрабатывает новый пакет, уменьшает время его жизни на 1 и передаёт дальше. Следующий маршрутизатор тоже выполняет проверку хоста назначения и, если пакет предназначен не ему, уменьшает TTL, отбрасывает пакет и отправляет ICMP-сообщение источнику. Tracert запоминает второй хоп, снова увеличивает TTL на 1 и отправляет следующий пакет. Эти действия будут повторяться до тех пор, пока пакет не достигнет целевого хоста. Когда запрос попадёт к целевому хосту, этот хост в ответ направит ICMP «Echo Reply». Источник воспримет это как завершение трассировки.
Утилита Traceroute вместо ICMP-запроса отправляет 3 UDP-пакета на определенный порт целевого хоста и ожидает ответа о недоступности этого порта. Первый пакет отправляется с TTL=1, второй с TTL=2 и так далее, пока запрос не попадёт адресату. Отличие от Tracert в том, как Traceroute понимает, что трассировка завершена. Так как вместо ICMP-запроса он отправляет UDP-запрос, в каждом запросе есть порт отправителя (Sourсe) и порт получателя (Destination). По умолчанию запрос отправляется на закрытый порт 34434. Когда запрос попадёт на хост назначения, этот хост отправит ответ о недоступности порта «Destination port unreachable» (порт назначения недоступен). Это значит, что адресат получил запрос. Traceroute воспримет этот ответ как завершение трассировки.
Если Tracert работает по протоколу ICMP, то какой протокол используется командой Traceroute? По умолчанию используется протокол UDP, но traceroute может отправить и ICMP-запрос «Echo Request», как Tracert. Такой способ пригодится, если хоп не отвечает на UDP-пакет.
Как использовать Traceroute и Tracert
Кириллические домены необходимо вводить в формате Punycode. Для перевода домена в Punycode воспользуйтесь сервисом.
How to Install and run Traceroute on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
Traceroute is a network detection tool. It is using to track the path that an IP travels from source to destination by a packet on a network, and reports the IP address of all routers in between. Traceroute also records the time spent for each pack hop along its route to the destination. In this article, we try to learn you how to install and run Traceroute on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS. You can see the packages available in Eldernode to purchase the Ubuntu VPS server.
Tutorial Install and run Traceroute on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
Traceroute typically uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo packets with TTL values. The response time of each hop is calculating. To ensure accuracy, each hop is questioned several times (usually three times) to better assess the answer to that particular hop. Traceroute uses ICMP messages and TTL ports in the IP address header to function. Traceroute tools are usually included as a tool by operating systems such as Windows and Unix. TCP-based Traceroute tools are also available.
Traceroute is a useful tool for determining response delays and routing loops in the network path between packed loops. It also helps to find the breakdowns that we encounter when going to a specific destination. In the continuation of this article, join us to learn you how to install Traceroute on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
Description of the traceroute tool
It may be interesting for you to know the following. The traceroute tool uses the path specified by IP packets to reach a network host or the Internet. This tool shows the IP number and hostname of the machines in the path that the packets are going through. It should also be noted that Traceroute is used as a network troubleshooting tool. So if users encounter network connection problems, the tracker shows them where the problem is coming from along the way.
Install Traceroute on Ubuntu 20.04 | Ubuntu 18.04
Follow the steps below to quickly install the traceroute instructions on Ubuntu. You can simply follow the steps below and place it in your command line terminal using the built-in APT package manager.
The first step is to use the following command to update:
Once the update is successful, the next step is to install Traceroute. You can install Traceroute using the following command:
sudo apt-get install -y traceroutesudo apt-get install -y tracerouteFinally you should check the system reports for any related errors.
How to Run Traceroute on Ubuntu 20.04
Once you have successfully installed traceroute you can easily run it. You can use the following command to run traceroute on Ubuntu:
Note that in the above command you have to enter your desired destination address instead of example.com.
It should be noted that some types of Linux distributions require users to specify a protocol after -I, such as the following command:
traceroute -I ICMP example.comConclusion
When you connect to a website like www.eldernode.com, the traffic is sent through various routes and intermediaries to reach the destination. You can also use Traceroute to see the amount of latency at each stop. If you sometimes have trouble getting to that website but you know that website is working properly, there is definitely a problem along the way. The Traceroute command shows you which part of the path is the problem. Technically, the Traceroute command sends a sequence of packets using the ICMP protocol. Each of these packets checks a value and has a specific time. Whenever the time of each packet reaches zero, the router returns it and an error message is displayed. By sending packets this way, Traceroute makes sure that each router is on the active path or not.
In this article, we tried to ;earn you how to install and run Traceroute on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS. You can refer to the Routing tutorial with PowerShell article if you wish.
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
How to Install and Run Traceroute on Ubuntu 22.04?
In Linux, the traceroute command traces packet route from the source to the destination. It is quite useful for network administrators to examine the network’s performance. In Ubuntu, the working pattern of this command is similar to the “tracert” command that works in Windows OS.
This guide will demonstrate how to install and run the Traceroute command in Ubuntu 22.04.
The content that illustrates this tutorial is mentioned below:
Let’s start with the guide.
How to Install Traceroute on Ubuntu 22.04?
In Ubuntu 22.04, the traceroute command diagnoses or traces out any issue during transferring the packet from source to destination. To install the traceroute in Ubuntu, the step-by-step instructions are provided below:
Step 1: Update System Packages
To acquire the latest state of system packages, the below script is as follows to update the system packages:
Step 2: Install traceroute
Now, install the traceroute utility by issuing the following command:
$ sudo apt install traceroute
The installation of the traceroute has been completed.
Let’s explore the practical usage of the traceroute command on Ubuntu 22.04.
How to Run Traceroute on Ubuntu 22.04?
The traceroute command has multiple usage and options that assist in identifying any malicious activity in the network. To run the traceroute command, follow the below-mentioned command:
How Does Traceroute Command Work?
The “traceroute” command can send packets of different sizes, hops, probes, and many more.
The basic syntax of traceroute is as follows:
$ traceroute [options] host [pkt_len]
In the above syntax, the “host” specifies the host address, and “pkt_len” represents the packet length.
Various options of the traceroute command are explained below:
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| -d | This option enables debugging. |
| -i | It specifies the interface of probes. |
| -p | It represents the port for any query. |
| -w | It shows the maximum waiting time for a reply. |
| -m | This option denotes the maximum hop number. |
| -g | It defines the route of the gateway. |
How to Use Traceroute Command?
In the Ubuntu-based operating system, the practical usage of the “traceroute” command is demonstrated below with various examples:
Example 1: Tracerouting of Website
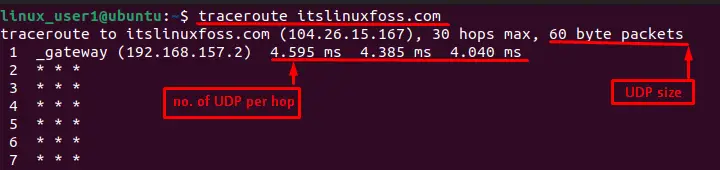
To find the traceroute of any website, write the name of the website after the traceroute command such as below:
$ traceroute itslinuxfoss.com
It provides some basic information that is enlisted as below:
- IP Address: It refers to the IP address of destination such as 104.26.15.167.
- Hops: It identifies the number of steps where packets travel from source to destination (Maximum 30).
- Packet Size: The packet size that transfers from the source address (By default value of packet size is 60).
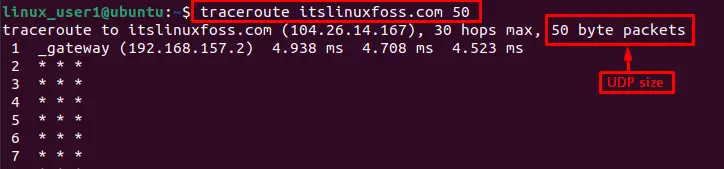
Example 2: Customize Packet Size
To change the packet size, write the numeric value (such as 50) the user wants to send from the source:
$ traceroute itslinuxfoss.com 50
By default value, the packet size is 60 bytes.
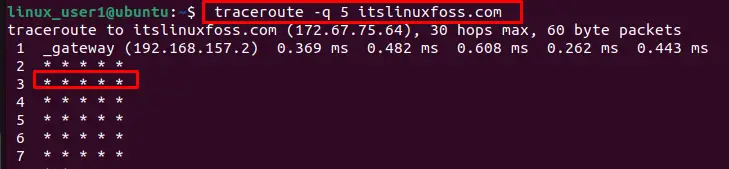
Example 3: Customize Number of Probes
To change the number of probes in every hop, utilize the “-q” flag with “5” probes after the traceroute command:
$ traceroute -q 5 itslinuxfoss.com
By default, three probes send through at each hop.
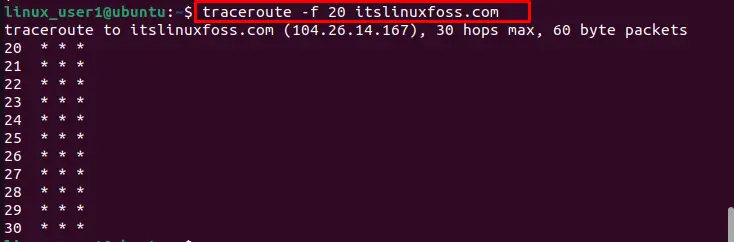
Example 4: Customize Number of Hops
To change the number of hops, users can utilize the “-f” flag to specify the starting point. In our case, specify the starting point 20 that can be verified in the below screenshot:
$ traceroute -f 20 itslinuxfoss.com
That is all about the usage of the traceroute command.
Note: For more details on the traceroute command usage, just read our article on traceroute.
Let’s explore the uninstallation of traceroute.
How to Uninstall Traceroute on Ubuntu 22.04?
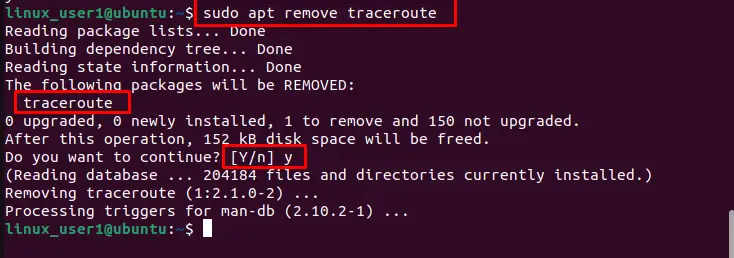
To uninstall the traceroute command from Ubuntu 22.04 system, execute the below script in the terminal:
$ sudo apt remove traceroute
After pressing the “y” key, the traceroute with all its executable files is removed from Ubuntu 22.04.
Bonus Tip: How to Install Traceroute on Other Linux Distributions?
It is additional information to install the traceroute commands on different linux based distribution systems. For this, the syntax is provided below:
For CentOS/RHEL:
The traceroute command can be installed in all CentOS or RHEL systems using “yum” as seen below:
$ sudo yum install traceroute
To install the traceroute command in Fedora OS, “dnf” is used here:
$ sudo dnf install traceroute
That’s all from this guide!
Conclusion
In Ubuntu 22.04, the “sudo apt install traceroute” and “traceroute” commands are utilized to install and run traceroute, respectively. It has multiple options that users can utilize to examine the number of hops, number of probes, packet size, and other activities. Network administrators utilize the “traceroute” command to diagnose any threat in the network. This guide has explained the traceroute installation, usage, and uninstallation methods in Ubuntu 22.04.