Reinstalling Ubuntu via Terminal
I’ve currently encountered some issues with ubuntu causing me to be stuck in tty mode. I already tried fixing the issue but since I’m not sure of what really happened for this issue to occur I now just want to reinstall ubuntu. I was wondering if there is a way to reinstall ubuntu via terminal? I’m currently running 12.04.4 lts and I already tried the command line: sudo dpkg-reconfigure -phigh -a But that didn’t do anything (after ~10 min of nothing happening a new command line appeard, I tried to restart but nothing changed) Any help is highly appreciated Thanks
Have you tried the second choice in the boot menu, the one saying ‘linux image generic [recovery mode]’, and not the first one which says ‘linux image generic’. Once you get to the recovery screen, choose the repair option from the menu. It should work especially if you have a working Internet connection up and running.
Thank you for your quick response, and Yeah I’ve tried that but it just goes to a bigger terminal screen and the last thing it says is «[9.122663] init: Failed to spawn console-setup main process: unable to execute: No such file or directory».
Change your keyboard, use another one, i mean use some USB keyboard or better a ps/2 keyvoard if you can plug it in. What you just experienced seems to be a bug which has something to do with the keyboard. Maybe it will work with a generic keyboard.
@floppy, the recovery screen gives you the option to repair ( fsck ) a damaged filesystem, which has no need for a network connection, and is quite unlikely to help anyhow.
The recovery screen fixed my issues for a few times in the past. It uses sudo apt-get update and sudo apt-get upgrade, and it can download missing packages from the Internet or fix broken packages. I may be wrong since I am completely new to all this Linux experience.
How to Update Ubuntu in the Command Line
Want to update Ubuntu quickly and simply? Here’s how to open a terminal prompt and install Ubuntu in the command line.
Readers like you help support MUO. When you make a purchase using links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Read More.
Knowing how to update Linux in the command line is an absolute must for skilled users. Staying updated keeps your system safe, secure, and stocked with the latest features. Today we’ll learn how to update an Ubuntu desktop or server from the terminal, or through an SSH connection.
Why You Should Update Via Command Line
Why use the command line to update Linux?
Because it’s often faster than using a GUI tool like Software Updater, and you can see the updates happening in real time. It’s also one of the easiest commands to learn, as you’re about to find out.
In addition to Ubuntu, these instructions will work on most Ubuntu-based distributions, like Linux Mint and Kali Linux.
Keep in mind going forward, however, that any time you upgrade Ubuntu software, you’ll need to have administrative privileges. That means you’ll always be asked to confirm your password.
Update Ubuntu in the Terminal
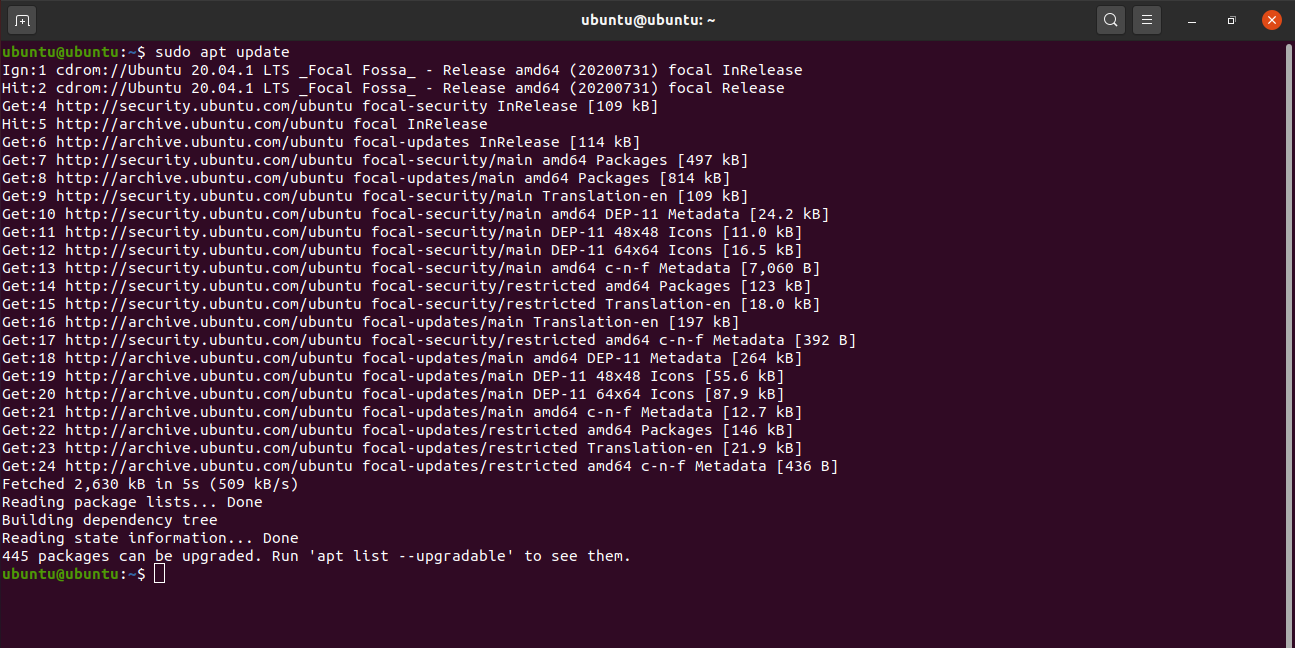
The Ubuntu update command is apt, or sometimes apt-get. Apt is Ubuntu’s primary package manager.
Using the update option tells apt to search your software repositories (everything listed in /etc/apt/sources.list) and take inventory of what Ubuntu package updates are available.
Note: You might see certain Linux guides telling you to use apt-get, like sudo apt-get update, instead of apt. Don’t be confused: both commands perform the same function, but we recommend apt over apt-get, as it’s a little more user-friendly.
Once the update command has completed, you’ll be ready to apply the package updates using the upgrade option.
The above command will apply all upgrades found in the previous update command as long as they don’t require removal of any already installed packages. If some packages seem to refuse to upgrade, using the full-upgrade option, which can remove certain packages, may resolve the problem.
With either command, after listing out the available upgrades, you’ll be asked to confirm the installation by entering y or yes.
You can skip the confirmation by adding the -y flag to the end of an upgrade command, and you can combine both update and upgrade into one command by utilizing the && operator.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y Update Ubuntu Server in the Command Line
Updating an Ubuntu server is essentially the same experience as updating an Ubuntu desktop through the command line.
However, in this instance, you should use apt-get instead of apt, and follow the upgrade with the dist-upgrade option to ensure your server stays completely up to date.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade Update Ubuntu via SSH
If you’ve set up an SSH connection with your Ubuntu system, you can upgrade remotely and securely after signing into your SSH.
ssh username@REMOTE.IP.ADDRESS.HERE
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade Make sure you replace «username» and «REMOTE.IP.ADDRESS.HERE» with the appropriate information.
Ubuntu Package Upgrades
Your Ubuntu system is now updated and ready for you to continue using it safely, and with all the latest Linux features.
Some Linux apps you won’t actually find in the software store or apt repositories. We’ve gathered several websites that offer the best in DEB downloads that will work with Ubuntu.