- You asked: How do I install missing packages on Linux?
- How do I fix broken packages in Ubuntu?
- How do I run apt fix broken install?
- How do I install sudo apt?
- How do I find packages on Linux?
- What command is used to install packages on Linux?
- What does Y mean in Linux?
- How do I fix sudo apt-get update?
- How do I force apt-get to reinstall?
- What is sudo apt-get update?
- How to Fix Broken Packages in Ubuntu
- Check for Updates
- Force APT to Correct Missing Dependencies or Broken Packages
- Force Reconfigure or Remove Broken Packages with DPKG
- Resolve DPKG Lock Issue
- Use apt-get to fix missing and broken packages
- Using apt-get to fix missing and broken packages
- Other methods
- Method 2:
- About the author
- Karim Buzdar
- stefan c
You asked: How do I install missing packages on Linux?
First, run an update to make sure there are no newer versions of the required packages. Then you can try forcing apartment to find and fix missing dependencies or broken packages. This will actually install any missing packages and repair existing installations.
How do I fix broken packages in Ubuntu?
the problem of a broken package still exists the solution is edit dpkg status file by hand. Locate the corrupted package, remove the entire information block, and save the file.
How do I run apt fix broken install?
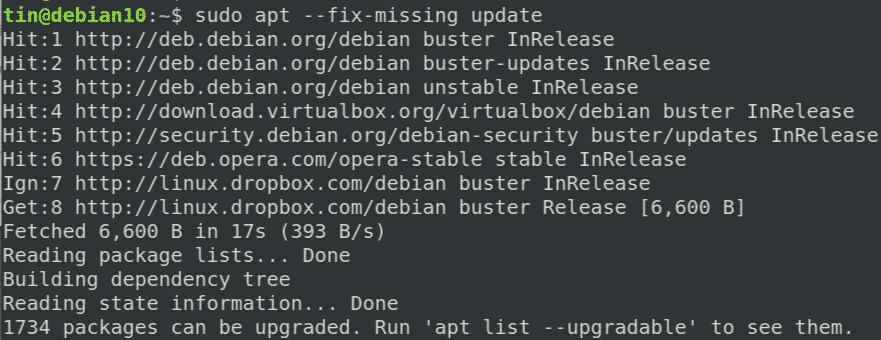
- Open your terminal by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T on your keyboard and enter: sudo apt –fix-missing update.
- Update the packages on your system: sudo apt update.
- Now force install the broken packages using the -f flag.
How do I install sudo apt?
If you know the name of the package you want to install, you can install it using this syntax: sudo apt-get install package1 package2 package3 … You can see that it is possible to install multiple packages at once, which is useful for acquiring all the software needed for a project in one step.
How do I find packages on Linux?
Open the terminal app or log in to the remote server using ssh (for example, ssh user@server-name) Run the command apt list —installed to list all packages installed on Ubuntu. To display a list of packages that meet certain criteria, such as showing matching apache2 packages, run apt list apache.
What command is used to install packages on Linux?
The apt command is a powerful command line tool that works with Ubuntu’s Advanced Packaging Tool (APT) and performs functions like installing new software packages, updating existing software packages, updating package list index and even updating the entire Ubuntu system.
What does Y mean in Linux?
-and, -yes, -assume-Yes. Automatic yes to prompts; assume «yes» for all prompts and run non-interactively. If an unwanted situation occurs, such as changing a held package, trying to install an unauthenticated package, or removing an essential package, apt-get will abort.
How do I fix sudo apt-get update?
However, if the problem occurs again, open Nautilus as root and navigate to var/lib/apt and then delete the old “lists.” directory. Then open the “lists” folder and delete the “partial” directory. Finally, run the above commands again.
How do I force apt-get to reinstall?
You can reinstall a package with sudo apt-get install —reinstall package name. This completely removes the package (but not the packages that depend on it), then reinstalls the package. This can be convenient when the package has many reverse dependencies.
What is sudo apt-get update?
The sudo apt-get update command is used to download package information from all configured sources. Sources are often defined in /etc/apt/sources. list of files and other files located in /etc/apt/sources.
How to Fix Broken Packages in Ubuntu
Linux packages are compressed archives containing programs and files necessary to run them. The package distribution system is designed to be robust and simplify the application installation process.
However, a bad internet connection or misconfigured third-party installers can corrupt packages and cause problems on your system.
This article will show you how to troubleshoot and fix broken packages on Ubuntu using the available APT and DPKG tools.
Check for Updates
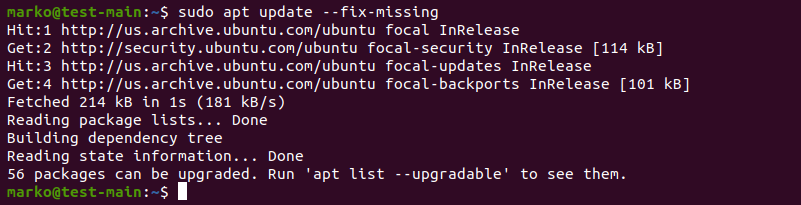
Start troubleshooting by rebuilding the list of dependencies. The —fix-missing option tells APT to ignore missing packages. The option ensures the update process is performed without APT returning an error.
sudo apt update --fix-missingForce APT to Correct Missing Dependencies or Broken Packages
Missing package dependencies are a common reason for package-related errors.
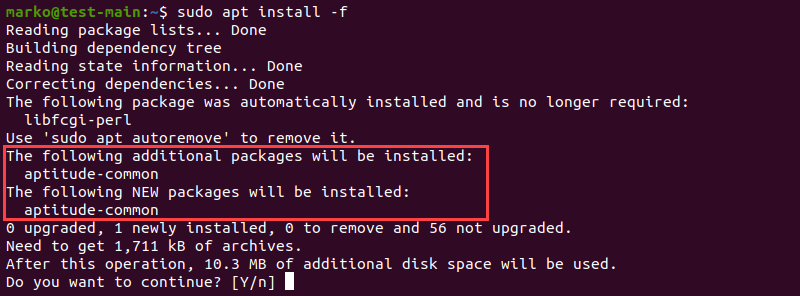
1. Use apt install with the -f flag to tell APT to locate the missing packages and install them.
APT lists the missing packages on your system.
2. Press ENTER to start the installation.
Note: If troubleshooting has led to Ubuntu needing to be reinstalled, please refer to our reinstallation guide How to Reinstall Ubuntu.
Force Reconfigure or Remove Broken Packages with DPKG
Broken packages may cause package manager configuration problems.
1. Reconfigure DPKG, the base package management system, with the following command:
2. Check if DPKG marked some packages as needing a reinstall.
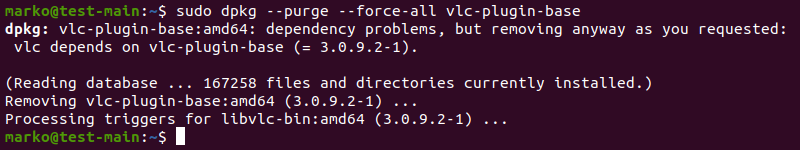
3. If the command above returns a list of one or more packages, try removing the packages by typing:
sudo dpkg --purge --force-all [package-name]The example below shows how to remove the corrupted vlc-plugin-base package.
Warning: The dpkg —purge —force-all command removes a package even if the removal causes further dependency issues. Use the command with care.
4. After you finish troubleshooting, run the following command to clean up the system:
5. Then update the repositories again:
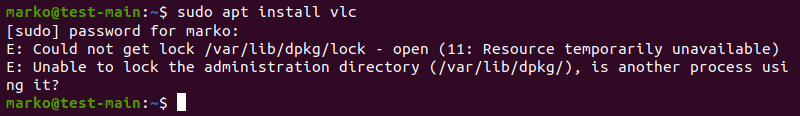
Resolve DPKG Lock Issue
The DPKG lock error appears when trying to install a package while another process is using DPKG.
However, sometimes the error occurs even if no other processes are using the package management system.
1. To fix the problem, remove the lock file manually:
sudo rm /var/lib/apt/lists/lock2. Also, remove the lock in cache:
sudo rm /var/cache/apt/archives/lockDeleting the lock enables you to use APT and DPKG again.
The article provided common ways of resolving problems caused by broken packages on Ubuntu.
For more information related to package management on Ubuntu, read:
Use apt-get to fix missing and broken packages
Package managers in Linux are the most useful programs that are used to add additional capabilities in a system. They can be used for installing, removing, updating, and upgrading the packages, also featuring the dependency resolution capabilities. However, like any other program, things can also go wrong with these package managers. Sometimes, while updating or installing a third-party program, installation goes wrong and results in errors that require you to install the missing dependencies and broken packages. This error may also occur because of improper package management, incorrect installation of packages, and installation of unnecessary packages. Whatever the reason may be, the problem is that you receive an error and left with a condition where you cannot add a new package nor update or delete the existing packages until you fix the problem.
In this article, we will learn how to fix the missing dependencies and broken packages using the apt-get command. Note that, we have run the commands and procedure mentioned in this article on a Debian 10 system. The same procedure can be followed in Ubuntu and older Debian versions.
We will use the command-line Terminal for trying the solutions and fixing the problem. To open the Terminal application in Debian, hit the super key on the keyboard and search for it using the search bar that appears. When the search result appears, click on the Terminal icon to open it.
Using apt-get to fix missing and broken packages
Apt-get is a Terminal based package management tool used for installing, upgrading, and removing packages. Along with these features, it also has flags that can be used for fixing missing dependencies and broken packages.
Use the “fix-missing” option with “apt-get update” to run the updates and ensure the packages are up to date and there is no new version available for the packages.
Once you are done with the update, execute the below command in order to force the package manager to find any missing dependencies or broken packages and install them.
Another approach to solving the broken package issue via apt-get is to edit the “/etc/apt/sources/list” file and adding sites with newer versions of packages available. Then running the “apt-get update” command to update the repository list.
If the above method does not fix the issue of broken dependencies and broken packages and still you are receiving the error, then try the following methods.
Other methods
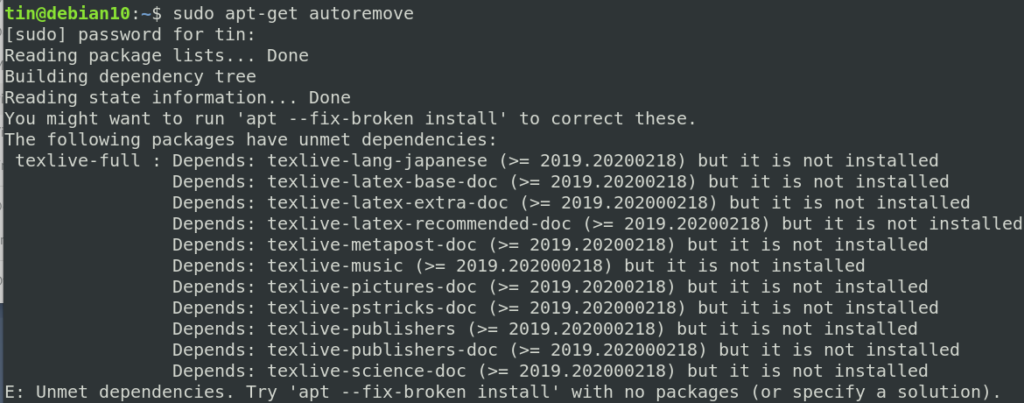
In this method, we will use the “apt-get autoremove” and the “dpkg” in order to fix missing dependencies and broken packages.
1. Update the repository index by executing the below command in Terminal:
2. Next, execute the below command to clean out the local repository:
3. Execute the below command to remove all the unnecessary packages that are no longer needed:
The above command will display the unmet dependencies or broken package’s name.
4. Then try executing the below command in Terminal to force remove the broken package:
Method 2:
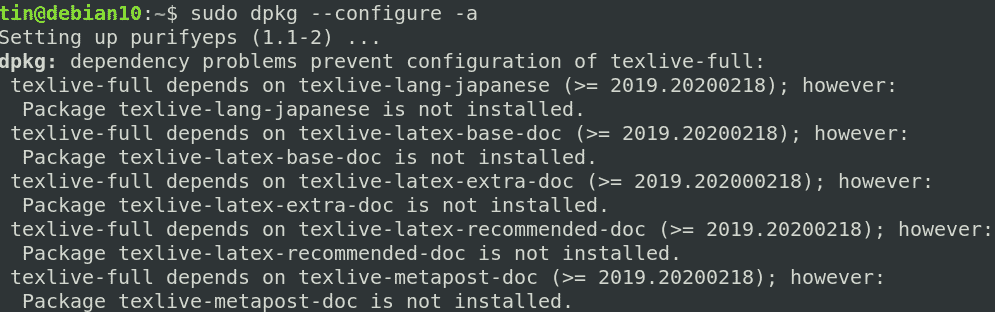
In the following method, we will use the “dpkg—configure” command in order to fix missing dependencies and broken packages.
Dpkg is a package management tool that can be used to install, remove and manage packages. Similar to apt-get, it can also help to fix broken packages and missing dependencies. If you receive some errors while installing or updating the packages, try the following solution with dpkg:
1. Execute the below command in the Terminal to reconfigure all the partially installed packages.
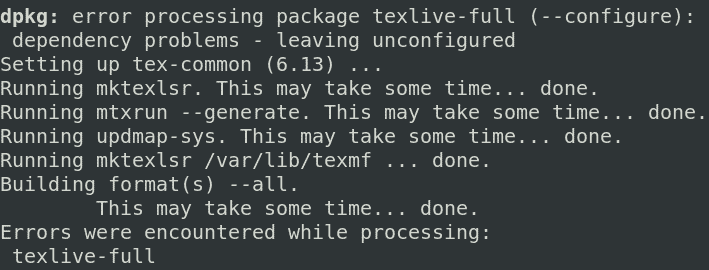
If the above command does not work, like in our case and you see similar results displaying the erroneous package, then try removing the package.
2. Execute the below command in Terminal in order to remove the erroneous package.
3. Then use the below command to clean out the local repository:
After trying any one of the above solutions, run the update command to ensure the dependencies are resolved and broken packages are fixed or removed.
Fixing the dependency and broken packages errors and then returning the system to the normal state may take hours. Sometimes it gets so complicated that when you finally fix it, you feel so lucky. We have presented some solutions regarding this error, so please give them a try. If you know some of the possible solutions we did not mention, please let us know in the comments.
About the author
Karim Buzdar
Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. He blogs at LinuxWays.
stefan c
This is a quick tip to making the installation of missing packages in certain Linux flavors easier.
Many Linux distributions come with a program called command-not-found pre-installed (e.g., Ubuntu or Debian), that helps to discover missing packages. Say you just freshly installed Linux and type hg status in a shell. Because hg is not installed yet, you instead see the following:
$ hg status The program 'hg' is currently not installed. You can install it by typing: sudo apt-get install mercurial Now this very useful, especially when the package has a different name from the command you are trying to run (like with mercurial). But why do I have to type (or copy) that message if I want to install the package? Turns out, there is an environment variable which when set, asks to install the package directly, like this:
$ hg status The program 'hg' is currently not installed. You can install it by typing: sudo apt-get install mercurial Do you want to install it? (N/y) Entering y will install the package. Very convenient. To enable this feature, add the following line to ~/.bashrc (or ~/.zshrc , or wherever your shell initialization is):
export COMMAND_NOT_FOUND_INSTALL_PROMPT=1 Life just got so much better!
Questions or comments? Send me an email or find me on twitter @stefan_heule.