- 3 Command Line Tools to Install Deb Packages in Ubuntu
- 1. Install .deb Package Using dpkg Command
- Remove Deb Packages Using dpkg Command
- 2. Install .deb Package Using Apt Command
- Remove Deb Packages using apt Command
- 3. Install .deb Package Using Gdebi Command
- Install .deb Packages Using Gdebi GUI
- Глава 8. Инструменты управления пакетами Debian
- 8.1. Какие программы для управления пакетами имеются в Debian?
- 8.1.1. dpkg
- 8.1.2. APT
3 Command Line Tools to Install Deb Packages in Ubuntu
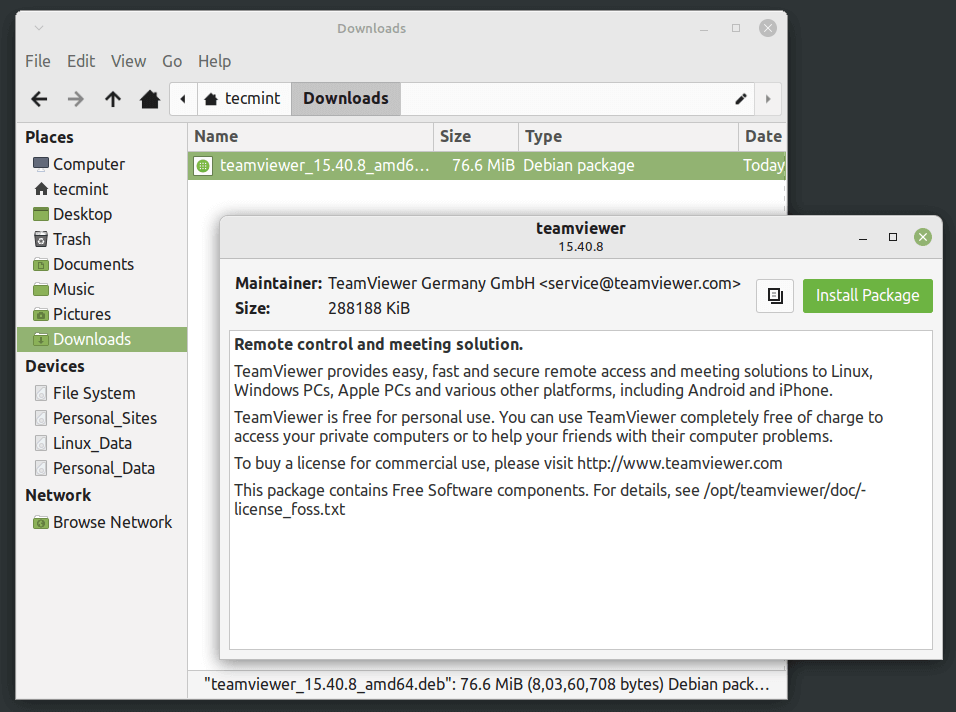
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install local software packages (.DEB) in Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint using three different command line tools and they are dpkg, apt, and gdebi.
This is useful to those new users who have migrated from Windows to Ubuntu or Linux Mint. The very basic problem they face is installing local software on the system.
However, Ubuntu and Linux Mint have their own Graphical Software Center for easy software installation, but we will be looking forward to installing deb packages through the terminal way.
1. Install .deb Package Using dpkg Command
Dpkg is a package manager for Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint. It is used to install, build, remove, and manage .deb packages. but unlike other Linux package management systems, it cannot automatically download and install packages with their dependencies.
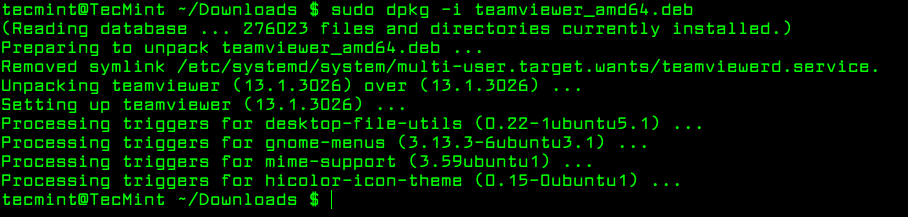
To install a .deb package, use the dpkg command with the -i flag along with the package name as shown.
$ sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_amd64.deb
If you get any dependency errors while installing or after installing and launching a program, you can use the following apt command to resolve and install dependencies using the -f flag, which tells the program to fix broken dependencies.
Remove Deb Packages Using dpkg Command
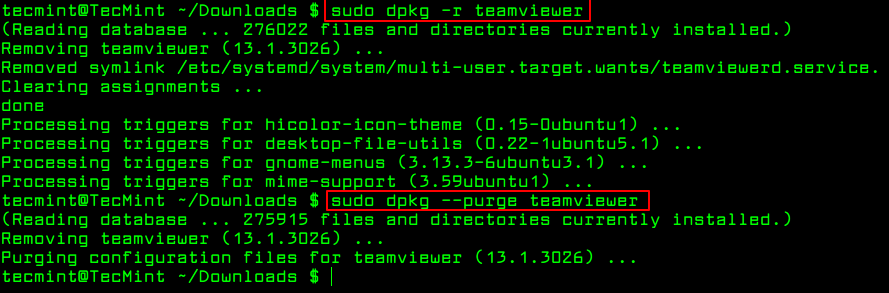
To remove a .deb package use the -r option or if you want to remove all its files including configuration files, you can purge it using the —purge option as shown.
$ sudo dpkg -r teamviewer [Remove Package] $ sudo dpkg --purge teamviewer [Remove Package with Configuration Files]
To know more about installed packages, read our article that shows how to list all files installed from a .deb package.
2. Install .deb Package Using Apt Command
The apt command is an advanced command-line tool, which offers new software package installation, existing software package upgradation, updating of the package list index, and even upgrading the whole Ubuntu or Linux Mint system.
It also offers apt-get and apt-cache command-line tools for managing packages more interactively on Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint systems.
Essentially, apt-get or apt do not understand .deb files, they are designed to primarily handle package names (for example teamviewer, apache2, mariadb, etc..) and they retrieve and install .deb archives associated with a package name, from a source specified in the /etc/apt/sources.list file.
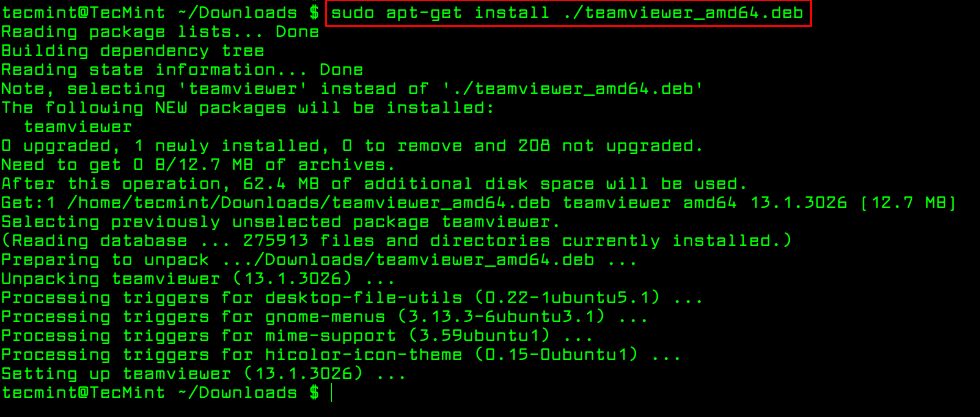
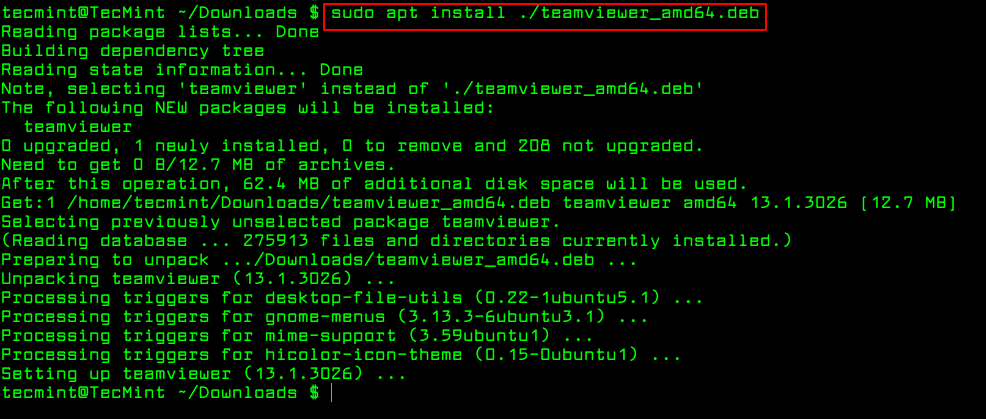
The only trick to installing a .deb Debian package using apt-get or apt is by specifying a local relative or absolute path ( ./ if in current dir) to the package, otherwise it will try to retrieve the package from remote sources and the operation will fail.
$ sudo apt install ./teamviewer_amd64.deb $ sudo apt-get install ./teamviewer_amd64.deb
Remove Deb Packages using apt Command
To remove a .deb package use the remove option or if you want to remove all its files including configuration files, you can purge it using the purge option as shown.
$ sudo apt-get remove teamviewer $ sudo apt-get purge teamviewer OR $ sudo apt remove teamviewer $ sudo apt purge teamviewer
3. Install .deb Package Using Gdebi Command
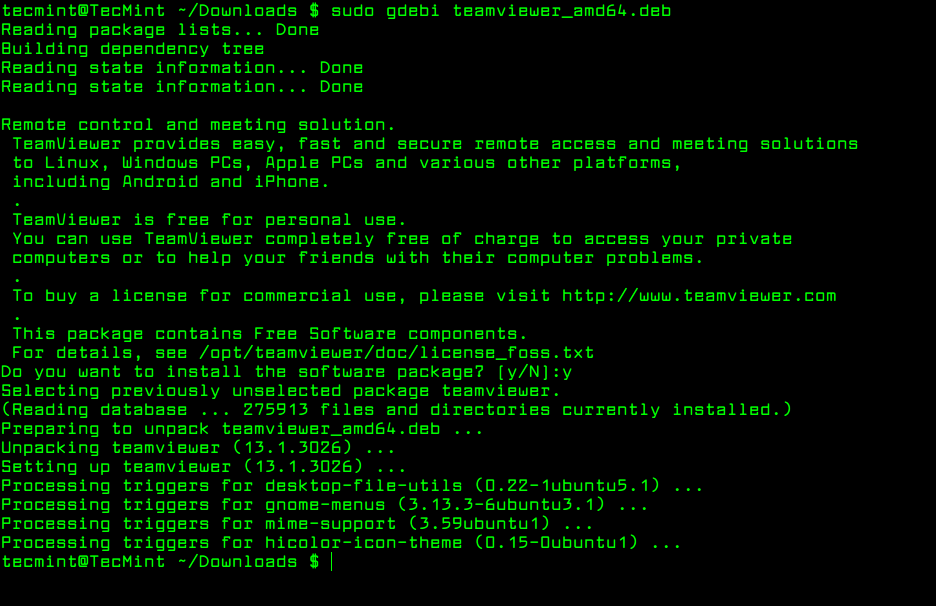
gdebi is a tiny command line and GUI tool for installing local deb packages. It resolves and installs package dependencies on the fly. To install a package, use the following command.
$ sudo gdebi teamviewer_13.1.3026_amd64.deb
To remove a .deb package installed from gdebi, you can use apt, apt-get or dpkg commands using purge option as shown.
$ sudo apt purge teamviewer OR $ sudo apt-get purge teamviewer OR $ sudo dpkg --purge teamviewer
Install .deb Packages Using Gdebi GUI
The most recommended way for beginners to installing .deb files is through the Gdebi GUI installer. Simply, go to the directory where you have downloaded the file and double-click to install it as shown.
That’s It! In this tutorial, we have explained three different command line tools for installing or removing .deb Debian packages in Ubuntu and Linux Mint.
If you know any other way of installing local packages, do share with us using our comment section below.
Глава 8. Инструменты управления пакетами Debian
8.1. Какие программы для управления пакетами имеются в Debian?
В Debian для управления пакетами имеется множество средств, от программ с графическими или текстовыми интерфейсами, до низкоуровневых утилит установки пакетов. Корректная работа всех доступных инструментов зависит от низкоуровневых утилит, и все они представлены здесь в порядке уменьшения уровня сложности.
Важно понимать, что высокоуровневые инструменты управления пакетами, такие как aptitude или synaptic , для управления пакетами используют apt , который, в свою очередь, использует dpkg для управления пакетами системы.
See Chapter 2. Debian package management of the Debian reference for more information about the Debian package management utilities. This document is available in various languages and formats, see the Debian Reference entry in the DDP Users’ Manuals overview.
8.1.1. dpkg
Это основная программа управления пакетами. dpkg может вызываться с многими параметрами. Наиболее часто используемые из них:
- Показать список всех параметров: dpkg —help
- Показать управляющий файл (и другую информацию) для указанного пакета: dpkg —info foo_VVV-RRR.deb
- Установить пакет на жёсткий диск (т. е. распаковать и настроить): dpkg —install foo_VVV-RRR.deb
- Распаковать архив Debian на жёсткий диск (но не настраивать): dpkg —unpack foo_VVV-RRR.deb . Учтите, что в результате данной операции пакет не обязан быть в рабочем состоянии; для правильной работы может потребоваться внесение изменений в некоторые файлы. Данная команда удаляет любую ранее установленную версию программы и запускает сценарий preinst указанного пакета (см. Раздел 7.6, «Зачем нужны сценарии preinst, postinst, prerm и postrm?»).
- Настроить пакет, который был распакован ранее: dpkg —configure foo . Кроме всего прочего, эта команда запускает сценарий postinst указанного пакета (см. Раздел 7.6, «Зачем нужны сценарии preinst, postinst, prerm и postrm?»). Она также обновляет файлы, перечисленные в conffiles . Обратите внимание, что в качестве аргумента для параметра configure указывается имя пакета (т. е. foo), а не имя файла-архива Debian (т. е. foo_VVV-RRR.deb).
- Распаковать файл с именем «blurf» (или группу файлов с именем «blurf*») из архива Debian: dpkg —fsys-tarfile foo_VVV-RRR.deb | tar -xf — ‘blurf*’
- Удалить пакет (но не его файлы настроек): dpkg —remove foo
- Удалить пакет (вместе с файлами настроек): dpkg —purge foo
- Вывести состояние установки пакетов, содержащих в имени строку (или регулярное выражение) «foo*»: dpkg —list ‘foo*’
8.1.2. APT
APT is the Advanced Package Tool , an advanced interface to the Debian packaging system which provides the apt-get program. It provides commandline tools for searching and managing packages, and for querying information about them, as well as low-level access to all features of the libapt-pkg library. For more information, see the User’s Guide in /usr/share/doc/apt-doc/guide.html/index.html (you will have to install the apt-doc package).
Starting with Debian Jessie, some frequently used apt-get and apt-cache commands have an equivalent via the new apt binary. This means some popular commands like apt-get update , apt-get install , apt-get remove , apt-cache search , or apt-cache show now can also be called simply via apt , say apt update , apt install , apt remove , apt search , or apt show . The following is an overview of the old and new commands:
apt-get update -> apt update apt-get upgrade -> apt upgrade apt-get dist-upgrade -> apt full-upgrade apt-get install package -> apt install package apt-get remove package -> apt remove package apt-get autoremove -> apt autoremove apt-cache search string -> apt search string apt-cache policy package -> apt list -a package apt-cache show package -> apt show package apt-cache showpkg package -> apt show -a package
Инструмент apt совмещает функциональность apt-get и apt-cache, а также по умолчанию использует красивый цветной формат вывода, что очень удобно. Для использования в сценариях или для продвинутого использования предпочтительнее использовать apt-get (а иногда он просто необходим).
apt-get provides a simple way to retrieve and install packages from multiple sources using the command line. Unlike dpkg , apt-get does not understand .deb files, it works with the packages proper name and can only install .deb archives from a source specified in /etc/apt/sources.list . apt-get will call dpkg directly after downloading the .deb archives [5] from the configured sources.
Часто используемые команды apt-get :