- KVM: Configure Intel X710 — E810 series NICs for High Performance¶
- Prerequisites¶
- Add Intel IOMMU to the Linux grub file¶
- Modify driver settings to enable SR-IOV¶
- Verify the OS has loaded the Intel driver¶
- Install the supplied Intel Ice PF driver¶
- Install the supplied Intel IAVF driver¶
- Upgrade X710-E810 NIC firmware using supplied NVM tool¶
- Create VF’s¶
- Use the rc.local file¶
- Initialize the VFs for the driver¶
- Deploy BIG-IP VE in KVM¶
- Diagnostics and troubleshooting tips¶
- Related Links¶
KVM: Configure Intel X710 — E810 series NICs for High Performance¶
This document supports the following Intel NIC series:
- F5 BIG-IP Virtual Edition (VE) 13.0.0 and later for Intel X710
- F5 BIG-IP VE 15.1.7 and later for Intel E810
This document explains the basic driver and SR-IOV setup of the Intel X710 and E810 series of NICs on Linux.
F5 BIG-IP VE currently supports the Intel E810 NIC series using a sock driver only. Contact your F5 Support Sales Emgimeer for details.
The document assumes the built-in driver is loaded in the base OS and that BIG-IP 13.0.0 and later is using the default optimized driver.
To configure your KVM host, verify the required prerequisites , and then complete the following steps:
Prerequisites¶
Before you begin, ensure you have completed the following tasks.
- Enable Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT) in the host machine BIOS.
- Enable SR-IOV in the BIOS.
- Optional. Optimize power management settings:
- Turn off speed-stepping.
- Change power management from Balanced to Performance.
- Disable C-State power controls.
Linux lshw utility
Use the lshw tool to extract detailed information on the hardware configuration.
- To install lshw, type: yum install -y lshw
- To look up i40e driver information, type: Modinfo i40e
- Other lshw commands include:
lshw -c network -businfo ip l | grep vf virsh nodedev-list –tree ifconfig -a lsmod or lsmod |grep igb iplink show ethtool -i enp134s0f0
Add Intel IOMMU to the Linux grub file¶
Modify the Linux grub file to add Intel input–output memory management unit (IOMMU) support. Depending on the Linux distribution, use grub or grub2. Grub files are located in the following directories:
- View the current config by typing: grubby —info=ALL
- Configure intel_iommu=on in the grub file, and add iommu=pt (pass-through) to the grub file, when using SR-IOV. When in pass-through mode, the adapter does not use DMA translation to the memory, improving performance.
- Append the IOMMU settings to the grub file: grubby —update-kernel=ALL —args=»intel_iommu=on iommu=pt»
- Type, update-grub .
For an example on RHEL 7.6 using Grubby, consult this RHEL article.
To modify the hugee page file size settings, use this command:
grubby —update-kernel=ALL —args=»hugepagesz=2M hugepages=320 default_hugepagesz=1G hugepagesz=1G hugepages=16″
Modify driver settings to enable SR-IOV¶
Intel NIC’s ship with the SR-IOV Virtual Functions (VF) set to zero. You must modify the operating system driver settings so the VF’s will persist (even after an OS reload).
PF and VF drivers for the X710 and XL710 server adapters are included in Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Centos and Ubuntu. 7.x distribution are named i40e and i40evf respectively. Newer versions of these drivers are available on the Intel Downloads site.
The driver or software for your Intel® component may have changed or been replaced by the computer manufacturer. F5 recommends you work with your computer manufacturer, before installing the mainstream Intel driver, so you don’t lose OEM features or customizations.
Verify the OS has loaded the Intel driver¶
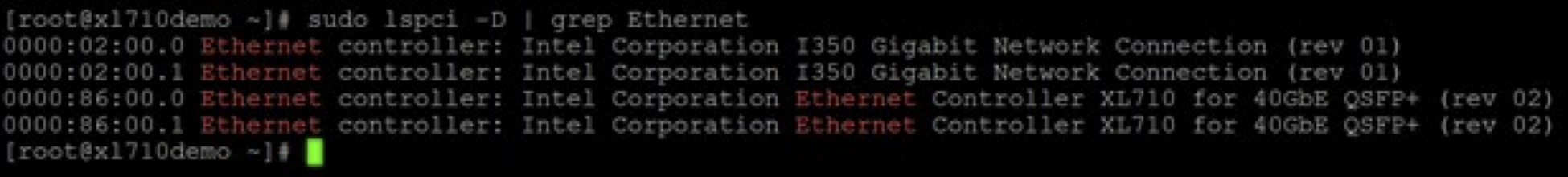
- Check that the adapters are recognized by running the following lspci command: sudo lspci -D | grep Ethernet A list of network adaptors similar to the following is returned:
- Port 0 of the PF is at PCI address 0000:86:00.0
- Port 1 of the PF is at PCI address 0000:86:00.1
Install the supplied Intel Ice PF driver¶
Visit the Intel Downloads Center for Intel® Ethernet 810 NIC series that uses Ice PF driver. The X710 NIC series uses the i40E PF driver.
- Download the supplied Intel Ice PF X710-E810 driver ice-1.3.2.tar.gz file.
- Change to the driver src directory, type:
sudo yum install elfutils-libelf-devel -y sudo make install
modinfo ice Example Output: [root@prototype src]# modinfo ice filename: /lib/modules/4.18.0-240.10.1.el8_3.x86_64/updates/drivers/net/ethernet/intel/ice/ice.ko firmware: intel/ice/ddp/ice.pkg version: 1.3.2 license: GPL v2 description: Intel(R) Ethernet Connection E800 Series Linux Driver author: Intel Corporation, rhelversion: 8.3 srcversion: 22DB853ECEFB6FC0EDAB51C
Install the supplied Intel IAVF driver¶
Both the Intel X710 and E810 NIC series uses the IAVF driver.
- Set VF’s to zero before upgrading IAVF driver:
echo 0 > /sys/class/net/ens818f0/device/sriov_numvfs echo 0 > /sys/class/net/ens818f1/device/sriov_numvfs
lshw -class network -businfo # example output [root@prototype ~]# lshw -class network -businfo Bus info Device Class Description ============================================================ pci@0000:b1:00.0 ens801f0 network Ethernet Controller E810-C for QSFP pci@0000:b1:00.1 ens801f1 network Ethernet Controller E810-C for QSFP pci@0000:b1:01.0 network Ethernet Adaptive Virtual Function pci@0000:b1:01.1 network Ethernet Adaptive Virtual Function pci@0000:b1:11.0 network Ethernet Adaptive Virtual Function pci@0000:b1:11.1 network Ethernet Adaptive Virtual Function
Note The make install command creates /etc/modprobe.d/iavf-blacklist-i40evf.conf that contains denylisti40evf . ##. Adds the line alias i40evf iavf to the modprobe configuration.
Upgrade X710-E810 NIC firmware using supplied NVM tool¶
This is an OPTIONAL step for most hypervisors. However, for VMware, upgrading the Intel X710 firmware is a requirement. The Intel E810 firmware must be version is 2.32 or higher. Consult the VMware setup guide for firmware details.
You must first upgrade to the Intel ice driver or the NVM tool will fail.
- Download the Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) Update Utility for Intel® Ethernet Network Adapter E810_NVMUpdatePackage_v2_32.zip file to the /installs/NVMUpdatePackage directory.
- Change directories to /installs/NVMUpdatePackage and unpack the E810_NVMUpdatePackage_v2_32.zip file.
tar xzvf E810_NVMUpdatePackage_v2_32_Linux.tar.gz chmod +x * ./nvmupdate64e -i -l -o inventory.xml ./nvmupdate64e*
Create VF’s¶
Create as many virtual functions as needed using the following:
Use the rc.local file¶
The following example initializes the VFs using two VFs per PF. Assigning MACs is optional.
sudo vi /etc/rc.d/rc.local echo 2 > /sys/class/net/ens801f0/device/sriov_numvfs ip link set ens801f0 vf 0 trust on ip link set ens801f0 vf 0 spoofchk off #ip link set ens801f0 vf 0 mac [insert mac address] ip link set ens801f0 vf 1 trust on ip link set ens801f0 vf 1 spoofchk off #ip link set ens801f0 vf 1 mac [insert mac address] echo 2 > /sys/class/net/ens801f1/device/sriov_numvfs ip link set ens801f1 vf 0 trust on ip link set ens801f1 vf 0 spoofchk off #ip link set ens801f1 vf 0 mac [insert mac address] ip link set ens801f1 vf 1 trust on ip link set ens801f1 vf 1 spoofchk off #ip link set ens801f1 vf 1 mac [insert mac address]
Initialize the VFs for the driver¶
Module options are not persistent from one boot to the next. To ensure that the desired number of VFs are created, each time you power cycle the server, append the rc.local file, located in the /etc/rc.d/ directory. The Linux OS executes the rc.local script at the end of the boot process. Edit /etc/rc.d/rc.local to initialize the VFs for the driver.
- Modify the rc.local file to initialize the VFs for the driver. On a new install the rc.local file may not be set to initialize on startup. To allow for initialization, modify the file attributes:
sudo chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.localecho 24 > /sys/class/net/enp24s0f0/device/sriov_numvfs echo 24 > /sys/class/net/enp24s0f1/device/sriov_numvfs
This example assumes 24 VFs on two ports. The variables are <#ofVFs>and :
echo > /sys/class/net//device/sriov_numvfssudo systemctl start rc-local sudo systemctl enable rc-local
Deploy BIG-IP VE in KVM¶
To deploy BIG-IP VE, download an image from F5 and deploy it in your environment.
- Do not change the configuration (CPU, RAM, and network adapters) of the KVM guest environment with settings less powerful than those recommended and described here.
- When using F5’s virtio synthetic driver, use the default i440FX machine type. The QEMU Q35 machine type is not supported.
- In a browser, open the F5 Downloads page and log in.
- On the Downloads Overview page, click Find a Download .
- Under Product Line , click the link similar to BIG-IP v.x/Virtual Edition .
- Click the link similar to x.x.x_Virtual-Edition .
- If the End User Software License is displayed, read it and then click I Accept .
- Download the BIG-IP VE file package ending with qcow2.zip .
- Extract the file from the Zip archive and save it where your qcow2 files reside on the KVM server.
- Use VNC to access the KVM server, and then start Virt Manager.
- Right click localhost (QEMU) , and from the popup menu, select New . The Create a new virtual machine, Step 1 of 4 dialog box opens.
- In the Name field, type a name for the connection.
- Select import existing disk image as the method for installing the operating system, and click Forward .
- Type the path to the extracted qcow file, or click Browse to navigate to the path location; select the file, and then click the Choose Volume button to fill in the path.
- In the OS type setting, select Linux , for the Version setting, select Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 , and click Forward .
- In the Memory (RAM) field, type the appropriate amount of memory (in megabytes) for your deployment. (For example 4096 for a 4GB deployment). From the CPUs list, select the number of CPU cores appropriate for your deployment, and click Forward.
- Select Customize configuration before install, and click the Advanced options arrow.
- Select the network interface adapter that corresponds to your management IP address, and click Finish . The Virtual Machine configuration dialog box opens.
- Click Add Hardware . The Add New Virtual Hardware dialog box opens.
- If SR-IOV is not required, select Network .
- From the Host device list, select the network interface adapter for your external network, and from the Device model list, select virtio . Then click Finish . Do this again for your internal and HA networks.
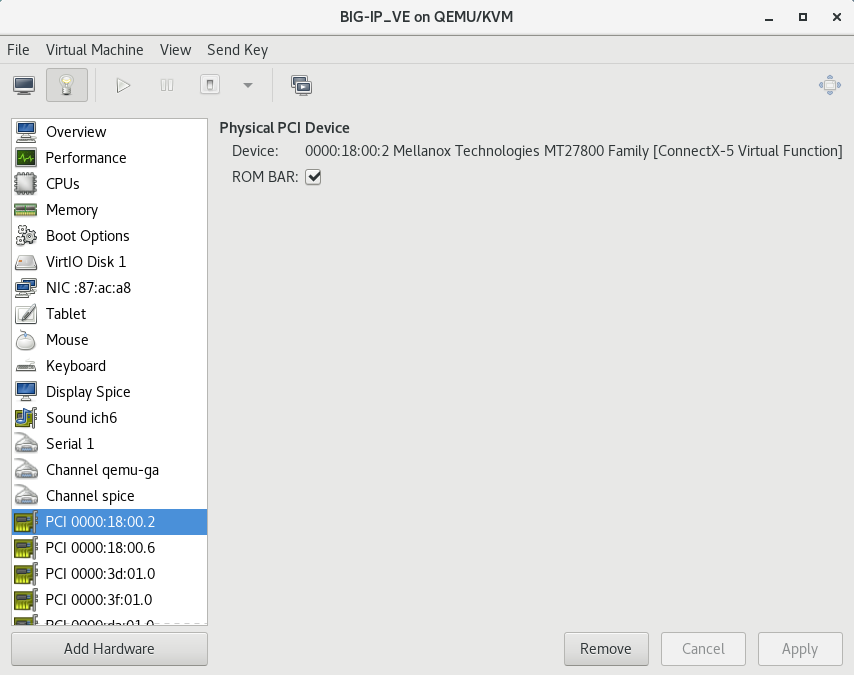
- If SR-IOV is required, select PCI Host Device and then select the PCI device for to the virtual function mapped to your host device’s external VLAN. Then click Finish . Be sure to use the Virtual Function (VF) PCI Host Device instead of the Physical Function (PF) to take advantage of VE high-speed drivers. The following image illustrates adding a PCI VF Network Interface within the Virtual Machine Manager:
Virtual Machine Manager creates the virtual machine just as you configured it.
Diagnostics and troubleshooting tips¶
When using ifconfig to bring down the ports, the physical link can continue to indicate that it is up on the Switch side.
- Use the following commands at the OS level (not BIG-IP VE) to change this behavior, and close any VM’s and zero-out the VF’s.
ethtool --set-priv-flags ens801f0 link-down-on-close on ethtool --set-priv-flags ens801f1 link-down-on-close on
ethtool -i ens4f0 driver: ice version: 4.18.0-408.el8.x86_64 firmware-version: 2.15 0x800049c3 1.2789.0 expansion-rom-version: bus-info: 0000:8a:00.0 supports-statistics: yes supports-test: yes supports-eeprom-access: yes supports-register-dump: yes supports-priv-flags: yes
Related Links¶
- K17204 F5 support article
- Intel Downloads Center
- Intel Ice PF X710-E810 driver
- tar xzf iavf-4.0.2.tar.gz
- E810_NVMUpdatePackage_v2_32.zip
- Intel Port Configuration Tool
- Intel X710 (download .PDF file)
- Intel E810 (download .PDF file)