Configure a virtual environment
PyCharm makes it possible to use the virtualenv tool to create a project-specific isolated virtual environment . The main purpose of virtual environments is to manage settings and dependencies of a particular project regardless of other Python projects. virtualenv tool comes bundled with PyCharm, so the user doesn’t need to install it.
For Python 3.3+ the built-in venv module is used, instead of the third-party virtualenv utility.
Create a virtualenv environment
- Do one of the following:
- Click the Python Interpreter selector and choose Add New Interpreter .
- Press Control+Alt+S to open Settings and go to Project: | Python Interpreter . Click the Add Interpreter link next to the list of the available interpreters.
- Click the Python Interpreter selector and choose Interpreter Settings . Click the Add Interpreter link next to the list of the available interpreters.
- Select Add Local Interpreter .
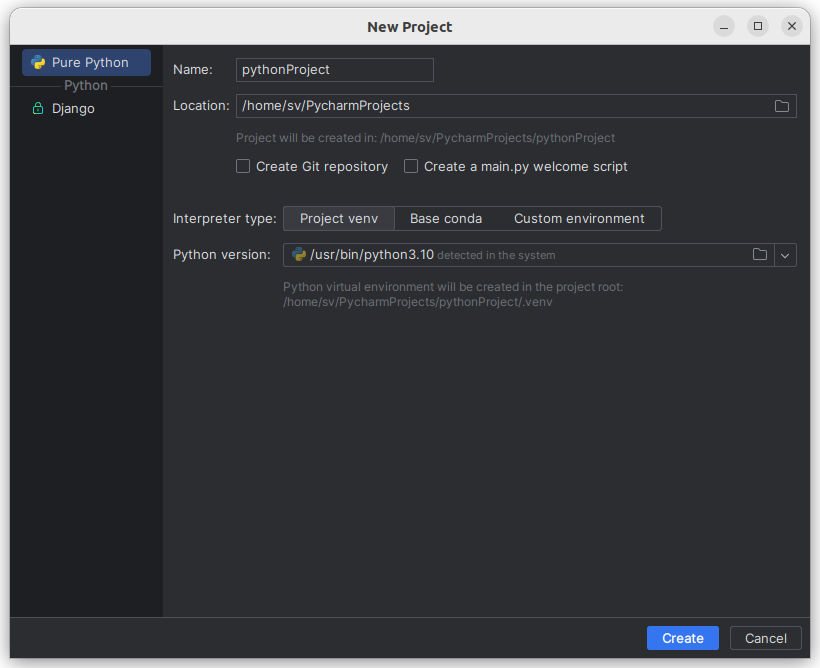
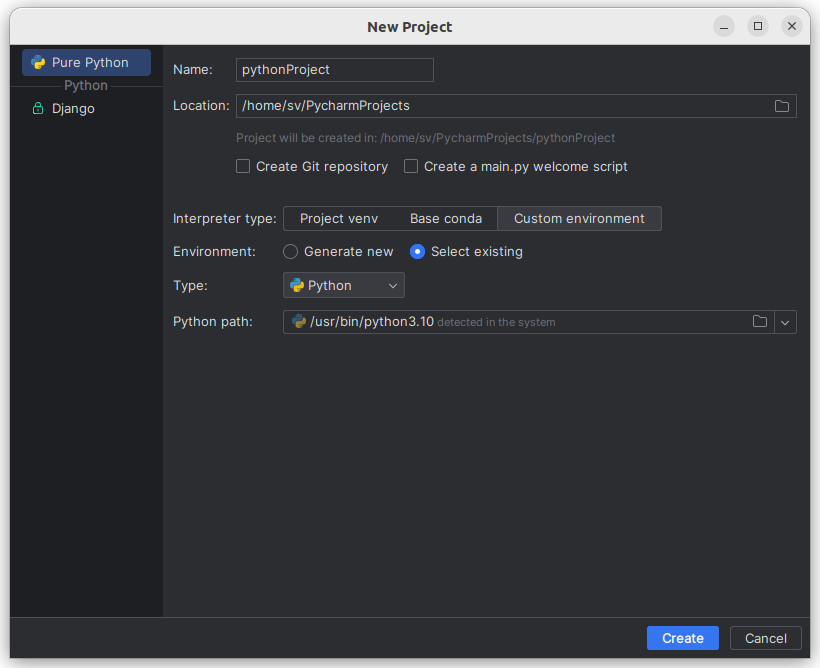
- In the left-hand pane of the Add Python Interpreter dialog, select Virtualenv Environment .
- The following actions depend on whether you want to create a new virtual environment or to use an existing one. New virtual environment
- Specify the location of the new virtual environment in the Location field, or click and browse for the desired location in your file system. The directory for the new virtual environment should be empty.
- Choose the base interpreter from the list, or click
and find the desired Python executable in your file system.
- Select the Inherit global site-packages checkbox if you want all packages installed in the global Python on your machine to be added to the virtual environment you’re going to create. This checkbox corresponds to the —system-site-packages option of the virtualenv tool.
Existing virtual environment
- Choose the desired interpreter from the list.
- If the desired interpreter is not on the list, click , and then browse for the desired Python executable (for example, venv/bin/python on macOS or venv\Scripts\python.exe on Windows).
The selected virtual environment will be reused for the current project.
If PyCharm displays the Invalid environment warning, it means that the specified Python binary cannot be found in the file system, or the Python version is not supported. Check the Python path and install a new version, if needed.
You can create as many virtual environments as required. To easily tell them from each other, use different names.
Use an existing interpreter
- Press Control+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and select Project | Python Interpreter .
- Expand the list of the available interpreters and click the Show All link. Alternatively, click the icon and select Show All .
Virtual environments are marked with .
- Select the target environment from the list and click OK to confirm your choice.
PyCharm can create a virtual environment for your project based on the project requirements.
Create a virtual environment using the project requirements
- Open any directory with your source files that contains the requirements.txt or setup.py file: select File | Open from the main menu and choose the directory.
- If no virtual environment has been created for this project, PyCharm suggests creating it:
- Keep the suggested options, or specify the environment location or base Python interpreter. Click OK to complete the task.
Once you click OK , PyCharm creates an environment and installs all the required packages. On the completion, see the notification popup:
Note that if you ignore a suggestion to create a virtual environment, PyCharm won’t create a Python interperter for your project. So, any time when you open a .py file, you’ll see the warning with the options for configuring a project interpreter:
This approach is particularly helpful when you want to upgrade a version of Python your environment is based on, for example, from 3.5 to 3.9. You can specify a new base interpreter and use requirements.txt to ensure all the needed packages are installed.
For any of the configured Python interpreters (but Docker-based), you can:
Once you have create a new virtual environment, you can reuse it for your other projects. Learn more how to setup an existing environment as a Python interpreter.
PyCharm Community. Основы работы
PyCharm – это одна из наиболее удобных сред разработки на языке Python. Существует в двух версиях:
- PyCharm Community – свободно-распространяемая версия с открытым исходным кодом.
- PyCharm Professional – проприетарная платная версия с триальным периодом.
В версии Community вы сможете программировать в основном на Python, в Professional – также на смежных языках (веб-программирование), использовать множество фреймворков.
В данном уроке мы рассмотрим создание проекта в PyCharm Community, первоначальную настройку среды и некоторые особенности работы в ней. Полную документацию смотрите на сайте разработчика данной IDE.
PyCharm не содержит самого интерпретатора Python, поэтому последний уже должен быть установлен в системе. В дистрибутивах Linux обычно это так и есть: пакет интерпретатора Python устанавливается вместе с операционной системой. Пользователи Windows, если еще не сделали этого, могут скачать интерпретатор Питона с официального сайта: https://www.python.org/downloads/
В Linux, распаковав установочный пакет PyCharm, вы найдете в нем файл Install***.txt , в котором описано, что надо сделать, чтобы установить и запустить среду разработки.
Процесс может выглядеть следующим образом:
- Перемещаем каталог с файлами среды разработки в директорию /opt командой
sudo mv pycharm-community-2022.3.3/ /opt/
cd /opt/pycharm-community-2022.3.3/bin/
При первом запуске PyCharm будет предложено принять пользовательское соглашение, также появится окно с вопросом отправлять или нет анонимные данные о том, как вы используете продукт.
Далее появится приветственное окно, в котором среди прочего предлагается создать новый проект.
При создании проекта появляется диалоговое окно, в котором следует указать адрес нового каталога (или согласиться с заданным по-умолчанию), создавать ли для проекта собственное виртуальное окружение.
Если вы только учитесь языку Питона, во избежание большого количества непонятных файлов в каталоге проекта, может быть целесообразнее выбрать пункт Previously configured interpreter . После этого через список Interpreter: выбрать системный интерпретатор ( System Interpreter ), указав его адрес.
Вернувшись в предыдущее окно, снимем флажок Create a main.py welcome script .
Далее запустится среда разработки, в ней будет открыт только что созданный проект.
Окно Tip of the Day и сообщение Code With Me следует закрыть, если они появятся. Возможно потребуется подождать, пока среда настроит проект. Сообщение об этом вы увидите в строке состояния.
Слева на панели Project управляют файлами проекта. На скрине выше в каталоге pythonProject нет ни одного файла. Чтобы создать файл, в котором будет написана программа на Python, кликнем по этой папке правой кнопкой мыши. В контекстном меню выбираем New → Python File .
После этого в центральной части среды разработки появится небольшое окно, в которое вписываем имя файла.
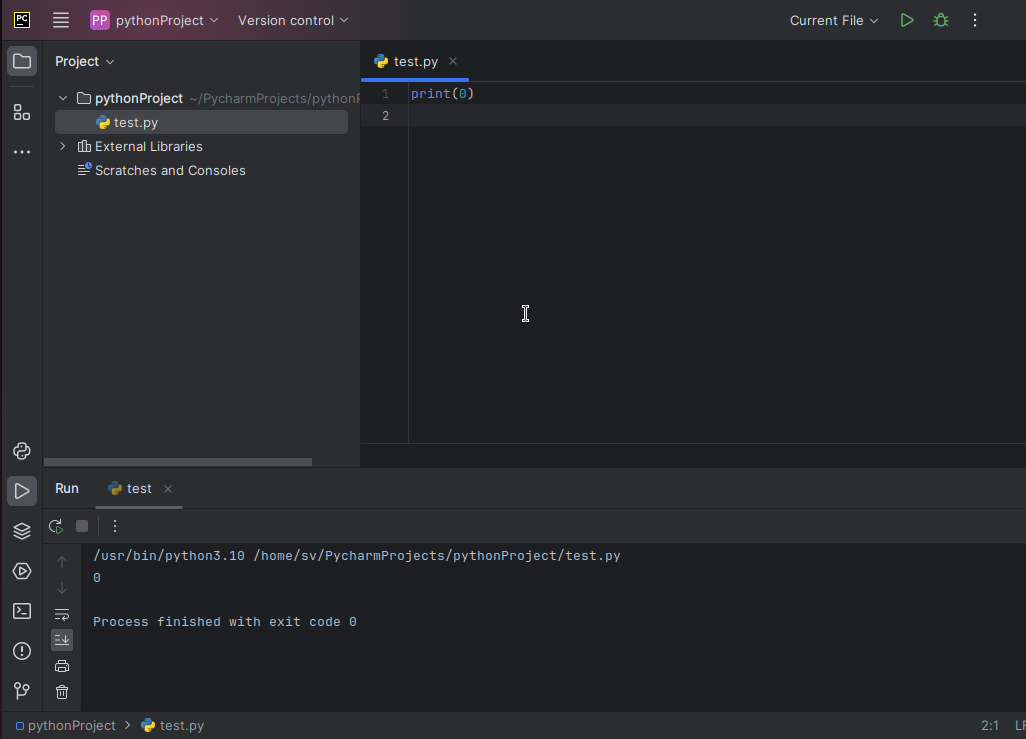
Нажав Enter , вы увидите файл на панели Project . Также он будет открыт в центральной части окна PyCharm.
После того, как исходный код написан, чтобы первый раз запустить программу, проще всего нажать Ctrl+Shift+F10 . Внизу раскроется вкладка Run , в которой отобразиться результат выполнения.
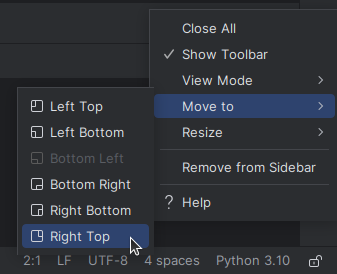
Иногда удобнее, чтобы панель выполнения программы открывалась не снизу, а, например, справа. В этом случае в настройках панели (справа значок похожий на гайку) следует выбрать Move to → Right Top .
После этого интерфейс среды разработки примет такой вид:
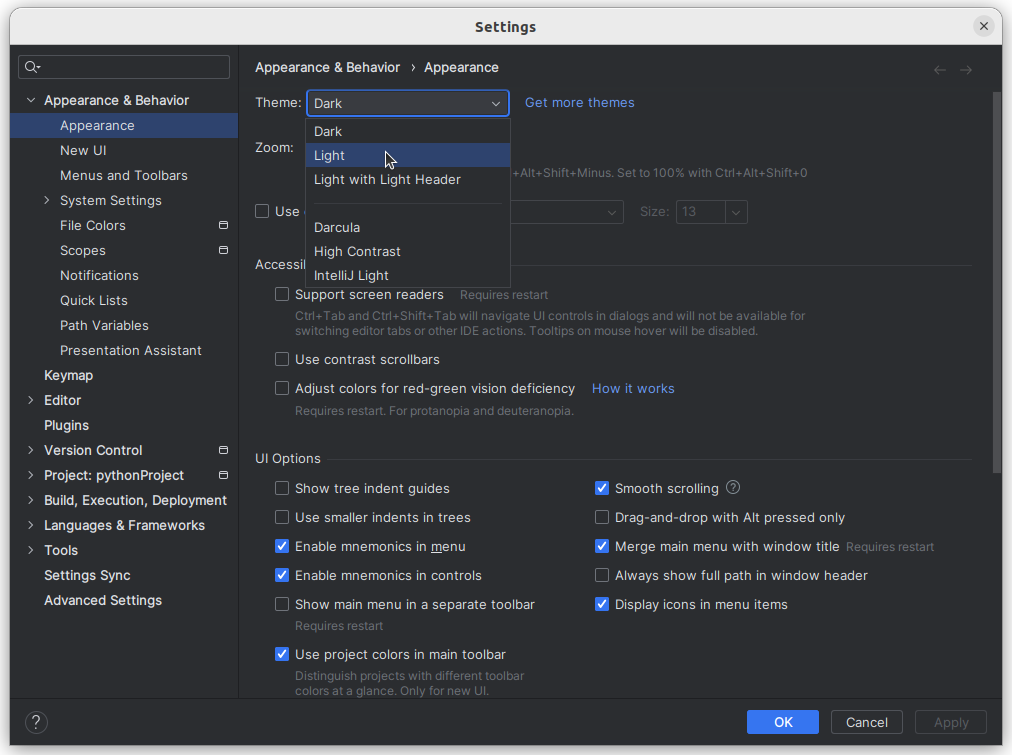
Внешний вид среды и множество других ее свойств, поведение настраиваются в окне Settings (меню File → Settings ). На скрине ниже показано, как изменить темную тему оформления PyCharm на светлую.
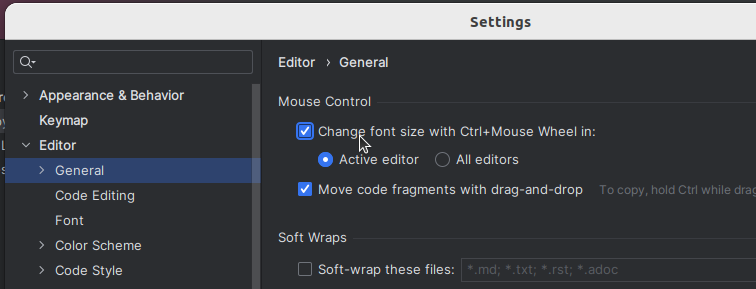
Бывает удобно менять размер шрифта в редакторе кода, зажав Ctrl и прокручивая колесо мыши. Чтобы воспользоваться этой возможностью в PyCharm, надо установить соответствующий флажок в разделе Editor → General окна настроек.
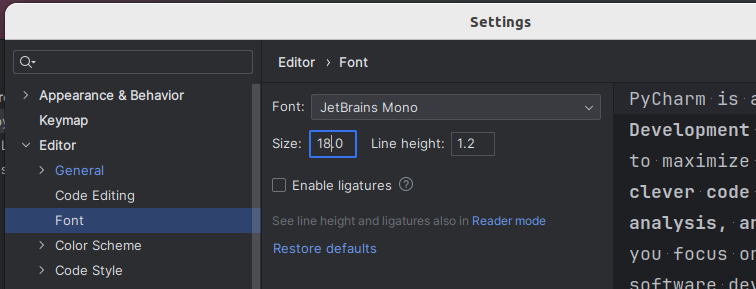
Изменить по-умолчанию заданный размер шрифта можно в разделе Editor → Font .
В PyCharm встроена интерактивная консоль, в которой выполняют небольшие фрагменты кода без создания файлов.
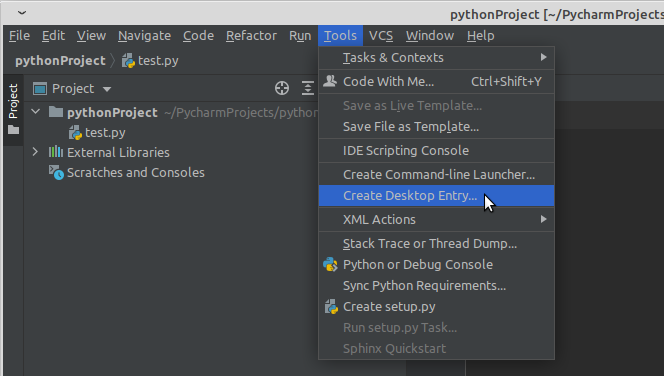
В дистрибутивах Linux обычно значок PyCharm не устанавливается в системное меню. И для последующего запуска среды вам снова надо будет обращаться к файлу pycharm.sh . Однако вы можете создать ярлык на приложение выполнив команду Tools → Create Desktop Entry… .
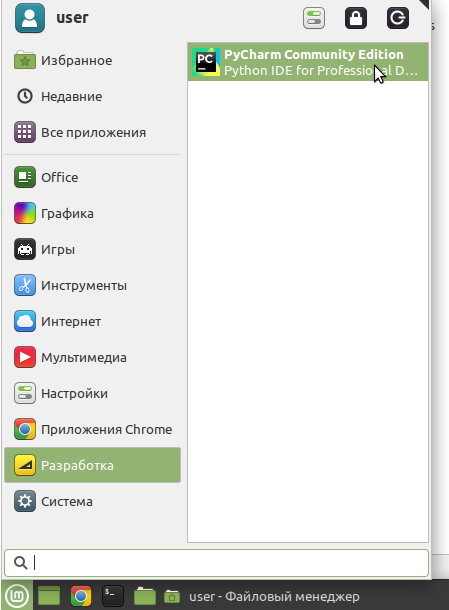
После этого в вашем системном меню должен появиться значок быстрого запуска. На скрине ниже показано, как это выглядит в Linux Mint.
Теперь рассмотрим некоторые особенности работы в PyCharm, точнее в его редакторе кода. Многие из них универсальны, характерны для других сред разработки. Так нажатие Ctrl + D дублирует строку, в которой находится курсор.
Ctrl + C копирует строку, в которой находится курсор, выделять строку при этом не надо. Потом копию можно вставить в любое место программы командой Ctrl + V .
Если надо скопировать или продублировать участок в несколько строк, его следует выделить.
Выделенный участок можно сдвинуть вправо (сделать вложенным), нажав Tab . Смещение влево (на внешний уровень) выполняется комбинацией Shift + Tab .
Поднять/опустить (поменять местами с предшествующей/нижестоящей) строку или выделенный участок можно с помощью сочетаний Shift + Ctrl + стрелка вверх или стрелка вниз клавиатуры.
Примеры решения и дополнительные уроки в pdf-версии курса
Python. Введение в программирование
Configure a system interpreter
To work with your Python code in PyCharm, you need to configure at least one interpreter. A system interpreter is the one that comes with your Python installation. You can use it solely for all Python scripts or take it as a base interpreter for Python virtual environments.
Configure a system interpreter
- Ensure that you have downloaded and installed Python on your computer. Installing Python on Windows from Microsoft Store If you are on Windows, you can download Python from the Microsoft Store and install it as a Python interpreter. Once the Python application is downloaded from the Microsoft Store, it becomes available in the list of the Python executables.
Note that interpreters added from the Microsoft Store installations come with some limitations. Because of restrictions on Microsoft Store apps, Python scripts may not have full write access to shared locations such as TEMP and the registry.
- Do one of the following:
- Click the Python Interpreter selector and choose Add New Interpreter .
- Press Control+Alt+S to open Settings and go to Project: | Python Interpreter . Click the Add Interpreter link next to the list of the available interpreters.
- Click the Python Interpreter selector and choose Interpreter Settings . Click the Add Interpreter link next to the list of the available interpreters.
- Select Add Local Interpreter .
- In the left-hand pane of the Add Python Interpreter dialog, select System Interpreter .
- In the Interpreter field, type the fully-qualified path to the required interpreter executable, or click and in the Select Python Interpreter dialog that opens, choose the desired Python executable.
You will need admin privileges to install, remove, and upgrade packages for the system interpreter. When attempting to install an interpreter package through an intention action, you might receive the following error message:
As prompted, consider using a virtual environment for your project.
- Click OK to complete the task.
For any of the configured Python interpreters (but Docker-based), you can: