- List all MAC addresses and their associated IP addresses in my local network (LAN)
- 12 Answers 12
- How to Find Network MAC Address in Linux System
- Approaches to Finding MAC Address in Linux
- 1. Find Linux System Mac Address Using IP Command
- 2. Find Linux System Mac Address Using Ifconfig Command
- Как узнать IP и MAC-адрес из командной строки в Linux
- команда ip
- Определение IP-адреса системы Linux
- Определение MAC-адреса системы Linux
- Сервер NTP и лучшие практики
- Debian vs. Ubuntu: все, что вам нужно знать, чтобы выбрать
- Как создать собственный дистрибутив Linux с помощью Yocto
List all MAC addresses and their associated IP addresses in my local network (LAN)
How can I list all MAC addresses and their associated IP addresses of the machines connected to my local network (LAN)?
it’s important to understand that as soon as you go throught a level 3 network layer equipement it will not be possible to get the MAC and ip behind this equipement
sudo tail -f /var/log/messages , then unplug and replug in the device you’re trying to find the MAC address of, or grep/read through messages to find the device.
12 Answers 12
You can use the Nmap utility for this. Nmap is a free network scanner utility.
Please substitute your network identifier and subnet mask.
How to find a network ID and subnet mask
bash~$ ip a 1: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: wlan0: mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000 link/ether c4:85:08:94:ee:9a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.3.66/24 brd 192.168.3.255 scope global wlan0 inet6 fe80::c685:8ff:fe94:ee9a/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever Here at point 2, I have the wlan0 device. It says inet 192.168.3.66/24 brd 192.168.3.255 scope global wlan0 , IP address: 192.168.3.66 , subnet mask: 24 . Network ID is 192.168.3.0 , just substitute the last number by 0.
Here is a little quote from the man page, nmap(1):
This option tells Nmap not to do a port scan after host discovery, and only print out the available hosts that responded to the scan. This is often known as a “ping scan”, but you can also request that traceroute and NSE host scripts be run. This is by default one step more intrusive than the list scan, and can often be used for the same purposes. It allows light reconnaissance of a target network without attracting much attention. Knowing how many hosts are up is more valuable to attackers than the list provided by a list scan of every single IP address and host name.
Systems administrators often find this option valuable as well. It can easily be used to count available machines on a network or monitor server availability. This is often called a ping sweep, and is more reliable than pinging the broadcast address because many hosts do not reply to broadcast queries.
The default host discovery done with -sn consists of an ICMP echo request, TCP SYN to port 443, TCP ACK to port 80, and an ICMP timestamp request by default. When executed by an unprivileged user, only SYN packets are sent (using a connect call) to ports 80 and 443 on the target. When a privileged user tries to scan targets on a local Ethernet network, ARP requests are used unless —send-ip was specified. The -sn option can be combined with any of the discovery probe types (the -P* options, excluding -Pn ) for greater flexibility. If any of those probe type and port number options are used, the default probes are overridden. When strict firewalls are in place between the source host running Nmap and the target network, using those advanced techniques is recommended. Otherwise hosts could be missed when the firewall drops probes or their responses.
In previous releases of Nmap, -sn was known as -sP .
How to Find Network MAC Address in Linux System
The term MAC Address is a derived abbreviation for Media Access Control Address. The network interface controller (NIC) uses the MAC address as its assigned unique identifier within an existing network segment.
To practically relate to or understand what a MAC address is, think of it as the postal or physical address to a house. The house in this case is the network interface controller (NIC).
There is a key difference between MAC address and IP address and therefore we should not confuse the two. MAC address identifies the device you are using since it is imprinted on the device hardware whereas IP address identifies the connection status among devices seeking to communicate on an existing/configured network.
The MAC address of any device is represented by a 12-digit hexadecimal number. Its display includes a colon or hyphen after every two MAC address digits for easy readability.
For instance, a MAC address can be represented in the following manner.
aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff or gg-hh-ii-jj-kk-ll
Approaches to Finding MAC Address in Linux
Depending on the number of network interfaces on your Linux machine like Wi-Fi built-in and Ethernet port, your computer can be associated with more than one MAC Address.
1. Find Linux System Mac Address Using IP Command
The ip command is part of the iproute2 package and can be used to display both the MAC address and IP address of your Linux-powered machine using either of the following commands.
$ ip addr or $ ip address or $ ip address show
Depending on the network adapter or interface present, we can see the availed MAC addresses. In the above screen capture, three distinct MAC addresses can be identified from the ip address command.
Another useful command is the ip link which only focuses on the MAC address and does not display the IP addresses.
2. Find Linux System Mac Address Using Ifconfig Command
The ifconfig command is another effective approach to identifying the MAC address of your Linux machine. We however need to install it first since it is a member of the net-tools package and not installed on Linux by default.
$ sudo apt install net-tools [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install net-tools [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/net-tools [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo pacman -S net-tools [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install net-tools [On OpenSUSE]
Once installed, run the ifconfig command to find the IP address and MAC address of your Linux system.
Different network interfaces or adapters showcase different MAC addresses as highlighted in the above screen capture.
We have successfully defined and understood how to get the MAC address(es) on our Linux machines.
Как узнать IP и MAC-адрес из командной строки в Linux
А В другой день, еще один учебник по командной строке. Сегодня давайте поговорим о важной сетевой команде в Linux, ip. Эта команда удобна для определения сетевых параметров компьютера Linux.
Он работает во всех дистрибутивах Linux, включая Ubuntu, Arch Linux, Debian, Fedora и т. Д.
команда ip
ip command — это очень мощная команда, которая заменила ныне устаревшие ifconfig команда, которая была частью пакета net-tools. Общий синтаксис команды следующий:
Где xx необходимо заменить одним из следующих, чтобы получить желаемый результат.
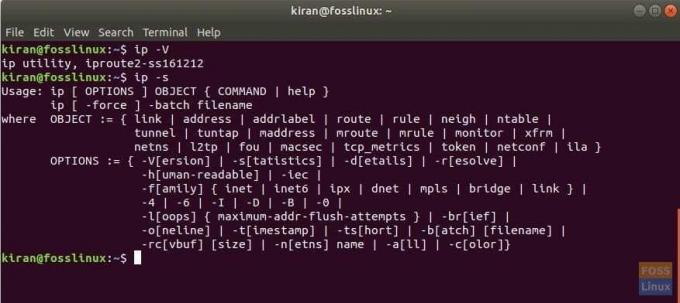
-V для отображения версии утилиты ip
-s для отображения дополнительной информации о команде
Определение IP-адреса системы Linux
Запустите «Терминал» и введите следующую команду, чтобы вывести список всех IP-адресов.
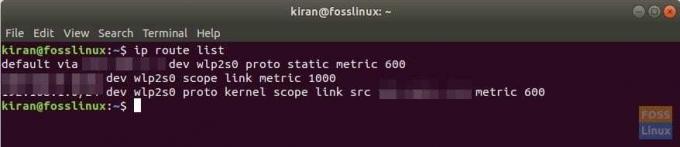
Он должен отображать все доступные IP-адреса, включая имена устройств. Если вас интересует только IP-адрес по умолчанию, который подключается к Интернету, используйте grep параметр для перечисления этого.
список IP-маршрутов | grep по умолчанию
В качестве альтернативы вы также можете использовать имя устройства, в частности, но для этого вы должны знать имена сетевых устройств. Использовать IP-адрес шоу команда:
1: вот:mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link / loopback 00: 00: 00: 00: 00: 00 brd 00: 00: 00: 00: 00: 00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 хост области действия lo valid_lft навсегда предпочтительный_lft навсегда inet6:: 1/128 хост области действия valid_lft навсегда предпочтительный_lft навсегда. 2: enp1s0: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast состояние DOWN группа по умолчанию qlen 1000 link / ether xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx. 3: wlp2s0: mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP группа по умолчанию qlen 1000 link / ether yyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyy inet 12121212121/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global dynamic wlp2s0 valid_lft 61791sec предпочтительный_lft 61791sec inet6 AB: AD: AK: AI / 64 область глобального временного динамического valid_lft 548176sec предпочтительный_lft 61403sec inet6 1: 2: 00: 33: 333/64 область видимости глобальный mngtmpaddr noprefixroute динамический valid_lft 548176sec предпочтительный_lft 548176sec inet6 3: 22: 33: 333/64 ссылка области действия valid_lft навсегда предпочтительный_lft навсегда
Обычно eth0 предназначен для подключения к сети Ethernet, и wlp2s0 для беспроводного подключения.
Например, используйте eth0:
Определение MAC-адреса системы Linux
MAC-адрес — еще один важный параметр сетевого устройства, включая оборудование вашего ПК или сервер. У каждого сетевого устройства ПК должен быть уникальный MAC-адрес.
Запустите Терминал и войдите в IP ссылка команда:
1: вот:mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000 link / loopback 00: 00: 00: 00: 00: 00 brd 00: 00: 00: 00: 00: 00. 2: enp1s0: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast состояние UP mode DEFAULT группа по умолчанию qlen 1000 link / ether XXXXXXXXXXXX brd ff: ff: ff: ff: ff: ff. 3: wlp2s0: mtu 1500 qdisc mq состояние DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000 link / ether YYYYYYYYYYYY brd ff: ff: ff: ff: ff: ff
Утилита ip должна перечислить несколько параметров устройства. Для каждого устройства в двух строках должны быть указаны состояние и характеристики канала. В первой строке суммируются текущее имя устройства, флаги, установленные на устройстве, максимальная единица передачи (MTU) и т. Д.
Вторая строка всегда должна указывать тип используемого канального уровня и текущий аппаратный адрес (MAC-адрес). В приведенном выше примере XXXXXXXXXXXX и YYYYYYYYYYY — это MAC-адрес двух используемых подключений LAN.
Сервер NTP и лучшие практики
NTP означает «Протокол сетевого времени». Это протокол, используемый устройствами, подключенными к Интернету, для синхронизации системного времени с привязкой ко времени. Есть несколько важных моментов, почему важно поддерживать точное время, а пр.
Debian vs. Ubuntu: все, что вам нужно знать, чтобы выбрать
CВступая в мир Linux, первая и самая сложная задача — решить, какой дистрибутив вы хотите использовать. Есть множество вариантов на выбор, каждый из которых имеет свои преимущества и недостатки. Два из самых популярных существующих дистрибутивов -.
Как создать собственный дистрибутив Linux с помощью Yocto
Знаете ли вы, что вы можете создать свой собственный дистрибутив Linux, имея некоторый опыт программирования? Создание вашего дистрибутива имеет преимущества, заключающиеся в том, что вы можете настроить каждый аспект в соответствии с вашими конкр.