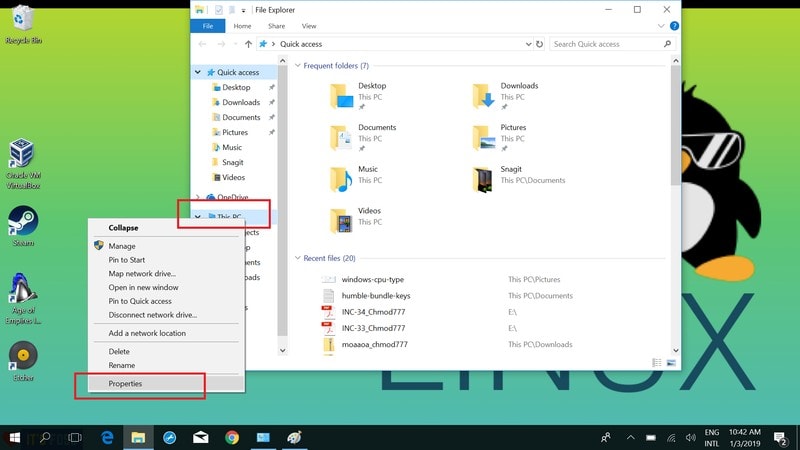
- How To Check If A Linux System Is 32 bit Or 64 Bit
- Check If A Linux System Is 32 bit Or 64 Bit
- Method 1 — Using uname command
- Method 2 — Using arch command
- Method 3 — Using file command
- Method 4 — Using lscpu command
- Method 5 — Using dpkg command
- Method 6 — Using getconf utility
- Method 7 — Using lshw utility
- Method 8 — Using HOSTTYPE environment variable
- Method 9 — Using /proc/cpuinfo
- Method 10
- Help us to help you:
- Как узнать разрядность Linux
- Как посмотреть разрядность Linux
- How To Know If You Have 32 Bit or 64 Bit Computer in Linux and Windows
- 32-bit vs 64-bit Systems: What’s the difference?
- How to know whether your computer is 32-bit or 64-bit on Linux
- How to tell if Ubuntu is 32- or 64-bit
- Checking if you have 32-bit or 64-bit ARM processor
How To Check If A Linux System Is 32 bit Or 64 Bit
We already knew how to check if a Linux system is physical or virtual machine. Now, it is time to find out if the installed Linux OS is either 32 bit or 64 bit. If your Linux system has GUI, it is really easy. Just navigate to System Settings -> Details, and there you go, you will know the architecture. In CLI based Linux systems, it is bit different. This guide will explain how to check if a Linux system is 32 bit or 64 bit. It is not that difficult. Read on.
Most Linux OS versions have ditched 32 bit support. So, this article may not useful for everyone out there. If you still have a good old hardware that supports 32 bit OS, this article will definitely be helpful.
Check If A Linux System Is 32 bit Or 64 Bit
There might be many ways to find out the architecture of your system. These are only the methods I am aware of now. I will keep update this guide if I find any other ways to do this. Bookmark this page, and keep visiting.
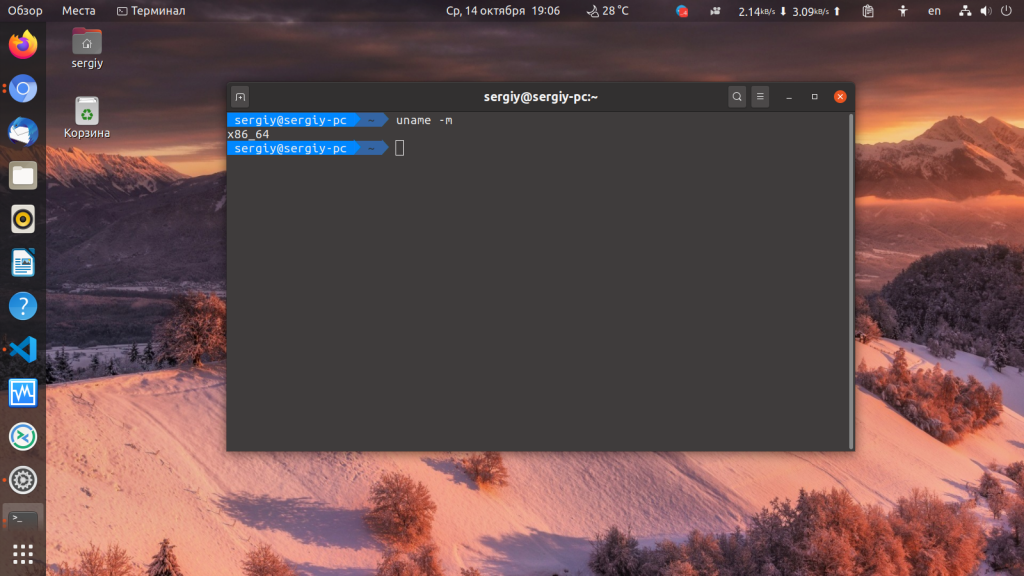
Method 1 — Using uname command
My preferred way to find out a Linux system’s architecture is using uname command. The uname is part of GNU coreutils that displays certain system information, such as hostname, Kernel version, Kernel release, OS version, and system’s architecture etc.
To find if your Linux system is 32 bit or 64 bit, just run the following command from the Terminal:
Sample output:
As you see above, my Linux OS architecture is 64 bit. If you want to display all details, just use ‘-a’ flag.
Sample output:
Linux sk 4.16.11-1-ARCH #1 SMP PREEMPT Tue May 22 21:40:27 UTC 2018 x86_64 GNU/Linux
This command not just displays the architecture, but all other details, such as Kernel name, version, system name etc.
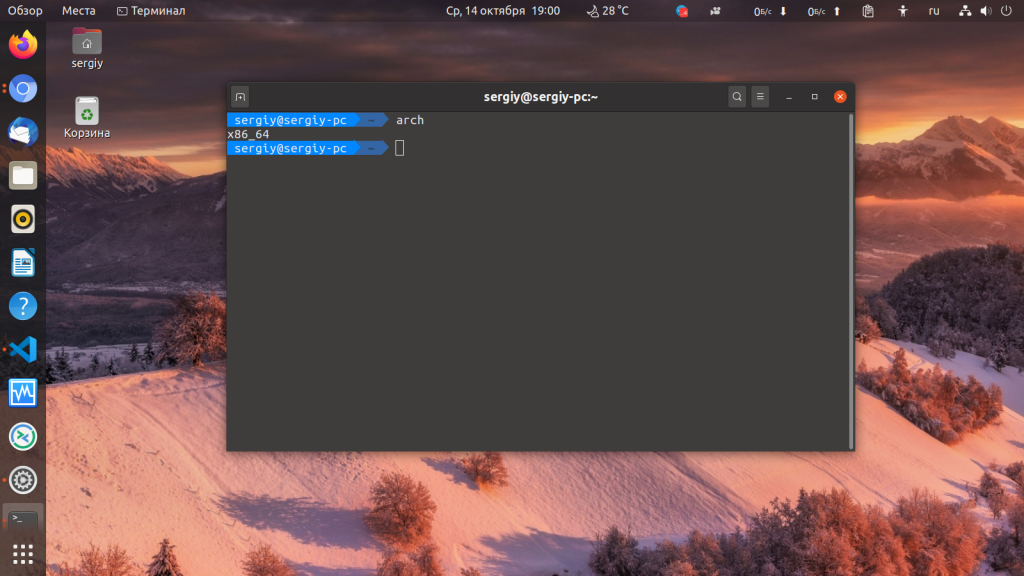
Method 2 — Using arch command
Yet another way to find out the system’s architecture is to use arch command. The arch command is same as ‘uname -m’ command which displays the machine hardware name.
Sample output from my machine:
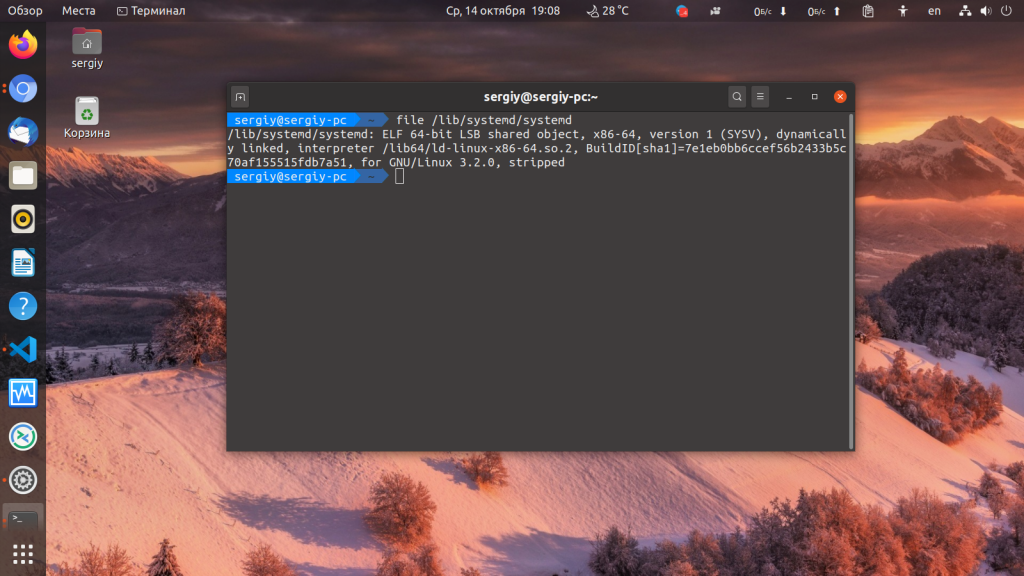
Method 3 — Using file command
You can also check your Linux system’s architecture using file command.
Or, use the following command on systems that use systemd.
Sample output:
/lib/systemd/systemd: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=8d3cb750275dc2f474dc7f049fdffb3a649b1d49, stripped, with debug_info
Also, you can use the following command to check your system’s architecture:
Sample output:
/usr/bin/id: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=ca513ae4d630324b1eadcd78122490248a27b8b6, stripped
Method 4 — Using lscpu command
The lscpu command is part of the util-linux package that displays the information about the CPU architecture.
To find if your Linux system is 32 bit or 64 bit, just run:
Sample output would be:
Architecture: x86_64 CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit Byte Order: Little Endian CPU(s): 4 On-line CPU(s) list: 0-3 Thread(s) per core: 2 Core(s) per socket: 2 Socket(s): 1 NUMA node(s): 1 Vendor ID: GenuineIntel CPU family: 6 Model: 42 Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i3-2350M CPU @ 2.30GHz Stepping: 7 CPU MHz: 799.890 CPU max MHz: 2300.0000 CPU min MHz: 800.0000 BogoMIPS: 4591.21 Virtualization: VT-x L1d cache: 32K L1i cache: 32K L2 cache: 256K L3 cache: 3072K NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-3 Flags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht tm pbe syscall nx rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon pebs bts rep_good nopl xtopology nonstop_tsc aperfmperf pni pclmulqdq dtes64 monitor ds_cpl vmx est tm2 ssse3 cx16 xtpr pdcm pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic popcnt tsc_deadline_timer xsave avx lahf_lm epb tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority ept vpid xsaveopt dtherm arat pln pts
Method 5 — Using dpkg command
The dpkg is a package manager that can be used to to install, build, remove and manage Debian packages. We can tell if our system OS is either 32 bit or 64 bit as shown below.
Sample output:
[For 64 bit OS] amd64 [For 32 bit OS] i386
This method will work only on Debian and other APT based systems such as Ubuntu, Linux Mint.
Method 6 — Using getconf utility
We can find our system’s architecture using getconf utility. It displays your system’s configuration variables and their values.
To find if the installed OS is 32 or 64 bit, just run:
Method 7 — Using lshw utility
The lshw utility can also be used to discover whether your Linux is 32 bit or 64 bit. It will display detailed information on the hardware configuration of a Linux system.
To display whether your Linux OS is either 32 or 64 bit, just run:
Sample output:
*-cpu product: Intel(R) Core(TM) i3-2350M CPU @ 2.30GHz vendor: Intel Corp. physical id: 2 bus info: cpu@0 width: 64 bits capabilities: fpu fpu_exception wp vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 syscall nx rdtscp x86-64 constant_tsc rep_good nopl xtopology nonstop_tsc pni pclmulqdq monitor ssse3 cx16 sse4_1 sse4_2 popcnt xsave avx hypervisor lahf_lm
Or, you can be more specific:
$ sudo lshw -c cpu | grep width
Method 8 — Using HOSTTYPE environment variable
The another way to find out your system’s OS architecture is using HOSTTYPE environment variable like below.
Sample output:
[64 bit system] x86_64 [32 bit system] i386
Method 9 — Using /proc/cpuinfo
We can find our system’s OS architecture from /proc/cpuinfo file.
$ sudo grep flags /proc/cpuinfo
Sample output:
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 syscall nx rdtscp lm constant_tsc rep_good nopl xtopology nonstop_tsc pni pclmulqdq monitor ssse3 cx16 sse4_1 sse4_2 popcnt xsave avx hypervisor lahf_lm
- lm flag means 64-bit (Long mode cpu)
- tm flag means 32-bit (Protected mode)
- rm flag means 16-bit CPU (Real Mode)
As you see in the output, I use 64 bit.
Method 10
Finally, you can also find your OS architecture type by looking into the installed packages and libraries on your system.
Sample output:
drwxr-xr-x 22 root root 4096 May 17 15:07 lib drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 May 17 15:10 lib64
Suggested read:
And, that’s all for now. I hope this helps. If you find our guides useful, please share them on your social, professional networks and support OSTechNix.
Thanks for stopping by!
Help us to help you:
Have a Good day!!
Как узнать разрядность Linux
Разрядность операционной системы определяет набор инструкций процессора, которые будут использоваться для работы с данными и памятью компьютера. Существует две самые популярные разрядности, это i386 или 32 битная разрядность и x86_64 или 64 битная разрядность. Первая уже устаревшая и поддерживает работу с не больше чем 4 гигабайта оперативной памяти.
Вторая же более современная и сейчас используется практически везде. Все современные процессоры поддерживают обе архитектуры, однако многие дистрибутивы Linux уже отказались от поддержки i386 в пользу x86_64. В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим как узнать разрядность Linux.
Как посмотреть разрядность Linux
Самый простой способ узнать разрядность операционной системы Linux — это воспользоваться утилитой arch. Она просто выводит разрядность и больше ничего:
Команда uname выводит архитектуру ядра Linux если передать ей опцию -m, архитектура ядра соответствует архитектуре системы, поэтому этот метод можно использовать:
Команда file позволяет просматривать информацию о файлах в файловой системе. Для исполняемых файлов отображается их архитектура. Если вы посмотрите архитектуру какого-либо важного системного файла, то узнаете и разрядность системы. Например:
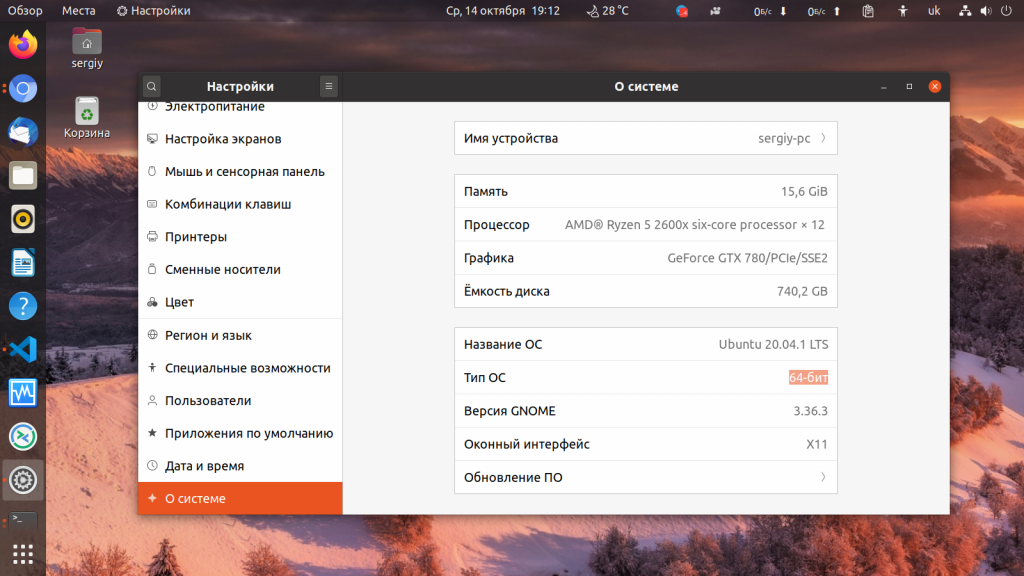
Вы можете узнать разрядность системы и в графическом интерфейсе. Например, в Ubuntu, для этого надо открыть утилиту Настройки, а затем раздел О системе:
Тут есть пункт Тип ОС, в котором указана разрядность системы. В данном случае, это 64 бит. Обратите внимание, что то, что система имеет архитектуру 64 бит не означает, что она не может запускать 32 битные программы и библиотеки. Эта архитектура сохраняет обратную совместимость и процессоры всё ещё могут выполнять 32 битные программы. Для этого достаточно установить пакет совместимости и необходимые 32 битные библиотеки. Но в обратную сторону это не работает, 32 битные системы не могут выполнять 64 битные программы. Во всяком случае теперь вы знаете как посмотреть разрядность системы Linux.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How To Know If You Have 32 Bit or 64 Bit Computer in Linux and Windows
Do I have a 32-bit system or 64-bit system? How to tell if my computer is 32-bit or 64-bit? How to find out if my system is 64 bit capable or not? Am I running 32-bit Ubuntu or 64-bit Ubuntu? Am I running 32-bit Ubuntu on a 64-bit CPU? Do I have 32- or 64-bit Windows?
These are some common questions that users often wonder about. Finding out whether a computer is 32-bit or 64-bit is fairly simple. Before we see how to tell whether your computer is 32-bit or 64-bit, first let’s see the difference between the two systems.
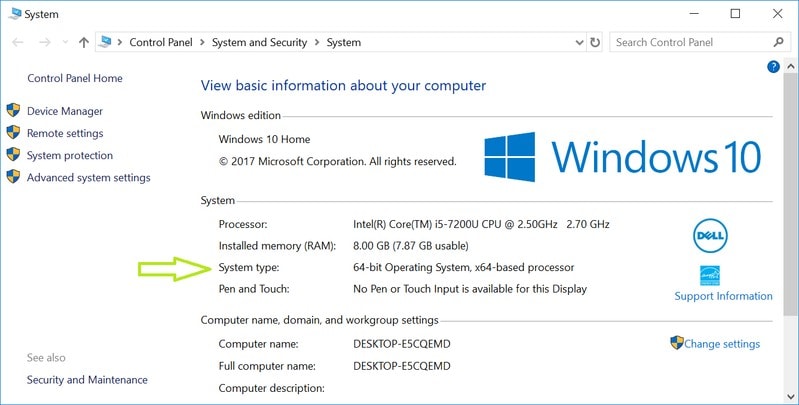
32-bit vs 64-bit Systems: What’s the difference?
You’ll see the system information on the next screen. In here, you should look for System Type.
As you can see in the image above, it says “64-bit Operating System, x64-based processor”.
Which means that I have the 64-bit Windows operating system installed on a 64-bit CPU.
That’s how it works on Windows. Now let me show you how to find out whether you have a 32-bit or 64-bit system on Linux.
How to know whether your computer is 32-bit or 64-bit on Linux
If you’re using Ubuntu or any other form of Linux, it’s still easy to find out whether your system is 32-bit or 64-bit. Mind that we’re talking about the processor here, not the OS itself.
Open a terminal and run the following command:
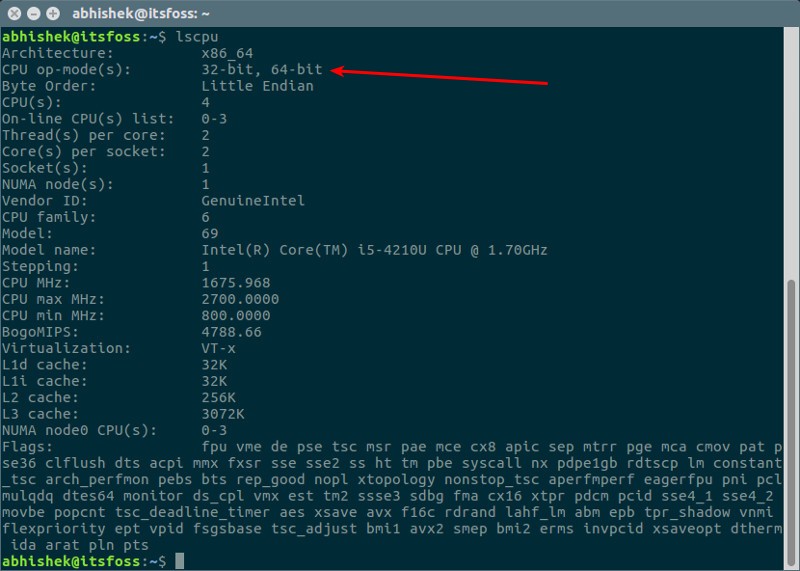
You should see a result like this:
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 4
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-3
Thread(s) per core: 2
Core(s) per socket: 2
Socket(s): 1
NUMA node(s): 1
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 69
Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4210U CPU @ 1.70GHz
Stepping: 1
CPU MHz: 1694.812
CPU max MHz: 2700.0000
CPU min MHz: 800.0000
BogoMIPS: 4788.66
Virtualization: VT-x
L1d cache: 32K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 256K
L3 cache: 3072K
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-3
Flags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht tm pbe syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon pebs bts rep_good nopl xtopology nonstop_tsc aperfmperf eagerfpu pni pclmulqdq dtes64 monitor ds_cpl vmx est tm2 ssse3 sdbg fma cx16 xtpr pdcm pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand lahf_lm abm epb tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority ept vpid fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid xsaveopt dtherm ida arat pln pts
You need to look for the line that starts with CPU op-mode. As you can see in the above result, my CPU can support 32-bit and 64-bit. This means I have a 64-bit CPU.
If you see only 32-bit under CPU op-mode, you have a 32-bit system.
How to tell if Ubuntu is 32- or 64-bit
So, we just saw how to find out whether our system is 32 bit or 64-bit. But how can you learn whether the Ubuntu you installed on your system is 32-bit or 64-bit?
I mean, a 64-bit system can support both 32-bit and 64-bit operating systems. So if you have a 64-bit system, it’s better (and recommended) to install a 64-bit OS.
To check whether the installed Ubuntu OS is 32-bit or 64-bit, we’ll use the same command we used in the previous section:
In the result, look for the line starting with Architecture. This will tell you the OS architecture.
In my case, I had x86_64 in the result, which means I have 64-bit Ubuntu installed.
Alternatively, you can use this command that we saw in an older article about finding your Ubuntu Unity version:
The result will be x86, i686, i386, x86_64, x64, etc. And you can easily work out the OS architecture from it.
You can also use the arch command:
The output will indicate whether your installed Linux system is 32-bit or 64-bit.
Checking if you have 32-bit or 64-bit ARM processor
As suggested by It’s FOSS reader, Hugh, the above suggestions may not work for ARM based devices like Raspberry Pi.
Here, you can install the inxi tool and get the necessary information:
The output may show something like this:
“System: Host: rpiB3 Kernel: 5.10.63-v7+ armv7l bits: 32 Console: tty 0 Distro: Raspbian GNU/Linux 10 (buster) ”As you can see, it says 32 bits, signifying it to be a 32-bit processor.
I hope this quick post helped you find out whether you have a 32-bit or 64-bit CPU and a 32-bit or 64-bit operating system.