- How to Restart Network Interfaces on Linux?
- How to Restart Network Interfaces on Debian-based Linux Distributions?
- Alternative Method: Restart the Network Interfaces on Debian/Ubuntu with GUI
- How to Restart Network Interfaces on RHEL-based Linux Distributions?
- How to Restart Network Interfaces on Arch-based Linux Distributions?
- How to Restart Network Interfaces on Slackware Linux Distribution?
- How to Restart Network Interfaces on Gentoo Linux Distribution?
- How to Restart Network Interfaces on Alpine Linux Distribution?
- Conclusion
- Как перезагрузить сеть в Ubuntu?
- Перезагрузка сети в Ubuntu с помощью командной строки
- Network manager service
- How to Restart Network on Ubuntu 20.04
- Restart network from GUI
- Restart network from the desktop
- Restart network from GNOME Settings
- Restart network from CLI
- Restart network manager service
- Restart network service using systemd
- Restart network using nmcli
- Restart network using ifup and ifdown
- Restart network using nmtui
- Restart network using IP command
- Final thoughts
- About the author
- Sidratul Muntaha
How to Restart Network Interfaces on Linux?
After making changes in the configuration of the network interfaces, it is recommended to restart the network interface. The network interface is the device responsible for connecting the network and the computer.
In this blog, different methods of restarting the network interface have been demonstrated for various Linux distributions, and the blog contents are:
- For Debian-based Linux Distributions
- For RHEL-based Linux Distributions
- For Arch-based Linux Distributions
- For Slackware Linux Distributions
- For Gentoo Linux Distributions
- For Alpine Linux Distributions
Let us start with the Ubuntu-based Distributions.
How to Restart Network Interfaces on Debian-based Linux Distributions?
In Debian-based Linux distributions, the network interfaces can be managed with the “NetworkManager”. To restart the Network interfaces on Linux, we will use the command:
$ sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager
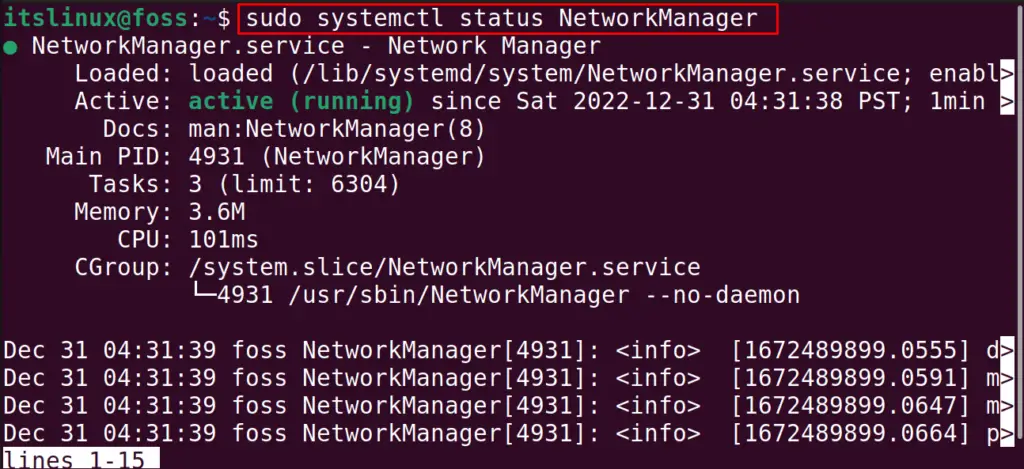
The service has been restarted, and the status of the NetworkManager can be verified using the command:
$ sudo systemctl status NetworkManager
The Network Manager is in active status.
Alternative Method: Restart the Network Interfaces on Debian/Ubuntu with GUI
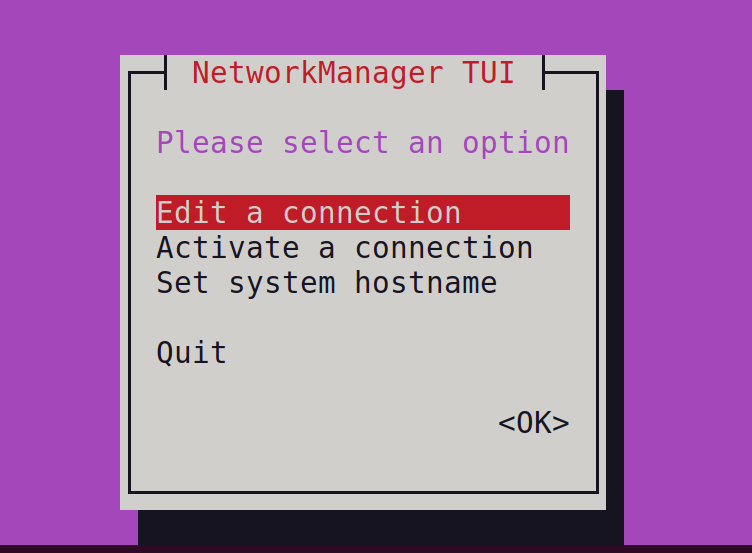
Another more convenient method is to restart the network interface with the GUI method. For it, launch the network manager with the nmtui command:
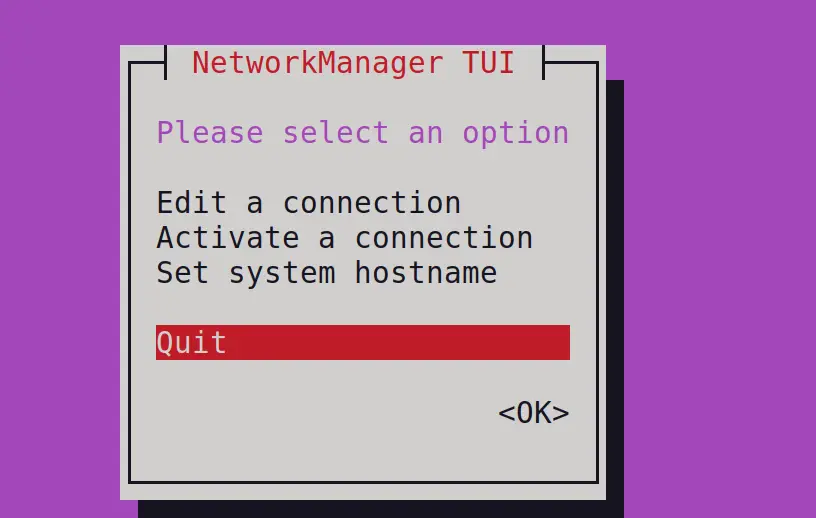
The application’s menu will be displayed on the screen:
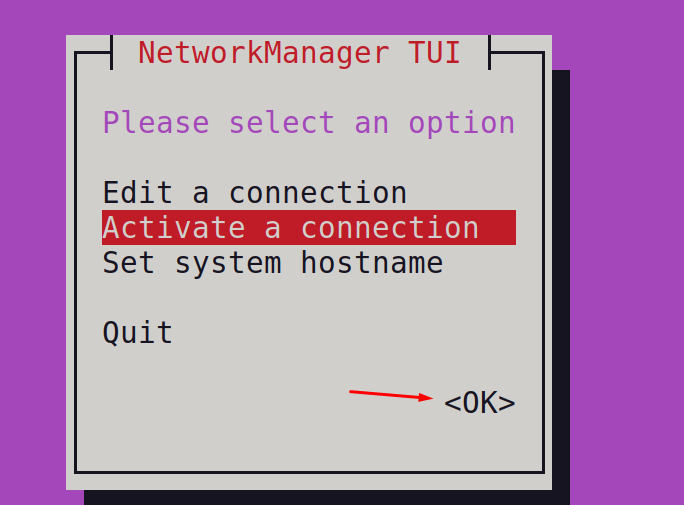
Choose “Activate a connection” and then click on “OK”:
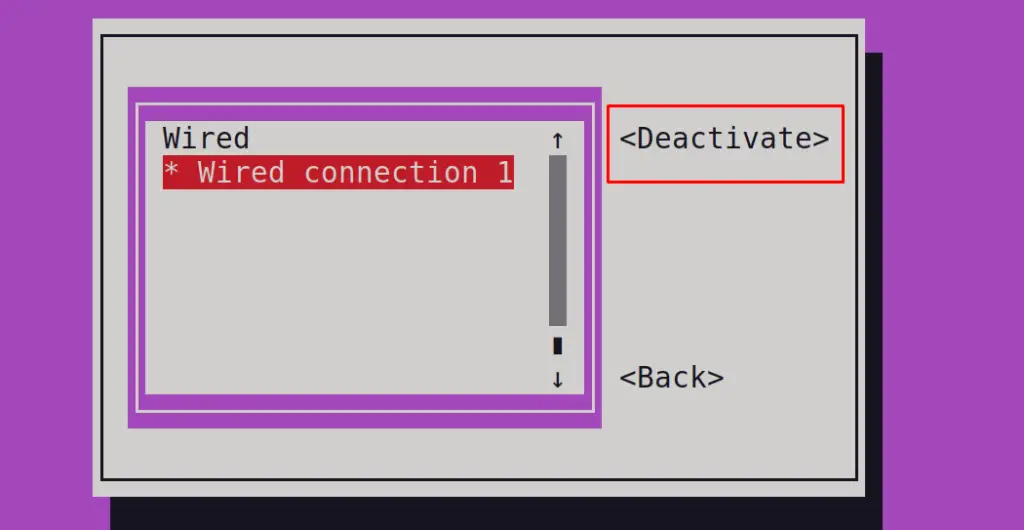
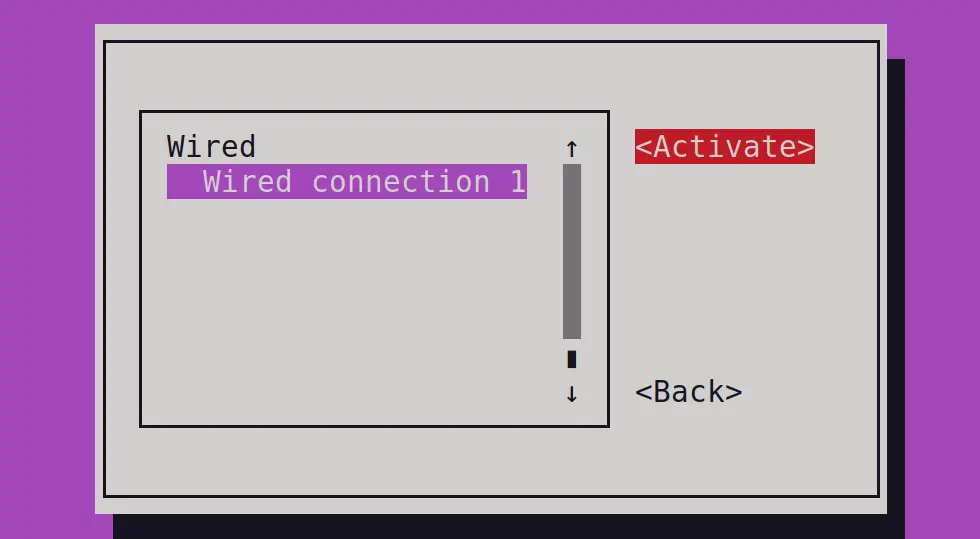
Now, select the interface and click on “Deactivate”:
Then, again click on “Activate” to restart the connection:
Then, close the nmtui tool by clicking on “Quit”:
The network interface has been restarted.
How to Restart Network Interfaces on RHEL-based Linux Distributions?
In the RHEL-based Linux distributions, including CentOS, the network interfaces can be managed either by using the nmcli command utility or the systemctl command utility. If the nmcli command is supposed to use, then execute the command to stop the service:
$ sudo nmcli networking off
After stopping the service, start it again with the command:
Similarly, the network manager can be restarted with using the systemctl command:
$ sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager.service
How to Restart Network Interfaces on Arch-based Linux Distributions?
In the Arch-based Linux distributions, including the Manjaro, the network interface can be restarted using the command:
$ sudo systemctl restart systemd-networkd.service
How to Restart Network Interfaces on Slackware Linux Distribution?
If the Slackware Linux distribution is being used, use the command:
$ sudo /etc/rc.d/rc.inet1 restart
How to Restart Network Interfaces on Gentoo Linux Distribution?
In Gentoo, the specific network interface can be restarted simultaneously. For example, we will restart the eth0 network interface, then use the command:
How to Restart Network Interfaces on Alpine Linux Distribution?
To restart the network interface in the Alpine, run the command:
$ service networking restart
By the above commands, users can restart the network interfaces on different Linux distributions.
Conclusion
To restart the network interface on Linux, we must be familiar with the network service backing up the system. For instance, to restart the network interfaces on Debian/Ubuntu-based Linux distributions, use the command “sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager”.
This post has also presented a list of commands to restart the network interfaces on various Linux distributions.
Как перезагрузить сеть в Ubuntu?
Вы используете систему на основе Ubuntu и просто не можете подключиться к своей сети? Вы будете удивлены, сколько проблем можно исправить простым перезапуском.
Перезагрузка сети в Ubuntu с помощью командной строки
Если вы используете Ubuntu Server Edition, вы уже находитесь в терминале. Если вы используете настольную версию, вы можете получить доступ к терминалу с помощью сочетания клавиш Ctrl + Alt + T в Ubuntu.
Теперь у вас есть несколько команд для перезагрузки сети в Ubuntu. Некоторые (или, возможно, большинство) упомянутые здесь команды должны быть применимы для перезапуска сети в Debian и других дистрибутивах Linux.
Network manager service
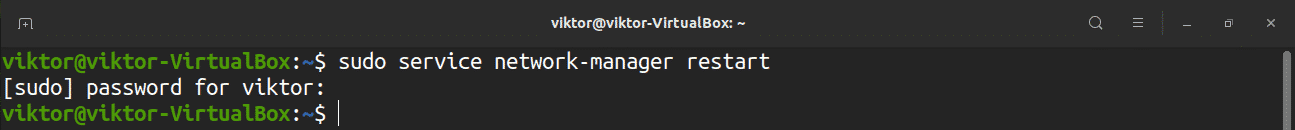
Это самый простой способ перезагрузить сеть с помощью командной строки. Это эквивалентно графическому способу сделать это (перезапускает службу Network-Manager).
sudo service network-manager restart
Значок сети должен на мгновение исчезнуть, а затем снова появиться.
systemd
Второй способ – это команда systemctl, которая гораздо более универсальна, чем service.
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager.service
Значок сети снова должен исчезнуть на мгновение. Чтобы проверить другие параметры systemctl, вы можете обратиться к его справочной странице.
nmcli
Это еще один инструмент для работы с сетями на компьютере с Linux. Это довольно мощный инструмент, и многие системные администраторы предпочитают его, поскольку он прост в использовании.
Этот метод состоит из двух шагов: выключить сеть, а затем снова включить ее.
sudo nmcli networking off
Сеть отключится и значок исчезнет. Чтобы включить его снова:
Вы можете проверить справочную страницу nmcli для большего количества вариантов.
ifup & ifdown
Эти команды управляют сетевым интерфейсом напрямую, изменяя его состояние на состояние, при котором он может или не может передавать и получать данные. Это одна из самых известных сетевых команд в Linux.
Чтобы закрыть все сетевые интерфейсы, используйте ifdown, а затем используйте ifup, чтобы снова включить все сетевые интерфейсы.
Хорошей практикой было бы объединить обе эти команды:
sudo ifdown -a && sudo ifup -a
nmtui
Это еще один метод, часто используемый системными администраторами. Это текстовое меню для управления сетями прямо в вашем терминале.
Это должно открыть следующее меню:
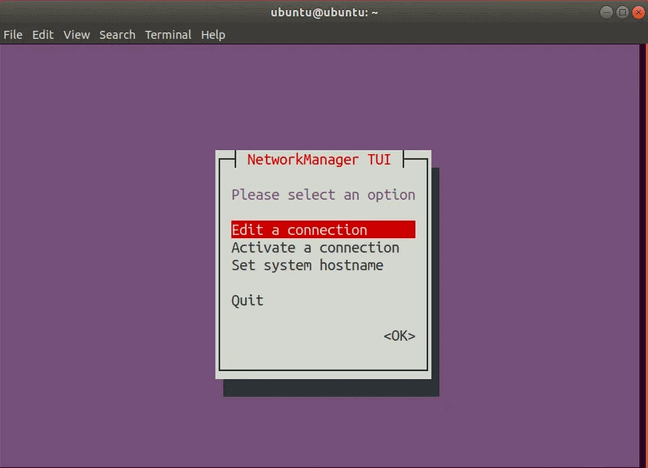
Обратите внимание, что в nmtui вы можете выбрать другой вариант, используя клавиши со стрелками вверх и вниз.
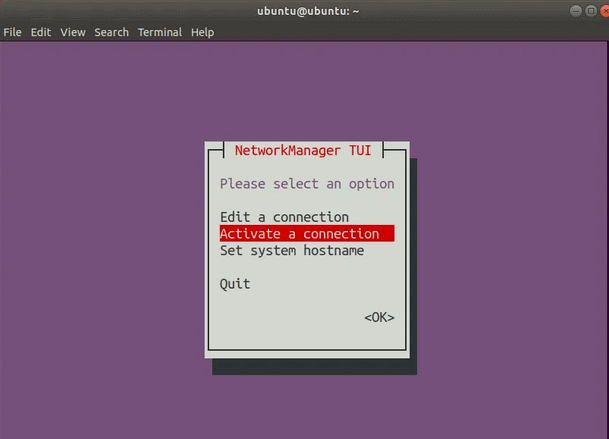
Выберите Activate a connection
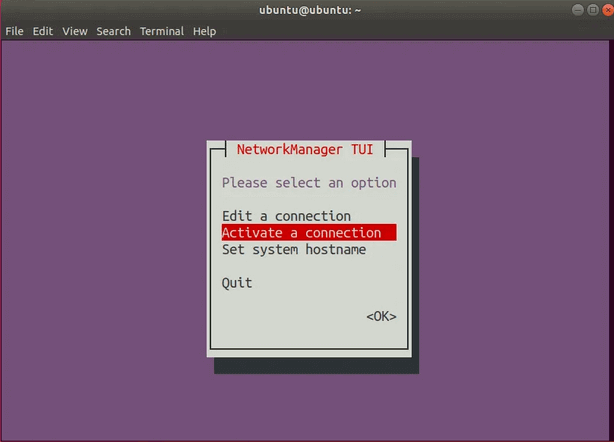
Нажмите Enter. Должно открыться меню с соединениями.
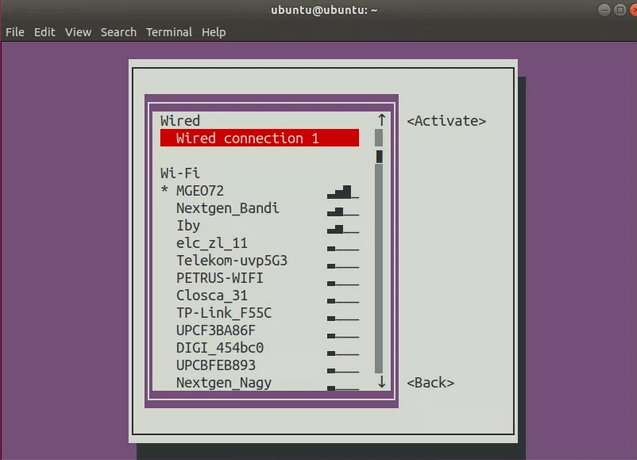
Далее, выберите сеть со звездочкой (*) рядом с ней и нажмите Enter. Это должно деактивировать это соединение.
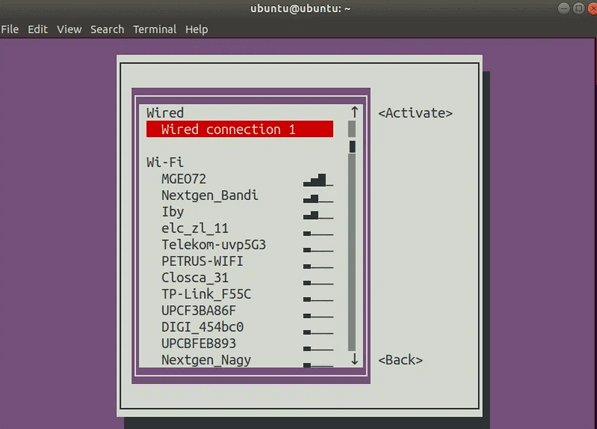
Выберите соединение, которое вы хотите активировать
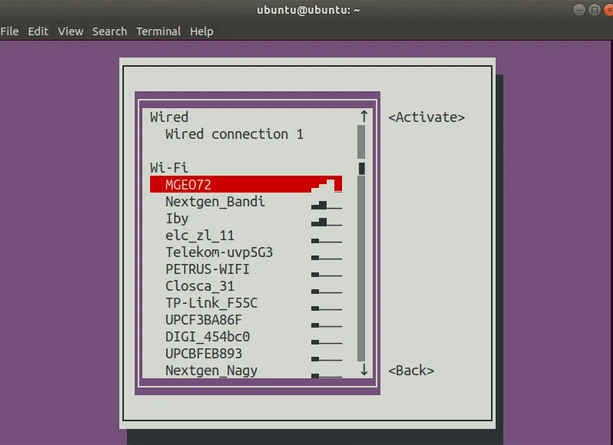
Нажмите Enter, соединение должно снова стать активным.
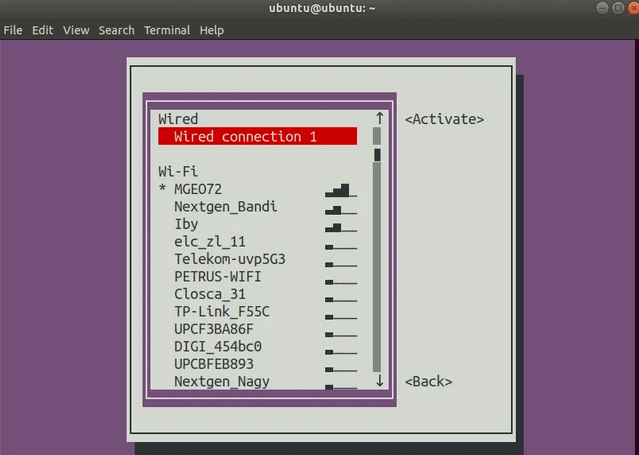
Дважды нажмите Tab чтобы выбрать пункт Back
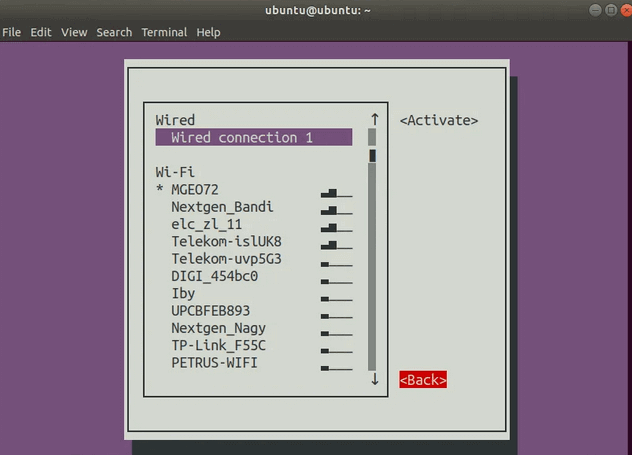
Нажмите Enter, это вернет вас в главное меню.
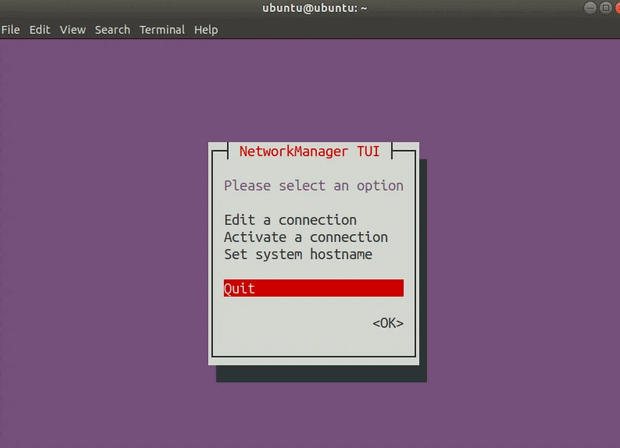
Это должно закрыть приложение и вернуть вас в ваш терминал.
Перезапуск сети в Ubuntu графически
Это, конечно, самый простой способ перезапустить сеть для пользователей настольных компьютеров Ubuntu. Если это не работает, вы можете сделать это из командной строки как было описано в предыдущем разделе.
Чтобы открыть окно управления сетью, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши значок сети в правом верхнем углу и найдите сетевое соединение, которое вы хотите перезагрузить, затем нажмите «Выключить».
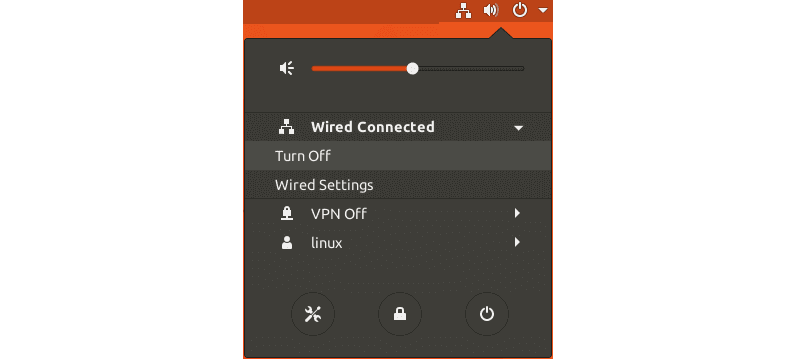
Значок сети исчезнет. Чтобы снова включить сеть, щелкните левой кнопкой мыши в правом верхнем углу стрелку вниз, найдите сетевой интерфейс и нажмите «Подключиться».
How to Restart Network on Ubuntu 20.04
There are various situations where you may have to restart the network on Ubuntu. It may be because the network settings were changed. It may be because the network connection is acting weird. Generally, whenever there’s a problem with the system, a common treatment is performing a reboot. However, if it’s a problem related to the network, then it’s possible to just restart the network.In this guide, check out how to restart the network on Ubuntu 20.04. There are various methods you can follow to restart the network on Ubuntu. It can be performed directly from the GUI or through the terminal. Depending on your preference, follow the one that suits you.
Restart network from GUI
In this section, I’ll be assuming that you’re using Ubuntu 20.04 with the default GNOME desktop.
Restart network from the desktop
Click on the top-right network icon on the screen.
Select the network connection and press “Turn Off”. It will disable the network connection.
To enable it again, go through the same process. This time, there’ll be a different option “Connect”. Click “Connect” to re-establish the network connection.
Restart network from GNOME Settings
You can also do this directly from the GNOME “Settings”.
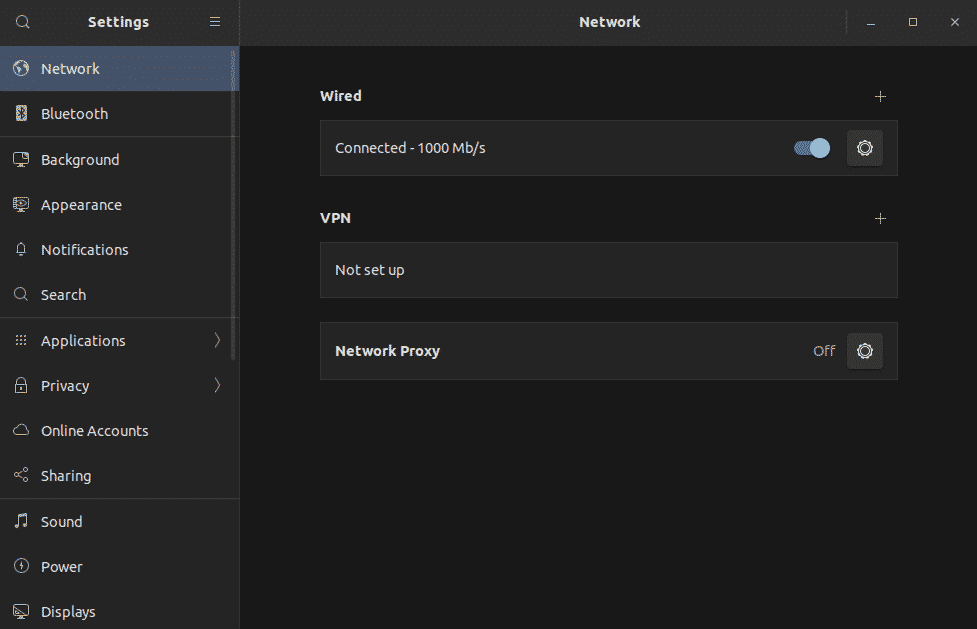
From the left panel, select “Network”.
Disable and enable the connected network(s).
Restart network from CLI
When working with the CLI, there are multiple ways of taking action. We can take action on the network manager service or use other tools like nmcli, ifup, nmtui, etc.
Restart network manager service
This is one of the easiest ways of restarting the network service. It’s equivalent to the graphical method demonstrated above.
Fire up a terminal and run the following command.
Restart network service using systemd
Systemd offers an array of system components to the system. Part of it is handling the services. The previous method is only an alternative one of this method. Systemd is directly told to restart the service rather than going through any hoops.
Restart network using nmcli
The nmcli tool is a powerful tool for managing the network connection on Linux machines. It’s a popular one among system admins because of its ease of use.
First, turn off the network connection.
Restart network using ifup and ifdown
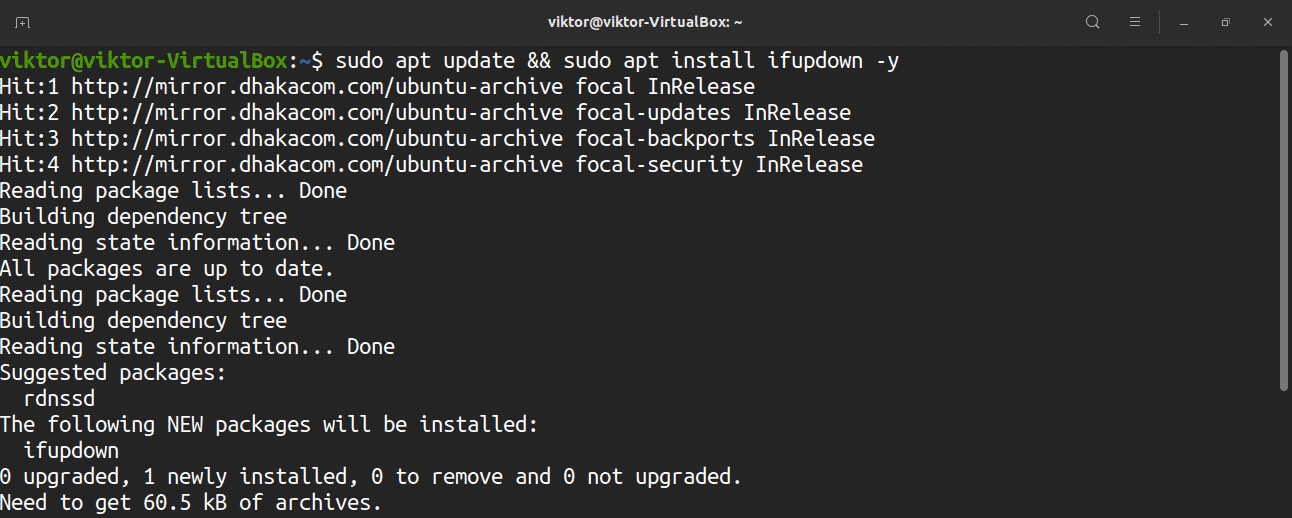
The ifup and ifdown commands handle a network interface directly. It’s one of the most basic networking commands on Linux. The ifdown command turns off all network interfaces and the ifup command turns them on.
The ifup and ifdown commands come with the ifupdown package. By default, it doesn’t come with Ubuntu. Thankfully, it’s directly available from the official Ubuntu repo. Install them right away.
Once the installation is complete, perform the network restart.
It’s a good practice to combine both commands in a single line.
Restart network using nmtui
The nmtui tool is yet another network management tool that’s widely popular among system admins. Unlike the other CLI tools, it offers an interactive way of managing network connections that’s similar to the GUI method.
In the case of Ubuntu 20.04, it comes by default. Launch the tool.
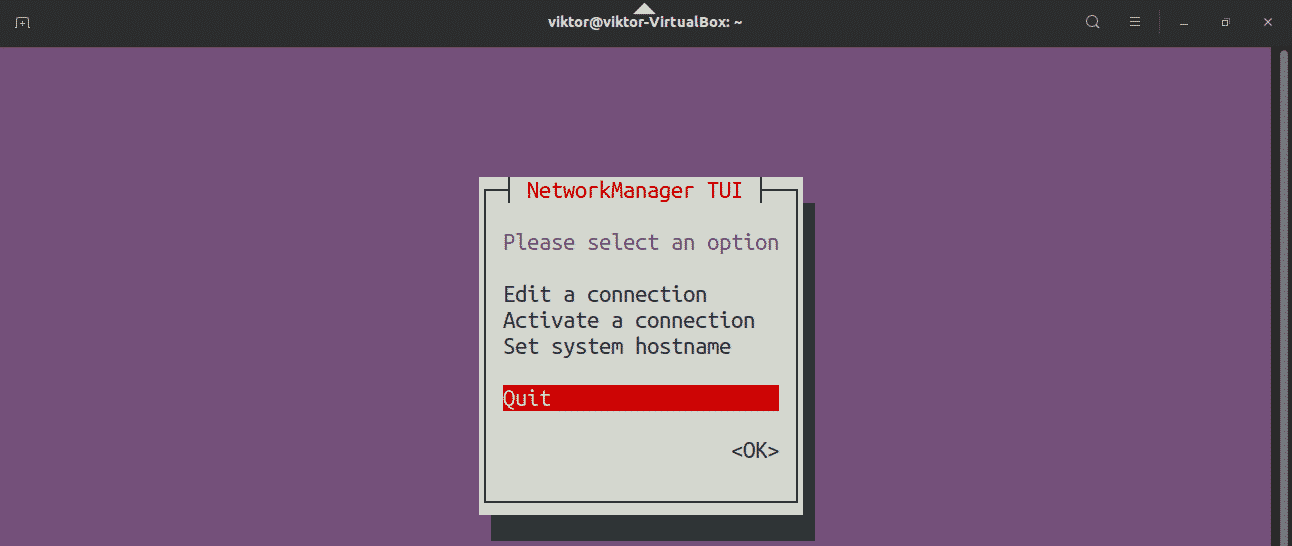
To navigate the tool, use the arrow keys. Select “Activate a connection”.
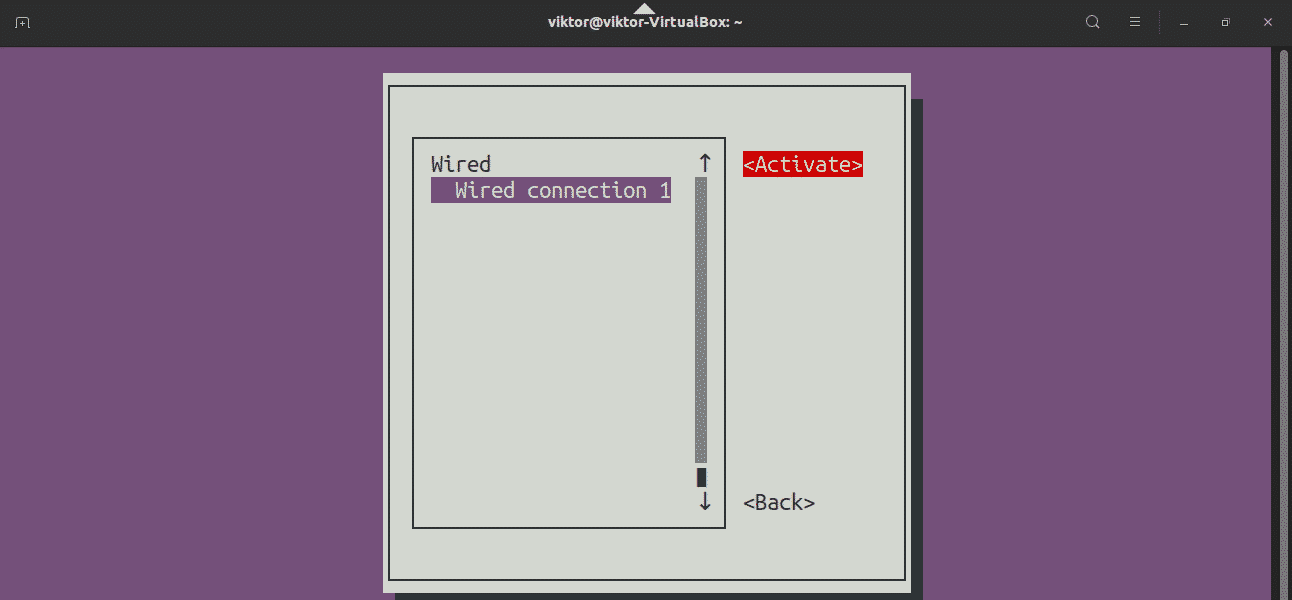
You’ll land on a screen with a list with all the network connections. Select the appropriate one and select “Deactivate”.
Once deactivated, activate the connection.
The network has been successfully restarted. Quit the application.
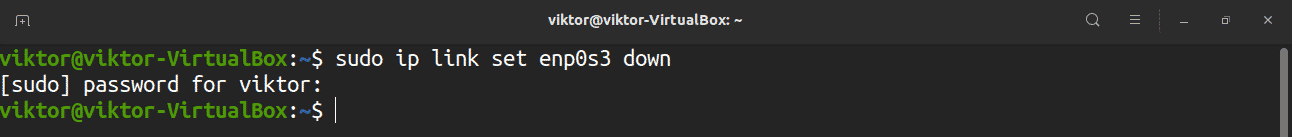
Restart network using IP command
The ip command is a powerful way of managing the network connections on Linux. It can be used for restarting the network connection. This method is applicable to any Linux distro.
To work with the ip command, first, we need to know the target network interface. Use the following command for the network interface.
In my case, the target network interface is enp0s3. Let’s restart the network.
Final thoughts
Restarting the network is a common solution to various network-related problems. If it didn’t yet solve the issue, then the next recommended action is restarting the system. If the problem persists, then it’s worth investigating further.
Interested in learning more about network configuration? Check out this guide on Ubuntu 20.04 network configuration.
About the author
Sidratul Muntaha
Student of CSE. I love Linux and playing with tech and gadgets. I use both Ubuntu and Linux Mint.