- Kali Linux
- Installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox: Quickest & Safest Way
- How to Install Kali Linux on VirtualBox
- 3. Install Kali Linux on Virtual Box
- How to install Kali Linux on VirtualBox using VDI
- Bonus: Free Kali Linux Guide
- Kali Linux Rolling Virtual & ARM Images
- VMware and VirtualBox Kali Rolling Images
- Kali Rolling ARM Images
- Kali Linux Support for NanoPi2 by FriendlyARM
Kali Linux
Kali Linux is a Debian-derived Linux distribution designed for digital forensics and penetration testing. it is an open source project that is maintained and funded by Offensive Security Ltd, a provider of world-class information security training and penetration testing services. It was developed by Mati Aharoni and Devon Kearns of Offensive Security through the rewrite of BackTrack, their previous forensics Linux distribution. Kali Linux is preinstalled with numerous penetration-testing programs, including nmap (a port scanner), Wireshark (a packet analyzer), John the Ripper (a password cracker), and Aircrack-ng (a software suite for penetration-testing wireless LANs). It is a supported platform of the Metasploit Project’s Metasploit Framework, a tool for developing and executing security exploits.
Special Features Available in Kali Linux:
- Kali Linux ISO of doom, the perfect hardware backdoor.
- Customizing and bending Kali Linux to your will using Kali Linux live build recipes.
- Mastering Kali Linux tool sets with Kali Metapackages.
- Kali Linux in the cloud – Kali Amazon EC2 images available.
- Kali Linux LUKS Full Disk Encryption (FDE).
- Nuking your Kali Linux hard disk with the Kali LUKS nuke option.
- Kali Linux running on Android through Linux Deploy.
- Kali Linux accessibility features, adding support for blind and visually impaired users.
- Kali Linux on a Raspberry Pi and a bunch of other interesting ARM devices.
- Kali Linux Live USB persistence with LUKS encryption.
- Kali Linux Evil Wireless Access Point recipe.
- Kali Linux EFI Boot Support.
Installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox: Quickest & Safest Way
Kali Linux is one of the best Linux distributions for hacking and security enthusiasts. Since it deals with a sensitive topic like hacking, it’s like a double-edged sword. We have discussed it in the past with a detailed Kali Linux review, so I am not going to bore you with the same stuff again. While you can install Kali Linux by replacing the existing operating system, using it via a virtual machine would be a better and safer option. With VirtualBox, you can use Kali Linux as a regular application in your Windows/Linux system. It’s almost the same as running VLC or a game in your system. Using Kali Linux in a virtual machine is also safe. Whatever you do inside Kali Linux will NOT impact your ‘host system’ (i.e. your original Windows or Linux operating system). Your actual operating system will be untouched and your data in the host system will be safe.
How to Install Kali Linux on VirtualBox
I’ll be using VirtualBox here. You may also install Kali Linux on VMWare. VirtualBox is a wonderful open source virtualization solution for anyone (professional or personal use). It is available free of cost. In this tutorial, we will talk about Kali Linux in particular but you can install almost any other OS using the ISO file or a pre-built virtual machine save file.
As I already mentioned, you can have either Windows or Linux installed as your host. But, in this case, I have Windows installed (don’t hate me!), where I try to install Kali Linux in VirtualBox step by step. And, the best part is that even if you use a Linux distro as your primary OS, the same steps will be applicable! Wondering how? Let’s see… As the file size is around 3 GB, you should either use the torrent option or download it using a download manager, whichever is fastest for you.
3. Install Kali Linux on Virtual Box
Once you have installed VirtualBox and downloaded the Kali Linux 7z image, you just need to add it to VirtualBox in order to make it work. Here’s how to add the VirtualBox image for Kali Linux: Step 1: Extract the downloaded 7z file. You can use 7zip for extracting the file.
The Kali Linux Virtual Machine storage will be on the same location as you extracted the 7z file. If you want a different location for the VM, you need to extract the 7z file to a location where you have sufficient storage available. I would never recommend the C: drive on Windows.
Step 2: Launch VirtualBox. You will notice an Add button – click on it. 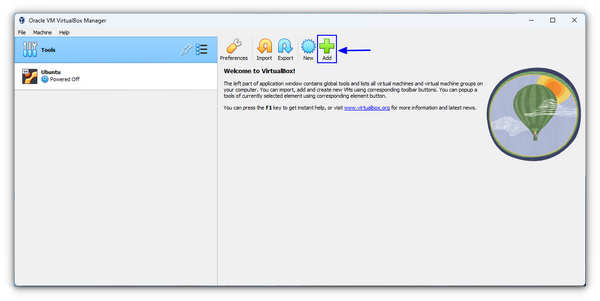
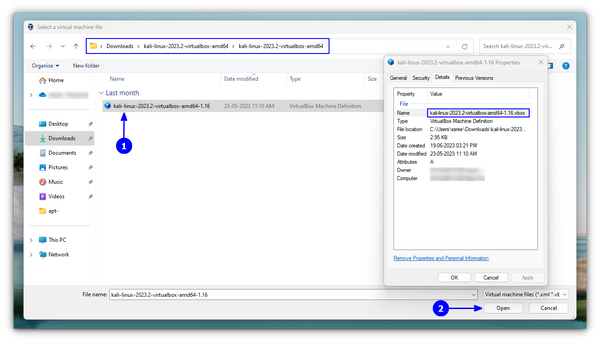
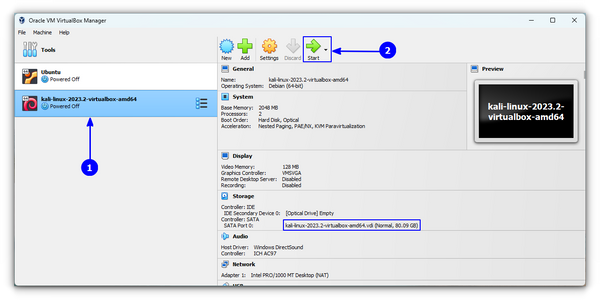
You might get an error at first for USB port 2.0 controller support, you can disable it to resolve it or just follow the on-screen instruction of installing an additional package to fix it. And, you are done!

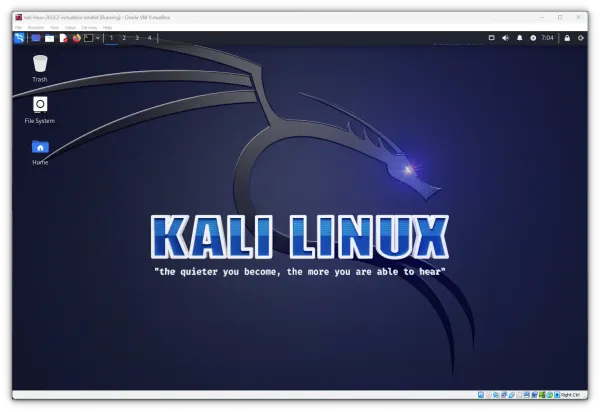
Of course, Kali Linux has a lot of useful tools in it for penetration testing – so you can explore those after installation.
Both Kali Linux and Ubuntu are Debian-based. If you face any issues or error with Kali Linux, you may follow the tutorials intended for Ubuntu or Debian on the internet.
Suggested Read 📖
How to install Kali Linux on VirtualBox using VDI
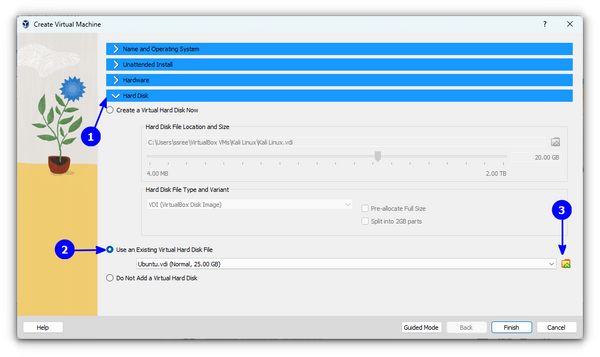
While you can always follow the instructions recommended above, there’s also another way of installing Kali Linux. You will notice a VDI file when extracting the 7z file of Kali Linux. You can use this VDI file to create a Kali Linux Virtual Machine. Open VirtualBox and select New option. 
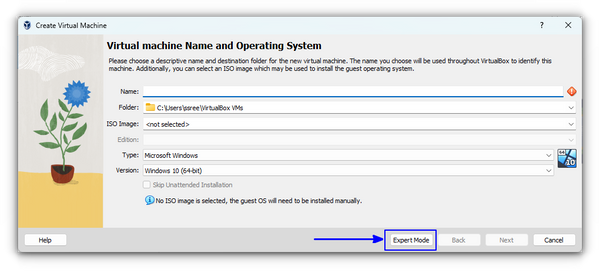
- Name of VM: Kali Linux
- Type: Linux
- Version: Debian 64-bit
- Under Hardware, Base Memory (RAM): 4GB (Recommended)
- Processors: More than one, as per availability
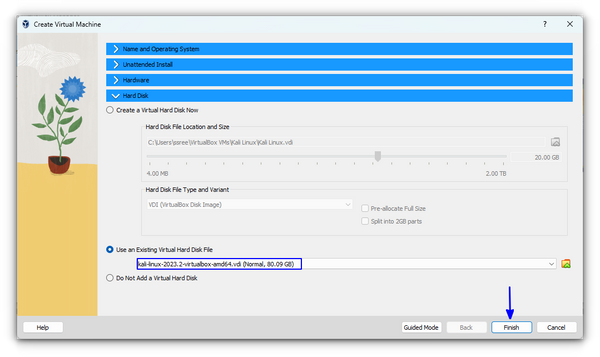
Now, for the Hard Disk part, select Use an existing Virtual Hard Disk File and browse for the extracted .vdi file of Kali Linux.
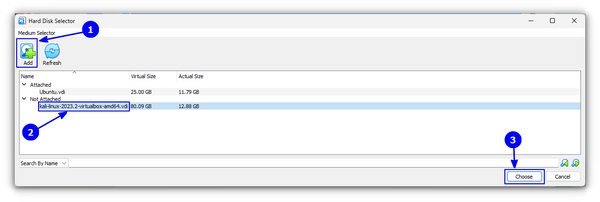
On the new dialog box, click on Add and search for the VDI file in resulting file browser. Once you find the file, select it and then press choose.
You can now press the Finish button.
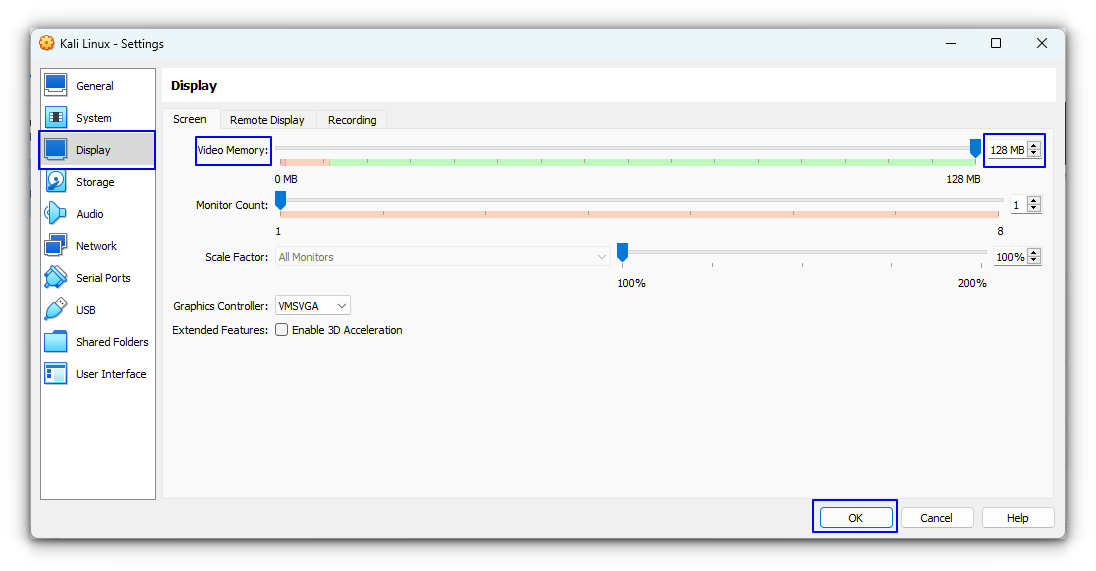
The VM created will have several settings like Display Memory, Network etc set to default. You should give the Display memory as 128 MB and choose to enable 3D acceleration.
You can now start the VM, and use username and password «kali» once asked to log in.
You can always install Kali Linux using the ISO file, which has same process like any other Linux distribution.
Bonus: Free Kali Linux Guide
If you are just starting with Kali Linux, it will be a good idea to know how to use Kali Linux.
Offensive Security, the company behind Kali Linux, has created courses that explains the basics of Kali Linux, configuration, and more. It also has a few chapters on penetration testing and security tools.
Basically, it has everything you need to get started with Kali Linux. And the best thing is that the course is available for free. You can go to the portal to explore courses and certification exams, and learn them there.
Let us know in the comments below if you face an issue or simply share your experience with Kali Linux on VirtualBox. If you are curious, you can also try Kali Linux on Windows using WSL.
Kali Linux Rolling Virtual & ARM Images
With the recent release of Kali Rolling 2016.1 completed, we’ve gone ahead and updated our custom Kali VMware, VirtualBox, and ARM images. Here’s a few news items and updates that we have regarding these images for those who prefer to get them pre-built.
VMware and VirtualBox Kali Rolling Images
The VMware and VirtualBox images were built from scratch and for the first time, installed together with packaged, native guest tools. What this means is that for both images, the guest tools are installed with apt commands and enjoy upgrades just like all other Kali packages. What this means for you is that you no longer need to recompile and update the guest tools manually anymore. These virtual images also have a weeks worth of updates compared to the 2016.1 ISO releases, including a fix for a Ralink wireless driver monitor mode regression in kernel 4.3.
Kali Rolling ARM Images
Our extensive collection of Kali ARM images have also undergone a massive overhaul – they have all been updated to Kali rolling and now enjoy the same range of updated tools as the regular distribution. This makes those little ARM devices just that more effective at their nefarious deeds! We’ve also updated our Github ARM build script repository, for those who want to build these images from scratch or modify the build process to their liking.
Kali Linux Support for NanoPi2 by FriendlyARM
One of the more exciting updates we have in our ARM hardware collection is a newcomer to the field, the NanoPi2, by FriendlyARM. It has an impressive Samsung Quad Core Cortex-A9 1.4 GHz CPU, 1GB DDR3 RAM, along with built in Wireless and Bluetooth. Whats more, its adoption of the Raspberry Pi’s GPIO pin header makes it compatible with both Raspberry Pi external GPIO modules and Arduino shield boards. We’re definitely excited about this newcomer to our collection and expect to see it adopted for various projects quite quickly.