- Tool Documentation:
- reaver Usage Example
- Packages and Binaries:
- reaver
- reaver on Kali Linux
- 2. Uninstall / Remove reaver package
- 3. Details of reaver package
- 4. References on Kali Linux
- 5. The same packages on other Linux Distributions
- Pixiewps, Reaver & Aircrack-ng Wireless Penetration Testing Tool Updates
- Pixiewps — Bruteforce WPS pins in seconds
- Aircrack-ng v1.2 RC2 Update
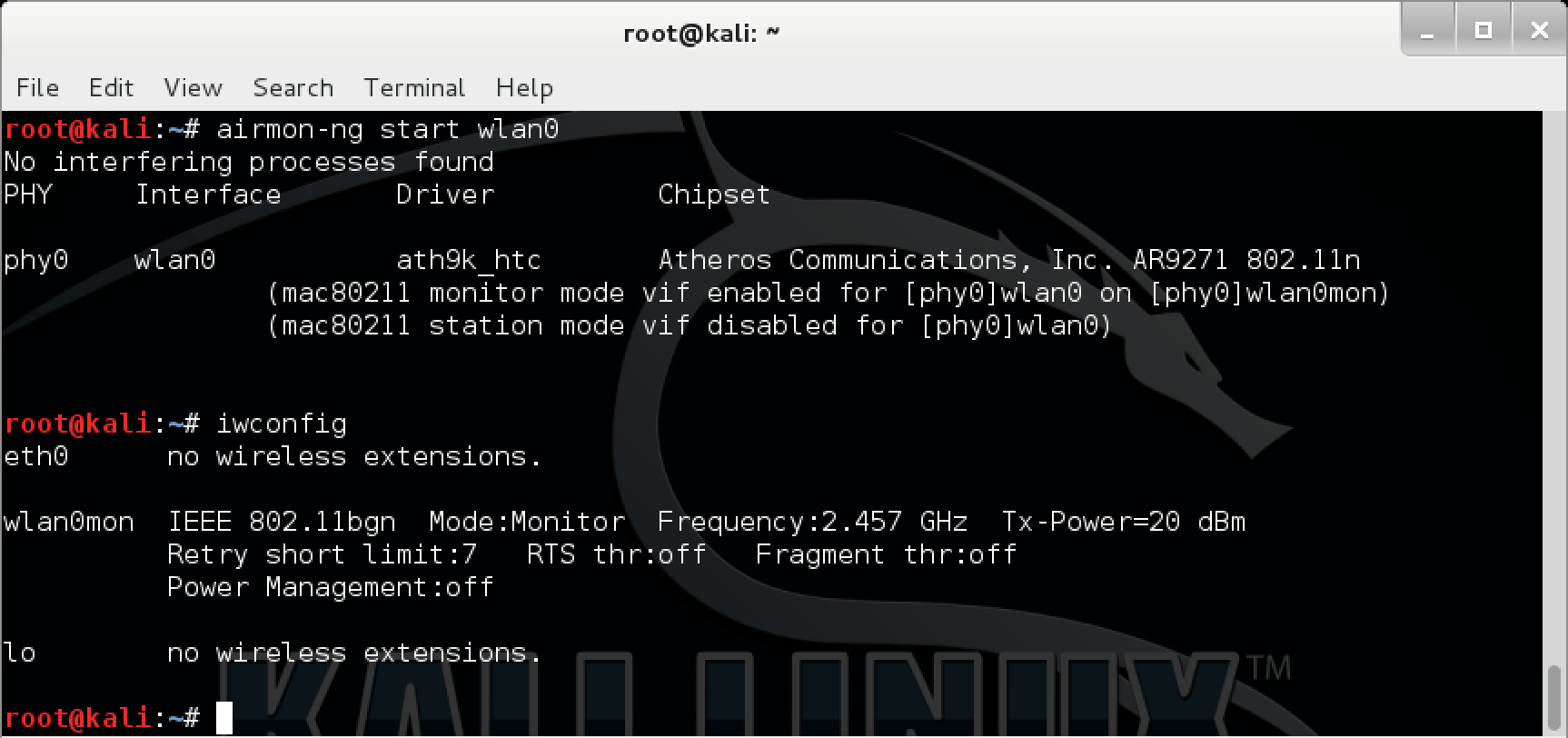
- Goodbye mon0, hello wlan0mon!
- More verbose airmon-ng output
- Updated Reaver WPS attack tool
- The Kali Community Rocks
- Stay fresh with Kali-Linux
Tool Documentation:
Scan for networks using the monitor mode interface ( -i wlan0mon ) on channel 6 ( -c 6 ), while ignoring frame checksum errors ( -C ):
[email protected]:~# wash -i wlan0mon -c 6 -C BSSID Ch dBm WPS Lck Vendor ESSID -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- E0:3F:49:6A:57:78 6 -73 1.0 No Unknown ASUS reaver Usage Example
Use the monitor mode interface ( -i mon0 ) to attack the access point ( -b E0:3F:49:6A:57:78 ), displaying verbose output ( -v ):
[email protected]:~# reaver -i wlan0mon -b E0:3F:49:6A:57:78 -v Reaver v1.6.5 WiFi Protected Setup Attack Tool Copyright (c) 2011, Tactical Network Solutions, Craig Heffner [email protected]> [+] Waiting for beacon from E0:3F:49:6A:57:78 [+] Associated with E0:3F:49:6A:57:78 (ESSID: ASUS) [+] Trying pin 12345670 Packages and Binaries:
reaver
Reaver performs a brute force attack against an access point’s WiFi Protected Setup pin number. Once the WPS pin is found, the WPA PSK can be recovered and alternately the AP’s wireless settings can be reconfigured.
Installed size: 1.62 MB
How to install: sudo apt install reaver
reaver
[email protected]:~# reaver -h Reaver v1.6.6 WiFi Protected Setup Attack Tool Copyright (c) 2011, Tactical Network Solutions, Craig Heffner [email protected]> Required Arguments: -i, --interface= Name of the monitor-mode interface to use -b, --bssid= BSSID of the target AP Optional Arguments: -m, --mac= MAC of the host system -e, --essid= ESSID of the target AP -c, --channel= Set the 802.11 channel for the interface (implies -f) -s, --session= Restore a previous session file -C, --exec= Execute the supplied command upon successful pin recovery -f, --fixed Disable channel hopping -5, --5ghz Use 5GHz 802.11 channels -v, --verbose Display non-critical warnings (-vv or -vvv for more) -q, --quiet Only display critical messages -h, --help Show help Advanced Options: -p, --pin= Use the specified pin (may be arbitrary string or 4/8 digit WPS pin) -d, --delay= Set the delay between pin attempts [1] -l, --lock-delay= Set the time to wait if the AP locks WPS pin attempts [60] -g, --max-attempts= Quit after num pin attempts -x, --fail-wait= Set the time to sleep after 10 unexpected failures [0] -r, --recurring-delay= Sleep for y seconds every x pin attempts -t, --timeout= Set the receive timeout period [10] -T, --m57-timeout= Set the M5/M7 timeout period [0.40] -A, --no-associate Do not associate with the AP (association must be done by another application) -N, --no-nacks Do not send NACK messages when out of order packets are received -S, --dh-small Use small DH keys to improve crack speed -L, --ignore-locks Ignore locked state reported by the target AP -E, --eap-terminate Terminate each WPS session with an EAP FAIL packet -J, --timeout-is-nack Treat timeout as NACK (DIR-300/320) -F, --ignore-fcs Ignore frame checksum errors -w, --win7 Mimic a Windows 7 registrar [False] -K, --pixie-dust Run pixiedust attack -Z Run pixiedust attack -O, --output-file= Write packets of interest into pcap file Example: reaver -i wlan0mon -b 00:90:4C:C1:AC:21 -vv wash
[email protected]:~# wash -h Wash v1.6.6 WiFi Protected Setup Scan Tool Copyright (c) 2011, Tactical Network Solutions, Craig Heffner Required Arguments: -i, --interface= Interface to capture packets on -f, --file [FILE1 FILE2 FILE3 . ] Read packets from capture files Optional Arguments: -c, --channel= Channel to listen on [auto] -n, --probes= Maximum number of probes to send to each AP in scan mode [15] -O, --output-file= Write packets of interest into pcap file -F, --ignore-fcs Ignore frame checksum errors -2, --2ghz Use 2.4GHz 802.11 channels -5, --5ghz Use 5GHz 802.11 channels -s, --scan Use scan mode -u, --survey Use survey mode [default] -a, --all Show all APs, even those without WPS -j, --json print extended WPS info as json -U, --utf8 Show UTF8 ESSID (does not sanitize ESSID, dangerous) -p, --progress Show percentage of crack progress -h, --help Show help Example: wash -i wlan0mon reaver on Kali Linux
This is a short guide on how to install reaver package:
2. Uninstall / Remove reaver package
Please follow the instructions below to uninstall reaver package:
3. Details of reaver package
Package: reaver
Version: 1.6.6-0kali1
Architecture: amd64
Maintainer: Kali Developers
Installed-Size: 1665
Depends: libc6 (>= 2.29), libpcap0.8 (>= 1.0.0), pixiewps, aircrack-ng
Homepage: https://github.com/t6x/reaver-wps-fork-t6x
Priority: optional
Section: net
Filename: pool/main/r/reaver/reaver_1.6.6-0kali1_amd64.deb
Size: 171680
SHA256: c494e4c8606f4faaba7c170b096cc0589ac0d0a04f8422d33328d2d53764d732
SHA1: 50fd8ac00cd4a611642ccc67cbcb89adc1fa5d08
MD5sum: 69bbb9baaefb529e07dbf23f5df7b97b
Description: brute force attack tool against Wifi Protected Setup PIN number
Reaver performs a brute force attack against an access point’s WiFi
Protected Setup pin number.
Once the WPS pin is found, the WPA PSK can be recovered and alternately
the AP’s wireless settings can be reconfigured.
Description-md5: c70abce7e7881fde1f10820ab1e59498
4. References on Kali Linux
5. The same packages on other Linux Distributions
reaver (1.4-2build1) Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (Bionic Beaver)
reaver (1.4-2) Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus)
reaver (1.6.5-1) Ubuntu 20.10 (Groovy Gorilla)
reaver (1.6.5-1) Ubuntu 21.10 (Impish Indri)
reaver (1.6.5-1) Ubuntu 22.04 LTS (Jammy Jellyfish)
reaver (1.6.5-1) Debian 10 (Buster)
Pixiewps, Reaver & Aircrack-ng Wireless Penetration Testing Tool Updates
A short while ago, we packaged and pushed out a few important wireless penetration testing tool updates for aircrack-ng, pixiewps and reaver into Kali’s repository. These new additions and updates are fairly significant, and may even change your wireless attack workflows. Here’s a short run-down of the updates and the changes they bring.
Pixiewps — Bruteforce WPS pins in seconds
Pixiewps is a tool used for offline brute forcing of WPS pins, while exploiting the low or non-existing entropy of some wireless access points also known as the pixie dust attack, discovered by Dominique Bongard (slides and video). The pixiewps tool (developed by wiire), was born out of the Kali forums, and the development of the tool can be tracked throughout an interesting forum post.
In the correct environment, pixiewps dramatically speeds up the WPS brute force attack time from what was taking up to 12 hours to a a few seconds. This new attack is mind numbing, and we are somewhat surprised that it hasn’t been discussed on a wider basis. Watch our following video closely, and see how we extract the WPA shared key of this EdiMAX wireless access point in a few seconds using updated versions of pixiewps and reaver, already packaged in Kali:
Aircrack-ng v1.2 RC2 Update
Aircrack-ng is the de facto penetration tool suite — essential for any wireless penetration tests or assessments. In this latest Aircrack-ng release, amongst the normal bug fixes and code improvements there has been a significant change to airmon-ng, the tool used to put wireless cards into monitor mode. Other new and notable features are that airtun-ng is now able to decrypt WPA as well as several new airodump-ng flags, such as — -wps and — -uptime.
Also notice the new naming convention of the wireless virtual interfaces — wlanXmon, as opposed to monX.
Goodbye mon0, hello wlan0mon!
For the latest few releases, the aircrack-ng suite had bundled with it airmon-zc, which uses an improved method of placing wireless cards into monitor mode, as well as more verbose output options. With the release of Aircrack-ng 1.2 RC2, airmon-zc has officially replaced the original aircrack-ng, as the new standard.
More verbose airmon-ng output
When things are going right, everything is great! However when this isn’t the case, and you need to troubleshoot wireless issues, you can now use a single command airmon-ng –verbose start wlan0 to gather all the relent information needed:
[email protected]:~# airmon-ng --verbose start wlan0 No interfering processes found No LSB modules are available. Distributor ID: Kali Description: Kali GNU/Linux 1.1.0 Release: 1.1.0 Codename: moto Linux kali 3.18.0-kali3-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 3.18.6-1~kali2 (2015-03-02) x86_64 GNU/Linux Detected VM using dmi_info This appears to be a VMware Virtual Machine If your system supports VT-d, it may be possible to use PCI devices If your system does not support VT-d, you can only use USB wifi cards K indicates driver is from 3.18.0-kali3-amd64 V indicates driver comes directly from the vendor, almost certainly a bad thing S indicates driver comes from the staging tree, these drivers are meant for reference not actual use, BEWARE ? indicates we do not know where the driver comes from. report this X[PHY]Interface Driver[Stack]-FirmwareRev Chipset Extended Info K[phy0]wlan0 rtl8187[mac80211]-N/A Realtek Semiconductor Corp. RTL8187 (mac80211 monitor mode vif enabled for [phy0]wlan0 on [phy0]wlan0mon) (mac80211 station mode vif disabled for [phy0]wlan0) [email protected]:~# You can find aircrack-ng’s full change log at the following address: aircrack-ng.org/doku.php?id=Main#changelog.
Updated Reaver WPS attack tool
The reaver project was originally developed by Craig Heffner, and the last release was 1.4. As the project seems to have been abandoned, several forks have cropped up — one belonging to a member of the Kali forums, t6_x, who has also integrated the pixiewps attack into a newly minted 1.5.2 release. This new version implements an array of improvements on the original version, and will hopefully be activity maintained by the community.
The Kali Community Rocks
One of the advantages of being a Kali forum moderator is that you get to witness the community grow and interact. Since the original pixiewps thread started by soxrok2212, it has received over 300 responses, bringing about the implementation of new ideas and updates to the tool. Watching this project emerge from a single forum post all the way to the release of the tool, and seeing the co-operation between the various tool developers while working to get interoperability between their tools was a real privilege.
Stay fresh with Kali-Linux
You don’t need to do anything special to get this awesome tool chain, just keep your Kali-Linux up-to-date:
Happy penetration testing!