- How To Start, Stop, Restart Networking On Linux?
- Get Status Of Network Service
- Debian, Ubuntu, Kali
- Fedora, CentOS
- Stop Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
- Fedora,CentOS
- Start Network
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
- Fedora,CentOS
- Restart Network
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
- Fedora,CentOS
- How to restart network interfaces on Linux
- What is a network interface?
- How to list network interfaces on Linux
- 1. The ifconfig command
- Restarting, Starting, Stopping, Checking the Status of the Network Service in Linux
- Network Operations
- Stop Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- Start Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- Status Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- Restart Network
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- How to restart network services in Linux
- Get network Service Status
- For latest (Ubuntu/Debian/Mint)
- For CentOS 8 / Fedora
- Stop Network Services
- For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
- For CentOS 8/Fedora
- Start Network Service
- For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
- For CentOS 8/Fedora
- Restart Network Service
- For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
- For CentOS 8/Fedora
- Conclusion
- Fix Wired Network interface in Kali linux
- Enabling Interface Management
- Restart Network Manager
How To Start, Stop, Restart Networking On Linux?
I have changed my network configuration and want to restart to make changes effective. Or there are some problems with my network and I think restarting it will solve my problems. Here we will look at how to restart networking service in various network distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, CentOS.
Get Status Of Network Service
We will get status of network with the following command.
Debian, Ubuntu, Kali
For deb based distributions we will use init.d system. We will provide status option to the networking script.
$ /etc/init.d/networking statusAs we cab see that networking service is active from given date. Its PID is 897 .
Fedora, CentOS
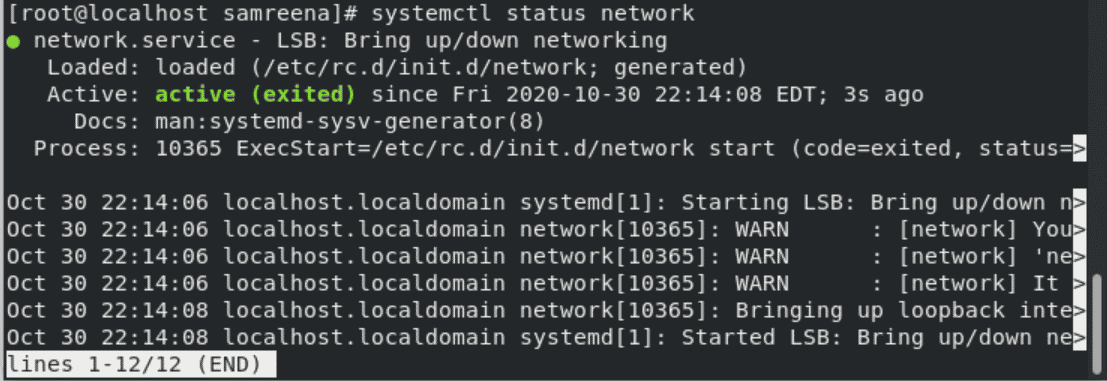
For distributions like CentOS, RedHat, Fedora we will use systemctl command. We will provide the options status and network which is the networking service.
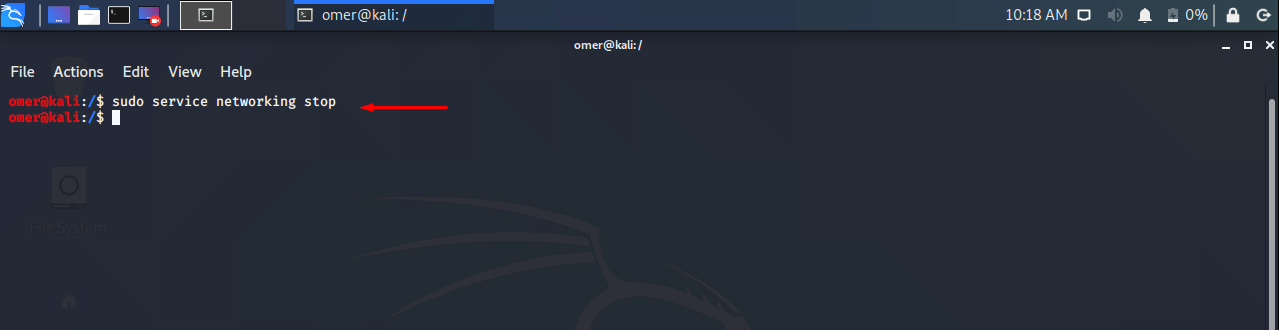
Stop Network Service
We can stop network like below. Bu keep in mind for remote connection it can be create problems with ssh
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
We will use stop option with networking command in order to stop network services in Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc.
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking stopFedora,CentOS
We will use systemctl again with stop option which will stop network services. We also require root privileges that will beget with sudo command.
$ sudo systemctl stop networkStart Network
We can start network like below.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
We will provide start option in order to start network services in deb based distributions.
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking startFedora,CentOS
We will use start network option in order to start network services in rpm based distributions.
$ sudo systemctl start networkRestart Network
Now we can restart our network or network services.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali
$ /etc/init.d/networking restartFedora,CentOS
$ systemctl restart networkHow to restart network interfaces on Linux
O nce you make changes in the network interface, they affect the network services manager of your system. To enable the system or machine to connect to the network, one needs to restart the network interface to apply the changes without rebooting your server.
This article will guide you on restarting the network interface in various Linux distributions.
Note: When running SSH/ VNC or other remote-based sessions, you should take precautions since restarting the network interface or service can result in network disconnectivity, resulting in connection loss.
We will handle the following topics.
What is a network interface?
A network interface refers to the point of connection between a computer and the network. It can be either software (especially with Virtual machines) or a hardware component. When dealing with network interfaces, there is one term that you will likely come across – NIC (Network Interface Card).
A Network Interface Card is a circuit board chip inserted/ soldered on the motherboard allowing your computer to connect to the internet. If you have worked with many earlier Desktop computers (even some today), you know that most cannot connect to a WiFi network, and that’s because they don’t have a wireless NIC. You are advised to purchase a USB Network Adapter that will act as your wireless interface connection in such a situation.
How to list network interfaces on Linux
You can use different ways to see all the available network interfaces on your system. You can use the GUI or the Command-line (CLI). In this post, we highly recommend using the Terminal (CLI) since the GUI settings app might not list specific interfaces.
1. The ifconfig command
This command has long been used to list and configure network interfaces on Linux. Unfortunately, this command is marked as ‘deprecated’ and does not come pre-installed in certain distributions like recent Debian and Kali Linux releases.
To list network interfaces using ifconfig, execute the command below.
Restarting, Starting, Stopping, Checking the Status of the Network Service in Linux
In Linux-based operating systems, information about network operations such as network settings, network commands or network configuration is included. In Linux operating systems, as everything is a file, network settings are also kept in files. The settings can be edited with any text editor or by various tools.
Network settings are located in the following files and directories.
/ etc / sysconfig / network file / etc / sysconfig / network-scripts directory / etc / hosts /etc/resolv.conf /etc/nsswitch.conf / etc / services
Each of the settings files is used for different operations. The files in the network-scripts directory are used for network settings. Network settings are eth0, eth1, etc. according to the network card in files starting with ifcfg. kept by names.
Inside the network settings;
DEVICE - Name of the network card. ONBOOT - The state that the network is activated at startup. BOOTPROTO - How to set network settings (static, dhcp, bootp). IPADDR - IP address. NETMASK - Network mask. BROADCAST - Broadcast address. GATEWAY - Specifies the gateway address.
It also has various settings such as MAC address, Network type. When you want to get IP using DHCP , it will be sufficient to write the DEVICE, BOOTPROTO and ONBOOT settings.
Network Operations
In Linux systems, we can use the following commands to examine the Stop, Start, Restart and Status of our Network services.
Stop Network Service
You can stop the network service as follows. Check before stopping the service. There will be a problem with your connection. We recommend that you try it in your test environment.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
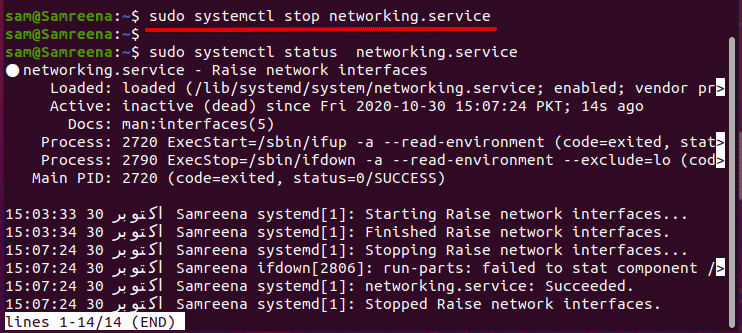
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking stop command to service networking stop.
sudo service networking stop
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to systemctl stop network.target.
systemctl stop network.target
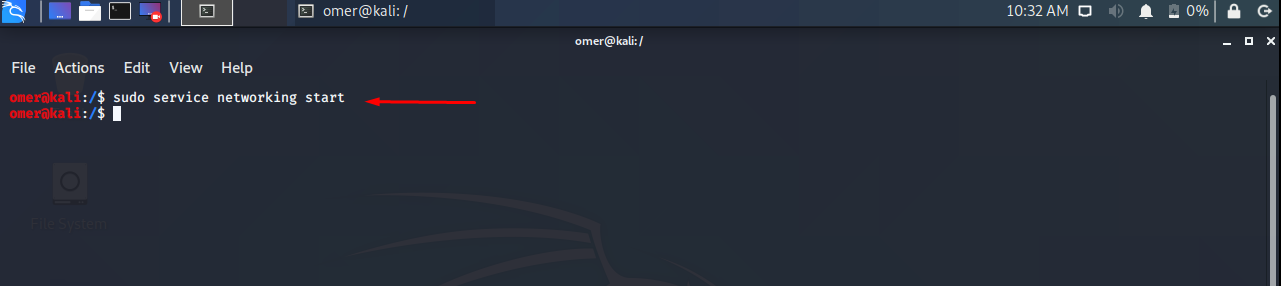
Start Network Service
You can start the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking start.
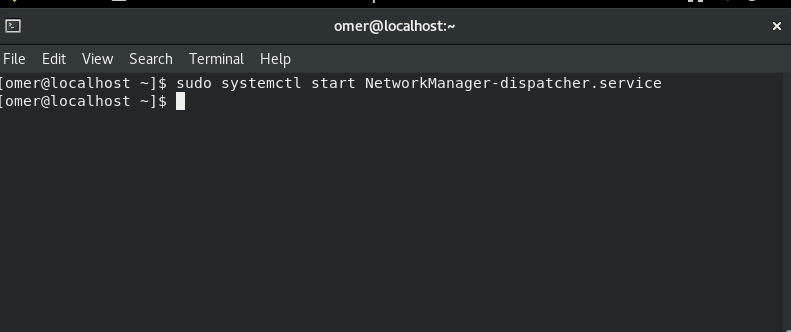
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
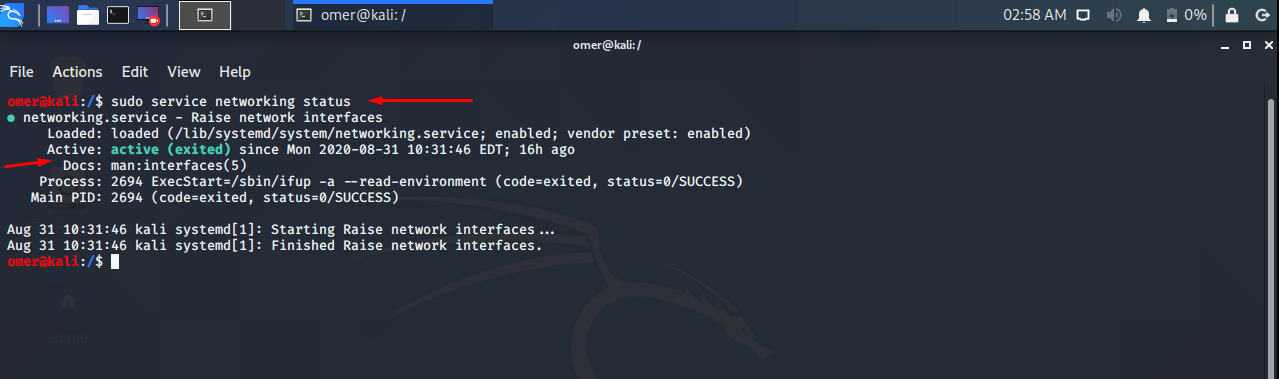
Status Network Service
You can status the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking status.
sudo service networking status
Fedora and CentOS
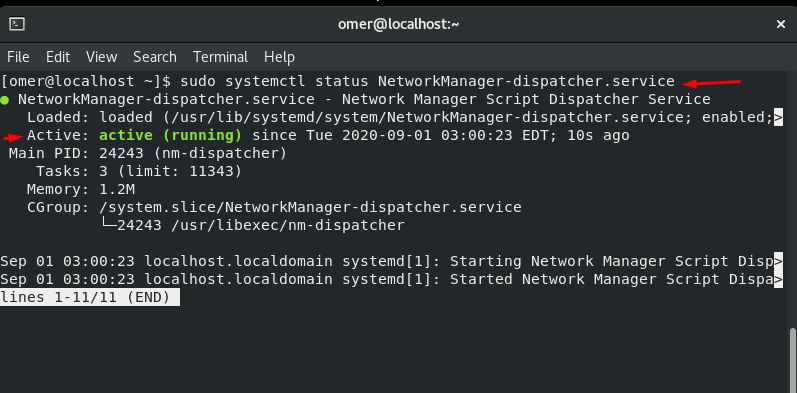
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl status NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl status NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
Restart Network
You can restart the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
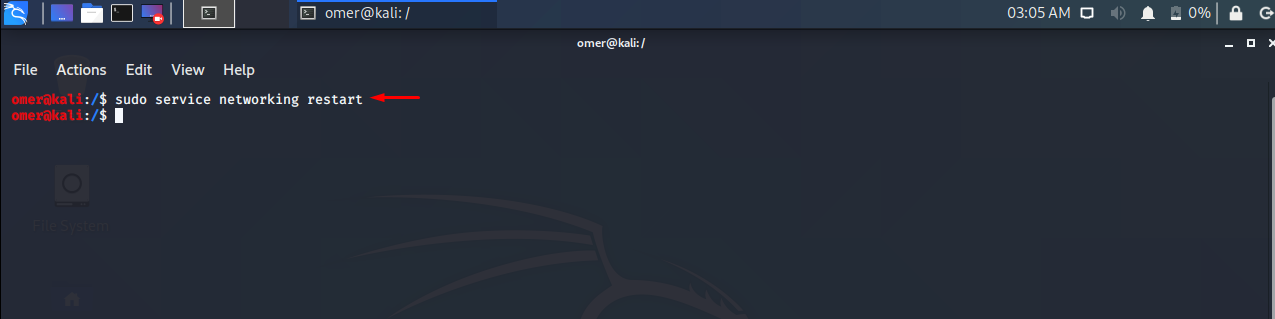
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking restart.
sudo service networking restart
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
How to restart network services in Linux
Sometimes, when you changed the network configuration or due to some network problems, you may need to restart the network services again on your Linux system to solve your problem. In this article, we will talk about how to restart the networking services on in different Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Debian, LinuxMint and CentOS) by using the command line. We have implemented different commands on Ubuntu 20.04 and CentOS 8 system. All commands which we have executed on Ubuntu 20.04 can be also used for Debian and LinuxMint distributions.
Get network Service Status
You can get the network services running status by using the following command:
For latest (Ubuntu/Debian/Mint)
To check the networking services are running on your system or not, by using the following ‘systemctl’ command you can view the networking service status on your Ubuntu/Debian/Mint system:
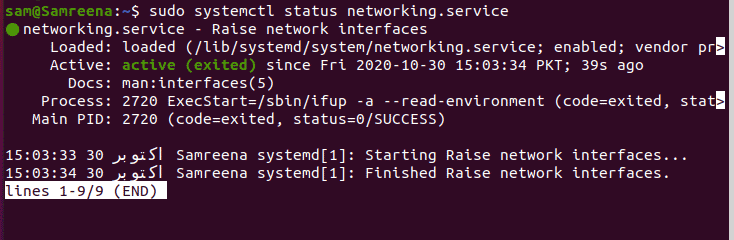
$ sudo systemctl status networking
$ sudo systemctl status networking.service
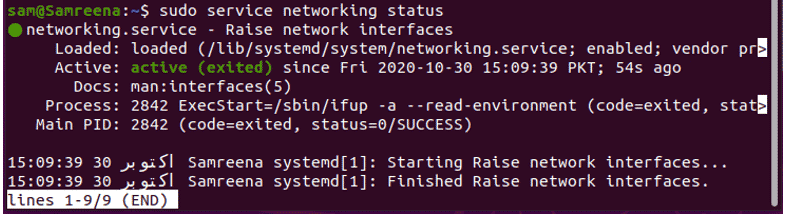
You can also display the networking service status by using the service command which is given as follows:
$ sudo service networking status
$ /etc/init.d/networking status
For CentOS 8 / Fedora
If you are using CentOS 8 then you can check the network service status by using the following command:
If you received an error like ‘network.service unit not found’ then, you will run the following command to start the network manager:
# systemctl start NetworkManager
Now, start the network services and you can get network status by using the above-mentioned command.
Stop Network Services
You can stop your network services through the method which is mentioned below. But, if you have a remote connection with SSH, we are not recommended you to stop the service because it may create problems.
For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
You can use the ‘stop’ option with the above ‘networking’ command on Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint distributions in order to stop network services.
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking stop
$ sudo systemctl stop networking.service
For CentOS 8/Fedora
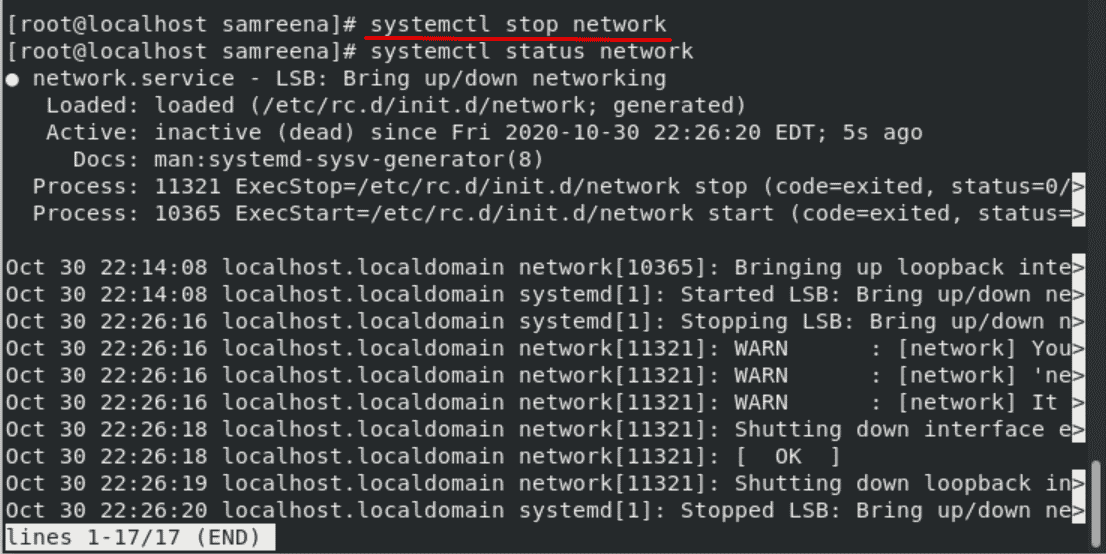
In CentOS 8, using the following command you can stop network services:
Now, if you will check the network status you will see that network services are stopped on your system.
Start Network Service
If networking services are stopped on your system then, you start these services on the Linux system.
For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
You can also start the network services by using the service command. Use ‘start’ option to start the network service on your Ubuntu. Debian and LinuxMint distributions.
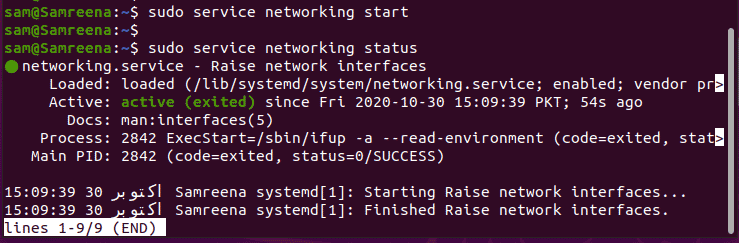
$ sudo service networking start
$ sudo systemctl start networking.service
$ $ sudo /etc/init.d/networking start
For CentOS 8/Fedora
In CentOS 8, by using the following command you can start the network service on your system:
Restart Network Service
You can also restart the network service by using the following command on Linux distributions:
For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
Type the following command to restart the network service on Ubuntu, Debian, and Linux Mint:
$ /etc/init.d/networking restart
$ sudo systemctl restart networking.service
$ sudo systemctl restart networking
For CentOS 8/Fedora
Use the following command to restart the network service on CentOS 8:
# systemctl restart network
If you get the following error on the terminal then, you need to start the NetworkManager services on your system by using the following command:
# systemctl start NetworkManager
Now, again restart the network service. You will see the following output on the CentOS system:
Conclusion
From the above information, we have explored how to start, stop, and restart the network service on different Linux distribution like Ubuntu, Debian, Linux Mint, and CentOS 8. Moreover, you can troubleshoot the network error through the NetworkManager tool on CentOS 8. If you need more details then, you can implement all command on your system and then let us know about your problems. Please don’t stop services if you have a remote ssh connection that may create a problem.
Samreena Aslam holds a master’s degree in Software Engineering. She’s a technical writer and has written various articles on different Linux flavours including Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS and Mint as well as programming guides in various programming languages
Fix Wired Network interface in Kali linux
Unmanaged devices means Network Manager doesn’t handle those network devices.
So this is what you see in GUI
An roor@alexandria# ifconfig -a show you this:
This occurs when two conditions are met:
The file roor@alexandria# /etc/network/interfaces contains anything about the interface, even:
allow-hotplug eth0 iface eth0 inet dhcp
And roor@alexandria# /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf contains:
plugins=ifupdown,keyfile [ifupdown] managed=false
Enabling Interface Management
If you want Network Manager to handle interfaces that are enabled in
roor@alexandria# /etc/network/interfaces
Set managed=true in /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf . So this file looks like:
[main] plugins=ifupdown,keyfile [ifupdown] managed=true
Restart Network Manager
Issue the following command to restart network-manager.
roor@alexandria#service network-manager restart
Now Network Manager should come up with a connected interface. For wired, eth0 with DHCP will show you something like the following image:
Just to wrap it up, lets do another roor@alexandria# ifconifg -a from command line