How to Recover Deleted Files on Kali Linux?
Probably one of the questions for Linux users is whether there are programs like recover my file on Windows for Kali Linux? Is it possible to Recover Deleted Files on Kali Linux if we do not have any backup files? Fortunately, in the process of data recovery in Linux, like Windows, there are many free and powerful tools that we can use to Recover Deleted Files on Kali Linux.
Basically, no information on your system will be deleted by itself, unless you delete it yourself. This deletion may be due to your ignorance. Because a very simple command in the command environment (rm) can easily delete your data and the only thing we can do in this situation is to stare at the black screen of the system command environment.
How to Recover Deleted Files on Kali Linux?
Before going a step further, make sure that you log in with the Root user. If you use the basic user, later you will face some issues. Also, for this article I am going to recover deleted files of a USB flash drive, however, you can use the same method to recover data from the drives inside the Kali Linux.
Step #1. Open the terminal and go to the desktop and create a new directory using the mkdir on the desktop. In my case, the directory that I create is called “recovers”. Once you create the directory, go to the same directory using the cd command.
Step #2. The tool by which I am going to recover the deleted files is known as Foremost, so make sure you install it using the following command on the Terminal.
Sudo apt install ForemostInstall Foremost on Kali Linux
Step #3. Now I am going to find out the path or to put it simply the location of the USB flash drive. Just type the following command, and in the end, you will see it, just copy the path.
Look at the below codes in the snippet, the last two lines in the following code are the path of the USB flash drive and it is /dev/sdb1, make sure you copy it.
┌──(root💀kali)-[/home/kali/Desktop/recovers] └─# fdisk -l Disk /dev/sda: 80 GiB, 85899345920 bytes, 167772160 sectors Disk model: VMware Virtual S Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disklabel type: dos Disk identifier: 0x3fbdf554 Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type /dev/sda1 * 2048 165771263 165769216 79G 83 Linux /dev/sda2 165773310 167770111 1996802 975M 5 Extended /dev/sda5 165773312 167770111 1996800 975M 82 Linux swap / So Disk /dev/sdb: 15.23 GiB, 16357785600 bytes, 31948800 sectors Disk model: Flash Disk Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disklabel type: gpt Disk identifier: D4FC65D6-0839-4A5B-BE7F-F90EFDA6EEE5 Device Start End Sectors Size Type /dev/sdb1 2048 31946751 31944704 15.2G Microsoft basic data Step #4. Once you find out the USB flash drive’s path, we need to find the attributes of the foremost command. Type Foremost -help and press enter.
┌──(root💀kali)-[/home/kali/Desktop/recovers] └─# foremost -help foremost version 1.5.7 by Jesse Kornblum, Kris Kendall, and Nick Mikus. $ foremost [-v|-V|-h|-T|-Q|-q|-a|-w-d] [-t ] [-s ] [-k ] [-b ] [-c ] [-o ] [-i To recover every type of file, we need to add the -t attribute following by “all“. If you want to recover only jpeg or png or any other type of file, just instead of “all” type it.
I am also using the -v (stands for verbose), – o (Stands for output directory), and -i ( insert the USB drive’s path).
To combine all the attributes together, it will be Foremost -t all -i /dev/sb1 -v -o /root/Desktop/recovers/

Recover the deleted files using the Foremost command
Once the files are recovered, you will bunch of directories in the output directory you mentioned.

Conclusion:
It is not really hard to Recover Deleted Files on Kali Linux, just make sure you have the root privileges. Then install the Foremost tool and finally combine the attributes and recover the deleted files. I hope this article helped you.
If the article is confusing, you can watch the below video.
How To Recover Deleted Files on Kali Linux?
The article here covers two practical Kali Linux data recovery tools for recovering deleted files on the Kali Linux operating system.

Khalid Abdullahi

You may have accidentally deleted important files on your Kali Linux system. The unfortunate event of accidentally deleting critical files can happen to anyone and cause significant workflow disruptions. The need for Kali linux data recovery is crucial as it is a popular operating system among information security professionals and enthusiasts.
This article will cover various methods to recover deleted files on Kali Linux, including graphical interface and command-line tools.
In this article
Overview of Kali Linux
Previously known as BackTrack Linux, Kali Linux is a Debian-based open-source Linux distribution designed for advanced penetration testing and security auditing. It offers a comprehensive set of tools, configurations, and automation features to enhance efficiency and allow users to focus on the target task at hand.

The distribution comes with over several hundred tools pre-installed and configured to work together, making it easy for users to perform a wide range of tasks without manually setting up and configuring individual tools. Some of the most popular tools included are Nmap for network scanning, Wireshark for packet analysis, Metasploit for exploitation, and many others.
It is available as a free resource.
How To Recover Deleted Files on Kali Linux?
Make sure you sign in with the Root user before moving forward.
Way 1: Kali Linux Data Recovery With Foremost (CLI Tool)
Foremost is a command line tool included in Kali Linux and is used for data recovery. It scans a given disk or partition to identify and recover the deleted files based on their headers, footers, and data structures. It can recover many file types, including JPEG, GIF, PDF, DOC, XLSX, and many other formats. This Kali Linux data recovery tool is efficient, lightweight, and easy to use.
Follow the steps below to recover deleted files on Kali Linux using Foremost.
Case 1. Recovering Files From a USB drive
- Press "Ctrl + Alt + T" to open the Terminal.
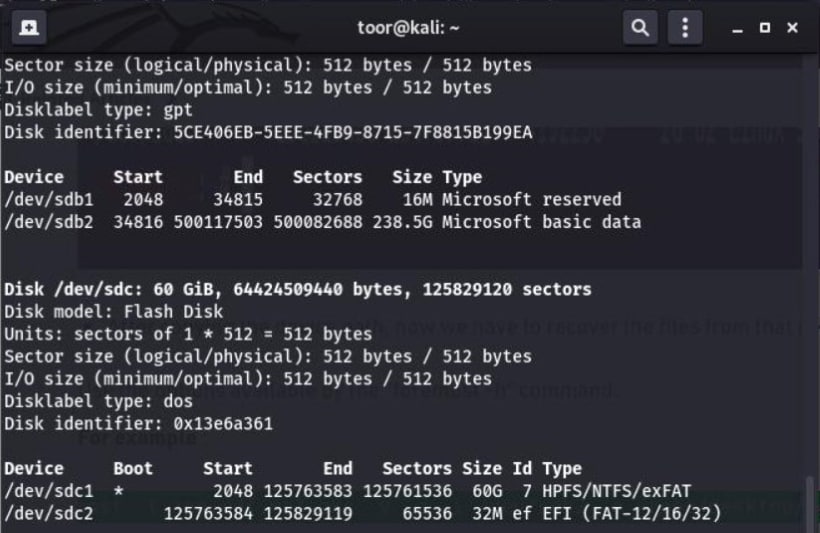
- Determine the path of your USB drive by using the command "sudo fdisk -l" in the Terminal to list all connected storage drives on the system.
You will receive the following output.

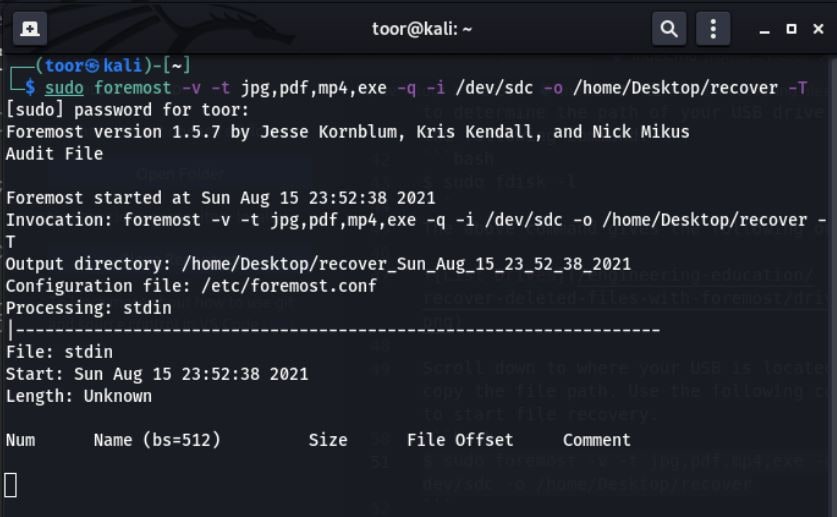
- Locate the path of your USB drive by using the command "sudo foremost -v -t jpg,pdf,mp4,exe -q -i /dev/sdc -o /home/Desktop/recover -T" and use that path as an input for the Kali Linux data recovery process.
- Use the "-t" flag when running the recovery process to specify the types of files to be recovered per the requirement.
- Use the "-o" flag during the recovery process to specify the desired output file path where the recovered files will be saved.
- Use the "-i" flag to specify the drive you wish to recover files during the recovery process.
The above command will give you the following output:

- As the recovery process runs, it displays the files being recovered in real-time, which are subsequently saved in the specified output file path.
- Upon completion of the recovery process, the recovered files will be saved in the designated output file path. Note that the duration of the process may vary depending on the size of the drive. You can find the recovered files in the specified output file path.
Case 2. Recover Files From a Hard Disk
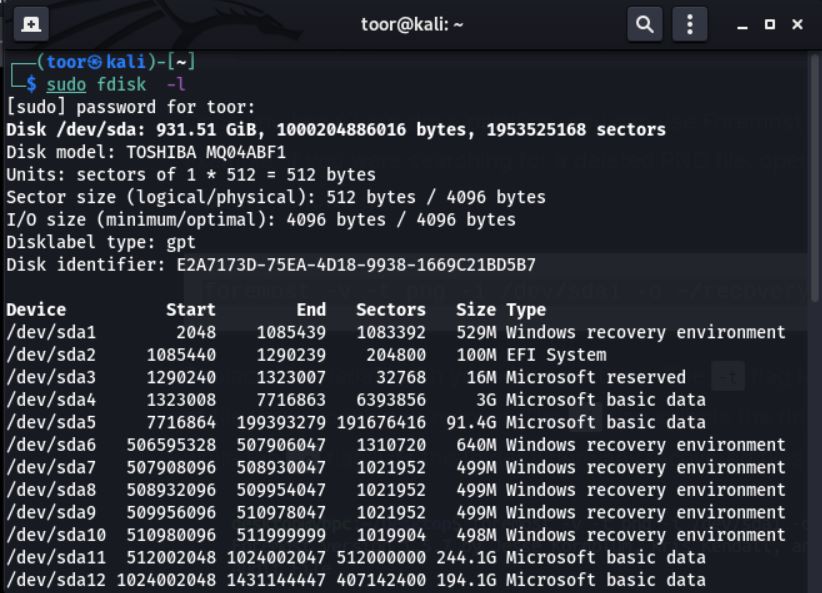
- Utilize the command "sudo fdisk -l" in the Terminal to list all the storage devices connected to the system and identify the specific device for data recovery
- The command "sudo fdisk -l" provides an overview of all the storage devices connected to your machine, along with their partitions, as demonstrated in the output illustrated below.

- Foremost can recover files from all partitions on the Linux hard drive, but it takes more time.
- When you know the partition containing the deleted files, you can use Foremost to recover files only from that specific partition. This allows for a more targeted and efficient recovery process.
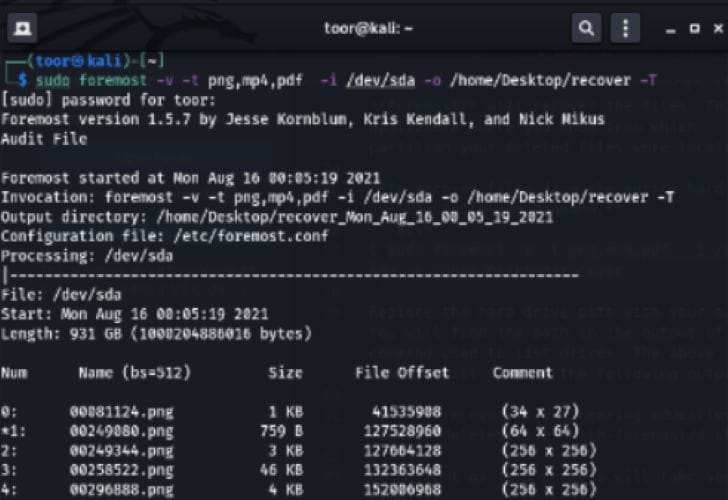
- To recover files from an entire hard drive, use the command "sudo foremost -v -t png,mp4,pdf -i /dev/sda -o /home/Desktop/recover -T".
- Use the appropriate hard drive path when running the recovery process. Additionally, the output of the above recovery command is illustrated below.
- Type the following command to recover files from a single partition: "sudo foremost -v -t png,mp4,pdf -i /dev/sda1 -o /home/Desktop/recover -T".
When recovering files from a specific partition, be sure to replace the partition path with the appropriate path for your system.

The Kali Linux data recovery process may take varying duration depending on the size of the partition.
Case 3. Recovering Files of All Types
- Type the command "sudo foremost -v -q -i /dev/sdc".
- When running the file recovery process, make sure to replace the drive path in the command with the appropriate path for the specific device you wish to recover files from. This process will automatically generate an output folder named "output" in the home directory that contains the recovered files.
Way 2: Kali Linux Data Recovery With Wondershare Recoverit (GUI Tool)
Wondershare Recoverit is a Kali Linux data recovery tool with a GUI interface. It is a powerful and easy-to-use Linux data recovery software that can help you to recover lost or deleted files from a wide range of devices, including NAS servers, computers/laptops, hard drives, USB drives, and memory cards. Besides, it supports various file systems, including NTFS, FAT16/32, exFAT, ext2/3/4, and btrfs.
How to Recover Deleted Data on Kali Linux? – PawanChauhan

Do you want to Recover Deleted Data on Kali Linux on Kali Linux?
If Yes, then this is the right place to find out the ways to Recover your Deleted data using Kali Linux, even you can recover your Pendrive or memory card data also.
So read the article completely to know How you can recover your Deleted Files and Folder on Kali Linux, Even If you delete your Data by mistake.
How to Recover Deleted Data on Kali Linux?

One day what happened, one of my friends gave me a Pendrive for formatting so I put that Pendrive in my Kali Machine and I select that Pendrive from Kali Terminal and gave the command for Format.
After some time my friend came back and said “still my Pendrive is not clean (format)”. But I said that I have already formatted your Pendrive, then I realized that by mistake I delete my complete Hard Disk. 😀
Then I decided to recover my complete Data from Hask Disk on Kali Linux, So there is a pre-installed tool that can help us to recover our deleted data by file extension.
So now I will share with you the different ways and complete the process to recover your deleted data on Kali Linux from USB or Hard Disk.
Recover Deleted File in Kali Linux using Foremost
Foremost is a pre-installed forensic tool to recover deleted files or data in Kali Linux, it takes a lot of time but really it’s working because I have already used it to recover my documents. You can recover multiple files like doc, jpg, mp4, pdf, etc at one time.
Now I will tell you how you can use this Foremost tool to recover your data, First of all,
open your terminal and type these commands.
sudo apt-get update && Upgrade
sudo apt-get install foremost
After this command gives permission to download this and if you get any error then search that error on youtube or google you will get the solution, otherwise tell me your error, and I’ll give you a solution.
Then I made a new directory on Desktop named “recover” and now I’ll recover my all files in this directory so type this command.
foremost -t jpg,pdf,mp4,exe -v -q -i /dev/sdb2 -o /root/desktop/recover
Explanation: In this command, I wrote “foremost” because I want to use it. then I wrote some file formats which I want to recover, you can replace them if you want to recover other files.
“/dev/sbd2” is one of the disk partitions, I wrote it because I want to recover my data from this disk you can replace your disk name by typing the command “fdisk -l“.
“/root/desktop/recover” is a directory location where I’ll save my recovered data, you can type this according to your directory location.
If you have liked this article and it helps you to recover your data, then you can share it with friends and family so that they do not ever get such a problem.
If you have any problem with any part of this article, or you want any more information related to the computer, then tell me in the comment box, and I will surely reply to you.
Please Share This Share this content
- Opens in a new window
- Opens in a new window
- Opens in a new window
- Opens in a new window
- Opens in a new window
- Opens in a new window
- Opens in a new window
- Opens in a new window
- Opens in a new window
- Opens in a new window
- Opens in a new window