- Connecting a Wireless Adapter to a Kali Linux Virtual Machine
- Problems With Built-in Wireless Cards
- Best WiFi Adapters for Hacking (With Monitor Mode)
- Connect a Wireless Adapter to Kali Linux Virtual Machine (VirtualBox)
- Automatically Connect the WiFi Adapter to a VirtualBox VM
- Connect a Wireless Adapter to Kali Linux Virtual Machine (VMware Player)
- Conclusion
- Kali linux сетевой адаптер
Connecting a Wireless Adapter to a Kali Linux Virtual Machine
In “Network hacking,” most people get confused when talking about Network adapters and Network cards.
Most don’t know what they are, why we need them, and how to select the best adapter since we have so many brands and models available in the market.
A wireless adapter is a device that you connect to your computer via the USB port, and it allows you to connect to WiFi networks and communicate with other devices on the network.
However, you might wonder: “Why would I need a USB network adapter since my laptop already has an inbuilt adapter that enables me to connect to wireless networks?”
Well, this is among the topics that we will discuss in this post:
- Problems with Built-in Wireless Cards
- Best WiFi adapters for hacking
- How to connect a wireless adapter to Kali Linux Virtual machine
Table of Contents
Problems With Built-in Wireless Cards
There are two main problems with built-in WiFi adapters.
- They can’t be used in Virtual machines – Kali inside a VM does not see the built-in WiFi card of your laptop as a WiFi adapter but will see it as an ethernet adapter. Hence you can have full internet access, but you cannot do packet injection or place the WiFi card into monitor mode.
- Most built-in cards are not suitable for hacking – In wireless hacking, there are two main factors that we look out for in adapters. That is ‘packet infection’ and support for ‘monitor mode.’ Unfortunately, most of the built-in adapters support non of these two features.
Best WiFi Adapters for Hacking (With Monitor Mode)
Before diving into the different WiFi adapter brands and models, we first need to understand the Wireless Chipset present in these adapters. Like the CPU we have in a computer, this chipset is the “Brains” of the wireless adapter.
It is responsible for all the processing and calculation of data flowing through it. It also determines the capability of the wireless adapter. Whether it can support monitor mode, packet injection, and works with Kali Linux or not.
Some of the chipset supported by Kali Linux include:
- Realtek RTL8812AU
- Realtek 8187L
- Ralink RT5370N
- Ralink RT3572
- Ralink RT5572
- Ralink RT3070
- Ralink RT307
- Atheros AR9271
- MT7610U
- MT7612U
I understand all this information looks gibberish as of now; however, you will appreciate it when we look at the different WiFi adapters available and the chipset they use.
You will notice that the ALFA Networks company highly dominates the Wireless adapter market. Over the past couple of years, the company has risen to stand as the perfect supplier for efficient and reliable WIFI adapters. Other companies include TP-Link and Panda .
The table below shows a list of wireless adapters supported by Kali Linux and the Chipset, Frequency, and Protocol they are using.
| Adapter Name | Chipset | Frequency | Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALFA AWUS036NEH | Ralink RT3070 | 2.4GHz | 802.11N |
| TP-LINK TL-WN722N 2.4GHz v1 | Atheros AR9271 | 2.4GHz | 802.11N |
| TP-LINK TL-WN722N 2.4GHz v2/v3 (with some workarounds) | Realtek RTL8188EUS | 2.4GHz | 802.11N |
| ALFA AWUS036NH | Ralink RT3070 | 2.4GHz | 802.11N |
| ALFA AWUS036NHA | Atheros AR9271 | 2.4GHz | 802.11N |
| Panda PAU09 | Ralink RT5572 | 2.4GHz | 802.11N |
| ALFA AWUS036ACH | Realtek RTL8812AU | 2.4GHz / 5GHz | 802.11AC |
| ALFA AWUS036H | Realtek 8187L | 2.4GHz | 802.11b/g |
| ALFA AWUS036ACHM | MT7610U | 2.4GHz / 5GHz | 802.11AC |
| ALFA AWUS036ACM | MT7612U | 2.4GHz / 5GHz | 802.11ac/a/b/g/n |
| ALFA AWUS1900 | Realtek RTL8814AU | 2.4GHz / 5GHz | 802.11ac/a/b/g/n |
| ALFA AWUS036AC | Realtek RTL8812AU | 2.4GHz / 5GHz | 802.11ac/a/b/g/n |
| ALFA AWUS036ACS | Realtek RTL8811AU | 2.4GHz / 5GHz | 802.11ac/a/b/g/n |
| ALFA AWUS036EAC | Realtek RTL8812AU | 2.4GHz / 5GHz | 802.11ac/a/b/g/n |
| ALFA AWPCIE-1900U | Realtek RTL8814AU | 2.4GHz / 5GHz | 802.11ac/a/b/g/n |
Important: When it comes to TP-LINK TL-WN722N, it’s important to know that you can also get v2/v3 to work with a few workarounds, although it’s sometimes assumed that only v1 works.
A great and detailed tutorial on this topic is this one from David Bombal – Kali Linux TP-Link TP-WN722N .
TL-WN722N is a decent budget WiFi adapter for our purposes, but it’s sometimes difficult to find v1 in your immediate area, so v2/v3 is definitely a good option.
In some cases you won’t find the adapter’s version in the product description, so I think it’s definitely good to know you can make it work no matter which of those versions it is.
Connect a Wireless Adapter to Kali Linux Virtual Machine (VirtualBox)
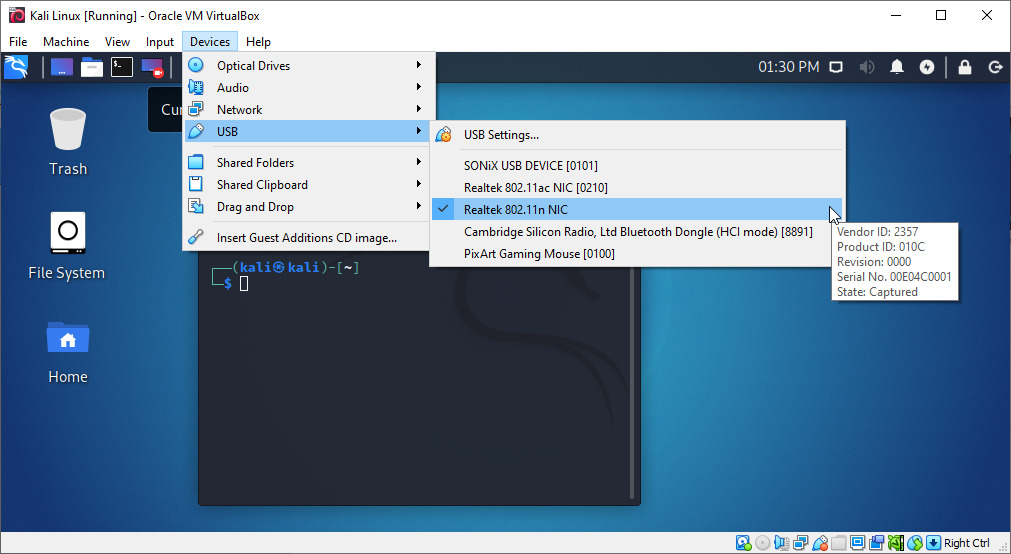
To connect a wireless adapter to your Kali Linux virtual machine, when using VirtualBox, you can go in the Oracle VM VirtualBox menu > Devices > USB > [select_your_adapter].
It may not list the name of the WiFi Adapter, but something related to the chipset, instead. Here, I’m using a TP-LINK TL-WN722N 2.4GHz v2/v3, and as you can see, it’s displaying Realtek 802.11n NC.
Automatically Connect the WiFi Adapter to a VirtualBox VM
You can also automatically connect a wireless adapter to your Kali Linux virtual machine, when running VirtualBox. This way, you don’t have to manually connect it every time
To do this follow the steps below:
- Shutdown the Kali virtual machine if it was already running
- Connect your Wireless USB adapter to your PC
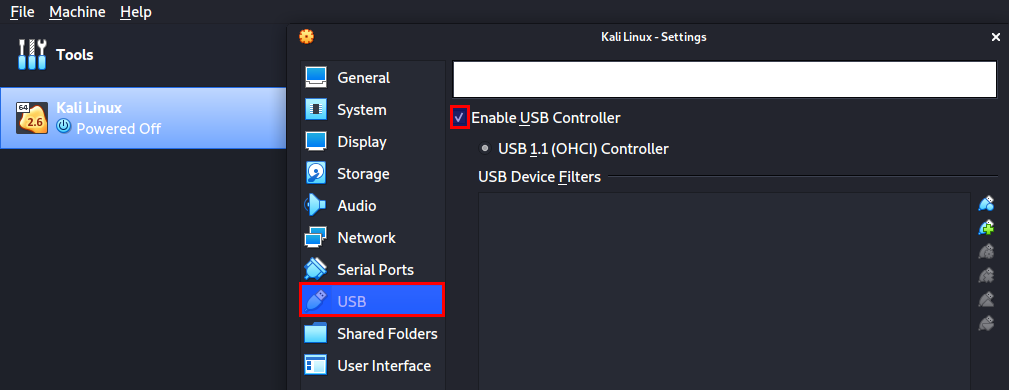
- Right-click on your Kali Virtual machine and select the Settings option. A window will open displaying all the different configuration options.
- Click on the USB option and check the Enable USB controller check box.
If you are not sure of the adapter’s name, just remove it, and you will notice the name that will disappear from the VirtualBox USB list.
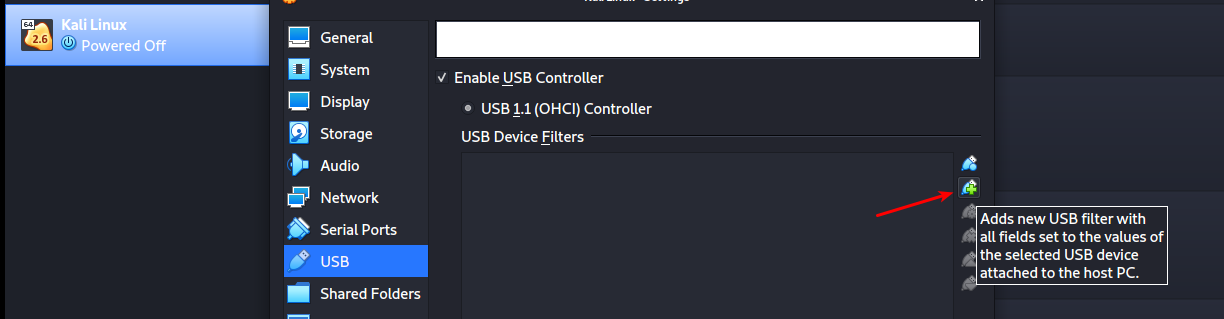
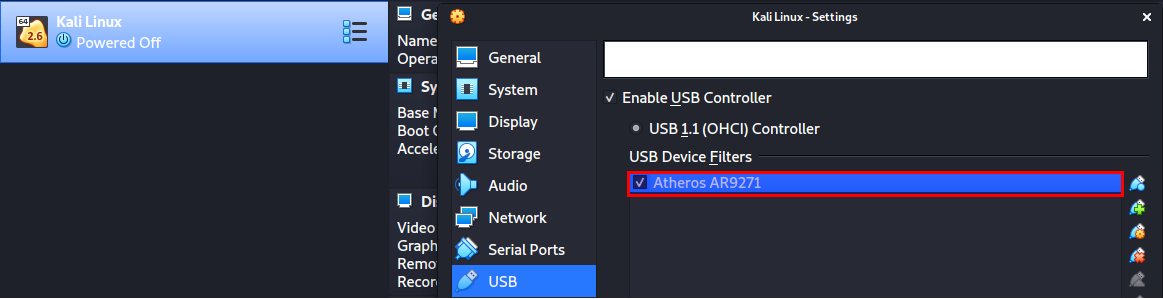
Your wireless adapter will be listed under the “USB Device Filters” section.
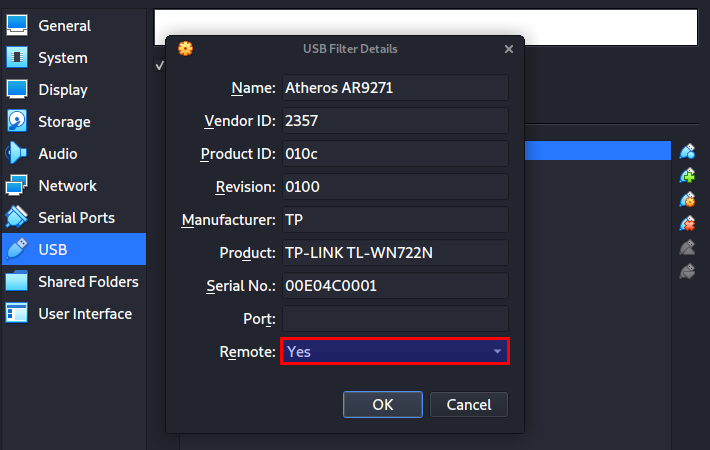
To finalize everything, right-click on your newly added USB filter and select the Edit Filters option.
A window will open listing all the details about your wireless adapter. Then, on the Remote option, click on the dropdown and select Yes.
Connect a Wireless Adapter to Kali Linux Virtual Machine (VMware Player)
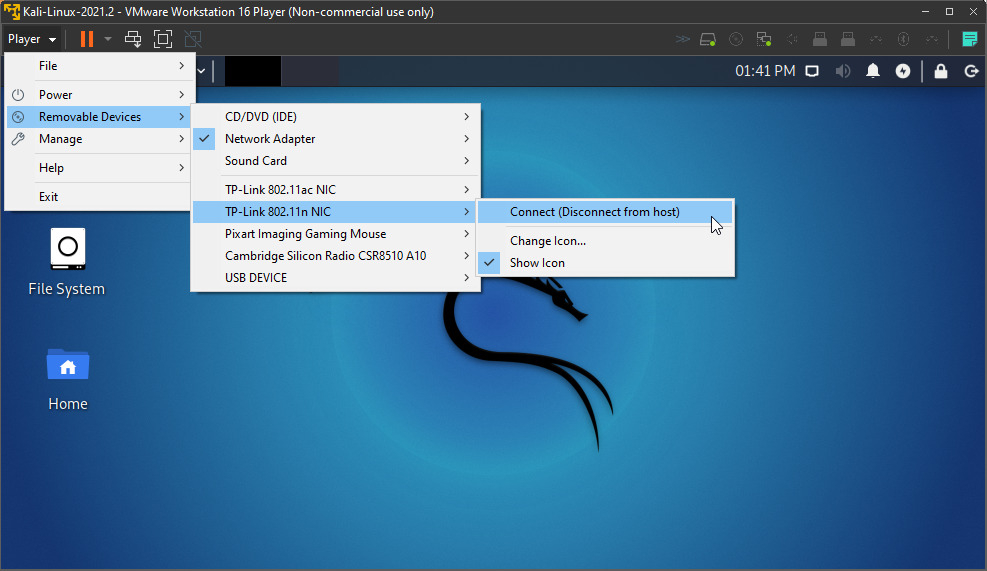
To connect a wireless adapter to your Kali Linux virtual machine, when using VMware Player, you can go to the VMware Player menu > Player > Removable Devices > [your_adapter] > Connect (Disconnect from host).
It may not list the name of the WiFi Adapter, but something related to the chipset, instead. Here, I’m using a TP-LINK TL-WN722N 2.4GHz v2/v3, and as you can see, it’s displaying Realtek 802.11n NC.
You should then receive a message informing you that the device will be safely stopped and disconnected from the host machine, so it can then be connected to Kali Linux in the VMware player.
I’m not sure of an easy way how you can automatically connect a WiFi Adapter with VMware Player, as we did with VirtualBox. The solution in VMware knowledge base seems to involve a bit of work https://kb.vmware.com/s/article/1648 , and I haven’t tried it myself. If anyone has an easier solution for this and would like to share, then we’d love to hear from you.
Conclusion
Now you can boot your Kali VM and start practicing your wireless hacking skills. You can list all the wireless networks around you and even put your card in monitor mode.
I believe up to this point, you have a working wireless adapter on your Kali Linux VirtualBox machine. Please remember when selecting an adapter for wireless hacking to ensure the chipset used is among the chipsets listed above.
Kali linux сетевой адаптер
External wireless cards are necessary because Android devices do not support monitor mode on most devices apart from some Qualcomm chips used in modern Snapdragon SOC. There are some devices that can support monitor mode with a modified firmware and kernel such as the Nexus 5, 7 (2012), and Nexus 6P. Right now, only a specially modified version of Nexus 5 supports monitor mode for Nethunter.
A couple of limitations are that Android devices require a USB-OTG cable and the power output is limited. Because of these limitations, not all wireless cards can receive the necessary power output and may not have external power (y-cable) support.
When asking the question “What is the best card for use with NetHunter?”, you need to ask yourself what your use case is. While all cards will likely perform similar at closer ranges, some of them have increased transmit power and antenna attachments which allow them to work at longer distances than small form factor cards. There is also the possibility that your device may only provide 450 or less mA of power over OTG rather than the full USB 500 mA specification. If this is the case, you may want to consider devices with lower transmit power.
The following chipsets are supported by default in most, if not all, NetHunter kernels:
- RTL8188EUS
- RTL8188CU
- RTL8188RU
- RTL8192CU
- RTL8192EU
- RTL8723AU
- RTL8811AU
- RTL8812AU
- RTL8814AU
- RTL8821AU
- RTW88-USB
Qualcomm internal wifi chipsets (wlan0)
The following devices are confirmed to be working with a NetHunter build:
- TP-Link TL-WN722N v1 (Please note that v2 & v3 have unsupported chipsets) but v2 and v3 may be supported using RTL8812AU drivers.)
- TP-Link TL-WN822N v1 — v4
- Alfa Networks AWUS036ACH
- Alfa Networks AWUS036NEH (recommended by @jcadduono)
- Alfa Networks AWUS036NHA
- Alfa Networks AWUSO36NH
- Panda PAU05 Nano
The following devices are confirmed to be partially working with a NetHunter build:
The following devices are confirmed to NOT be working with a NetHunter build:
Updated on: 2023-Mar-06
Author: re4son