- Kali linux ssh подключение
- SSH server: automatic host keys generation
- Как включить SSH в Kali Linux
- SSH
- Установка сервера SSH-OpenSSH в Kali Linux
- Включение службы Kali Linux SSH
- Изменение ключей SSH по умолчанию в Kali для предотвращения атак MITM
- Установите MOTD с помощью красивого ASCII
- Устранение неполадок
- Изменение порта сервера SSH для обеспечения безопасности
- Заключение
- Похожие записи:
- How to Enable and Start SSH on Kali Linux
- About the Author
- Corey Batiuk
Kali linux ssh подключение
Since our release of Kali Linux 2022.1 it is possible to easily configure the SSH client for wider compatibility to allow Kali to talk to as many SSH servers as possible. In wide compatibility mode, legacy key exchange algorithms (such as diffie-hellman-*-sha1) and old ciphers (such as CBC) are enabled. As a result, tools used inside of Kali are able to communicate using these outdated methods. This is done to help increase Kali’s ability to talk to older, obsolete SSH servers that are still using these older protocols. Older services using this may be at end of life, thus increasing the chances of discovering vulnerabilities or other problems.
Note that this is not the default. Out of the box, the SSH client in Kali Linux is configured for Strong Security to enforce communication over more secure channels.
This setting can be changed easily using the kali-tweaks tool. Simply:
- Open a terminal and run kali-tweaks .
- From there, select the Hardening menu.
- Now you can choose between Strong Security(the default) and Wide Compatibility.
Note: This is achieved by creating or deleting the configuration file /etc/ssh/ssh_config.d/kali-wide-compat.conf .
SSH server: automatic host keys generation
Since the release of Kali Linux 2022.1, the SSH host keys are automatically generated if missing. This is achieved via the systemd service regenerate-ssh-host-keys .
So what are SSH host keys exactly? Those keys are required for the SSH server to be functional. They are supposed to be unique for each machine. Those keys can be found under /etc/ssh and are named ssh_host_*_key . This is how it usually looks like:
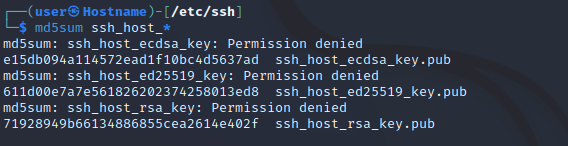
[email protected]:~$ ls -l /etc/ssh/ssh_host_* -rw------- 1 root root 1373 Feb 3 23:50 /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 599 Feb 3 23:50 /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key.pub -rw------- 1 root root 505 Feb 3 23:50 /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 171 Feb 3 23:50 /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key.pub -rw------- 1 root root 399 Feb 3 23:50 /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 91 Feb 3 23:50 /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key.pub -rw------- 1 root root 2590 Feb 3 23:50 /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 563 Feb 3 23:50 /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key.pub Since these keys must be unique for each machine, they can’t be embedded in pre-built Kali images such as the Kali Linux VM images or the ARM images. It’s usually up to the user to create those keys before running the SSH server for the first time. However, for most users who are not familiar with SSH, this is a hurdle, as they are not aware of this technical detail.
To make it easier, Kali Linux now comes with a systemd service that takes care of that automatically, and generate those keys if they are missing. In theory, it’s only during a first boot of a pre-built image that the service kicks in. On subsequent boots, the keys already exist and therefore nothing happens. This may not be the case for users who may remove these keys themselves.
For those who are not comfortable with this automatic behavior, it’s very simple and straightforward to disable it:
[email protected]:~$ sudo systemctl disable regenerate-ssh-host-keys.service Updated on: 2023-Mar-06
Author: arnaudr
Как включить SSH в Kali Linux
Если вы хотите включить SSH в Kali Linux, в этой статье вы узнаете, как это сделать.
SSH
В середине 90-х годов telnet породил безопасного преемника под названием secure shell. Это протокол для общения с другими компьютерами. Существуют и другие протоколы, в которых можно входить в систему и выполнять функции, выполняемые SSH, но они небезопасны, поскольку не зашифрованы, поэтому люди могут перехватить ваши сеансы и данные. Однако SSH шифрует данные через туннель, чтобы вы могли безопасно войти в систему на удаленной машине, передавать файлы или безопасно отдавать удаленные команды. SSH применяется в модели клиент-сервер для передачи и получения файлов. Здесь используются два термина: SSH-сервер и SSH-клиент. Одна система выступает в роли сервера, а другая — в роли клиента. Открытый ключ и закрытый ключ хранятся локально на сервере и клиенте SSH соответственно. Клиент SSH связывается с сервером SSH и предоставляет идентификатор пары ключей, которую он хочет использовать для подтверждения своей личности. Сервер SSH создает вызов, который шифруется открытым ключом и отправляется клиенту. Клиент получает вызов, расшифровывает его с помощью закрытого ключа, а исходный вызов отправляет обратно на SSH-сервер. После консультации устанавливается защищенное соединение. Протокол SSH был изобретен для замены туннеля, чтобы можно было идентифицировать сервер, к которому вы подключены.
Сейчас мы рассмотрим, как включить SSH в Kali Linux.
Установка сервера SSH-OpenSSH в Kali Linux
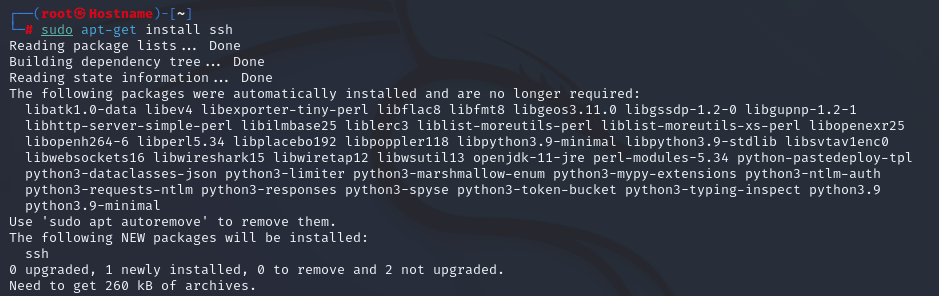
Обычно в Kali Linux запущен или установлен сервер OpenSSH. Запустив этот сервер, вы сможете войти в систему через SSH. Таким образом, вам не обязательно устанавливать сервер, но если вы оказались в ситуации, когда у вас его нет, то вы можете выполнить эту простую команду для установки и включения SSH сервера в Kali Linux.
Запустите SSH сервер следующей командой
Включение SSH-сервера довольно рискованно, так как любой, кто знает ваш пароль, может проникнуть на вашу машину. Защита пароля должна быть вашей первоочередной задачей. Если вы хотите, чтобы служба работала все время, выполните следующий шаг.
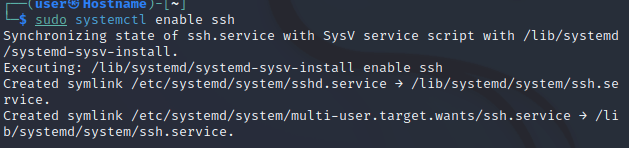
Включение службы Kali Linux SSH
Включение автозапуска службы
sudo systemctl enable ssh
Изменение ключей SSH по умолчанию в Kali для предотвращения атак MITM
Каждая установленная система Kali Linux имеет шанс подвергнуться атаке MITM (Man In The Middle). Атаки MITM обычно наблюдаются в среде клиент-сервер. Атака MITM происходит, когда хакер проникает между этими двумя компонентами. Хакеры могут воспользоваться преимуществами незашифрованной связи посредством атаки MITM и прослушивать весь ваш трафик. Чтобы избежать атак MITM, вы можете следовать приведенной ниже процедуре.
Первым шагом будет перемещение ключей Kali SSH в новую папку.
Создадим директорию для хранение старых ключей
sudo mkdir default_kali_keysи переместим текущие ключи
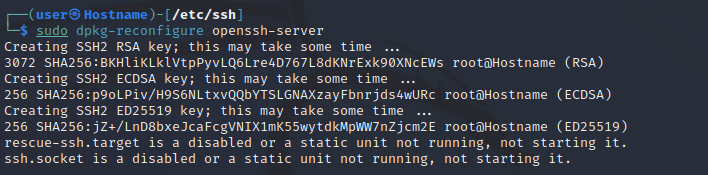
sudo mv ssh_host_* default_kali_keys/Вторым шагом будет регенерация ключей путем ввода следующей команды.
sudo dpkg-reconfigure openssh-server
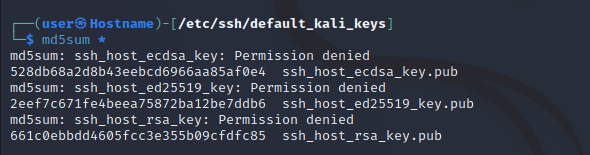
Третий шаг — проверка того, что хэши ключей SSH отличаются. Введите следующую команду для проверки.
Наконец, введите следующий командный код для перезапуска SSH.
Установите MOTD с помощью красивого ASCII
MOTD (Message of the Day) используется для отправки общего сообщения всем пользователям. Баннер обычно скучный, поэтому вы можете отредактировать файлы и добавить текст по своему выбору, а затем сохранить файл.
Устранение неполадок
При смене ключей SSH в середине может появиться предупреждающий знак. Введите следующую команду, чтобы устранить эту проблему.
sudo nano /root/.ssh/known_hostsУдалите строку, вызывающую неполадки, и перезапустите SSH.
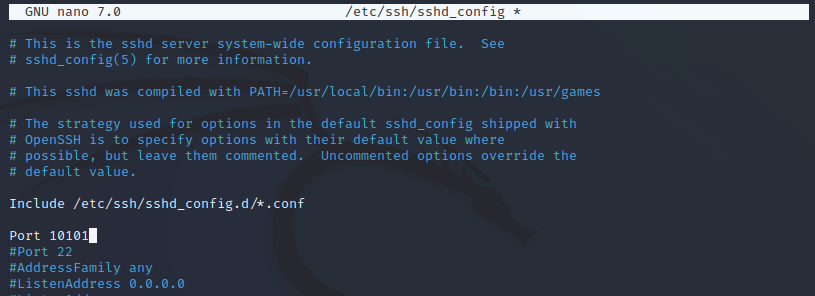
Изменение порта сервера SSH для обеспечения безопасности
Номер порта можно изменить, введя следующую команду.
sudo cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config_backupФайл SSH_config можно редактировать и дальше, введя следующую команду.
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Теперь вы можете перезапустить сервер OpenSSH
теперь можете подключиться к своей машине Kali Linux по SSH
Здесь 10101 — это порт назначения, p означает порт, а host может быть IP или FQDN.
Заключение
Термин «SSH» описывает набор правил и рекомендаций, который говорит вашему компьютеру, как пересылать данные из одного места в другое. Администраторы, такие как владелец приложения, администраторы, отвечающие за всю систему, или привилегированные пользователи с более высоким уровнем доступа в основном используют SSH-сервер. Надеюсь, эта статья помогла вам с включением SSH в Kali Linux.
Похожие записи:
How to Enable and Start SSH on Kali Linux
Here at LMG Security, we’re passionate about providing excellent cybersecurity services to organizations around the world. We’re also passionate about increasing cybersecurity awareness through our various training programs. Thanks for visiting our blog and we hope you find this post helpful!
The Linux distribution Kali used by many penetration testers (including those here at LMG Security) recently released version 2017.1 of their rolling release. For quite some time now (Since version 2.0) Kali has used Systemd (System Management Daemon) in place of an init system. This change brought with it a new way of enabling and starting services, even though many still use the old commands, which often still work but may also lead to errors. This post will go over the Systemd method for enabling and starting the SSH (Secure Shell) service on Kali Linux.
The openssh-server package should already be installed, to verify this you can use the following command:
You should see the version with [installed] after it like this:
If it’s not installed, you can use this command to install it:
# apt install openssh-server
When enabling the service, be sure to fully secure SSH first. I will cover some of the basics briefly, but this is not meant to be a guide on securely running an SSH server. Since Kali comes with pre-generated SSH keys, to make it more secure, the first thing we will do is generate new ones.
To backup the original keys first as a precaution use:
# mkdir /etc/ssh/default_keys # mv /etc/ssh/ssh_host_* /etc/ssh/default_keys/
Then to regenerate the keys:
# dpkg-reconfigure openssh-server
The next step is to edit the SSH server configuration file with the settings you need:
If you are only planning on using SSH briefly the defaults are probably fine. If you think you will use it for a length of time I would recommend at minimum enabling public key authentication:
Then disabling password authentication:
PasswordAuthentication no
You could also allow the root user login here, but instead consider creating a non-privileged user account instead.
It’s useful to know that Systemd has different units, a unit configuration file encodes information. The units relevant to SSH are ssh.service and ssh.socket. At a basic level a service unit controls a process and a socket unit controls a filesystem or network socket.
If you only need to temporarily start up the SSH service it’s recommended to use ssh.socket:
# systemctl start ssh.socket
To instead permanently enable the SSH service to start whenever the system is booted use:
# systemctl enable ssh.service
Then to use SSH immediately without having to reboot use:
# systemctl start ssh.service
To check the status of the service you can use:
# systemctl status ssh.service
To stop the SSH service use:
# systemctl stop ssh.service
And to disable the SSH service so it no longer starts at boot:
# systemctl disable ssh.service
This gives you the basics of starting and enabling the SSH service in Kali Linux. If you are planning on using the system for any length of time I highly recommend going further with securing the SSH service. If you have any questions or comments about SSH on Kali Linux, contact us at [email protected]
About the Author
Corey Batiuk
Corey Batiuk is LMG Security’s Pentest Team Lead and has been working in technology over 13 years. Corey has wide experience in testing, including: Internal and External Penetration Testing, Mobile Application Security Assessments, Web Application Security Assessments, Wireless Security Assessments, Social Engineering Testing, and Threat Hunting. Prior to that he worked as an engineer for a managed service provider. Corey graduated with honors from the University of Montana with a bachelor’s degree in Psychology and a minor in Sociology. Corey has also presented at several security conferences.