- NetworkManagement
- Bugs
- Reporting Bugs
- Bug handling
- The Stack
- The Hardware
- The Kernel
- WPA Supplicant
- NetworkManager
- User Clients
- When Things Go Wrong
- Where Does It Hurt?
- It’s All KDE’s Fault!
- Crashes
- Donate to KDE Why Donate?
- Visit the KDE MetaStore
- Точка доступа на KDE (Kubuntu 15.04)
- Как создать точку доступа WiFi на KDE Kubuntu 15.04
- Шаг первый
- Шаг второй
- Настройка точки доступа в KDE Network Manager
- Как управлять точкой доступа в KDE Network Manager
- Как посмотреть клиентов точки доступа на KDE Kubuntu 15.04
- Примечание 1
- Примечание 3
- Защита вашей WiFi сети
- Настройка точки доступа на других операционных системах
NetworkManagement
On several Linux distributions, the NetworkManager daemon provides user-configurable control of network connections. In KDE, the KNetworkManager (KDE3 and KDE4) and Network Management (KDE4) are the main user interfaces to NetworkManager.
Bugs
Reporting Bugs
To report a useful bug against Network Management, provide the following items of information:
- Your distro version
- Is NetworkManager in use? On some distributions it is optional, as it is out of place on a static, server-like system. Stop now if it is not.
- The version of the Network Management applet (NetworkManager-kde4.rpm on openSUSE, plasma-widget-network-manager in Kubuntu 9.04, plasma-widget-networkmanagment in Kubuntu 9.10, kde-plasma-networkmanagement on fedora)
- The version of the NetworkManager package
- The version of the ModemManager package
- Your computer’s hardware if not a vanilla x86 compatible. PPC user? I want to know.
- Your network hardware (use lshal to find this out)
- A system log from NetworkManager during the connection attempt
- for openSUSE: /var/log/NetworkManager
- for kubuntu: /var/log/syslog
- for fedora: /var/log/messages
- For wireless networks:
- Is it using a hidden SSID?
- Wireless security type: WEP/WPA-PSK/WPA-EAP?
- Key length
- Key type (passphrase or hex for WEP)
- Ciphers (TKIP/AES)
- Auth mechanisms (TLS/TTLS/PEAP/. )
- For mobile broadband:
- hardware
- driver in use (see dmesg when you connect the hardware)
- network in use
- network type (GSM/CDMA/UMTS)
- apn used, if any.
- ModemManager logs («killall NetworkManager», «killall modem-manager», start «modem-manager —debug», «NetworkManager —no-debug») may be helpful in debuggin whether NetworkManager detects your hardware.
And very importantly: Are you able to connect with another client? For example, nm-applet under GNOME or cnetworkmanager on the console. If so, please try to attach comparative troubleshooting information as described at the end of this article.
Bug handling
Network Management on most Linux desktops sits on top of a large and fragile stack of components. This is necessary to deal with the vast number of different configurations. When a connection fails, it can be for any one of a number of reasons throughout this stack, but the symptoms will usually be something like «Connection got to 28% and then failed». Bugs reported at bugs.kde.org will be triaged to try and find out at what layer the failure occurred, so that it can be fixed by those responsible.
The Stack
The Hardware
Wireless hardware has a surprising number of bugs. These are dealt with at the next layer, if you are lucky.
The Kernel
This is where the actual driver that controls the hardware is located. There are many interesting bugs here too. Since the introduction of a standard wireless MAC layer in the Linux kernel, this situation is improving. Some hardware doesn’t have a Linux driver, so people control it using the ndiswrapper tool, which loads Windows drivers and their bugs. You can see its output in the system log, and talk to the drivers using the iwtools set of commands.
WPA Supplicant
wpa_supplicant is a low level tool for talking to the driver, providing authentication and encryption settings. It is open source and generally of high quality. Before the advent of NetworkManager, users had to configure it manually with control files in /etc. This has been known to get people out of a tight spot occasionally. It usually logs to /var/log/wpa_supplicant.log. Nowadays it is mostly controlled remotely by.
NetworkManager
NetworkManager is the system daemon at the centre of the networking subsystem on most end user Linux installations. It has root privileges, needed to control the lower layers, and exposes some controls up to clients running in the user session via DBUS. It writes a log in /var/log. NM also controls DHCP clients as needed and rewrites /etc/resolv.conf with the DNS servers it has configured. NetworkManager also provides a SystemSettings service, which is responsible for reading your distribution’s network configuration files (system wide) and feeding them into NetworkManager.
User Clients
KNetworkManager applet for KDE 4, Network Management Plasmoid under KDE 4, KNetworkManager under KDE 3, nm-applet under GNOME, and cnetworkmanager is your last life. These are responsible for
- giving feedback on the networking status of this system,
- communicating the user’s actions to NetworkManager,
- and for storing and communicating the user’s network connection details (policy) to NM.
While they are the most visible part of the system, they are also the least important to making a successful connection. Since they share a standard interface to NetworkManager, they can be exchanged easily.
When Things Go Wrong
Where Does It Hurt?
Simple. Start at the top of the stack and work down. When you find something that works, you found the site of the problem. When you run out of things you can change, hand over to an expert (probably the responsible team at your Linux distribution).
- Are you actually using NetworkManager on your system? Mandriva doesn’t use it. Moblin uses Connman.
- Try a different NetworkManager client. If that helps, continue in the next section to try and further localize the problem in Network Management. Then bugs.kde.org, product «Network Management» is the place to go.
- Try to configure a connection using your distro’s system configuration tools, so SystemSettings picks it up. It’s unlikely but worth a go.
- Try a manually configured connection via wpa_supplicant. The documentation is rather sparse but there are example configurations include in the package. Here is the list of supported hardware. If wpa_supplicant on its own works, NetworkManager is at fault. Talk to your distro or report it at bugs.freedesktop.org.
- If that didn’t work, reconfigure a wireless router to use a different (weaker) encryption type or none at all. If this works, the problem is either in wpa_supplicant or the driver. Either way, take it to your distro.
It’s All KDE’s Fault!
If you are reading this, you will have been able to make a connection using a different NetworkManager client.
First, make sure that you are not running another client as well as Network Management. This will lead to unpredictable results. If you were, remove and restart Network Management. You can run it externally to Plasma as
plasmoidviewer networkmanagement
You should now try to figure out how the connection provided by Network Management differs from that provided by the other client. If you build Network Management from source you can use the tool ‘qdbusfornm’, which is a version of qdbus extended to handle NM’s data types.
If you do not build from source, just replace
in the command shown below. It is a bit harder to read but should give you the same output. If you use
please take the time to format the output so there is one key per line, similar to the qdbusfornm output below. This is easy and just takes time, so it is better for you to do this than a developer.
The value 0 below identifies the connection. Change it if you have more than one until you find the relevant connection.
./qdbusfornm --system org.freedesktop.NetworkManagerUserSettings /org/freedesktop/NetworkManagerSettings/0 org.freedesktop.NetworkManagerSettings.Connection.GetSettings
a>(==802-11-wireless== band: bg mode: infrastructure security: 802-11-wireless-security ssid: opensuse-guest ==802-11-wireless-security== auth-alg: open key-mgmt: wpa-psk wep-tx-keyidx: 0 ==connection== autoconnect: true id: openSUSE type: 802-11-wireless uuid: ==ipv4== dns-search: method: auto )
Now you should repeat using the other, working client and copy both sets of output, before attaching them securely to a bug report at bugs.kde.org. With this information we will quickly be able to implement a fix.
Crashes
If you have a crash ensure you install debugging symbols and take a backtrace. In Kubuntu you need to add the debug repository and install plasma-widget-networkmanagement-dbgsym.
Эта страница в последний раз была отредактирована 16 сентября 2011 в 09:13. Содержание доступно по лицензии Creative Commons License SA 4.0 (если не указано иное).
Donate to KDE Why Donate?
Visit the KDE MetaStore
Show your love for KDE! Purchase books, mugs, apparel, and more to support KDE.
Точка доступа на KDE (Kubuntu 15.04)
Эта статья описывает как сделать точку доступа на Linux, в графической оболочке KDE, используя Network Manager. Это инструкция, показывает весь процесс, шаг за шагом. Статья написана на примере KDE 5 и Kubuntu 15.04. Но в KDE 4 и в другом дистрибутиве Linux точка доступа настраивается точно так же. Это позволит вам раздавать Интернет с компьютера, через WiFi, на другие устройства.
Инструкции по настройке точки доступа WiFi для других операционных систем:
Как создать точку доступа WiFi на KDE Kubuntu 15.04
В KDE версий 4 и 5 можно настроить точку доступа используя программу Network Manage. Менеджер соединений в этой программе имеет опцию «Точка доступа», для WiFi соединений. Такой же Network Manager в Ubuntu Unity этой опции не имеет.
- Дистрибутив Linux с графической средой KDE 4 или 5. Не во всех дистрибутивах с оболочкой KDE есть возможность настройки точки доступа через Network Manager!
- WiFi адаптер, который поддерживает режим работы «мониторинг». Для этой статьи использовался USB WiFi адаптер TP-Link TL-WN722NC.
- Соединение с Интернет. Для этой статьи было использовано Ethernet соединение с роутером. Но это может быть например и USB модем (МТС, Билайн, Мегафон). Или другое соединение.
Шаг первый
Проверить наличие соединения с Интернет и его работу. Нужно убедиться в том, что Интернет на компьютере есть.
Шаг второй
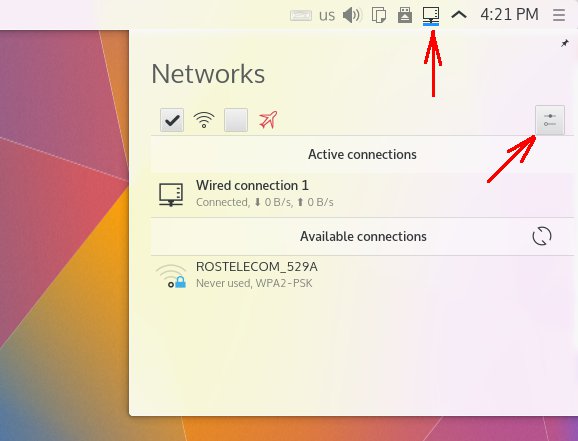
Нужно убедиться в том, что адаптер WiFi, подключен и все, что относится к WiFi, работает. Самый простой способ это кликнуть на значке «Сеть» в трее. В выпадающем меню должны быть строки с перечислением точек доступа. Конечно в том случае, если поблизости есть точки доступа.
Более сложный способ проверки — в терминале, например командой ifconfig -a.
Настройка точки доступа в KDE Network Manager
Кликнуть на значке «Сеть» в трее, затем в меню кликнуть на кнопке «Настройка»:
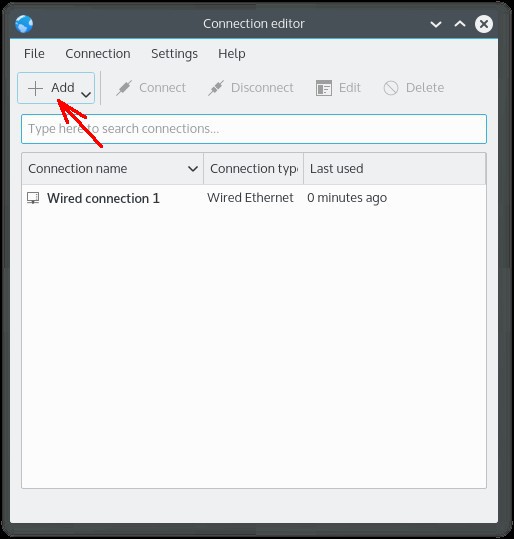
В открывшемся окне кликнуть на кнопке «Добавить» («Add») и в списке выбрать пункт «WiFi»:
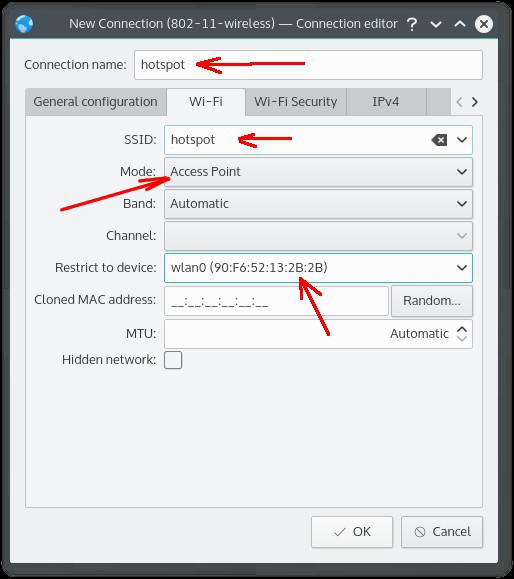
После этого откроется следующее окно, редактор соединения. В нем нужно заполнить несколько полей на разных вкладках. На вкладе «WiFi» заполнить четыре поля:
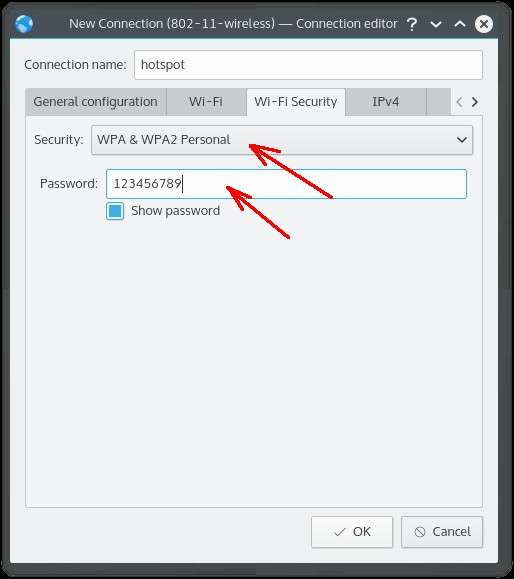
На вкладке «Безопасность» («WiFi Security») заполнить два поля. Длина пароля для WPA WPA2 должна быть минимум 8 символов:
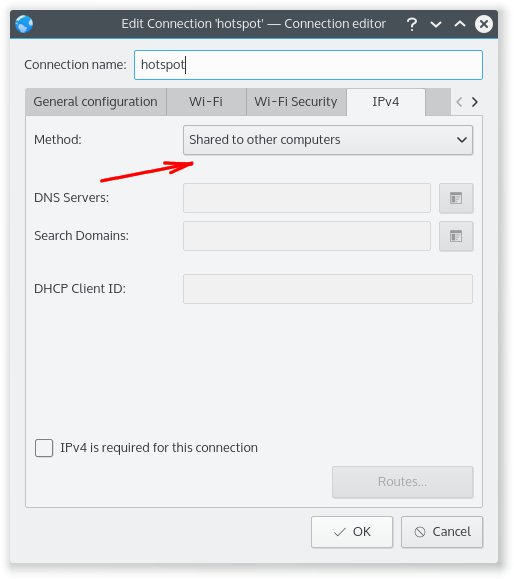
На вкладке «IPv4» заполнить одно поле (на русском языке это будет «Общее с другими компьютерами»):
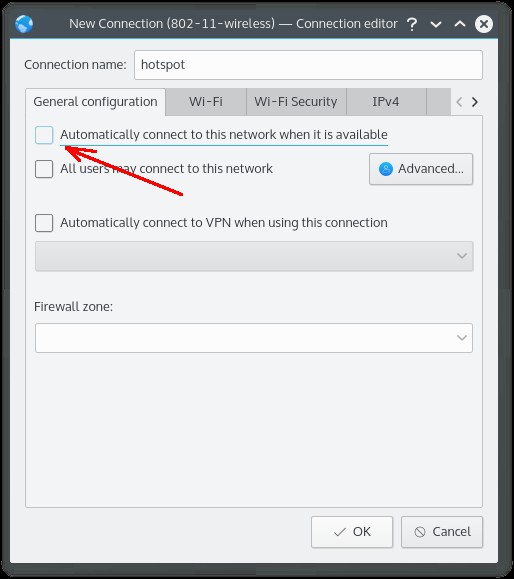
На вкладке «Общие» («General») убрать или оставить переключатель Автоматического включения точки доступа. Этот переключатель определяет как будет включаться точка доступа — вручную или автоматически при старте KDE:
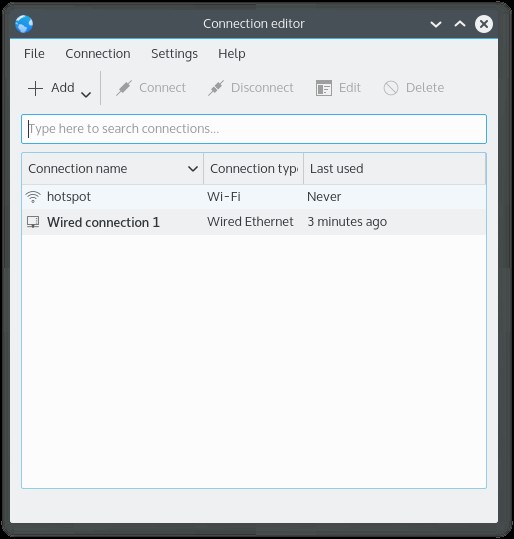
Далее нужно нажать кнопку «ОК» и после этого будет возврат в первое окно, списка соединений. Теперь в списке есть точка доступа:
Как управлять точкой доступа в KDE Network Manager
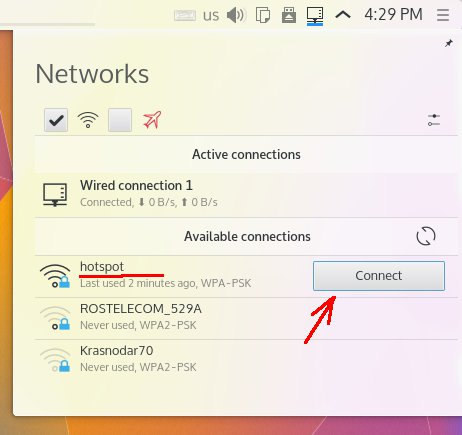
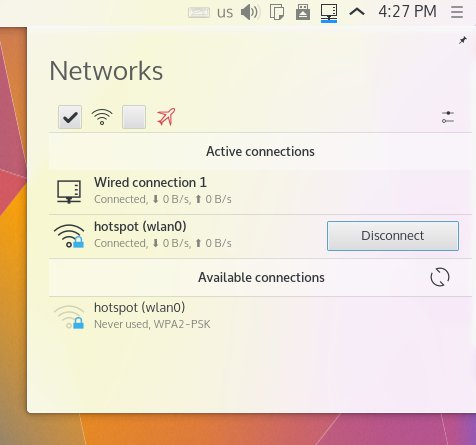
Включение через значок «Сеть», в трее:
Если в настройках точки доступа вы включите опцию «Автоподключения», тогда Network Manager будет автоматически включать ее, при загрузке KDE.
Выключение тоже через значок «Сеть», в трее:
Как посмотреть клиентов точки доступа на KDE Kubuntu 15.04
Узнать о подключенных к точке доступа клиентах можно только в терминале. Командой:
В выводе команды нужно смотреть по названию интерфейса wlan0:
(192.168.150.5) 58:12:43:6f:2d:bc [ether] на wlan0
Или можно скачать скрипт ap-clients, извлечь из архива и запустить его (тоже в терминале):
Вывод скрипта показывает клиентов подключенных к точке доступа:
# IP address lease name MAC address
192.168.150.5 android-73d63f2392091d87 58:12:43:6f:2d:bc
Примечание 1
Пароль конечно поставьте посложнее чем 12345678 или qwerty0987. И не забудьте, что минимальная длина пароля для WPA-WPA2 равна 8 символам.
Примечание 3
Настройки точки доступа записаны в файле /etc/NetworkManager/hotspot
Защита вашей WiFi сети
Настройка точки доступа на других операционных системах