- Get Kernel Version for Linux: A Guide
- uname Command
- dmesg Command
- Display the /proc/version File
- hostnamectl Command
- Final Thoughts
- Related Articles:
- About the Author: Neil Golden
- 4 Ways to Check CentOS or RHEL Version
- How to Check Linux Kernel Version in CentOS
- How to Check CentOS or RHEL Release Version
- 1. Using RPM Command
- 2. Using Hostnamectl Command
- 3. Using lsb_release Command
- 4. Using Distro Release Files
Get Kernel Version for Linux: A Guide
Linux kernel is the core of the Linux operating system and is responsible for managing system resources such as the CPU, memory, and input/output devices. It is a program that interacts between the hardware and the software, enabling communication between them.
It also enables multi-tasking, where multiple processes can run at the same time, and time-sharing, where the CPU time is shared between running processes.
The Linux kernel is also responsible for providing security features, such as access control, memory protection, and user management. It ensures that only authorized users can access system resources and that processes cannot interfere with other processes’ memory.
A Linux kernel is composed of three key components: the process scheduler, the memory manager, and the device driver. Understanding the role of the Linux kernel is essential for ensuring the optimal performance and security of your Linux system.
Kernel version information is crucial for identifying and resolving issues related to hardware, software, and system stability. Linux distributions are known for their flexibility in customization and support for a range of hardware architectures.
As a result, checking the kernel version on a Linux-based system is crucial in determining compatibility between software and hardware components.
Take a look at four methods for obtaining the kernel version on a Linux system: the uname command, the dmesg command, the /proc/version file, and the hostnamectl command.

uname Command
The first and most common method of obtaining the kernel version on a Linux system is to use the uname command. This command prints the kernel release, version, and a few other system-related details.
Get kernel version Linux by opening a terminal window and entering the following command.
The output of this command will show the kernel version, as shown below.
In the above example, the Linux kernel version is 6.2.15-300.fc38.x86_64.
You can obtain additional information by adding some of the additional flags to the uname command. In order to see all of the available flags for the uname command, enter the following command into your terminal.
The command will output the following.
Usage: uname [OPTION]. Print certain system information. With no OPTION, same as -s. -a, --all print all information, in the following order, except omit -p and -i if unknown: -s, --kernel-name print the kernel name -n, --nodename print the network node hostname -r, --kernel-release print the kernel release -v, --kernel-version print the kernel version -m, --machine print the machine hardware name -p, --processor print the processor type (non-portable) -i, --hardware-platform print the hardware platform (non-portable) -o, --operating-system print the operating system --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exit Full documentation dmesg Command
Another way to get the kernel version in Linux is to use the dmesg command. The dmesg command displays the kernel ring buffer messages, including the kernel version.
To use the dmesg command, open your terminal window and enter the following command.
dmesg | grep "Linux version"This command will output the current kernel version, as shown below.
[0.000000] Linux version 6.2.15-300.fc38.x86_64 (mockbuild@9ce97d1fde5043c6a5e6af84f9091fb1) (gcc (GCC) 13.1.1 20230426 (Red Hat 13.1.1-1), GNU ld version 2.39-9.fc38) #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Thu May 11 17:37:39 UTC 2023In the above example, the Linux kernel version is 6.2.15-300.fc38.x86_64.
Display the /proc/version File
The /proc/version file contains information about the current kernel version and the build details. This file can be used to get the kernel version in Linux.
To display information in the /proc/version file, open your terminal window and enter the following command.
This command will output the contents of the file, which includes the kernel version, build date, compiler version, and other build information, as shown below.
Linux version 6.2.15-300.fc38.x86_64 (mockbuild@9ce97d1fde5043c6a5e6af84f9091fb1) (gcc (GCC) 13.1.1 20230426 (Red Hat 13.1.1-1), GNU ld version 2.39-9.fc38) #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Thu May 11 17:37:39 UTC 2023You can easily see, from the output above, that the Linux kernel version is 6.2.15-300.fc38.x86_64.
hostnamectl Command
The hostnamectl command is used to view or modify the system hostname and related settings. This command can also be used to display the Linux kernel version. The hostnamectl command is a component of systemd, so it wouldn’t be available on a Linux distribution that isn’t using systemd by default, such as Gentoo.
To use the hostnamectl command, open your terminal window and enter the following command.
This command will output the current state of the system, including the operating system, kernel version, and other hardware-related information, as shown below.
Static hostname: linux-system Icon name: computer-vm Chassis: vm Machine ID: 4a14033b41c64c5a81b269cf866c57b5 Boot ID: e05b4580aeaf44889be57a9cb9631d8b Virtualization: vmware Operating System: AlmaLiunux 8.3 (Purple Manul) CPE OS Name: cpe:/o:almalinux:almalinux:8.3 Kernel: Linux 6.2.15-300.fc38.x86_64 Architecture: x86-64In the example presented above, the Linux kernel version is 6.2.15-300.fc38.x86_64.
Final Thoughts
You have learned four methods for obtaining the kernel version on a Linux system: the uname command, the dmesg command, the /proc/version file, and the hostnamectl command. Now you have the knowledge of how to check the Linux kernel version in almost every way possible. These methods are simple and effective and can be used to determine the current kernel version and identify issues related to hardware, software, and system stability.
Knowing the kernel version is essential for testing software compatibility, vulnerability assessments, and troubleshooting system issues. By utilizing one of the methods mentioned above, you can obtain the kernel version on your Linux system and ensure seamless operation.
Make sure that you are keeping your kernel updated. By doing so, you are keeping your system secured. Without an updated kernel, you may encounter compatibility issues, reduced functionality, or even complete inoperability of certain hardware devices. By keeping your kernel up to date, you will ensure that your system is fully compatible with the latest hardware advancements.
Liquid Web offers VPS Hosting, Cloud Dedicated Servers, and Dedicated Servers for your website hosting needs. Our highly professional support technicians will always be there to assist you with any kind of issue. Reach out to our sales team and publish your amazing website online today.
Related Articles:
About the Author: Neil Golden
Neil contributed to solving the complex puzzle of evolution for a long time by obtaining his Ph.D. in Archaeology. These days, he digs the Linux servers in his role within the Liquid Web Monitoring Department instead of Paleolithic stone tools in the caves on archaeological sites. Instead of mammoths, he is now hunting for bugs on Linux servers. He has written numerous scientific and technical articles because writing is one of his biggest passions. In his free time, Neil composes music, reads novels, and travels the world.
Join our mailing list to receive news, tips, strategies, and inspiration you need to grow your business
4 Ways to Check CentOS or RHEL Version
Do you know the version of CentOS/RHEL release you are running on your server? Why is this even important? There are several reasons to keep this information in mind: to quickly gather information about your system; keep up with bug fixes and security updates, and configure correct software repositories for a specific release, among others.
This is probably an easy task for experienced users, but it’s not usually the case for newbies. In this article, we will show how to check the version of CentOS or RHEL Linux installed on your server.
How to Check Linux Kernel Version in CentOS
Knowing the kernel version is just as important as knowing the distro release version. To check Linux kernel version, you can use the uname command.
$ uname -or OR $ uname -a #print all system information
From the output of the above command, the CentOS is powered by an old kernel version, to install or upgrade to the latest kernel release, follow the instructions in our article: How to Install or Upgrade to Kernel 4.15 in CentOS 7.
How to Check CentOS or RHEL Release Version
CentOS release version numbers have two parts, a major version such as “6” or “7” and a minor or update version, such as or “6.x” or “7.x”, which correspond to the major version and update set of RHEL receptively, used to build a particular CentOS release.
To elaborate more in this, take for instance CentOS 7.5 is built from the source packages of RHEL 7 update 5 (also known as RHEL version 7.5), which is referred to as a “point release” of RHEL 7.
Let’s take a look at these 4 useful ways to check CentOS or RHEL release version.
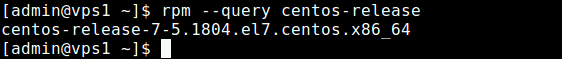
1. Using RPM Command
RPM (Red Hat Package Manager) is a popular and core package management utility for Red Hat based systems like (RHEL, CentOS and Fedora), using this rpm command, you will get your CentOS/REHL release version.
$ rpm --query centos-release [On CentOS] $ rpm --query redhat-release [On RHEL]
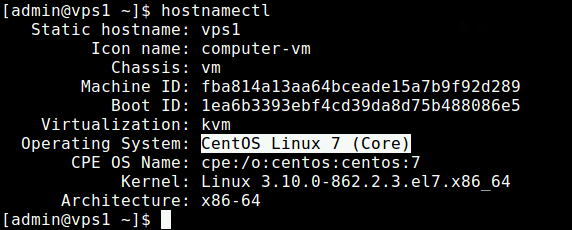
2. Using Hostnamectl Command
hostnamectl command is used to query and set Linux system hostname, and show other system related information, such as operating system release version as shown in the screenshot.
3. Using lsb_release Command
lsb_release command displays some LSB (Linux Standard Base) and distribution information. On CentOS/REHL 7, the lsb_release command is provided in the redhat-lsb package which you can install it.
$ sudo yum install redhat-lsb
Once you have installed it, you can check your CentOS/REHL version as shown.
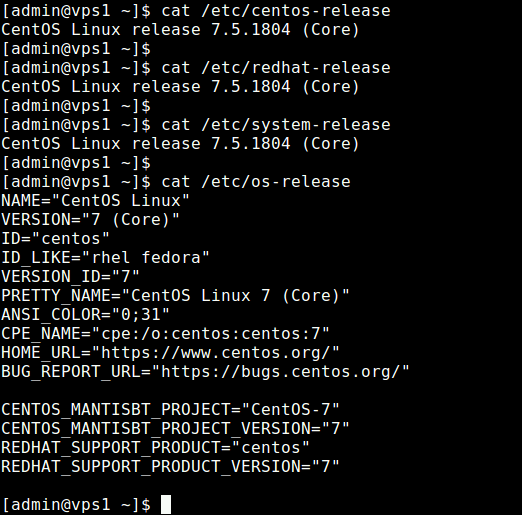
4. Using Distro Release Files
All the above commands retrieve OS release information from a number of system files. You can view the contents of these files directly, using the cat command.
$ cat /etc/centos-release [On CentOS] $ cat /etc/redhat-release [On RHEL] $ cat /etc/system-release $ cat /etc/os-release #contains more information
That’s all for now! If you know any other method that should be covered here, let us know via the comment form below. You can also ask any questions related to the topic.