- whereis command in Linux with Examples
- Find Path of a Command with whereis
- Basic Usage of the whereis Command:
- Printing the Full Path of Only Binaries/Executables:
- Printing the Full Path of Only Man Pages:
- Finding the Full Path of Linux Headers or Kernel Source Files Only:
- Printing the Directories the whereis Command Searched:
- Adding a New Search Directory or Directories:
- About the author
- Shahriar Shovon
- Команда whereis в Linux
- Как использовать команду whereis
- Выводы
whereis command in Linux with Examples
whereis command is used to find the location of source/binary file of a command and manuals sections for a specified file in Linux system. If we compare whereis command with find command they will appear similar to each other as both can be used for the same purposes but whereis command produces the result more accurately by consuming less time comparatively. whereis doesn’t require any root privilege to execute in any RHEL/CentOS 7.
The supplied names are first removed from leading pathname/directory components and any (single) trailing extension of the form .ext, for example, .c. Prefixes of s. resulting from use of source code control are also dealt with. whereis then attempts to locate the desired program in a list of standard Linux directories.
Points to be kept on mind while using whereis command:
- Since whereis command uses chdir(change directory 2V) to give you the result in fastest possible way, the pathnames given with the -M, -S, or -B must be full and well defined i.e. they must begin with a `/‘ and should be a valid path that exist in the system’s directories, else it exits without any valid result.
- whereis command has a hard-coded(code which is not dynamic and changes with specification) path, so you may not always find what you’re looking for.
Example 1: Let’s say, we want to find the location of apropos command then we need to execute the following command in the terminal:
Example 2: To find the location of lshw command.
- -b : This option is used when we only want to search for binaries.
Example: To locate binary of a Linux command let’s say gunzip. - -m : This option is used when we only want to search for manual sections. Example: To locate man page of false command.
- -s : This option is used when we only want to search for sources.
- -u: This option search for unusual entries. A source file or a binary file is said to be unusual if it does not have any existence in system as per [-bmsu] described along with “–u”. Thus `whereis-m-u *‘ asks for those files in the current directory which have unusual entries. Example: To display the files in the current directory which have no documentation file.
- -B : This option is used to change or otherwise limit the places where whereis searches for binaries. Example: To locate binary of lesspipe in the path, /bin.
- -M : This option is used to change or otherwise limit the places where whereis searches for manual sections. Example: To check man page of intro that is only in a specific location i.e. /usr/share/man/man1.
- -S : This option is used to change or otherwise limit the places where whereis searches for sources. Example: To Find all files in /usr/bin which are not documented in /usr/man/man1 with source in /usr/src.
- -f : This option simply terminate the last directory list and signals the start of file names. This must be used when any of the -B, -M, or -S options are used.
- -V: Displays version information and exit.
- -h: Displays this help and exit.
Find Path of a Command with whereis
whereis is used to find the path of the Linux binary /executable files, source files and man page files.There are many Linux distributions. Not every Linux distribution keeps the binary/executable files, source files and man page files in the same location. So, to find out the path of these files when needed, the whereis command is used. It is a very useful command for every Linux system administrator out there.
In this article, I am going to show you how to use the whereis command on Linux. So, let’s get started.
Basic Usage of the whereis Command:
You can find the full path of any standard Linux command that is in the PATH of your Linux operating system.
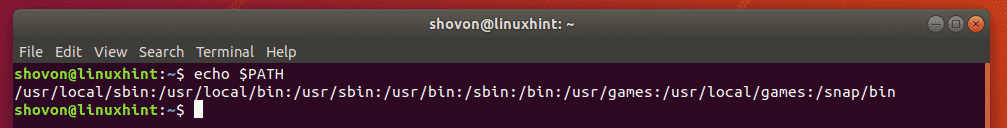
NOTE: The PATH contains the directories where the standard Linux commands and other commands are installed. You can run the following command to print the PATH on your console.
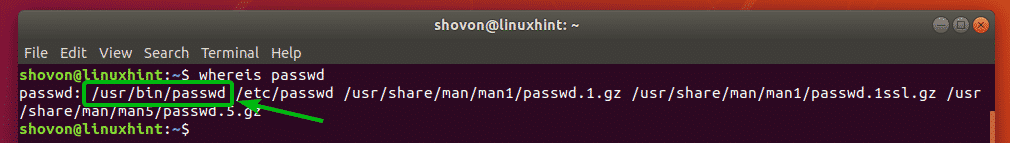
Let’s say, you want to know the full path of the Linux command passwd. To do that, run the whereis command as follows:
As you can see, the full path of the passwd command is /usr/bin/passwd.
The whereis command without any option prints the full path of the command, the full path of the configuration file that matches the query, and the full path of the matched man page files.
Printing the Full Path of Only Binaries/Executables:
If you only want to print the full path of specific Linux commands and configuration files, then you can do so with the -b option of whereis.
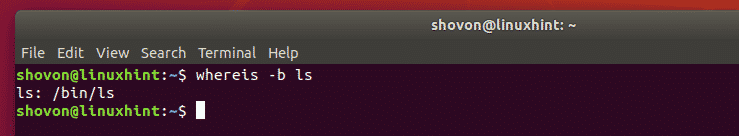
Let’s say, you want to print only the full path of the command ls, then run the whereis command as follows:
As you can see, the full path of the command ls is /bin/ls.
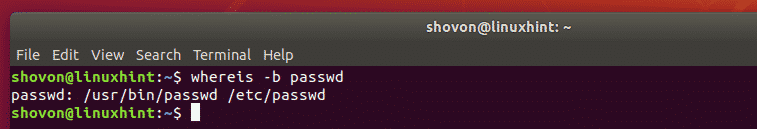
If there is a matching configuration file, it should be printed as well. For example, when you try to find the full path of the command passwd, you should also get the full path of the passwd configuration file as you can see in the screenshot below.
Printing the Full Path of Only Man Pages:
If you want to print the full path of only man pages on your computer, then you can use the -m option of the whereis command.
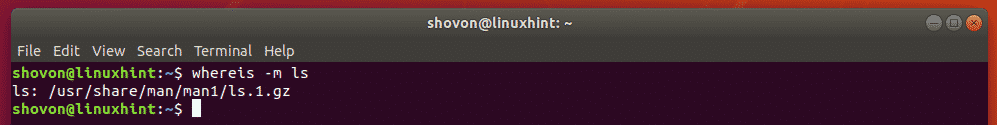
For example, let’s say, you want to find out the full path of all man page files of the ls command. To do that, run the whereis command as follows:
As you can see, the man page of the ls command is in the path /usr/share/man/man1/ls.1.gz.
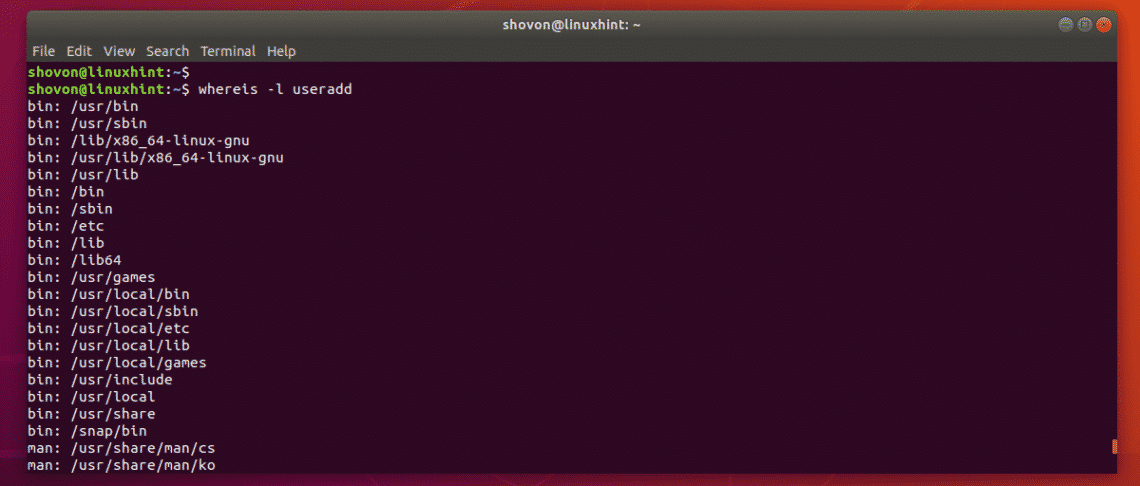
The same way, you can find the full path of all the man pages of the useradd command.
Finding the Full Path of Linux Headers or Kernel Source Files Only:
You can use the -s option of the whereis command to print the full path of the Linux headers or kernel source files used to develop system software.
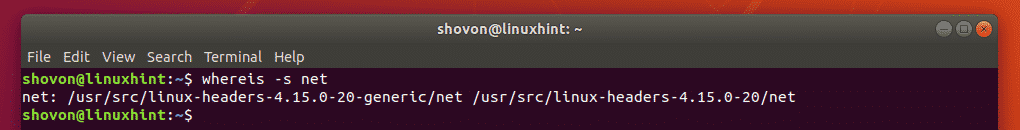
For example, to find the full path of the source file net, you can use the whereis command as follows:
As you can see, there are two locations where the net source header file is kept on my Ubuntu 18.04 LTS, /usr/src/linux-headers-4.15.0-20-generic/net and /usr/src/linux-headers-4.15.0-20/net.
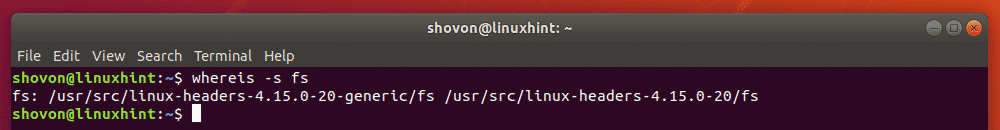
The same way, you can search for the fs source file with the whereis command as follows.
Printing the Directories the whereis Command Searched:
By default, the whereis command searches a lot of system directories. You can use the -l option to tell whereis to print the directories it searched.
As you can see, the whereis command searched a lot of directories by default.
Adding a New Search Directory or Directories:
You saw earlier that the whereis command searches a lot of directories by default. But if you have some directories that you want whereis to search, then you can use the -B, -M or -S option of the whereis command to specify binary/executable, manual or man pages, source or kernel header directories respectively.
Let’s say, you have some binary files in the ~/bin directory that you want to include in the whereis search. To do that, you can run the whereis command as follows:
NOTE: Whenever you use either the -B, -M or the -S option, you must also use the -f option as shown above. Otherwise, you will get an error.
As you can see, the full path of the CreateDirectory command is printed. So, it worked. We’ve successfully added a new binary directory to the whereis search path.
You can also add more than one search directories if you want.
For example, let’s say, you want to add the ~/bin and ~/bin2 binary directories to the whereis search path. To do that, run the whereis command as follows:
The same way, you can add manual or man page directories to the whereis search path as follows:
The same way, for the source or kernel headers, you can use the -S option to add addition search directories as follows:
You can also mix the -B, -M and -S options as required to add the required search path for the binary, manual or source files respectively.
So, that’s how you use the whereis command to find the path of commands/binaries/executables, man pages or manuals, and source files in Linux. Thanks for reading this article.
About the author
Shahriar Shovon
Freelancer & Linux System Administrator. Also loves Web API development with Node.js and JavaScript. I was born in Bangladesh. I am currently studying Electronics and Communication Engineering at Khulna University of Engineering & Technology (KUET), one of the demanding public engineering universities of Bangladesh.
Команда whereis в Linux
whereis — это служебная программа командной строки, которая позволяет вам найти расположение двоичных файлов, файлов исходного кода и файлов справочной страницы для данной команды.
В этой статье мы покажем вам, как использовать команду whereis в Linux.
Как использовать команду whereis
Синтаксис команды whereis следующий:
whereis [OPTIONS] FILE_NAME. При использовании без каких-либо опций, whereis выполняет поиск команды, указанной в качестве аргумента, в двоичных, исходных и ручных файлах.
По умолчанию whereis ищет файлы команды в жестко заданных путях и каталогах, перечисленных в переменных среды . Используйте параметр -l чтобы найти каталоги, в которых ищет команда whereis .
Например, чтобы получить информацию о команде bash , вы должны ввести следующее:
bash: /bin/bash /etc/bash.bashrc /usr/share/man/man1/bash.1.gz В выходных данных выше bash: — это команда, для которой вы хотите получить информацию, /bin/bash — это путь к двоичному файлу, /etc/bash.bashrc — это исходный файл и /usr/share/man/man1/bash.1.gz — это страница руководства.
Если whereis команда не существует, будет выведено только имя команды.
Вы также можете указать несколько аргументов для команды whereis :
Вывод будет включать информацию о командах netcat и uptime :
netcat: /bin/netcat /usr/share/man/man1/netcat.1.gz uptime: /usr/bin/uptime /usr/share/man/man1/uptime.1.gz Для поиска только двоичных файлов команд используйте параметр -p .
Например, чтобы найти расположение команды ping , вы должны ввести следующее:
При поиске только местоположения двоичного файла команды предпочтительнее использовать команды which или type .
Чтобы искать только исходные файлы, используйте параметр -s .
Если исходные файлы существуют, whereis напечатает их расположение.
Параметр -m позволяет искать только файлы man:
Чтобы ограничить места, где whereis ищет двоичные файлы, используйте параметры -B , для руководств параметр -M и -S для источников. Каждая опция принимает список абсолютных путей к каталогам, разделенных пробелом. Список каталогов должен заканчиваться параметром -f , указывающим начало имен файлов.
Например, чтобы найти двоичный файл cp в каталоге /bin , введите:
Параметр -u указывает, whereis искать необычные записи. Файлы, в которых нет ровно одной записи каждого запрошенного типа (двоичный, ручной и исходный), считаются необычными файлами (командами).
Например, для поиска всех двоичных файлов в каталоге /bin , в которых нет справочных страниц или более одной документации, вы должны ввести:
Подстановочный знак ( * ) после параметра -f означает все файлы в текущем рабочем каталоге ( /bin ).
Выводы
Утилита whereis используется для поиска двоичных файлов, исходных файлов и файлов руководства для данной команды.
Если у вас есть вопросы или отзывы, оставьте комментарий ниже.