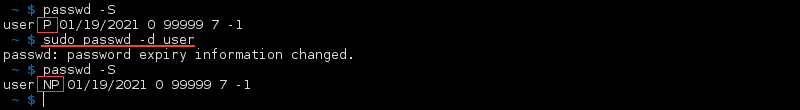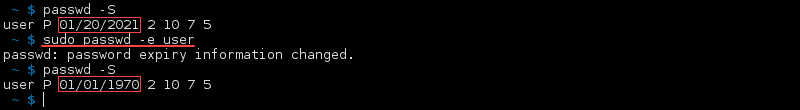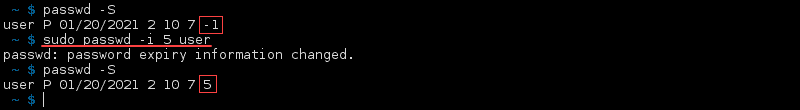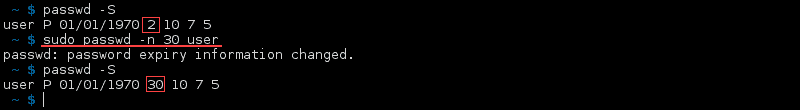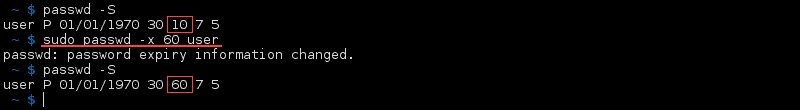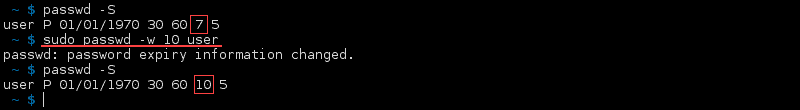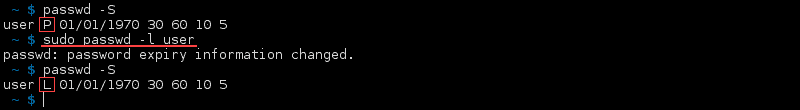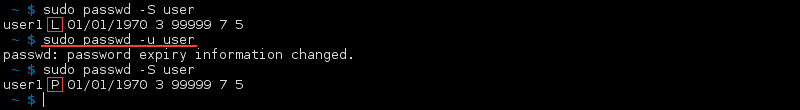- Как изменить пароль пользователя в Linux
- Введение
- Измените свой пароль пользователя
- Изменить пароль другого пользователя
- Заставить пользователя изменить пароль при следующем входе в систему
- Выводы
- Изменяем пароль пользователя в Linux
- Меняем пароль текущего пользователя
- Меняем пароль произвольного пользователя
- Дополнительная информация
- How To Use The Passwd Command In Linux
- passwd Command in Linux With Examples
- See Password Status Info
- See Password Status Info for All the Accounts
- Change a User Password
- Delete User Password
- Expire Account Password
- Set Number of Days After the Password Expires and the Account Deactivates
- Set the Minimum Number of Days Between Password Changes
- Set the Maximum Number of Days for Which the Password Remains Valid
- Change the Expired Password
- Display the Warning for Expiring Password
- Lock the Password
- Unlock the Password of an Account
- Use the Quiet Mode
- Change Password for Repository Named “Repo”
- Change the Root Directory for the passwd Command Process
- See All passwd Commands
Как изменить пароль пользователя в Linux
В этом руководстве мы объясним, как изменить пароль пользователя в Linux. Мы также покажем вам, как заставить пользователей изменить свой пароль при следующем входе в систему.
Инструкции должны работать с любым дистрибутивом Linux, включая Ubuntu, Debian и CentOS.
Введение
В Linux вы можете изменить пароль учетной записи пользователя с помощью утилиты passwd .
Зашифрованные пароли пользователей, а также другая информация, связанная с паролями, хранится в /etc/shadow .
Как обычный пользователь, вы можете изменить только свой собственный пароль. Пользователь root и пользователи с привилегиями sudo могут изменять пароли других пользователей и определять, как пароль может быть использован или изменен.
При смене пароля убедитесь, что вы используете надежный и уникальный пароль.
Надежный пароль — это самое важное, что вы можете сделать для защиты своей учетной записи. Часто надежный пароль состоит как минимум из 16 символов и содержит как минимум одну заглавную букву, одну строчную букву, одну цифру и один специальный символ.
По соображениям безопасности рекомендуется регулярно обновлять пароль и использовать уникальный пароль для каждой учетной записи.
Измените свой пароль пользователя
Чтобы изменить пароль учетной записи вашего собственного пользователя, запустите команду passwd без аргументов:
Вам будет предложено ввести текущий пароль. Если пароль правильный, команда попросит вас ввести и подтвердить новый пароль.
При вводе пароли не отображаются на экране.
В следующий раз, когда вы войдете в свою систему, используйте новый пароль.
Изменить пароль другого пользователя
Как мы упоминали во введении, только пользователь root и пользователи с доступом sudo могут изменить пароль другой учетной записи.
В следующем примере предполагается, что вы вошли в систему как пользователь с привилегиями sudo.
Чтобы изменить пароль другой учетной записи пользователя, выполните команду passwd , а затем введите имя пользователя. Например, чтобы изменить пароль пользователя с именем linuxize , выполните следующую команду:
Вам будет предложено ввести и подтвердить новый пароль:
Enter new UNIX password: Retype new UNIX password: В случае успеха команда напечатает что-то вроде этого:
passwd: password updated successfully Заставить пользователя изменить пароль при следующем входе в систему
По умолчанию срок действия паролей не истекает. Чтобы заставить пользователя изменить свой пароль при следующем входе в систему, используйте команду passwd с параметром —expire за которым следует имя пользователя:
sudo passwd --expire linuxizeПриведенная выше команда немедленно истечет срок действия пароля пользователя.
В следующий раз, когда пользователь попытается войти со старым паролем, ему будет показано сообщение, заставляющее его изменить пароль:
WARNING: Your password has expired. You must change your password now and login again! Changing password for linuxize. (current) UNIX password: Enter new UNIX password: Retype new UNIX password: passwd: password updated successfully Connection to 192.168.121.209 closed. Как только пользователь установит новый пароль, соединение будет закрыто.
Выводы
В этом руководстве вы узнали, как изменить пароли пользователей и как установить срок действия пароля.
Вы можете найти дополнительную информацию о команде passwd, набрав man passwd в своем терминале или посетив страницу руководства Linux passwd .
Если у вас есть какие-либо вопросы или отзывы, не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии.
Изменяем пароль пользователя в Linux
В данной статье я хочу рассказать о том, как изменять пароль пользователя в Linux. Я рассмотрю универсальный способ изменения пароля через командную строку, чтобы не привязываться к конкретному дистрибутиву.
Для изменения паролей в Linux служит команда passwd. Команду можно выполнять без указания каких-либо параметров, либо явно указать имя пользователя, пароль которого вы хотите сменить (в данном случае требуются права суперпользователя). После чего вам нужно будет ввести текущий пароль, а затем дважды ввести новый пароль.
Меняем пароль текущего пользователя
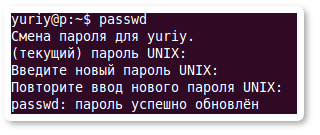
Чтобы сменить пароль текущего пользователя выполните команду passwd без параметров:
После этого нужно будет ввести текущий пароль и нажать клавишу Enter, затем ввести новый пароль и снова нажать Enter и, наконец, еще раз ввести новый пароль и нажать Enter.
Changing password for yuriy. (current) UNIX password: Enter new UNIX password: Retype new UNIX password: passed: password updated successfullyОбратите внимание на то, что когда вы вводите пароль, он не отображается на экране.
Если вдруг вы получили сообщение:
You must choose a longer passwordЭто означает, что вы ввели очень простой (или короткий) пароль. В таком случае повторите команду passwd и введите более сложный пароль (как минимум длиной от 6 до 8 символов, пароль должен включать цифры, прописные и строчные символы). Чтобы избежать проверки пароля на сложность необходимо выполнять команду passwd через sudo (см. ниже).
Меняем пароль произвольного пользователя
Чтобы сменить пароль любого пользователя вам необходимо запускать программу passwd под пользователем root или через sudo. Например, чтобы сменить пароль пользователя с именем pingvinus необходимо выполнить:
В данном случае вам нужно будет ввести только новый пароль:
Enter new UNIX password: Retype new UNIX password: passed: password updated successfullyЗдесь пароль не проверяется на сложность и можно задавать совсем простые и короткие пароли.
Дополнительная информация
Я рассмотрел два простых способа для быстрого изменения паролей пользователей. Получить полный список возможностей команды passwd можно, выполнив в терминале:
How To Use The Passwd Command In Linux
The passwd command modifies passwords for user accounts and manages the password validity period. This is a must-know utility for user account administration.
This article shows examples of how to use the passwd command in Linux, along with all the available options.
Note: To check if you have sudo privileges, type sudo whoami in the terminal.
passwd Command in Linux With Examples
Using the passwd command, a superuser changes and modifies settings for any user. Regular users are only allowed to change their own password.
The terminal prints out what user you are changing the password for. Type your current password, and then define and confirm your new password.
Any password that does not meet basic requirements is rejected and a user must re-enter a new password. Using a strong password is an important security aspect, and it helps prevent brute force attacks.
See Password Status Info
Using passwd with the —status option displays all the information about a password and the validity periods. The shorter version is -S :
Check another user’s password status by entering:
The password status has seven fields:
1. A user’s login name.
2. Whether a user has a locked password (L), no password (NP), or a password (P).
3. Date of last password change.
4. Minimum password age.
5. Maximum password age.
6. Warning period for password change.
7. Inactivity period for the password change.
The last three fields are in days.
See Password Status Info for All the Accounts
Check the status info for all accounts using passwd with the sudo command with the -S and -a options, or the extended version —all :
Note: You can create a sudo user and assign elevated permissions. Make sure it’s a trusted user.
Change a User Password
To change a specific user’s password, run the passwd command with sudo privileges and the account you wish to update:
This option comes in handy if a user has forgotten their password.
Note: Reset or change the sudo or root password in case you forget it.
Delete User Password
If a user has a password and you need to remove it, use:
When you check the password status, it changes the second field from P to NP:
The passwd —delete and passwd -d commands are a quick way to disable a password for an account.
Expire Account Password
To force expire a password use the —expire or -e options with the passwd command:
When you check the status, the date of the last password change is now 01/01/1970. The next time this user logs in, they must change their password.
Set Number of Days After the Password Expires and the Account Deactivates
An account can automatically deactivate after its password has expired and not changed for a certain number of days. Use the -i or —inactive option and set the number of days as an integer:
The last number in the status changes to the number of days you set for that user.
Set the Minimum Number of Days Between Password Changes
To change the minimum number of days between password changes, use the —mindays or -n option with the number of days as an integer:
In the status report for that user, the set number appears after the date.
Set the Maximum Number of Days for Which the Password Remains Valid
To change the maximum number of days between password changes, use the —maxdays or -x option with the number of days as an integer:
The status of that user shows that maximum number of days for the password validity has changed.
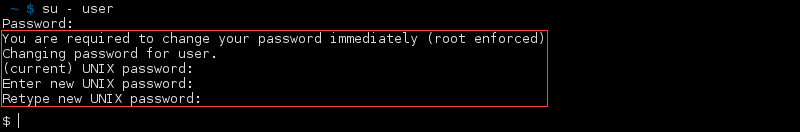
Change the Expired Password
Once a password expires, a prompt appears during next login to change the password. Enter the old password and then a new one twice for confirmation. In this example, the expiry was root enforced:
Note: In this example, the su command switches to the user account, but use the sudo command if possible. Read about the difference between sudo and su.
Display the Warning for Expiring Password
The warning period message displays for expiring passwords. Use the option —warndays or -w to set how many days before the expiry the warning appears:
Lock the Password
Locking a password makes the user unable to log in using their password. However, they are still able to log in using other authentication methods. To lock a password, use:
The password status for that user changes to L. In the example below, it changes from P to L:
Unlock the Password of an Account
To unlock a password for a locked account (L), use the —unlock or -u option:
The password status changes from locked (L) to the previous state of the password for the account, allowing the user to log in regularly.
Use the Quiet Mode
Quiet mode hides the “Changing the password for ” message:
The password status changes from locked (L) to the previous state of the password for the account, allowing the user to log in regularly.
The passwd -q command is useful when you do not want to display the username you are changing the password for on your screen.
Note: When you need to update passwords of multiple users, use the chpasswd command.
Change Password for Repository Named “Repo”
For more advanced usage, the /etc/nsswitch.conf file specifies the repositories where the password changes happen. Specify the repository with the command:
Change the Root Directory for the passwd Command Process
The passwd command process runs from the default root directory. Modify the root directory by running the —root option:
Or the -R option:
You need to set a password for root for the information update.
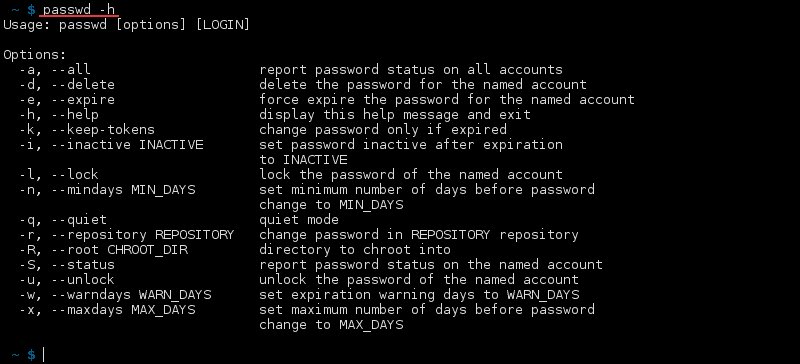
See All passwd Commands
There are numerous commands to use with the passwd tool. List all the options if you forget any by running:
A list of all the options along with a short description prints out:
The passwd command is vital for managing account security, both for an individual user and a system administrator. Automating password validity periods is convenient and easily configurable.
If you find it hard to keep track of all the different passwords and changes, there are many enterprise solutions for password management.
Milica Dancuk is a technical writer at phoenixNAP who is passionate about programming. Her background in Electrical Engineering and Computing combined with her teaching experience give her the ability to easily explain complex technical concepts through her content.
Speed up connecting to remote servers by enabling passwordless SSH login via public key authentication.
Are you looking to change the root password in Ubuntu? Changing passwords is a good practice and should be.
In Linux, root privileges (or root access) refers to a user account that has full access to all files.
MySQL is a database management system. It’s operated under the Open Source software model and has become a.