- Команда Uptime в Linux
- Как использовать команду Uptime
- варианты uptime
- Выводы
- Команда uptime в linux
- NAME
- SYNOPSIS
- DESCRIPTION
- OPTIONS
- FILES
- AUTHORS
- SEE ALSO
- REPORTING BUGS
- Linux Uptime Command With Usage Examples
- Using Uptime
- Check Linux Server Uptime
- Check Linux Server Starting Time
- Uptime Version & Help
- Linux Uptime Command
- How Does the Uptime Command Work?
- Example 1: Uptime in Human-Readable Format
- Example 2: Check the Start Time of the System
- Example 3: Check the Version of the Installed Uptime Command
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Syed Minhal Abbas
Команда Uptime в Linux
Как следует из названия, команда uptime показывает, как долго работает система. Он также отображает текущее время, количество вошедших в систему пользователей и среднюю загрузку системы за последние 1, 5 и 15 минут.
Как использовать команду Uptime
Синтаксис команды uptime следующий:
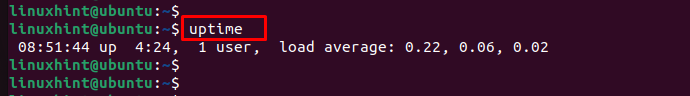
Чтобы отобразить время безотказной работы системы, вызовите команду без каких-либо параметров:
Результат будет выглядеть примерно так:
22:20:33 up 620 days, 22:37, 1 user, load average: 0.03, 0.10, 0.10 - 22:20:33 — Текущее системное время.
- up 620 days, 22:37 — Продолжительность работы системы.
- 1 user — количество вошедших в систему пользователей.
- load average: 0.03, 0.10, 0.10 — load average: 0.03, 0.10, 0.10 системы за последние 1, 5 и 15 минут.
Информация, отображаемая uptime аналогична информации, содержащейся в заголовке команды w .
Средняя загрузка Linux может немного сбивать с толку. В отличие от других операционных систем, которые показывают среднюю загрузку процессора, Linux показывает среднюю загрузку системы.
Измерение средней загрузки системы количества заданий, которые в настоящее время выполняются или ожидают ввода-вывода диска. Он в основном сообщает вам, насколько загружена ваша система в течение заданного интервала.
Если средние значения нагрузки равны 0.0 , то система в основном простаивает. Если среднее значение нагрузки за последнюю 1 минуту выше, чем среднее значение за 5 или 15 минут, то нагрузка увеличивается. В противном случае нагрузка уменьшается.
Средняя загрузка обычно увеличивается из-за более высокой загрузки ЦП или нагрузки на диск.
Чтобы лучше понять среднюю загрузку Linux, ознакомьтесь со статьей Брендана Грегга: Средние нагрузки Linux: разгадывая тайну .
варианты uptime
Команда uptime принимает только несколько редко используемых параметров.
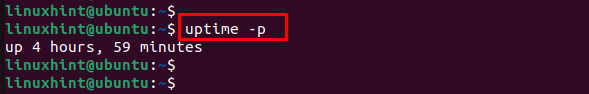
Параметр -p , —pretty указывает uptime отображать вывод в —pretty формате:
Команда отобразит только время работы системы:
up 1 year, 36 weeks, 4 days, 23 hours, 15 minutes Параметр -s , —since показывает дату и время с момента —since системы:
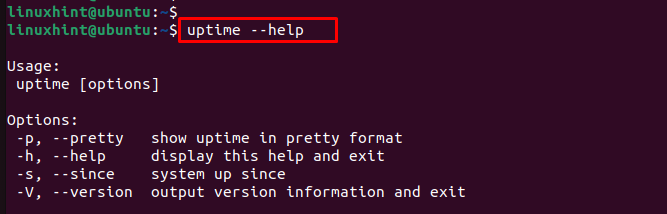
- -h , —help — отобразить справочное сообщение и выйти.
- -V , —version — показать информацию о версии и выйти.
Выводы
Команда uptime предоставляет информацию о текущем времени, онлайн-пользователях, длительности работы вашей системы и средней загрузке системы.
Если у вас есть какие-либо вопросы или отзывы, не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии.
Команда uptime в linux
NAME
uptime - Tell how long the system has been running.
SYNOPSIS
DESCRIPTION
uptime gives a one line display of the following information. The current time, how long the system has been running, how many users are currently logged on, and the system load averages for the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes. This is the same information contained in the header line displayed by w(1). System load averages is the average number of processes that are either in a runnable or uninterruptable state. A process in a runnable state is either using the CPU or waiting to use the CPU. A process in uninterruptable state is waiting for some I/O access, eg waiting for disk. The averages are taken over the three time intervals. Load averages are not normalized for the number of CPUs in a system, so a load average of 1 means a single CPU system is loaded all the time while on a 4 CPU system it means it was idle 75% of the time.
OPTIONS
-p, --pretty show uptime in pretty format -h, --help display this help text -s, --since system up since, in yyyy-mm-dd HH:MM:SS format -V, --version display version information and exit
FILES
/var/run/utmp information about who is currently logged on /proc process information
AUTHORS
uptime was written by Larry Greenfield ⟨greenfie@gauss.rutgers.edu⟩ and Michael K. Johnson ⟨johnsonm@sunsite.unc.edu⟩
SEE ALSO
ps(1), top(1), utmp(5), w(1)
REPORTING BUGS
© 2019 Canonical Ltd. Ubuntu and Canonical are registered trademarks of Canonical Ltd.
Linux Uptime Command With Usage Examples
The Linux Operating System is filled with several commands which any aspiring Linux expert or power user e.g. system admin must have a good grasp of. One of such commands is uptime and today, I’ll briefly discuss its purpose and syntax.
Uptime is a command that returns information about how long your system has been running together with the current time, number of users with running sessions, and the system load averages for the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes. It can also filter the information displayed at once depending on your specified options.
uptime uses a simple syntax:
Using Uptime
You can run the uptime command without any options like so:
It will display an output similar to:
09:10:18 up 106 days, 32 min, 2 users, load average: 0.22, 0.41, 0.32
In order of appearance, the command displays the current time as the 1st entry, up means that the system is running and it is displayed next to the total time for which the system has been running, the user count (number of logged on users), and lastly, the system load averages.
What are system load averages? It is the average number of processes that are in a runnable or uninterruptable state. A process is in a runnable state when it is using the CPU or waiting to use the CPU; while a process is in an uninterruptable state when it is waiting for I/O access like waiting for a disk.
To know more about uptime, check out our article: Understand Linux Load Averages and Monitor Performance of Linux
Now let’s see some useful uptime command usage with examples.
Check Linux Server Uptime
You can filter uptime’s result to show only the running time of the system with the command:
# uptime -p up 58 minutes
Check Linux Server Starting Time
Using option -s will display the date/time since when the system has been running.
# uptime -s 2019-05-31 11:49:17
Uptime Version & Help
As it is with most command line apps, you can display uptime’s version information and quick help page with the following command.
# uptime -h Usage: uptime [options] Options: -p, --pretty show uptime in pretty format -h, --help display this help and exit -s, --since system up since -V, --version output version information and exit For more details see uptime(1).
Having gotten to this point in the article, you can now use uptime for your daily runs and you’ll determine its level of usefulness to you. If you have any doubts, here’s its man page.
Linux Uptime Command
Any Linux distro comes with the “uptime” command. It’s an important command for system administrators to know. It helps troubleshoot the issues related to power and scheduling. Of course, there are other alternative tools available for this purpose but uptime is relatively simple and easy to use.
The content of this guide is as follows:
Let’s start the uptime command.
How Does the Uptime Command Work?
If you use the system’s uptime command via command prompt, you get many benefits out of it. For example, suppose you are facing a problem in connecting to the server. Then, you can easily run the uptime command on the server to check if there has been a recent reboot on the server. This helps in troubleshooting the situation and provides you with better visibility to apply the required solution.
The output specifies the current time. “Up” specifies that the system is up and running along with the total time that the system is up to the user count and the system load averages.
Running the uptime command of a Linux system via the command line, you get a specified output in the following order:
- The current time of the system.
- The total uptime of the system.
- The active users that are currently running the system.
- The average of the system loads that is available for the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes.
Uptime command comes with various options. To check the options, we can run the “help” command.
Example 1: Uptime in Human-Readable Format
With the use of the “-p” option, you can get a pretty clear output which displays the uptime in the number of days, hours, minutes, and seconds format:
Example 2: Check the Start Time of the System
Another option is to check the exact time when the system is first started rather than the time spent since it started. Run the following command on the command-line interface with the “-s” option:
Example 3: Check the Version of the Installed Uptime Command
If you want to check the version of the installed uptime package in the system, run the following command with the “-V” option:
The output shows the current version of the “uptime” command.
Conclusion
Linux is a well-known environment and is highly recommended for various projects due to its stability and various configurations. The “uptime” command checks the system information. We explained the “uptime” command with its various options.
About the author
Syed Minhal Abbas
I hold a master’s degree in computer science and work as an academic researcher. I am eager to read about new technologies and share them with the rest of the world.