- How to Run .jar File in Ubuntu 22.04 | Linux Mint 21[Beginner’s Guide]
- Step 1: Install Java
- Install OpenJDK Java
- Install Oracle Java
- Step 2: Open / Run .jar file
- Step 3: Create shortcut icon for your .jar application
- Summary:
- Как запустить jar в Linux
- Как запустить jar Linux
- Выводы
- How to Run Jar File in Ubuntu Linux
- Run jar files in Ubuntu
- Method 1: Using GUI
- Method 2: Using the Terminal
- Here’s how to set up the JAVA_HOME variable
- Launch jar file linux
How to Run .jar File in Ubuntu 22.04 | Linux Mint 21[Beginner’s Guide]
Got a .jar package from web? Here’s a step by step beginner’s guide shows you how to open and create shortcut icons for it in Linux!
File with .jar extension is mostly an application package or installer made by Java programming language. It’s a portable package that can run in Linux, Windows, and macOS within a Java Runtime Environment (JRE).
Step 1: Install Java
As mentioned above, you need Java JRE to run any .jar packages, but Ubuntu Linux does not come with Java pre-installed.
There are 2 Java available: the free and open-source OpenJDK Java, and Oracle Java which is NOT open-source but free for personal and even commercial use. Choose either one that you prefer.
Install OpenJDK Java
OpenJDK is available in system repository, so user can simply search for and install it from Ubuntu Software.
However, Ubuntu Software (aka Snap Store) always leads to Snap package that runs in sandbox! So I would recommend to open terminal by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T on keyboard and run command to install OpenJDK JRE:
sudo apt install default-jre
Install Oracle Java
Oracle Java is not available in Linux repositories. But Oracle offers official packages for Linux for downloading at the link below:
And, beginners can follow this tutorial to install and setup the Java environment in Linux.
Step 2: Open / Run .jar file
After installing Java JRE, you can run the .jar file to directly launch the application or app installer.
Firstly, you need to add executable permission to the .jar file by:
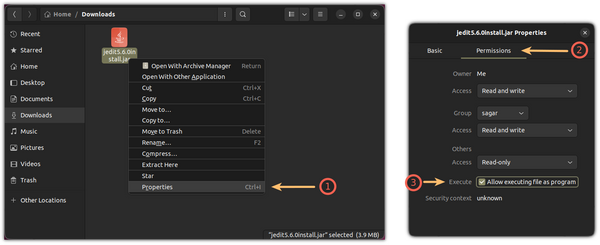
- Right-click on the .jar in file manager and go to ‘Properties’ dialog.
- Then, enable ‘Allow executing file as program‘ under Permissions tab.
Or, simply open terminal and run command to grant executable permission:
chmod u+x /PATH/TO/FILE_NAME.jar
In my case, the command can be chmod u+x ~/Downloads/JPDFViewer.jar .
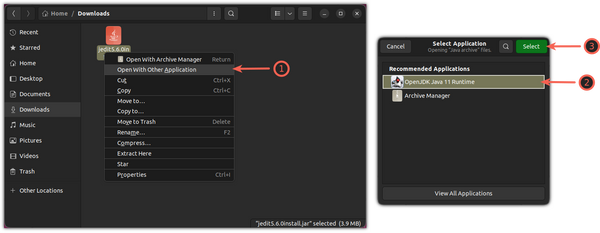
To open .jar file via OpenJDK, just right-click on it in file manager, and select “Open with Other Application” -> “OpenJDK Java 11 Runtime“.
To open .jar file via Oracle Java, do:
- Firstly, right-click on blank area in the folder (such as Downloads folder) that contains the .jar file, then select “Open in Terminal”.
- In pop-up terminal dialog, run command to open the .jar file (launch the java app or installer):
/usr/lib/jvm/jdk-19/bin/java -jar FILE_NAME.jar
Step 3: Create shortcut icon for your .jar application
To make the .jar application visible in system start menu (or search-able in ‘Activities’ overview), you can create a .desktop shortcut file.
- Firstly, it’s recommended to move the .jar file into user’s .local/bin folder, so you won’t delete it by accident.TIP: .local is hidden folder, press Ctrl+H to view it in user’s home folder. And, create bin folder if not exist.
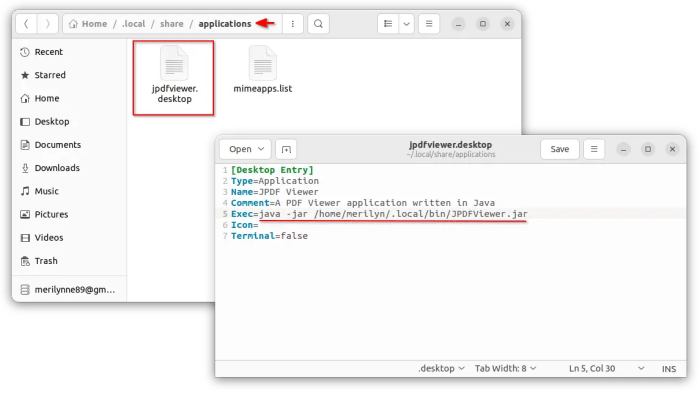
- Then, open Home folder and navigate to .local/share/applications/. Create an empty file and re-name to whatever_name.desktop .
- Edit that .desktop file you just created and add following lines:
[Desktop Entry] Type=Application Name=JPDF Viewer Comment=A PDF Viewer application written in Java Exec=java -jar /home/merilyn/.local/bin/JPDFViewer.jar Icon= Terminal=false
If you’ve correctly setup the .desktop file, you should be able to launch the .jar application from start menu or ‘Activities’ overview (depends on your DE).
In my case, I left the value of ‘Icon’ empty in the .desktop file, so it shows an universal gear icon instead.
Summary:
In general, file with .jar extension is a Java app or installer. User needs to install either OpenJDK or Oracle Java Runtime Environment for running it.
To create a shortcut icon for the .jar app, just create a .desktop file in user’s .local/share/applications folder with correct rules will do the trick.
Как запустить jar в Linux
Java — это кроссплатформенный язык программирования, благодаря которому программы, написанные один раз, можно запускать в большинстве операционных систем: в Windows, Linux и даже MacOS. И всё это без каких-либо изменений.
Но программы, написанные на Java, распространяются в собственном формате .jar, и для их запуска необходимо специальное ПО — Java-машина. В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим, как запустить jar-файл в Linux.
Как запустить jar Linux
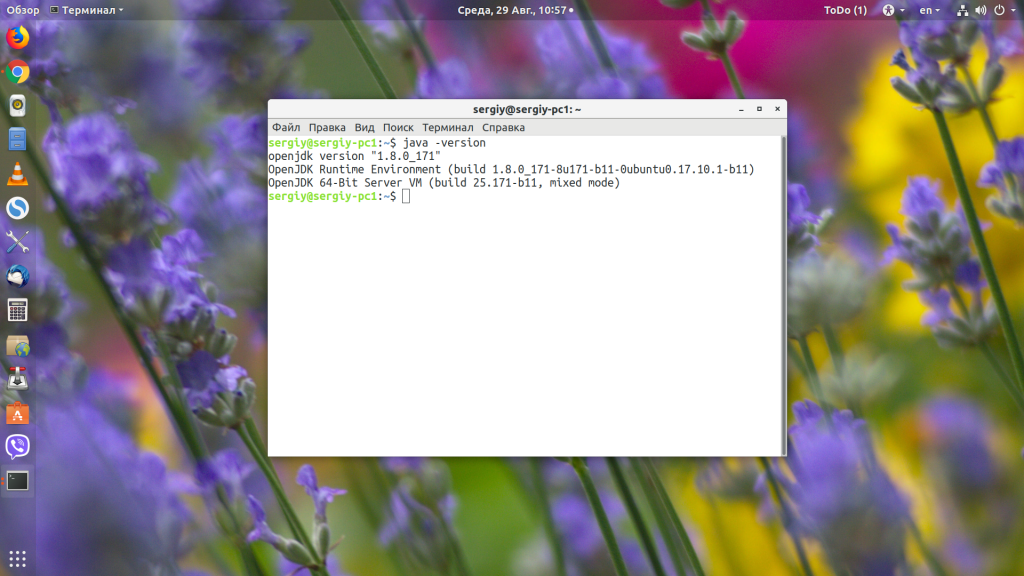
Как я уже сказал, для запуска jar-файлов нам необходимо, чтобы на компьютере была установлена Java-машина. Если вы не собираетесь ничего разрабатывать, вам будет достаточно Java Runtime Environment или JRE. Что касается версии, то, обычно, большинство программ работают с 7 или 8 версией. Если нужна только восьмая, то разработчики прямо об этом сообщают. Посмотреть версию Java и заодно убедиться, что она установлена в вашей системе, можно с помощью команды:
У меня установлена восьмая версия, с пакетом обновлений 171. Если вы получаете ошибку, что команда не найдена, то это значит, что вам нужно установить java. В Ubuntu OpenJDK JRE можно установить командой:
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jre
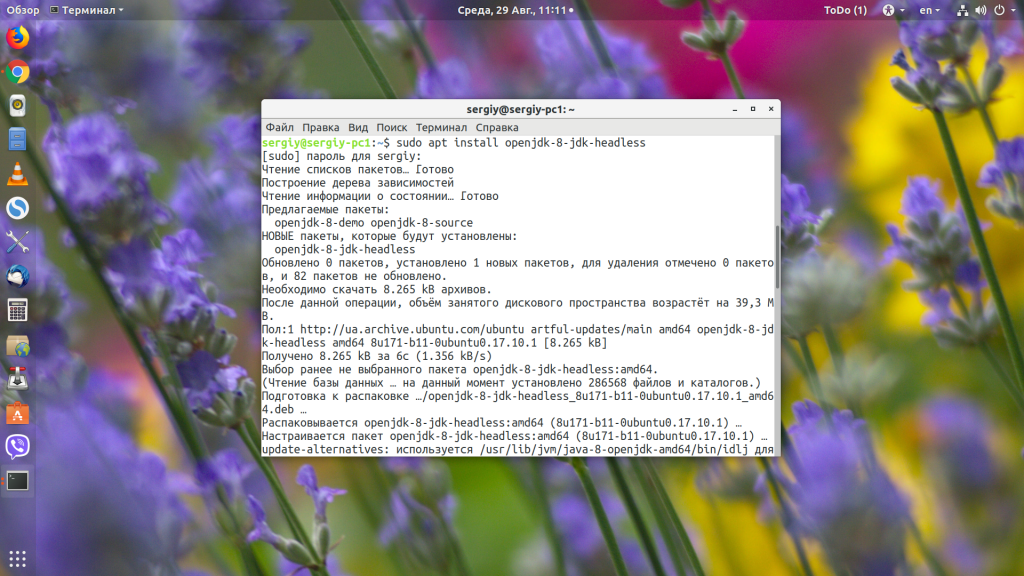
Если вы хотите скомпилировать пример из этой статьи, то вам понадобиться не JRE, а JDK, её можно установить командой:
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk-headless
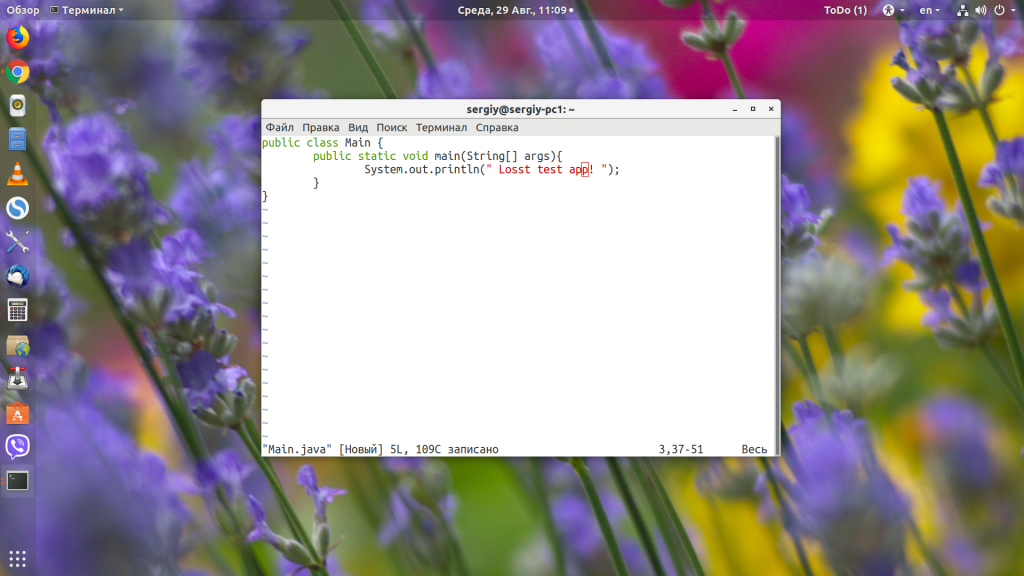
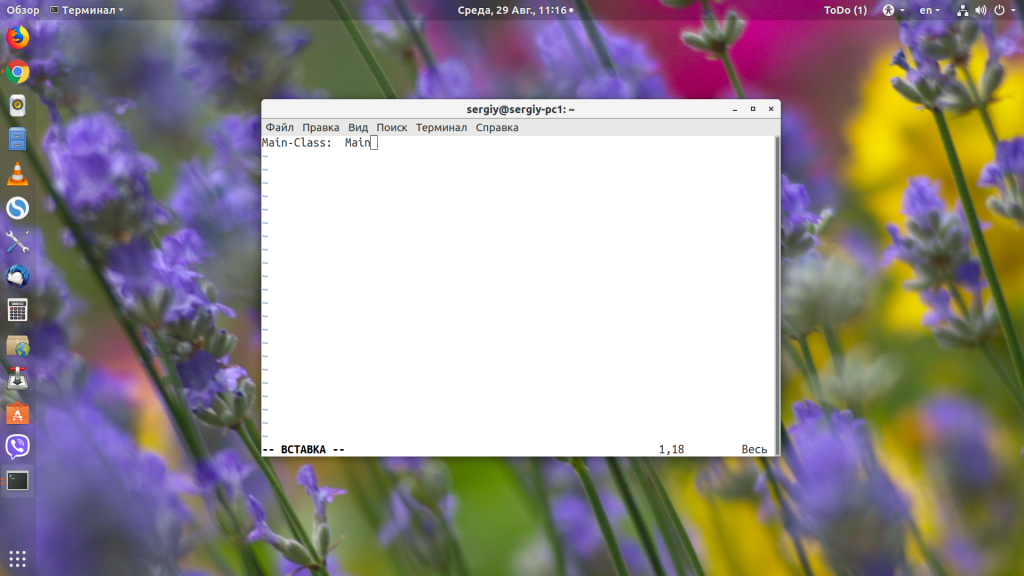
Чтобы узнать, как установить Java в других дистрибутивах, смотрите статью по ссылке выше. Когда Java будет установлена, вы можете очень просто запустить любой jar-файл в Linux, передав путь к нему в качестве параметра Java-машине. Давайте для примера создадим небольшое приложение:
public class Main public static void main(String[] args) System.out.println(» Losst test app! «);
>
>
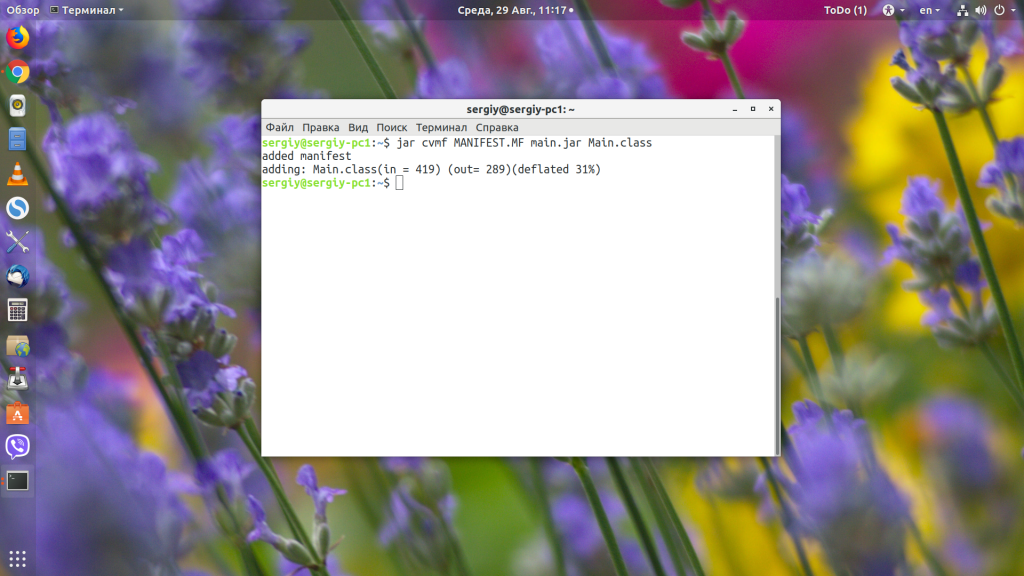
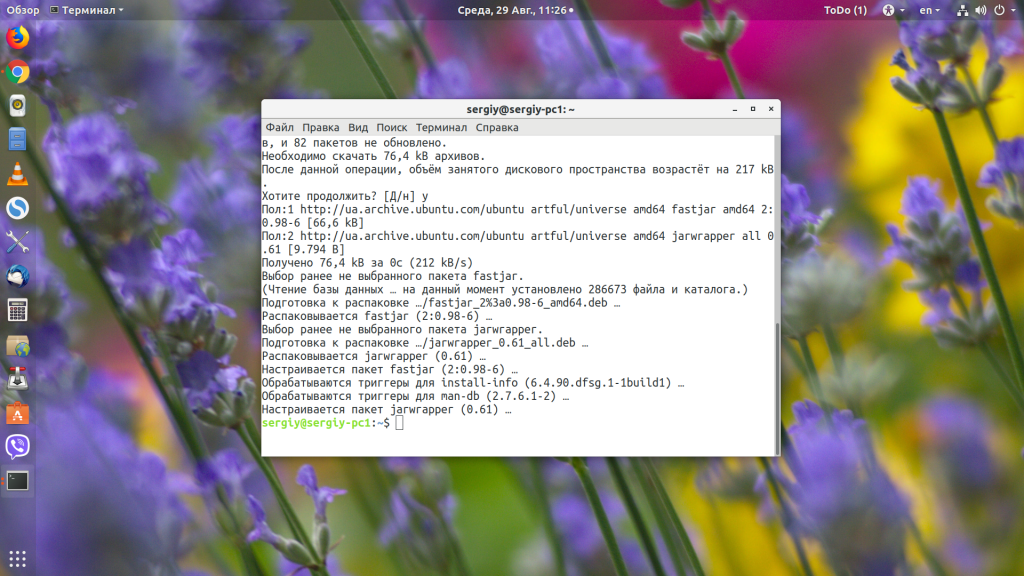
Затем скомпилируем наше приложение в jar-файл:
javac -d . Main.java
jar cvmf MANIFEST.MF main.jar Main.class
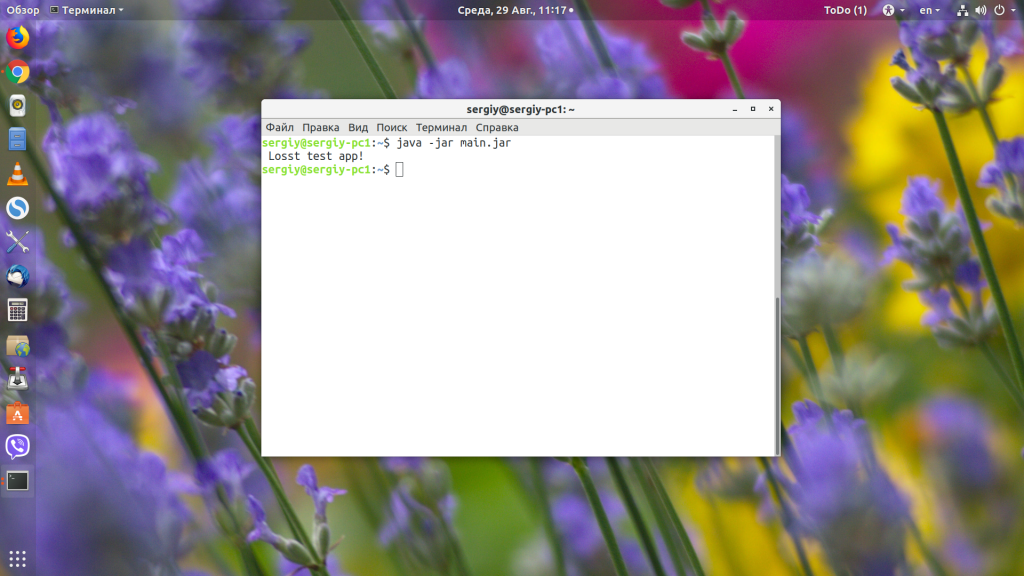
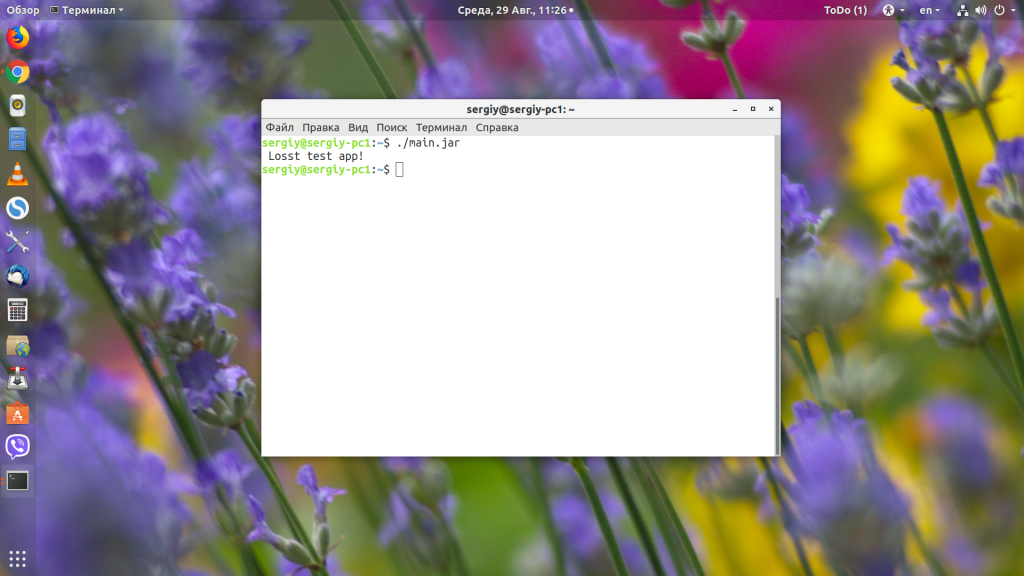
Теперь можно запустить наш jar-файл командой java с параметром -jar:
Таким образом вы можете запустить любой jar-файл, который собран для вашей версии Java. Но не очень удобно каждый раз открывать терминал и прописывать какую-либо команду. Хотелось бы запускать программу по щелчку мышки или как любую другую Linux-программу — по имени файла.
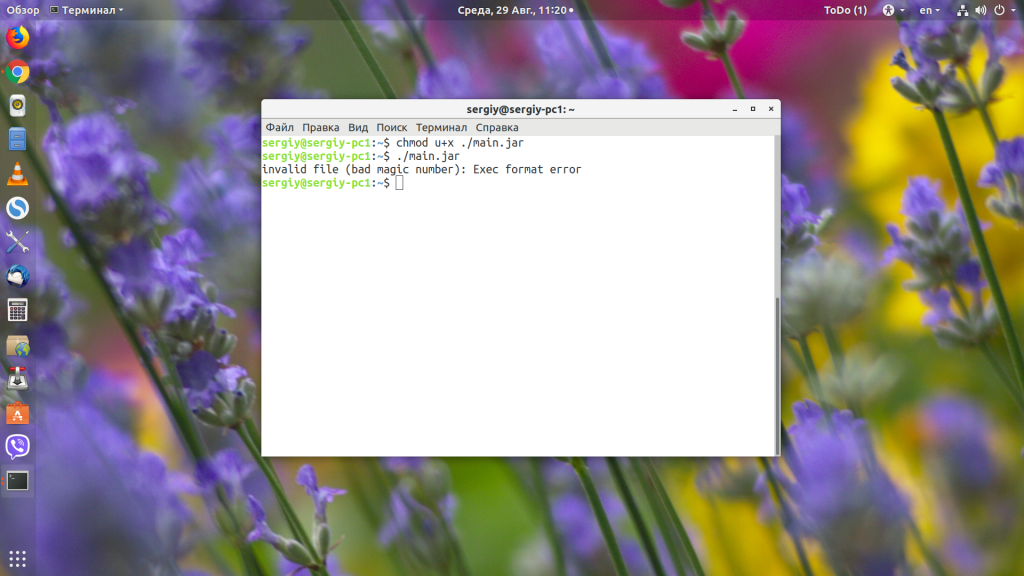
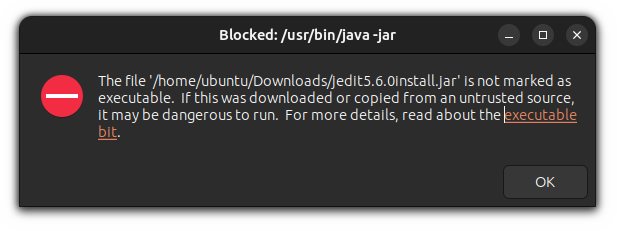
Если мы дадим программе право на выполнение:
И попытаемся её запустить, то получим ошибку:
Чтобы её исправить, нам понадобиться пакет jarwrapper:
sudo apt install jarwrapper
Теперь можно запускать java в Linux по щелчку мыши или просто командой.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрели, как запустить jar Linux с помощью java-машины, а также как упростить команду запуска. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to Run Jar File in Ubuntu Linux
Downloaded a JAR file and don’t know how to use it? Learn how to run JAR files in Ubuntu based Linux distributions.
If you install any package having the .jar extension and try to execute it, it may throw an error saying «The file is not marked as executable»: And in this tutorial, I will walk you through how you can install its prerequisites and run Jar files in Ubuntu and other Linux with multiple methods.
Run jar files in Ubuntu
If you don’t know, JAR stands for Java ARchive so you must have a working Java environment. If you have Java installed, you should be able to run it. Check if Java is installed with:
If you see an error instead of the version number, install Java runtime environment using the following command:
sudo apt install default-jreSo let’s start with the first one.
Method 1: Using GUI
The first step is to open the file manager from the system menu and navigate to the jar file which you want to run.
Then, right-click on the jar app and select Properties .
From there, select Permissions and enable Allow executing file as program :
That made the file executable.
But you have yet to select which app it should use to run the jar files.
To select an Application to start the jar files, again, click on the jar file and choose the second option Open with Other Application and choose the OpenJDK Java Runtime option:
Now, you can start the jar application like you do with any other files by pressing the Enter key.
In my case, it was an installer and it started as it should:
Method 2: Using the Terminal
If you believe in efficiency, I’m about to show you the terminal method will complete the task in only three commands.
First, open the terminal and navigate to the directory where the jar file is located using the cd command:
Once done, use the chmod command with the +x flag to make the file executable:
And finally, you can use the Java command with the -jar flag to run the jar file:
Here’s how to set up the JAVA_HOME variable
Most of the users set the JAVA_HOME variable incorrectly. So we thought, why not make a dedicated guide to get things done correctly?
I hope you will find this guide helpful.
Launch jar file linux
- Top developer relations trends for building stronger teams Learn about enterprise trends for optimizing software engineering practices, including developer relations, API use, community .
- 5 noteworthy challenges of automotive software development Modern cars are loaded with technology, but creating in-vehicle applications isn’t always a cakewalk. Here are five unique .
- New AWS service targets data security, genAI feature to come The cloud provider’s new service helps employees within organizations be more productive while securing their work. The vendor .
- The potential of ChatGPT for software testing ChatGPT can help software testers write tests and plan coverage. How can teams anticipate both AI’s future testing capabilities .
- Retail companies gain DORA metrics ROI from specialist tools DORA metrics and other measures of engineering efficiency are popping up in add-ons to existing DevOps tools. But third-party .
- Scrum master certification exam questions and answers Are you ready for the Scrum master certification exam? Test yourself on these 10 tough Scrum master exam questions and answers.
- Prices for cloud infrastructure soar 30% Tough macroeconomic conditions as well as high average selling prices for cloud computing and storage servers have forced .
- Deploy a low-latency app with AWS Local Zones in 5 steps Once you decide AWS Local Zones are right for your application, it’s time for deployment. Follow along in this step-by-step video.
- HPE bets big on public cloud offering for AI HPE is entering the AI public cloud provider market — but is it ready? Read more about its AI offerings for HPE GreenLake and .
- Risk & Repeat: How bad is Clop’s MoveIt Transfer campaign? Clop’s data theft and extortion campaign against MoveIt Transfer customers marks some of the most high-profile threat activity .
- Clop’s MoveIt Transfer attacks lead to mixed results Clop’s data theft extortion campaign against MoveIt Transfer customers has apparently compromised hundreds of organizations. But .
- For stronger public cloud data security, use defense in depth The amount of cloud-resident data is increasing — and so are the number of challenges to sufficiently secure it, especially .
- AWS Control Tower aims to simplify multi-account management Many organizations struggle to manage their vast collection of AWS accounts, but Control Tower can help. The service automates .
- Break down the Amazon EKS pricing model There are several important variables within the Amazon EKS pricing model. Dig into the numbers to ensure you deploy the service .
- Compare EKS vs. self-managed Kubernetes on AWS AWS users face a choice when deploying Kubernetes: run it themselves on EC2 or let Amazon do the heavy lifting with EKS. See .