- How do I connect to Wi-Fi on Linux Mint
- Prerequisites
- How to connect Wi-Fi on Linux Mint
- How to connect Wi-Fi on Linux Mint using Graphical Interface
- How to connect Wi-Fi on Linux Mint using the command-line interface
- Conclusion
- How to setup WiFi in Linux Mint
- How to connect to your wireless network
- Use your Linux machine as hotspot
- Related Posts
- How to disable threaded conversations in Thunderbird
- How to use Applets in Linux Mint Cinnamon – Linux Mint 21 edition
- How to prevent your Linux computer from falling asleep with Caffeine
- About John Been
- My Linux book is available now!
- Why this website
- New! My handcrafted desktop wallpaper series
- Most popular posts
- What if productivity influencer Ali Abdaal wants to be a Linux user – Is Linux usable for macOS users
- A first look at the new Zorin OS Upgrader
- How to use Applets in Linux Mint Cinnamon – Linux Mint 21 edition
- Mini Review – Bavarder is a simple ChatGPT-based AI App for Linux
- How to easily run multiple Linux distributions on one computer with Boxes
- Reader’s Posts
- There is always something new to learn and do in Linux
- Albert and Catfish – search tools, and horses for courses
- A non-technical Linux user’s tale
- Настраиваем WiFi в Linux Mint
- Используем графическую оболочку
- Используем терминал
- Настройка Wi-Fi сетей, защищенных по стандарту WPA2
How do I connect to Wi-Fi on Linux Mint
Wi-Fi is simply an internet connection that is used to connect the computing devices, laptops, smartphones or tablets to the internet. In this modern tech era, every computer needs an internet connection and to avoid inconvenience, a wireless connection is preferred. The internet service providers use Wi-Fi routers to convert the ethernet connection to wireless signals and any computing device can connect to that wireless connection by entering correct credentials. In this article, several ways are provided to connect to Wi-Fi on a Linux Mint.
Prerequisites
Before getting into connection with a wireless network, there are a set of prerequisites that are necessary to connect to a wireless network.
- The wireless adapter is in a functional state.
- And you are using a Linux Mint based operating system
How to connect Wi-Fi on Linux Mint
To connect your Linux Mint to Wi-Fi, there are two ways to do so, and they are mentioned below:
The upcoming sections briefly describe both methods.
How to connect Wi-Fi on Linux Mint using Graphical Interface
This section guides you to the graphical support of Linux Mint to connect to Wi-Fi. You must follow the steps carefully.
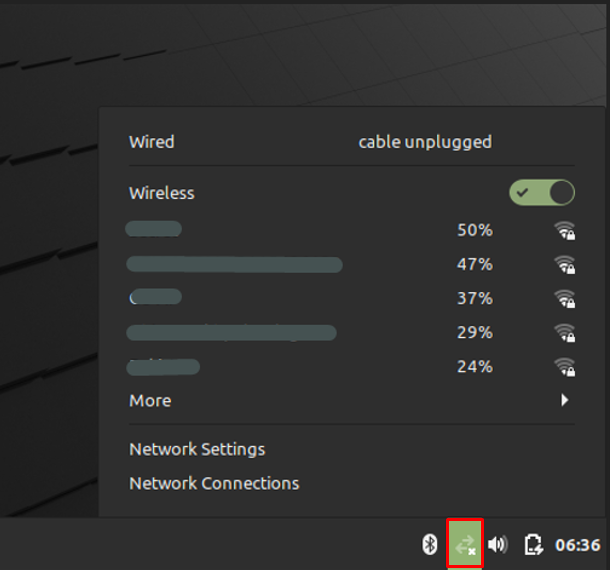
Step 1 : Navigate to the connection icon, and you would observe the available wireless connections.
Step 2 : Select on your wireless connection that you want to connect, and if it is encrypted you have to enter its password to connect successfully.
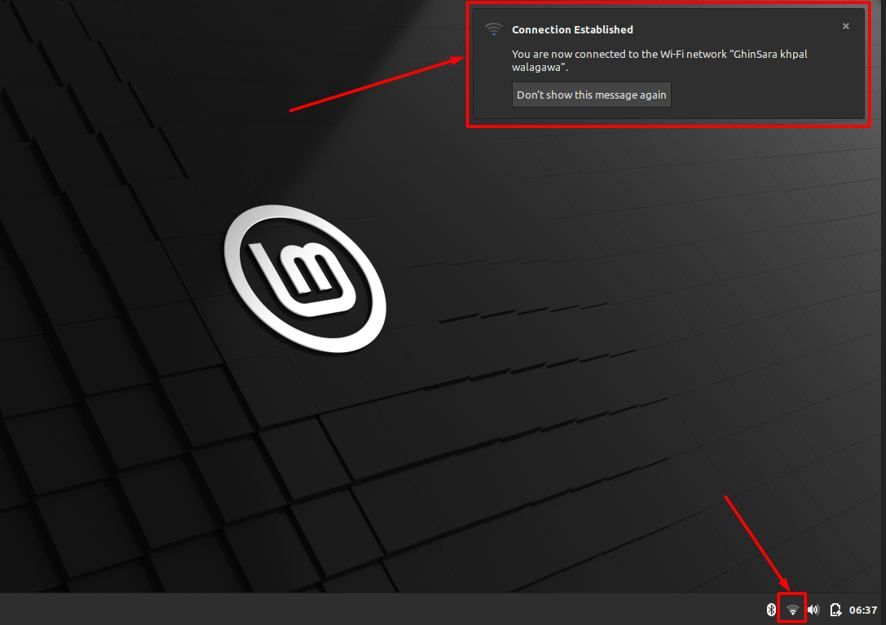
After connecting, the “Connection Established” prompt will appear.
How to connect Wi-Fi on Linux Mint using the command-line interface
The command-line interface of Linux-Mint is enriched in features as any terminal of Linux-based distribution. You have to execute several commands to enable Linux-Mint to connect with the Wi-Fi.
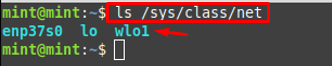
Step 1 : Firstly, it is recommended to trace your wireless network by navigating to the directory where network information resides. The directory’s address is “/sys/class/net“, and use the ls command to get the list of available networks.
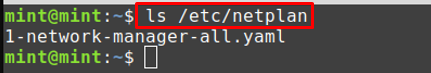
Step 2 : Look for the network configuration file using the netplan utility. By doing so, you would get the .yaml file, where you can put your wireless network configuration.
So, use the command written below to verify that the file exists in the “/etc/netplan” directory or not.
Note : Netplan is a Linux utility that is used to configure network interfaces. For that, a .yaml file is used to add the details of the network interface.
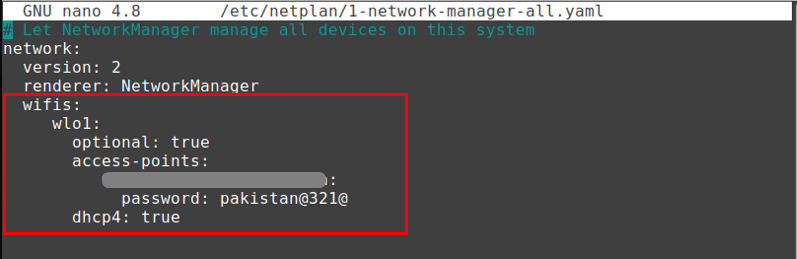
Step 3 : As the output of the above command returns the file 1-network-manager-all.yaml. Open the 1-network-manager-all.yaml file in nano(any editor can be used) editor.
The first three lines are already there; append the following lines after entering the details in the network-manager file, press “Ctrl+S” and “Ctrl+X” to save and exit the file.
Note: It is recommended that you keep the indentation in mind as you might not connect if proper indentation rules are not followed.
Wifis:
Wlp2s0:
optional: true
access points:
«SSID of wireless-connection»
Password: «password-of-wireless-connection»
dhcp4: true
Note: In the above syntax, SSID is the name of your wireless network, and the name selection depends on the user; thus, it varies from user to user.
For completing the configuration of netplan, you must execute the command written below.
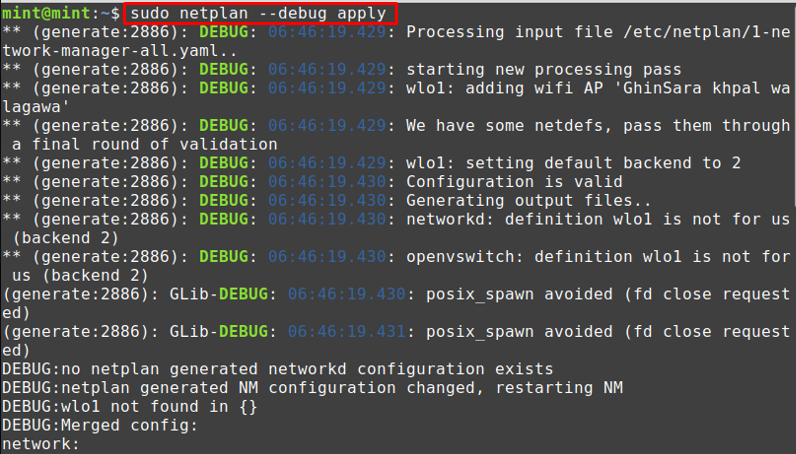
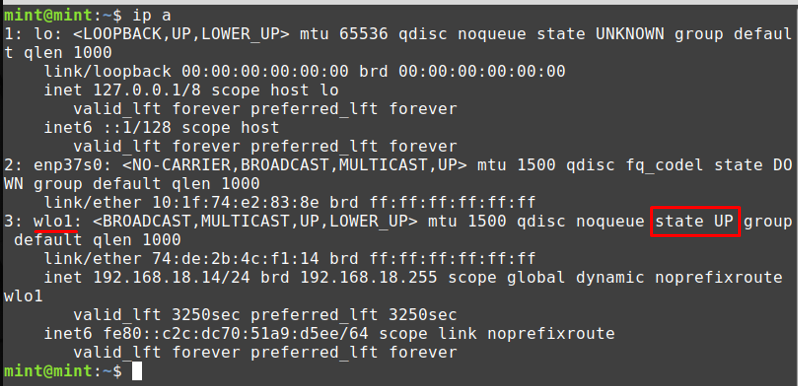
After applying the changes, the connection will be made, and you can use the ip command to check the state of your wireless network.
After this, you would be able to use the internet provided by your wireless network interface.
Conclusion
Wireless technology has emerged as a key player in revolutionizing the world. The Wi-Fi connection has eased the way of communicating with the world. Their application can be seen from computing devices to tablets/phones, from several electrical appliances to setting up an IoT-based network. This demonstration provides the procedural guide to connect your Linux Mint system with Wi-Fi. The two methods are mentioned here that can be followed to connect to a Wi-Fi network. The graphical interface is quite easy and quick to make a connection, whereas Linux users should be familiar with the command line method.
How to setup WiFi in Linux Mint
Setting up WiFi in Linux Mint is pretty easy, but of course you need to setup your WiFi adapter first, which in Linux can be everything between very easy and almost impossible. In the previous chapter of this Linux Mint beginner course I explained how to install WiFi drivers in Linux Mint. It all depends on which hardware components or which laptop you have. For my Dell Latitude E7450 it was a no brainer to have a working WiFi adapter, as it was recognized by Linux Mint out of the box. This is often the case for a lot of A-class laptops, like the Lenovo ThinkPad, HP Stream, Dell XPS and Dell Latitude. But on my custom build i7 workstation it was much more difficult to come up with a working solution for several usb WiFi adapters, so that one is wired. So now it is time to setup the WiFi connection itself.
How to connect to your wireless network
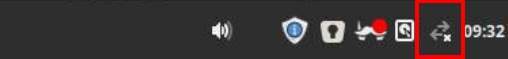
I assume you have a working WiFi adapter (based on the explanation in the previous chapter How to install WiFi drivers in Linux Mint), so it is time now to setup the WiFi connection itself. When you have your Linux Mint desktop in front of you and you didn’t yet connect to your wireless network you will see the following icon on the right hand side of your panel in what we call the system indicator area. This “two arrows with a small x” icon tells you that the wireless connection is not active yet.
If the wireless connection is active then you will see the WiFi indicator. There are embedded four levels in this icon that will give you information on the strength of your received signal. In this example the strength of your signal is approximately 75%.
But let’s assume this is the first time we try to activate a WiFi connection. Start by left-clicking on the “two arrows with a small x” icon and the following screen will pop-up.
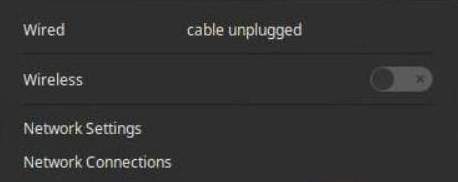
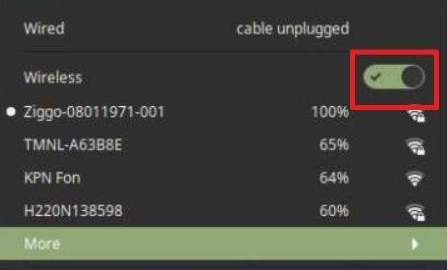
In this screen you see that both the wired and the wireless connections are not active. So click on the on/off switch on the right of the Wireless section.
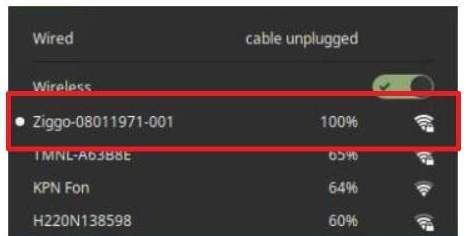
Now the activation switch will change to activated and one or more available WiFi networks will hopefully be shown with their strength levels. Here you can select your own wireless network.
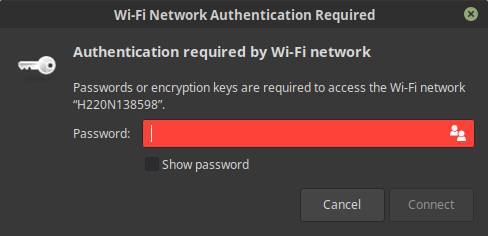
When you selected your preferred wireless network, a WiFi Network Authentication pop-up will be presented to you. Give your administrator password here and click Connect.
If everything goes as expected you are now connected to your wireless network and you can start surfing the web.
Use your Linux machine as hotspot
With respect to wireless connectivity Linux Mint has an additional trick under its sleeve. It is possible to use your workstation or laptop installed with a Linux Mint distribution as a wireless hotspot for other wireless devices like laptops, tablets and mobile phones. The only catch is that this Linux hotspot computer must be connected by wire to your internet router. When wireless connected your computer can’t be used as a wireless hotspot.
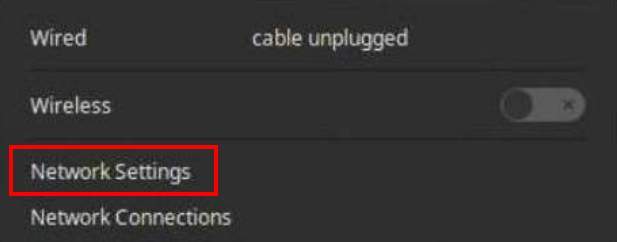
So to setup a wireless hotspot, first make sure your computer has a wired connection. Now left-click on the network icon in the system indicator area on the right hand side of the panel.
Click on Network Settings.
Now the Network settings screen will be opened. Here you find the button “Use as hotspot”.
So click on it to open the hotspot settings.
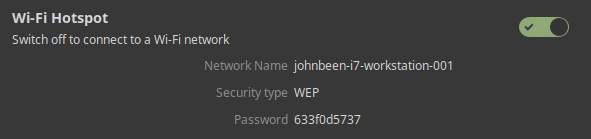
In the above screenshot you see that a Network Name has been created together with a Password. Now you simply search in the network settings of your mobile phone or tablet or another laptop for this network name and type the provided password to log in this wireless network. That’s all.
Related Posts
How to disable threaded conversations in Thunderbird
How to use Applets in Linux Mint Cinnamon – Linux Mint 21 edition
June 11, 2023 June 11, 2023
How to prevent your Linux computer from falling asleep with Caffeine
About John Been
Hi there! My name is John Been. At the moment I work as a senior solution engineer for a large financial institution, but in my free time, I am the owner of RealAppUser.com, RealLinuxUser.com, and author of my first book «Linux for the rest of us». I have a broad insight and user experience in everything related to information technology and I believe I can communicate about it with some fun and knowledge and skills.
My Linux book is available now!
Linux for the rest of us — my starter guide for all of you who just want to be productive with your Linux system. The book is available in Paperback and Kindle format. Click on the image below to see for yourself. Or maybe you want to have some information first.
Why this website
Hi, my name is John Been. I started this website because I think that many Linux-oriented websites are too technical to be of any interest for novice users or people who just want to be productive with their computer, and that scares off a potentially large group of new people to take the step to Linux. And that is a pity because Linux is a formidable platform and with the right user-centered approach Linux could get a much larger footprint. So this website tries to be different and will be simple and focused on users who just want to be productive with Linux and related software.
New! My handcrafted desktop wallpaper series
Most popular posts
What if productivity influencer Ali Abdaal wants to be a Linux user – Is Linux usable for macOS users
July 14, 2023 July 14, 2023
A first look at the new Zorin OS Upgrader
June 28, 2023 June 28, 2023
How to use Applets in Linux Mint Cinnamon – Linux Mint 21 edition
June 11, 2023 June 11, 2023
Mini Review – Bavarder is a simple ChatGPT-based AI App for Linux
How to easily run multiple Linux distributions on one computer with Boxes
April 4, 2023 April 4, 2023
Reader’s Posts
There is always something new to learn and do in Linux
April 7, 2022 April 7, 2022
Albert and Catfish – search tools, and horses for courses
January 25, 2022 January 25, 2022
A non-technical Linux user’s tale
December 22, 2021 December 22, 2021
Настраиваем WiFi в Linux Mint
Рассказываем, как настроить беспроводное подключение к интернету в Linux Mint.
Используем графическую оболочку
Linux Mint устроен таким образом, чтобы максимально упростить первичную настройку системы для пользователя. Поэтому и настройка Wi-Fi обычно проходит легко и логично. Так как все драйверы, скорее всего, будут загружены в систему еще на этапе установки, все, что остается сделать нам:
Обычно нужная нам иконка выглядит как-то так
- Найти в списке доступных сетей ту, к которой хотим подсоединиться и кликнуть по ней.
- Ввести пароль, если сеть им защищена.
У меня сетей нет. Имитируется проводное соединение. У вас тут будут все роутеры поблизости
И, собственно, все. Процесс такой же, как в Windows или macOS.
Если вы искушенный пользователь Linux, и хотите освоить настройку подключения через командную строку, то переходите к следующей секции статьи.
Используем терминал
- Открываем терминал.
- Устанавливаем набор необходимых сетевых утилит с помощью команды sudo apt-get install net-tools. Если сети нет, то придется сначала выйти в интернет по проводу или заранее подготовить флешку с нужным набором программ.
- Затем ищем свой интерфейс для подключения к беспроводным сетям. Для этого вводим команду ifconfig и в выдаче ищем строчку типа wlan0 (это стандартное название).
- Запускаем интерфейс командой ifconfig wlan0 up
- Теперь отыщем список доступных Wi-Fi-сетей неподалеку от нас. Для этого введем в терминал следующее: iwlist wlan0 scan
- Предыдущая команда выдаст список доступных подключений в формате ESSID: название сети. Ищем среди них свою и запоминаем.
- Теперь подключаемся с помощью команды следующего формата: iwconfig wlan0 essid название wi-fi-сети key пароль от wi-fi-сети
Этот вариант подходит для сетей, защищенных по стандарту WPE.
- Затем надо получить IP-адрес командой dhclient *название интерфейса для подключения
Настройка Wi-Fi сетей, защищенных по стандарту WPA2
Так как подключения WPA2 зашифрованы, нужно передавать им пароль в зашифрованном виде. Для этого:
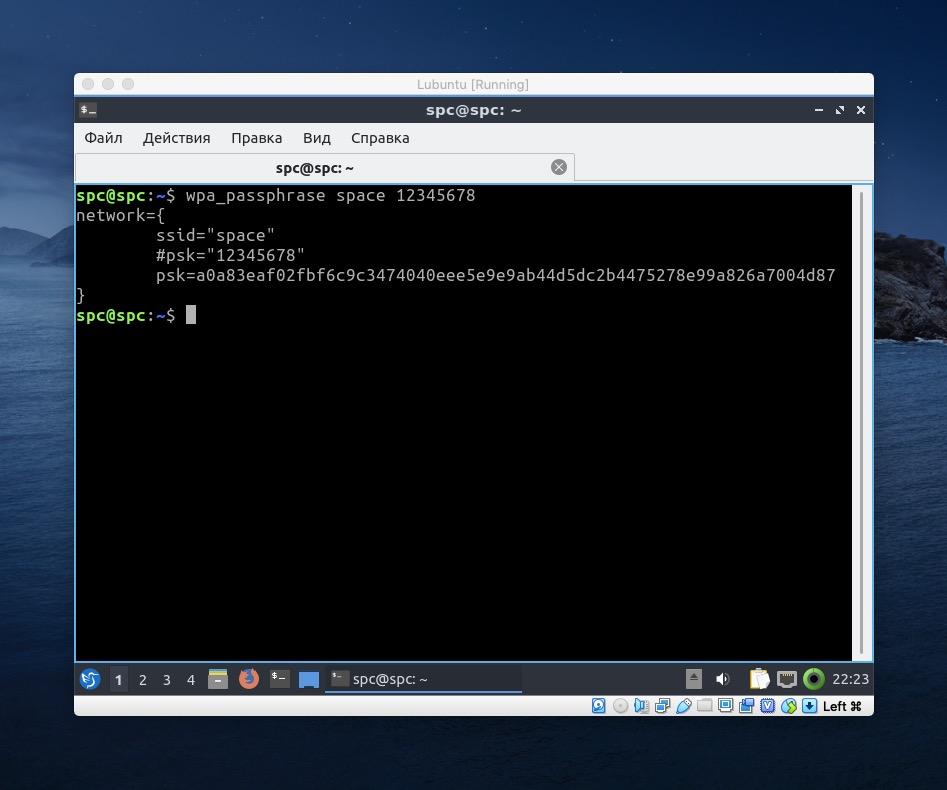
- Запускаем утилиту wpa_passphrase и передаем ей название сети с паролем. Это делается командой следующего формата: wpa_passphrase название сетипароль от нее
- В ответ вы получите хэш в виде psk=a0a83ea…. Нужно его весь скопировать.
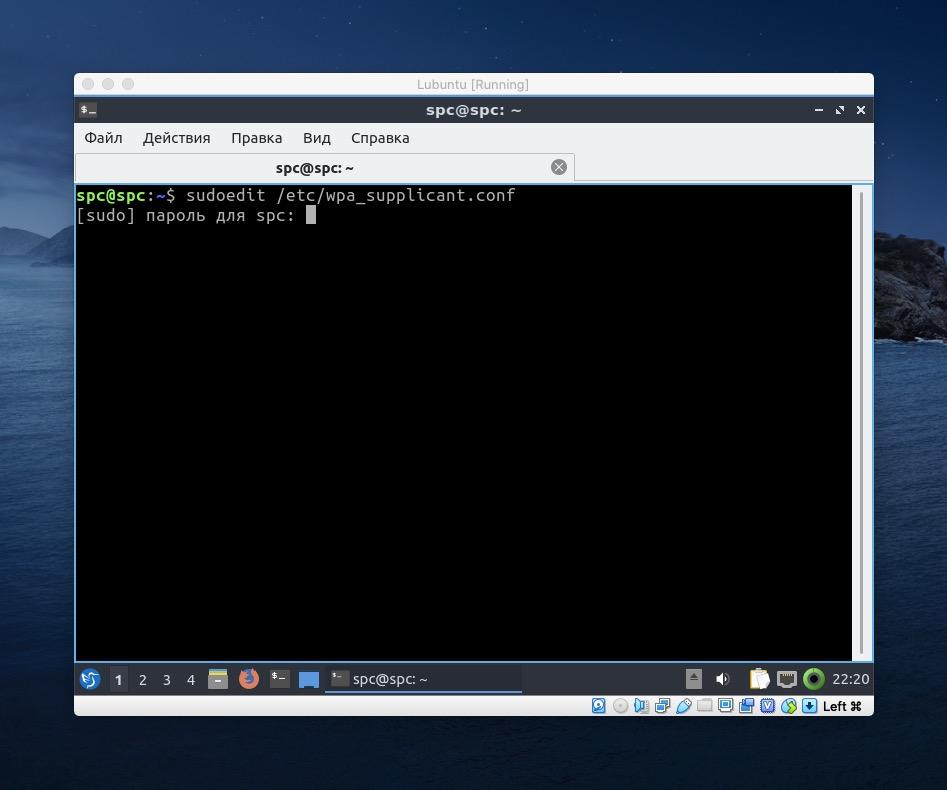
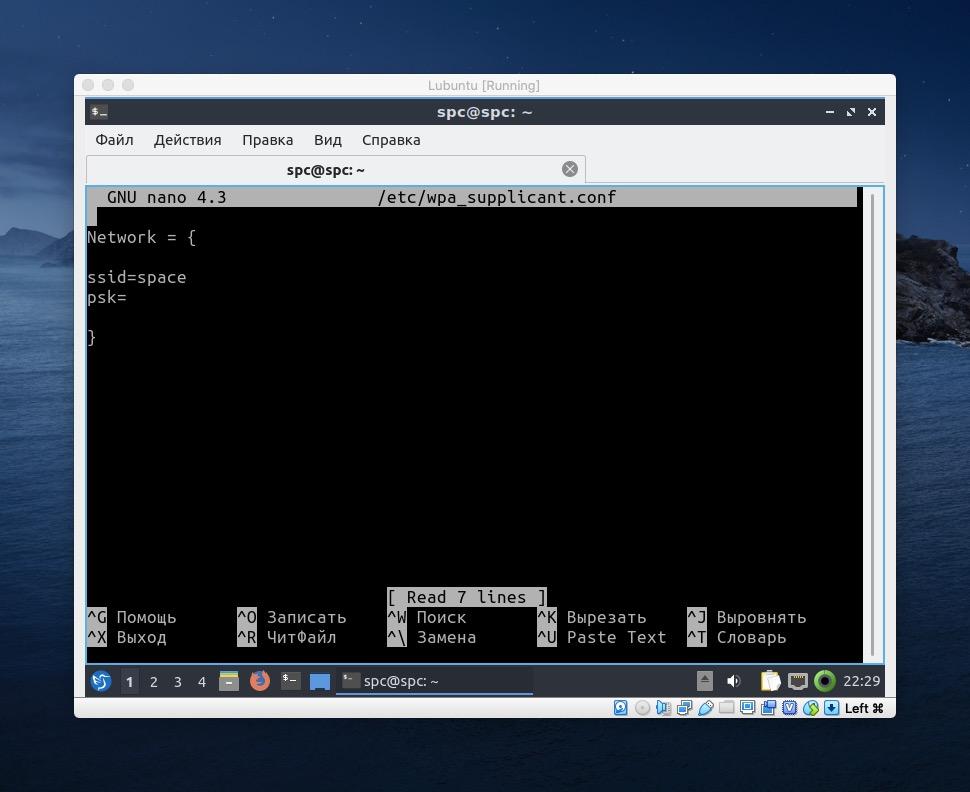
- Затем открываем конфигурационный файл с помощью команды sudo nano /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf
Можно использовать любой другой редактор текста
- Вводим внутрь данные сети, как на скриншоте. Вместо space вводим название своей сети. Вместо psk= тот хэш, что мы скопировали ранее.
Осталось указать шифр и все готово
- Потом вводим команду wpa_supplicant -B -i название интерфейса для подключения -DWext -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf
- И в конце снова получаем IP-адрес с помощью утилиты dhclient.