- Как подсчитать контрольные суммы файлов в Linux
- Подсчет контрольной суммы файлов
- Заключение
- Проверка контрольной суммы Linux
- Что такое MD5?
- Проверка контрольных сумм в Linux
- Выводы
- How to Use the md5sum Command in Linux
- The md5sum Command with Examples
- Read in Binary Mode
- Read in Text Mode
- Create a BSD-Style Checksum
- Validate md5 Checksum with a File
- Validate Multiple Files
- Display Only Modified Files
- Generate Status Only
- Check Improperly Formatted Checksum Lines
- Skip Reporting Status for Missing Files
- Show Help and Version Information
Как подсчитать контрольные суммы файлов в Linux
Контрольная сумма, это последовательность букв и цифр для проверки целостности файлов. При скачивании файлов, может возникнуть ошибка, по этому, важно проверять контрольную сумму что бы убедиться, что файл был скачан целиком, без ошибок. Для примера возьмем iso образ дистрибутива Linux. На нем и будем проводить подсчет контрольной суммы.
В случае iso образа, ошибка при скачивании может привести к неработоспособности дистрибутива. И лучше это выяснить перед установкой, чем во время нее. Для проверки контрольной суммы используются команды: cksum, md5sum, sha1sum, sha256sum, sha512sum.
Принцип проверки контрольной суммы довольно простой, указываете команду, к примеру sha512sum, а затем название файла.
Подсчет контрольной суммы файлов
Итак, для примера был взят образ дистрибутива Debian. На странице скачивания iso образа пользователю предлагается контрольная сумма:
Важно, что бы эти контрольные суммы совпадали. Для проверки контрольной суммы открываем терминал, вводим команду sha512sum и название файла, после чего высветится его контрольная сумма. Останется ее только сравнить, и в случае, если она совпадает, значит файл был скачан без ошибок:
Заключение
Как видите, подсчет контрольной суммы производится довольно легко. Сравнить последовательность цифр и букв контрольной суммы могут помочь онлайн-сервисы. Рекламировать какой-то конкретный не стану. Но, если не прибегать к онлайн-сервисам, достаточно сравнить начало и конец контрольной суммы, чаще всего этого бывает достаточно.
Также обратите внимания на то, что копировать команды с сайтов, а затем вставлять их в терминал, может быть весьма опасно, о чем вы можете прочесть перейдя по этой ссылке .
А на этом сегодня все, если статья оказалась вам полезна, подписывайтесь на рассылку журнала в pdf формате, а так же на социальные сети журнала Cyber-X:
По вопросам работы сайта, сотрудничества, а так же по иным возникшим вопросам пишите на E-Mail . Если вам нравится журнал и вы хотите отблагодарить за труды, вы можете перечислить донат на развитие проекта.
Проверка контрольной суммы Linux
Контрольная сумма — это цифра или строка, которая вычисляется путем суммирования всех цифр нужных данных. Ее можно использовать в дальнейшем для обнаружения ошибок в проверяемых данных при хранении или передаче. Тогда контрольная сумма пересчитывается еще раз и полученное значение сверяется с предыдущим.
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим что такое контрольная сумма Linux, а также как выполнять проверку целостности файлов с помощью контрольных сумм md5.
Что такое MD5?
Контрольные суммы Linux с вычисляемые по алгоритму MD5 (Message Digest 5) могут быть использованы для проверки целостности строк или файлов. MD5 сумма — это 128 битная строка, которая состоит из букв и цифр. Суть алгоритма MD5 в том, что для конкретного файла или строки будет генерироваться 128 битный хэш, и он будет одинаковым на всех машинах, если файлы идентичны. Трудно найти два разных файла, которые бы выдали одинаковые хэши.
В Linux для подсчета контрольных сумм по алгоритму md5 используется утилита md5sum. Вы можете применять ее для проверки целостности загруженных из интернета iso образов или других файлов.
Эта утилита позволяет не только подсчитывать контрольные суммы linux, но и проверять соответствие. Она поставляется в качестве стандартной утилиты из набора GNU, поэтому вам не нужно ничего устанавливать.
Проверка контрольных сумм в Linux
Синтаксис команды md5sum очень прост:
$ md5sum опции файл
Опций всего несколько и, учитывая задачи утилиты, их вполне хватает:
- -c — выполнить проверку по файлу контрольных сумм;
- -b — работать в двоичном формате;
- -t — работать в текстовом формате;
- -w — выводить предупреждения о неверно отформатированном файле сумм;
- —quiet — не выводить сообщения об успешных проверках.
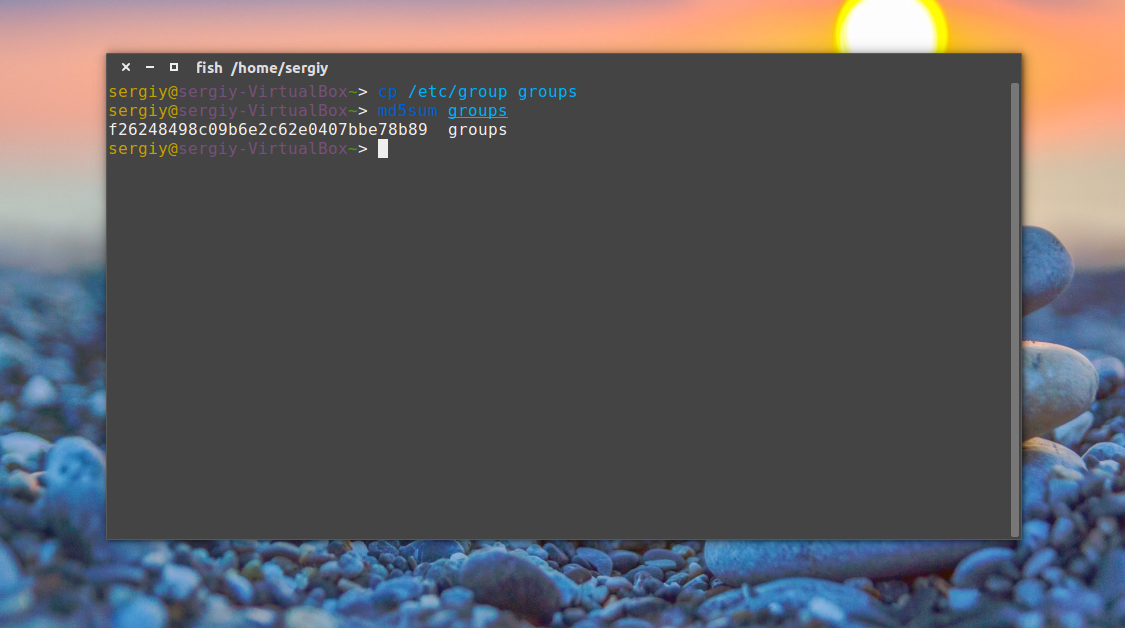
Сначала скопируйте файл /etc/group в домашнюю папку чтобы на нем немного поэкспериментировать:
Например, давайте подсчитаем контрольную сумму для файла /etc/group:
Или вы можете сохранить сразу эту сумму в файл для последующей проверки:
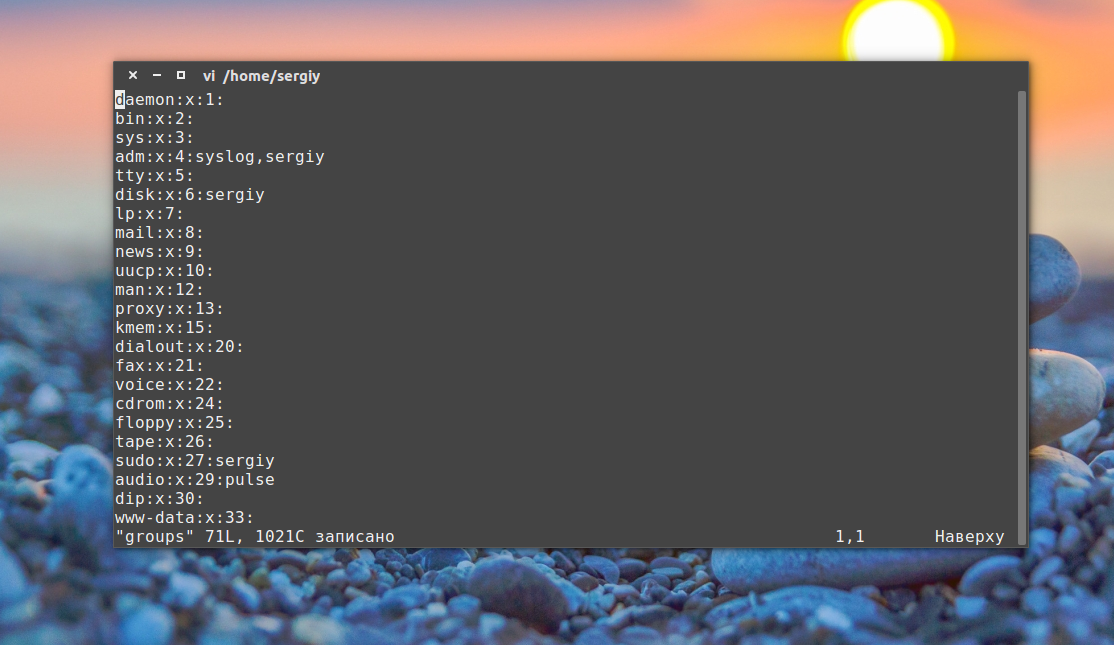
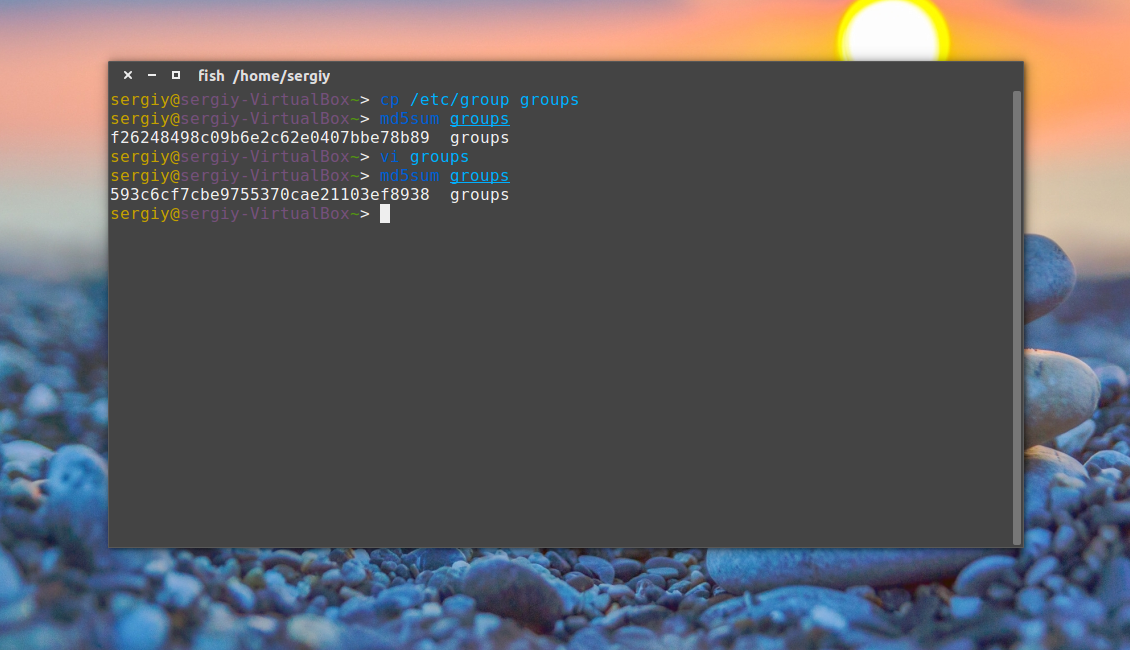
Затем каким-либо образом измените этот файл, например, удалите первую строчку и снова подсчитайте контрольные суммы:
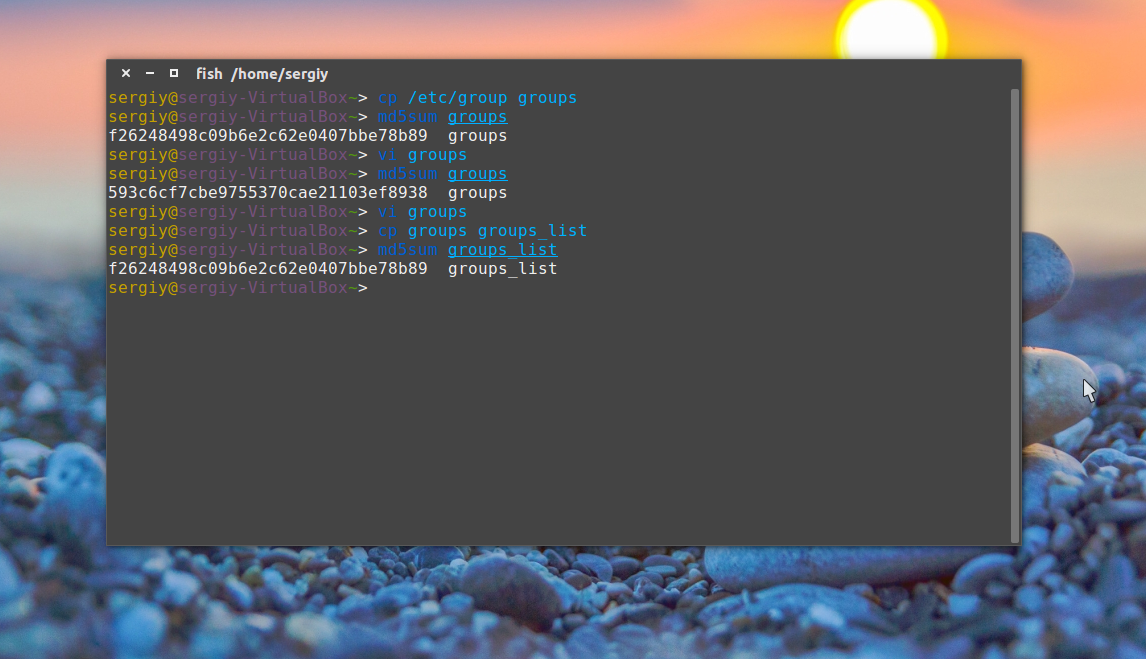
Как видите, теперь значение отличается, а это значит, что содержимое файла тоже изменилось. Дальше верните обратно первую строчку root:x:0: и скопируйте этот файл в groups_list и
Затем опять должна быть выполнена проверка контрольной суммы linux:
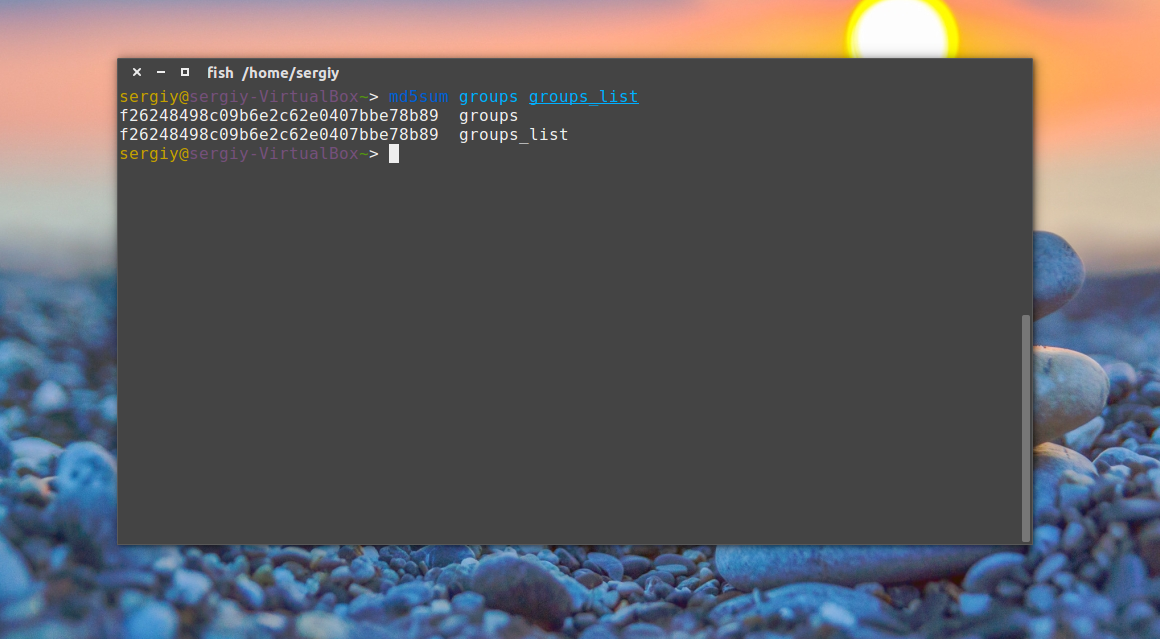
Сумма соответствует первому варианту, даже несмотря на то, что файл был переименован. Обратите внимание, что md5sum работает только с содержимым файлов, ее не интересует ни его имя, ни его атрибуты. Вы можете убедиться, что оба файла имеют одинаковые суммы:
md5sum groups groups_list
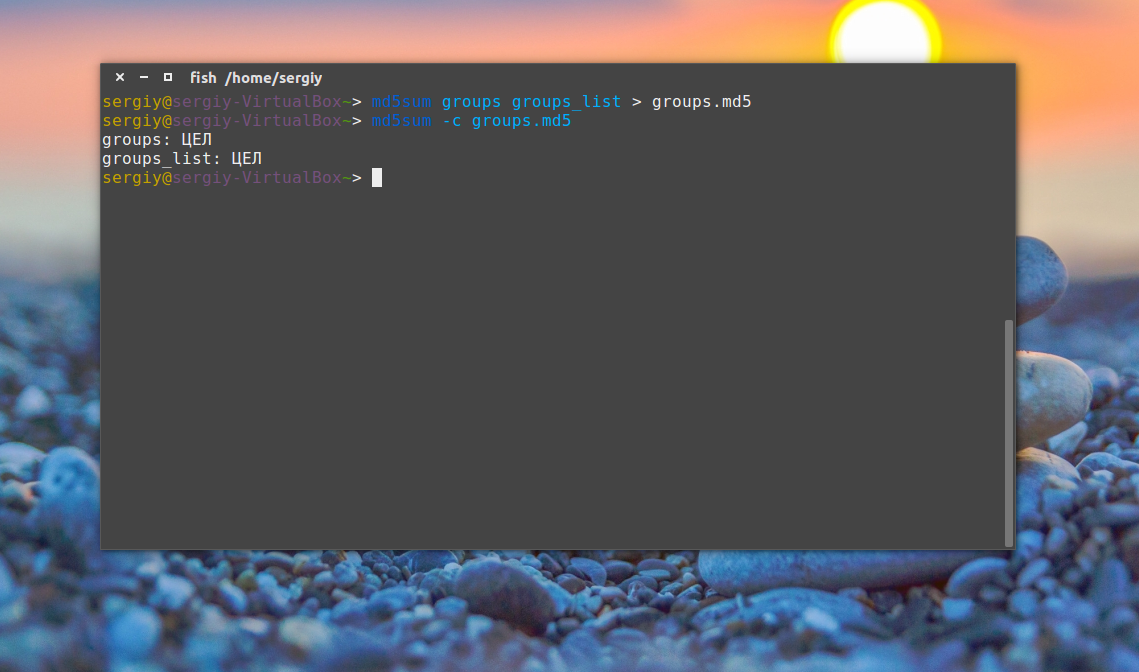
Вы можете перенаправить вывод этой команды в файл, чтобы потом иметь возможность проверить контрольные суммы:
md5sum groups groups_list > groups.md5
Чтобы проверить, не были ли файлы изменены с момента создания контрольной суммы используйте опцию -c или —check. Если все хорошо, то около каждого имени файла появится слово OK или ЦЕЛ:
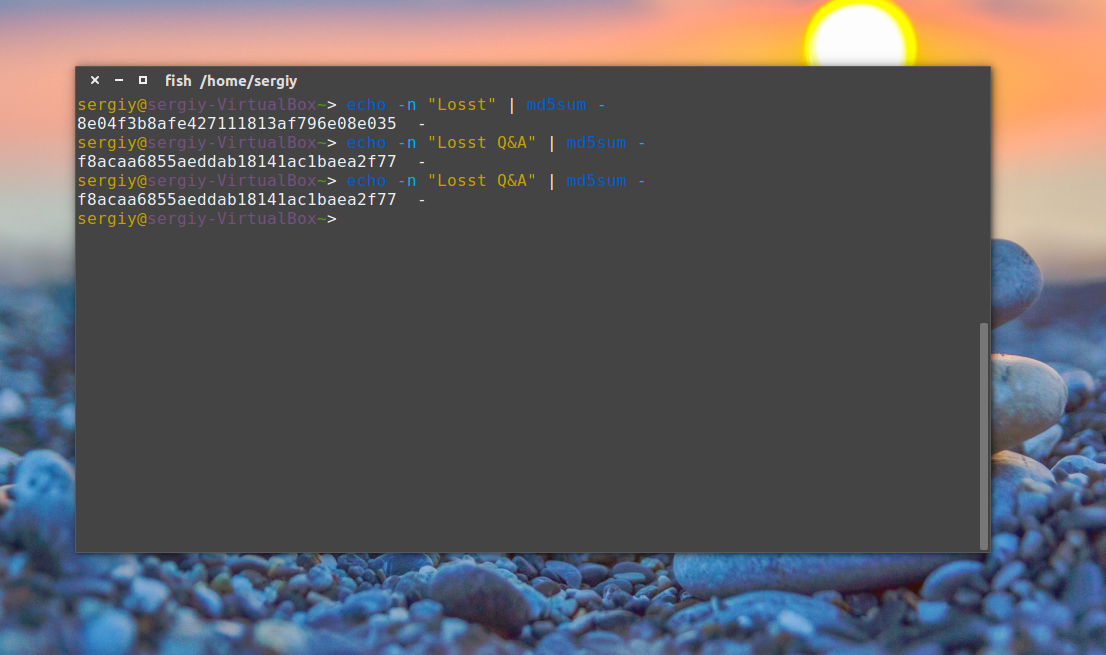
Но теперь вы не можете переименовывать файлы, потому что при проверке утилита будет пытаться открыть их по имени и, естественно, вы получите ошибку. Точно так же все работает для строк:
echo -n «Losst» | md5sum —
$ echo -n «Losst Q&A» | md5sum —
Выводы
Из этой статьи вы узнали как выполняется получение и проверка контрольной суммы linux для файлов и строк. Хотя в алгоритме MD5 были обнаружены уязвимости, он все еще остается полезным, особенно если вы доверяете инструменту, который будет создавать хэши.
Проверка целостности файлов Linux — это очень важный аспект использования системы. Контрольная сумма файла Linux используется не только вручную при проверке загруженных файлов, но и во множестве системных программ, например, в менеджере пакетов. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
На завершение небольшое видео по теме:

Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to Use the md5sum Command in Linux
When you download a file from the internet, it is a good safety practice to check whether you received the original version. Comparing checksums you received from the file creator with the ones you obtain by checking the file yourself is a reliable way to confirm your download’s integrity.
The md5sum command in Linux helps create, read, and check file checksums.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to use the md5sum command to validate the files you receive.
The md5sum Command with Examples
When used on a file without any options, the md5sum command displays the file’s hash value alongside the filename. The syntax is:
After obtaining the hash value, compare it with the MD5 value provided by the file creator.
Note: While md5sum is a reliable method for testing whether the file you received has been compromised, it is useful only if you know that the website you downloaded it from is secure. If hackers gain access to the website, they can change both the file and its checksum, making it appear as if the file you are downloading is safe.
Read in Binary Mode
To read the file in binary mode, use the -b option ( —binary ):
The * character before the file name means that md5sum read it in binary mode.
Read in Text Mode
Use the -t option ( —text ) to read the file in text mode:
Text mode is the default mode for reading files with md5sum .
Create a BSD-Style Checksum
Using the —tag option outputs the hash value in the BSD-style format:
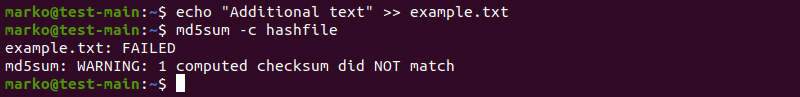
Validate md5 Checksum with a File
To check a file by comparing its hash value with the value provided in a hash file, use the -c option.
1. As an example, create a hash file containing the md5sum output:
md5sum [filename] > [file-containing-hashes]2. Use the following syntax to compare the hash value from the file you created against the current hash value of the .txt file:
md5sum -c [file-containing-hashes]3. If you change the contents of the file and repeat the check, a warning message is displayed:
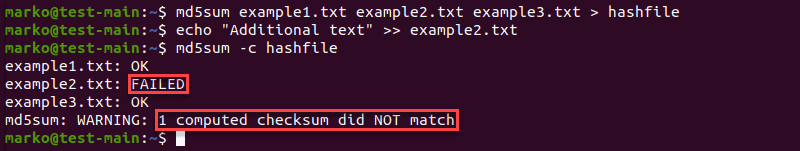
Validate Multiple Files
Use the same md5sum -c procedure to check the integrity of multiple files:
md5sum [filename1] [filename2] [filename3] > [file-containing-hashes]In the following example, the contents of example2.txt have changed, resulting in a warning message from md5sum :
Display Only Modified Files
The —quiet option displays only the files whose hash value has changed. It skips the output of validated files.
md5sum --quiet -c [file-containing-hashes]Generate Status Only
The md5sum command with the —status option does not produce any output but returns 0 if there are no changes and 1 if it detects changes. This argument is useful for scripting, where there is no need for standard output.
The example script below illustrates the use of the —status option:
#!/bin/bash md5sum --status -c hashfile Status=$? echo "File check status is: $Status" exit $StatusWhen the script executes, it shows status 1 , meaning that md5sum detected the change made earlier in example2.txt .
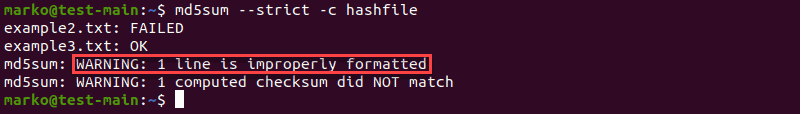
Check Improperly Formatted Checksum Lines
Add the —strict option to exit non-zero for improperly formatted hash values:
md5sum --strict -c [file-containing-hashes]The example shows the output of md5sum —strict when you put invalid characters in the first line of the file containing hashes:
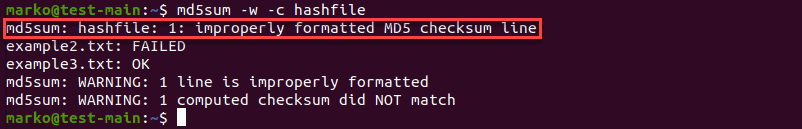
To display which line has an invalid hash, use -w ( —warn ):
md5sum -w -c [file-containing-hashes]The example above shows the -w option displaying that the improperly formatted MD5 checksum line is line 1 of the file.
Skip Reporting Status for Missing Files
By default, md5sum shows warnings about the files it cannot find on the system. To override this behavior, use the —ignore-missing option:
md5sum --ignore-missing -c [file-containing-hashes]In the example below, example1.txt was deleted before running the md5sum command. The output ignores the deleted file:
Show Help and Version Information
To get the official help for the md5sum command, type:
To check md5sum version, type:
Note: You should also check out our overview of the diff command to learn how to compare two files line by line.
After completing this tutorial, you should know how to properly use the md5sum command to create, print, or check MD5 checksums.
Marko Aleksić is a Technical Writer at phoenixNAP. His innate curiosity regarding all things IT, combined with over a decade long background in writing, teaching and working in IT-related fields, led him to technical writing, where he has an opportunity to employ his skills and make technology less daunting to everyone.
The echo command prints out a text string you provide as the output message. This tutorial covers the echo.
The ls command (short for list) lists information about directories and any type of files in the working.
A list of all the important Linux commands in one place. Find the command you need, whenever you need it or.
Creating a file in Linux might seem straightforward, but there are some surprising and clever techniques. In.