- How can I see what ports are open on my machine?
- 10 Answers 10
- nmap (install)
- How to check for open ports on your Ubuntu server
- Prerequisites
- The difference between addresses
- Check for open ports using nmap
- Check for open ports using lsof
- Check for open ports using netstat
- Check open ports using ss
- Conclusion
- Get Started For
- Как посмотреть открытые порты Linux
- 1) Посмотреть открытые порты с помощью команды ss
- 2) Посмотреть открытые порты с помощью команды netstat
- 3) Посмотреть открытые порты Linux с помощью команды lsof
- 4) Посмотреть открытые порты Linux с помощью утилиты Nmap
How can I see what ports are open on my machine?
I would like to see what ports are open on my machine, e.g. what ports my machine is listening on. E.g. port 80 if I have installed a web server, and so on. Is there any command for this?
10 Answers 10
If the netstat command is not available, install it with:
sudo apt install net-tools -l already filters for listening. grep LISTEN won’t help beyond hiding 2 lines of header information.
-t : tcp, -l : listening socket, -p : show pid and program name, -n : print 127.0.0.1:80 instead of localhost:http . Reference: linux.die.net/man/8/netstat
The expanded command is sudo netstat —tcp —listening —programs —numeric . There’s no need to use grep unless you want to eliminate column headers.
nmap (install)
Nmap («Network Mapper») is a free and open source utility for network exploration or security auditing.
Use nmap 192.168.1.33 for internal PC or nmap external IP address .
More information man nmap .
Zenmap is the official GUI frontend.
Remember that there is a difference between nmap localhost and nmap 192.168.0.3 (or what ever you machine IP is)
I think netstat is a better answer to this. netstat will list what the system is listening on directly, and without using an additional application or doing unnecessary calls over localhost or thought the network.
This is stupid. If you have access to the computer, just use netstat -ln . You’ll instantly see all the open ports.
nmap localhost didn’t find services that were bound only to localhost. For example, I run influxd with bind-address:localhost:8086 . That didn’t show up in sudo nmap localhost , but did show up in sudo netstat -tulpn .
Other good ways to find out what ports are listenting and what your firewall rules are:
To list open ports use the netstat command.
$ sudo netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 5452/dnsmasq tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1037/cupsd tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 . * LISTEN 1037/cupsd In the above example three services are bound to the loopback address.
IPv4 services bound to the loopback address «127.0.0.1» are only available on the local machine. The equivalent loopback address for IPv6 is «::1». The IPv4 address «0.0.0.0» means «any IP address», which would mean that other machines could potentially connect to any of the locally configured network interfaces on the specific port.
Another method is to use the lsof command:
$ sudo lsof -nP -i | grep LISTEN cupsd 1037 root 9u IPv6 11276 0t0 TCP [::1]:631 (LISTEN) cupsd 1037 root 10u IPv4 11277 0t0 TCP 127.0.0.1:631 (LISTEN) dnsmasq 5452 nobody 5u IPv4 212707 0t0 TCP 127.0.0.1:53 (LISTEN) For more details see man netstat or man lsof .
How to check for open ports on your Ubuntu server
This guide explains different methods to check for open ports on your Webdock server. An open port is a port on which some process or application is running and it can accept data. In this guide we will use different tools to find out which ports are open.
An open port is defined as a port which has a service listening and accepting connections. You may find that you have services listening on ports which despite this are not accessible from the internet. This is what your firewall does: Block access to ports which you haven’t explicitly allowed access to. For a guide on managing your firewall, take a look at our UFW guide here.
Prerequisites
The difference between addresses
It matters whether a service is listening to a port on 127.0.0.1 (localhost) or if it is listening on 0.0.0.0 — typically what this means is that a service listening on localhost is only accessible from the host machine itself and not the wider internet. If you see a service listening on all interfaces (*) or 0.0.0.0 then the service is accessible from the internet — unless actively firewalled, which you will need to check for in Iptables or by running «ufw status» if you use UFW to manage your firewall.
Check for open ports using nmap
Network mapper or nmap is an open source tool used to scan networks and find open ports on a host. The following command will scan all the ports on the host.
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2021-06-12 06:03 UTC Nmap scan report for localhost (127.0.0.1) Host is up (0.0000090s latency). Not shown: 995 closed ports PORT STATE SERVICE 21/tcp open ftp 22/tcp open ssh 80/tcp open http 443/tcp open https 3306/tcp open mysql Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.23 seconds
In order to check a specific port whether it is open or not, use the -p option to specify the port.
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2021-06-12 06:04 UTC Nmap scan report for localhost (127.0.0.1) Host is up (0.000054s latency). PORT STATE SERVICE 80/tcp open http Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.18 seconds
Be careful using nmap as if you accidentally start scanning the entire network, you risk that your IP address will be banned.
Check for open ports using lsof
The lsof (list open files) command, as name suggests, is used to list all the open files in linux. These files may be network sockets, disk files or devices opened by different processes. Use the lsof command along with the -nP options to list all open sockets.
$ sudo lsof -nP | grep LISTEN
. snip. redis-ser 511 513 redis-ser redis 6u IPv4 662257788 0t0 TCP 127.0.0.1:6379 (LISTEN) redis-ser 511 513 redis-ser redis 7u IPv6 662257789 0t0 TCP [::1]:6379 (LISTEN) redis-ser 511 515 redis-ser redis 6u IPv4 662257788 0t0 TCP 127.0.0.1:6379 (LISTEN) redis-ser 511 515 redis-ser redis 7u IPv6 662257789 0t0 TCP [::1]:6379 (LISTEN) redis-ser 511 517 redis-ser redis 6u IPv4 662257788 0t0 TCP 127.0.0.1:6379 (LISTEN) redis-ser 511 517 redis-ser redis 7u IPv6 662257789 0t0 TCP [::1]:6379 (LISTEN) . snip.
List only the TCP open sockets.
. snip. pure-ftpd 303 root 4u IPv4 662259745 0t0 TCP *:ftp (LISTEN) pure-ftpd 303 root 5u IPv6 662259746 0t0 TCP *:ftp (LISTEN) sshd 304 root 3u IPv4 662258731 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN) sshd 304 root 4u IPv6 662258733 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN) ..snip.
For UDP open sockets, use the following command.
systemd-r 254 systemd-resolve 12u IPv4 662203276 0t0 UDP localhost:domain
Check for open ports using netstat
The netstat (network statistic) command can be used to monitor and scan networks. Get a list of all tcp and udp open ports using the netstat command.
. snip. tcp 0 0 localhost:27017 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost:mysql 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost:6379 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost:11211 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN . snip.
. snip. tcp 0 0 localhost:27017 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost:mysql 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost:6379 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 localhost:11211 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:http 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp6 0 0 [::]:ftp [::]:* LISTEN tcp6 0 0 [::]:ssh [::]:* LISTEN . snip.
Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State udp 0 0 localhost:domain 0.0.0.0:*
Check open ports using ss
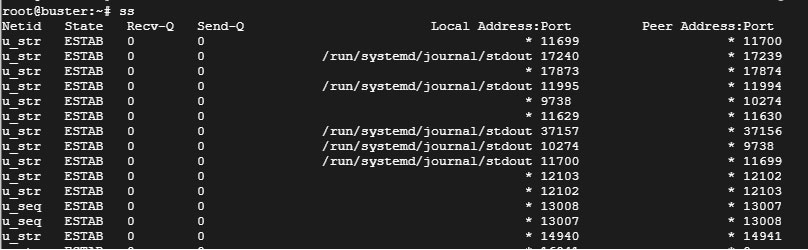
The ss command is used to list detailed information of the network sockets. It provides more detailed information than the netstat command. List all the listening ports on a linux system.
Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process nl UNCONN 0 0 rtnl:systemd/1 * nl UNCONN 0 0 rtnl:kernel * nl UNCONN 0 0 rtnl:systemd-resolve/254 * nl UNCONN 0 0 rtnl:systemd-resolve/254 * nl UNCONN 0 0 rtnl:systemd/1 * . snip.
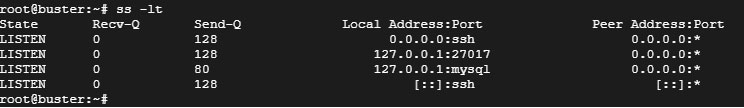
To list only TCP listening ports, use the -lt flag.
. snip. LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:ssh 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 511 0.0.0.0:https 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 4096 127.0.0.1:27017 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 70 127.0.0.1:mysql 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 511 127.0.0.1:6379 0.0.0.0:* . snip.
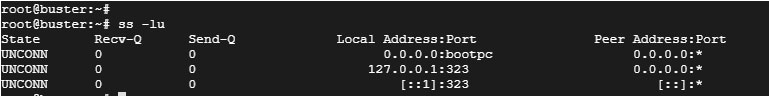
For UDP listening ports, use the -lu flag.
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process UNCONN 0 0 127.0.0.53%lo:domain 0.0.0.0:*
Conclusion
There are different tools available to monitor open ports on your server. In this guide we discussed how we can check for open ports on Webdock server using different command line tools like nmap, ss, netstat and lsof.
- Related
- Server Security Checklist
- How to work with your firewall (UFW — Uncomplicated Firewall)
- SSH Security Configuration Settings
- How to configure Fail2Ban for common services
- How to Secure Nginx with Naxsi Firewall on Ubuntu 18.04 VPS
- How to Secure Nginx with Naxsi Firewall on Ubuntu 20.04 VPS
- How to configure Security Headers in Nginx and Apache
- How to enable Encryption for MariaDB
- How to Scan Your Webdock Server for Malware and Virus
- How To Use Our Free BotGuard Bot Protection
If you need any help regarding this article or if you have any questions regarding hosting in general, please be in touch.
Webdock is a world-class hosting provider aimed at professionals and semi-professionals with the goal of providing an absolutely awesome and rock-solid hosting experience.
We use cookies. Please see our Privacy Policy. OK
Get Started For
- 24 hour free trial
- Free Control Panel
- Epic Support
- Free Snapshots
- Free Bot Protection
- Free SSL
Rated Excellent on Trustpilot
- Need Help
- Become An Affiliate
- Sign Up To Newsletter
Как посмотреть открытые порты Linux
Visitors have accessed this post 55559 times.
Во время устранения неполадок служб, работающих на ОС Linux, просмотр открытых портов является одной из задач, которую должен выполнять любой пользователь или администратор. Если служба должна по идее работать, но по какой-то причине она не работает, то, скорее всего, порт этой службы закрыт и его нужно открыть.
В этом туториале мы покажем, как в Linux посмотреть порты, которые открыты, из командной строки.
1) Посмотреть открытые порты с помощью команды ss
Команда Linux ss предоставляет подробную информацию об открытых портах и прослушиваемых сокетах. Она извлекает информацию из ядра Linux и она более популярна, чем команда netstat, которая уже устарела.
Чтобы отобразить прослушиваемые TCP-соединения, выполните команду
$ ss -tl
Пример вывода
l — показывает прослушиваемые сокеты
t — означает порт TCP
Чтобы посмотреть прослушиваемые UDP-соединения, введите команду
$ ss -lu
Пример вывода
u — означает порт UDP.
Или для того, чтобы отобразить tcp и udp одновременно, введите имя процесса
$ ss -lntup
p — выдает список имен процессов, которые открыли сокеты.
Чтобы вывести все соединения между сокетами, просто используйте команду ss в ее формате по умолчанию
$ ss
Пример вывода2) Посмотреть открытые порты с помощью команды netstat
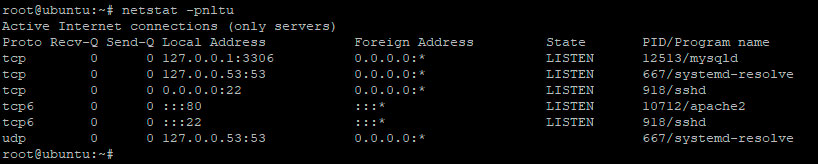
Команда netstat — это инструмент командной строки, который используется для проверки открытых портов TCP и UDP вместе с другими атрибутами. Чтобы в Linux проверить открытые порты, введите команду:
$ netstat -pnltu
Пример вывода
Давайте подробнее рассмотрим параметры команды:
p — показывает идентификатор услуги или название программы;
n — отображает числовой номер запущенного порта, например, 3306 для mysqld и 22 для sshd;
l — показывает прослушиваемые сокеты;
t — показывает TCP-соединения;
u — показывает UDP-соединения.3) Посмотреть открытые порты Linux с помощью команды lsof
Команда lsof — это сетевой инструмент, который также можно использовать, чтобы проверить открытые порты Linux. Для этого введите команду
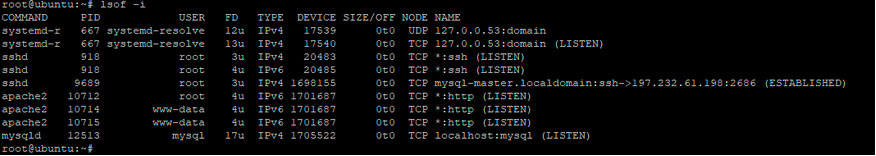
$ lsof -i
Пример вывода
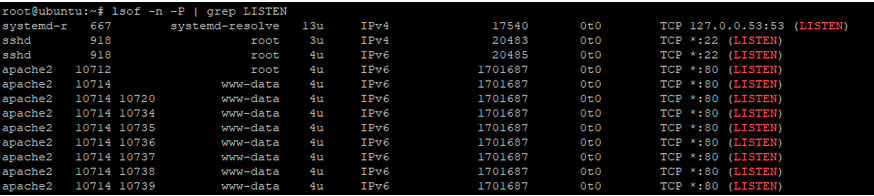
Чтобы посмотреть открытые сокеты, используйте команду lsof и перенаправьте вывод в grep, как показано ниже:
$ lsof -n -P | grep LISTEN
Пример вывода
Для просмотра всех TCP-соединений выполните следующую команду:
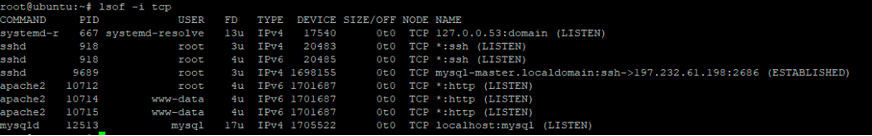
$ lsof -i tcp
Пример вывода
Чтобы посмотреть все UDP-соединения, выполните команду:
$ lsof -i udp
Пример вывода4) Посмотреть открытые порты Linux с помощью утилиты Nmap
Nmap — это бесплатный инструмент с открытым исходным кодом для сканирования сети, обычно используется для обнаружения открытых портов удаленных систем. По умолчанию Nmap не установлен в ОС Linux. Чтобы установить Nmap, введите команду:
$ sudo apt install nmap (для Debian/ Ubuntu)
$ sudo yum install nmap (для RedHat/ CentOS)
$ sudo dnf install nmap (для Fedora)
$ pacman -S nmap (ArchLinux)
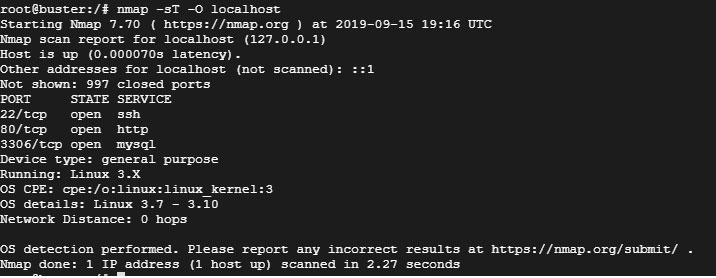
Чтобы найти открытые порты TCP, выполните команду:
$ nmap -sT -O localhost
Пример вывода
Чтобы найти открытые порты UDP, выполните команду:
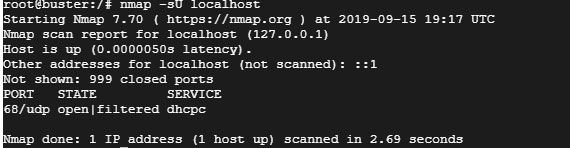
$ nmap -sU localhost
Пример выводаКаждую неделю мы в live режиме решаем кейсы на наших открытых онлайн-практикумах, присоединяйтесь к нашему каналу в Телеграм, вся информация там.
Если вы хотите освоить функционал системного администратора Linux на практике, приглашаем на наш практикум Linux by Rebrain.