- Install And Test Vulkan On Linux
- Install Vulkan on Linux
- Vulkan on Debian Linux
- Vulkan on Ubuntu Linux
- Vulkan on Fedora Linux
- Vulkan on OpenSUSE Linux
- Arch Linux
- Vulkan Linux Info
- DoTA 2
- Closing Thoughts
- Related Linux Tutorials:
- Vulkan® Open Source Driver
- Product support
- Operating system support
- Feature support and performance
- How to contribute
- More information
Install And Test Vulkan On Linux
Vulkan is the future of graphics on Linux. It’s the next generation replacement for OpenGL, and the performance improvements are immediately apparent. Vulkan was written from the ground up to be more usable for developers, which has spawned a host of great projects that take advantage of Vulkan’s potential.
For most people, Vulkan on Linux means better gaming experiences, and it’s already delivering on that. Games like DoTA 2 have been utilizing Vulkan for some time now, and new projects, like DXVK, are helping Linux users play their favorite games from Windows like never before.
Setting up Vulkan on Linux is fairly easy on every distribution, regardless of your graphics card.
The objective of this guide is to install and test Vulkan on Linux.
In this tutorial you will learn:
- How to install Vulkan on Linux
- How to test Vulkan on Linux
| Category | Requirements, Conventions or Software Version Used |
|---|---|
| System | Any Linux distro |
| Software | Vulkan |
| Other | Privileged access to your Linux system as root or via the sudo command. |
| Conventions | # – requires given linux commands to be executed with root privileges either directly as a root user or by use of sudo command $ – requires given linux commands to be executed as a regular non-privileged user |
Install Vulkan on Linux
DID YOU KNOW?
Optionally, you may also need to install the libvulkan-dev development library, which is required whenever you want to compile a program which relies and builds on Vulkan.
Obviously, the first step in taking advantage of all Vulkan has to offer is installing it.
Vulkan on Debian Linux
If you don’t mind doing something a bit crazy and experimental, you can follow the Ubuntu procedure to get the latest versions of Mesa. Otherwise, just run the linux command below.
# apt install libvulkan1 mesa-vulkan-drivers vulkan-utils
Download and install the latest drivers from NVIDIA. They include Vulkan support.
Also, install Debian’s Vulkan utilties.
Vulkan on Ubuntu Linux
It’s best to enable a PPA for the latest Mesa drivers. There is a PPA that packages and releases the latest changes straight from Mesa’s Git. Add the PPA to your system and update. Then, upgrade your system. It will automatically upgrade your existing Mesa packages.
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:oibaf/graphics-drivers $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt upgrade
When it’s done, install the Vulkan packages.
# apt install libvulkan1 mesa-vulkan-drivers vulkan-utils
Ubuntu also has a great repository for the NVIDIA proprietary drivers. Add it to your system, and update Apt.
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:graphics-drivers/ppa $ sudo apt upgrade
Now, install your drivers and Vulkan.
$ sudo apt install nvidia-graphics-drivers-396 nvidia-settings vulkan vulkan-utils
Vulkan on Fedora Linux
You should already have the latest AMD drivers installed on your computer. Install the Vulkan packages.
# dnf install vulkan vulkan-info
The proprietary NVIDIA drivers are available from the RPMFusion repository. Add it to your system, if you haven’t already.
# dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm
Then, install the drivers with Vulkan.
# dnf install xorg-x11-drv-nvidia akmod-nvidia vulkan vulkan-tools
Vulkan on OpenSUSE Linux
You should already have the latest available AMD drivers on your system. Install the Vulkan packages with zypper .
# zypper in vulkan libvulkan1 vulkan-utils mesa-vulkan-drivers
Head over to the the OpenSUSE documentation, and follow the procedure for your version of OpenSUSE.
When you have your drivers, install the Vulkan packages.
# zypper in vulkan libvulkan1 vulkan-utils
Arch Linux
You already have the latest AMD Mesa drivers. Just install Vulkan support.
# pacman -S vulkan-radeon lib32-vulkan-radeon
Install the NVIDIA drivers. They include Vulkan support.
# pacman -S nvidia lib32-nvidia-utils
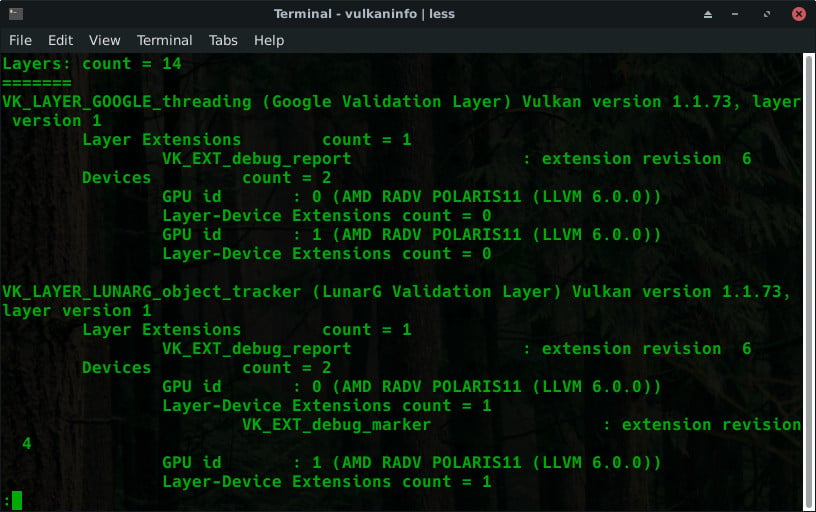
Vulkan Linux Info
The first ting that you can do to ensure that you have Vulkan installed and working on your system is run the vulkaninfo command to pull up relevant information about your system. If you get info about your graphics card, you’ll know that Vulkan is working.
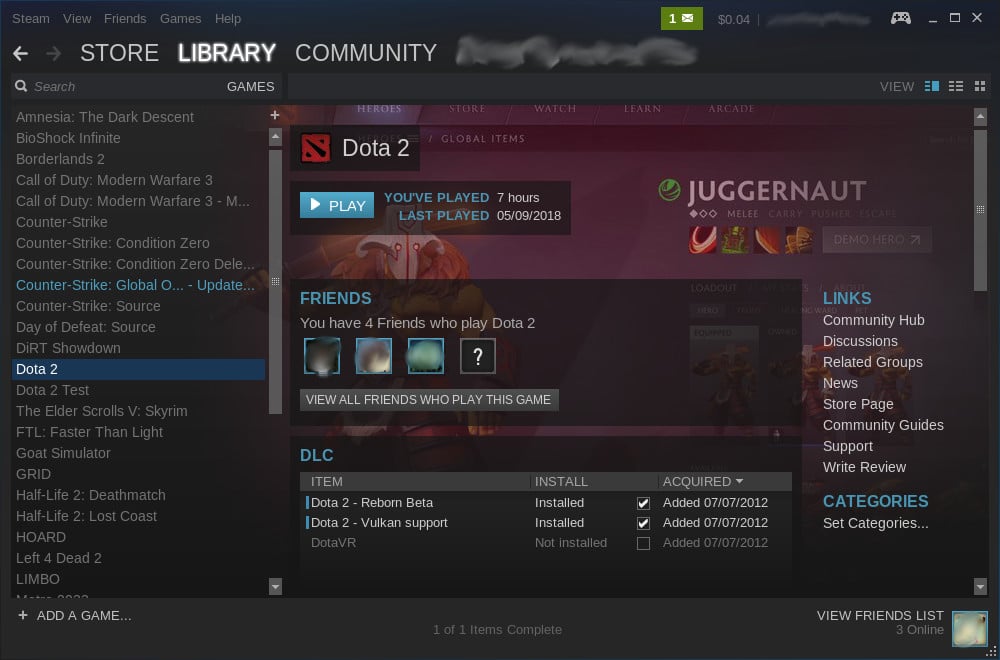
DoTA 2
There’s another more practical way to see how Vulkan performs on your system. You can install and play DoTA 2. It’s one of the first Linux games to support Vulkan completely, and it’s free to play. The only thing you need is a Steam account.
First, install Steam on your system. It’s available on all the distributions above. When you have Steam, you can install DoTA 2 easily enough.
When you have DoTA 2, you can see a series of checkboxes on the main game page. Check the one for Vulkan support. Steam will start downloading it.
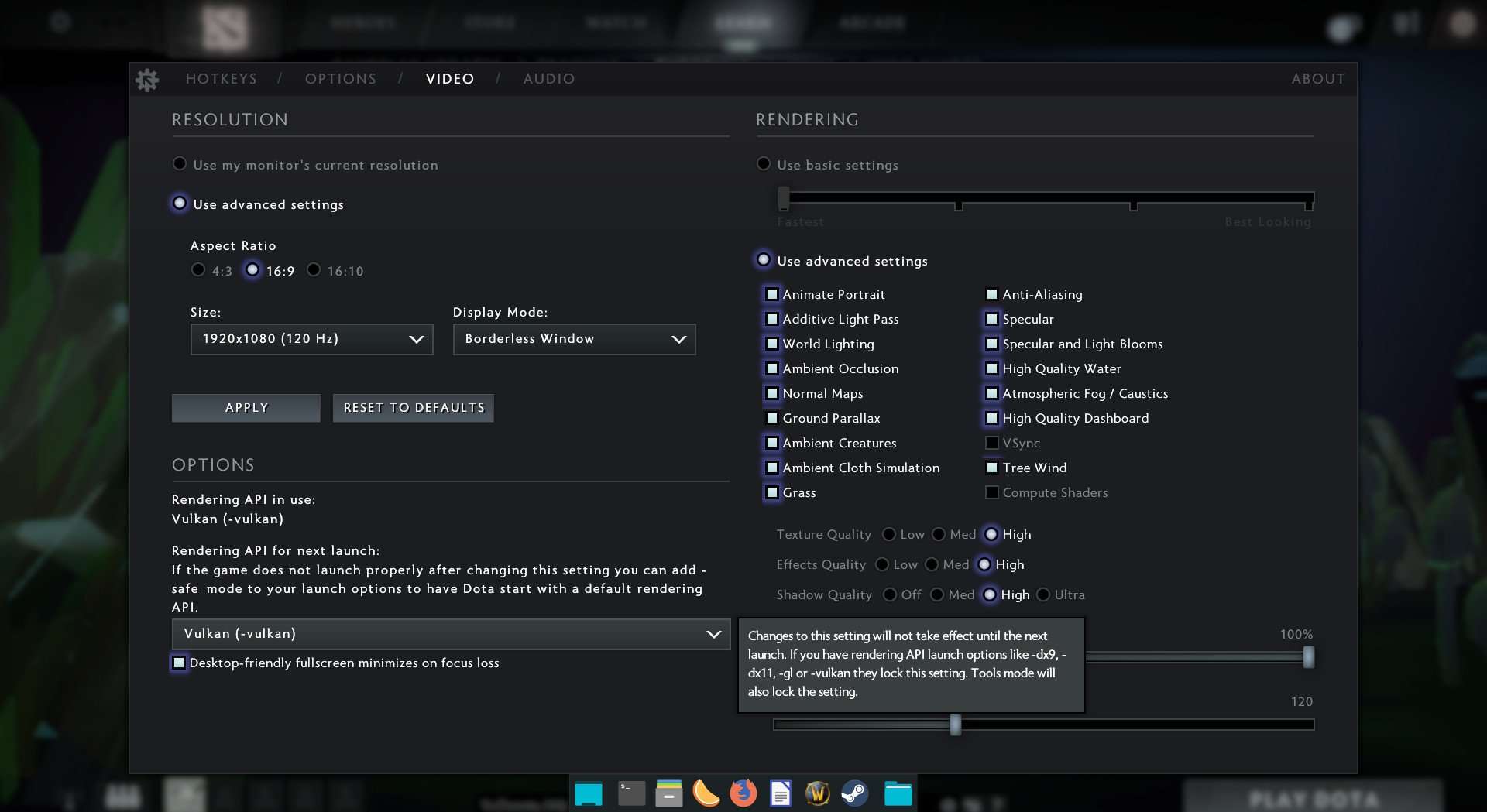
Start up DoTA 2, and open up the settings. Change the graphics API to Vulkan, and restart the game. When DoTA 2 starts back up, it’ll be running with Vulkan. Play the game a bit to test it out.
Closing Thoughts
You are now running Vulkan on your Linux desktop. If you followed along through DoTA 2, you already have a working game making use of it. All the other Vulkan based tools and programs are also open to you now too, including using it with Wine and DXVK. That opens up plenty of new games to play on your system.
Vulkan support is only getting better. More games are making use of it, and other Linux utilities are stepping up too. Wine is actually even developing support for DirextX 12 with Vulkan too. Keep your system updated and enjoy the progress.
Related Linux Tutorials:
Comments and Discussions
Vulkan® Open Source Driver
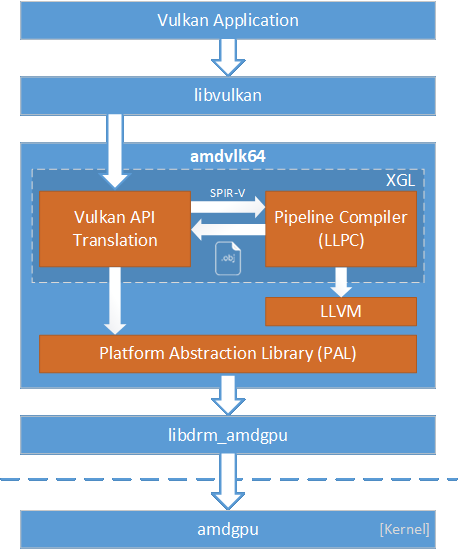
The AMD Open Source Driver for Vulkan® is an open-source Vulkan driver for AMD Radeon™ graphics adapters on Linux®.
The driver is built on top of AMD’s Platform Abstraction Library (PAL), a shared component that is designed to encapsulate certain hardware and OS-specific programming details for many of AMD’s 3D and compute drivers. Leveraging PAL can help provide a consistent experience across platforms, including support for recently released GPUs and compatibility with AMD developer tools.
Shaders that compose a particular VkPipeline object are compiled as a single entity using the LLVM-Based Pipeline Compiler (LLPC) library. LLPC builds on LLVM’s existing shader compilation infrastructure for AMD GPUs to generate code objects compatible with PAL’s pipeline ABI.
Product support
The AMD Open Source Driver for Vulkan is designed to support a wide range of AMD GPUs:
- Radeon™ RX 7900/7600 Series
- Radeon™ RX 6900/6800/6700/6600/6500 Series
- Radeon™ RX 5700/5600/5500 Series
- Radeon™ RX Vega Series
- Radeon™ RX 400/500 Series
- Radeon™ Pro WX 9100, x200 Series
- Radeon™ Pro W5700/W5500 Series
Note: For Pre-Polaris and Pre-Raven GPUs, please use v-2021.Q2.5 or older release.
Operating system support
The AMD Open Source Driver for Vulkan is designed to support following distros and versions on both the AMDGPU upstream driver stack and the AMDGPU Pro driver stack:
- Ubuntu 22.04 (amd64 version)
- Ubuntu 20.04 (amd64 version)
- RedHat 8.6 (x86-64 version)
- RedHat 9.0 (x86-64 version)
The driver has not been well tested on other distros and versions. You may try it out on other distros and versions of your choice.
Feature support and performance
- Vulkan 1.3
- More than 30 extensions
- Radeon™ GPU Profiler tracing
- Built-in debug and profiling tools
- Mid-command buffer preemption and SR-IOV virtualization
The following features and improvements are planned in future releases (Please refer to Release Notes for update of each release):
- Upcoming versions of the Vulkan API
- Hardware performance counter collection through RenderDoc
- LLPC optimizations to improve GPU-limited performance and compile time
- Optimizations to improve CPU-limited performance
How to contribute
You are welcome to submit contributions of code to the AMD Open Source Driver for Vulkan.
The driver is built from source code in four repositories: LLVM, LLPC, XGL, and PAL.
For changes to LLVM, you should submit contributions to the LLVM trunk. Commits there will be evaluated to merge back into the amd-gfx-gpuopen-master branch periodically.
For changes to XGL or PAL, please create a pull request against the dev branch. After your change is reviewed and if it is accepted, it will be evaluated to merge into the master branch in a subsequent regular promotion.
Important By creating a pull request, you agree to allow your contribution to be licensed by the project owners under the terms of the MIT license.
When contributing to XGL and PAL, your code should:
- Match the style of nearby existing code. Your code may be edited to comply with our coding standards when it is merged into the master branch.
- Avoid adding new dependencies, including dependencies on STL.
Please make each contribution reasonably small. If you would like to make a big contribution, like a new feature or extension, please raise an issue first to allow planning to evaluate and review your work.
Important Since PAL is a shared component that must support other APIs, other operating systems, and pre-production hardware, you might be asked to revise your PAL change for reasons that might not be obvious from a pure Linux Vulkan driver perspective.
More information
For more information, including detailed build instructions for both Ubuntu and RedHat Linux, installation instructions, how to get your new driver up and running, runtime settings customisation, and the built-in profiling present in the PAL layer, please head on over to GitHub and check out the README.md in the AMDVLK repository.