- Check Available Version of a Package in Ubuntu
- Apt Cache Command
- Installed
- Candidate
- Aptitude Command
- Bonus Tip
- Wrapping Up
- About the author
- Prateek Jangid
- How can I check the version before installing a package using ‘apt-get’?
- 11 Answers 11
- How can I see all versions of a package that are available in the archive?
- 5 Answers 5
- Output of apt-cache policy nautilus
- Output of apt-cache madison nautilus
Check Available Version of a Package in Ubuntu
There are several ways to determine the version number of an available package in Ubuntu. The command line provides quick access to the available packages in Ubuntu. In this article, we will see how to check the available version of the package in Ubuntu from the command line.
We will explain different methods in this section of checking the Ubuntu package’s available version.
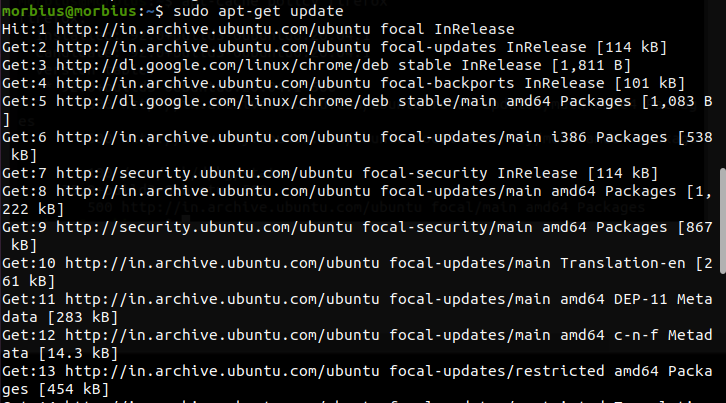
Always make sure to update your system as per the latest version available. So, execute the below command for it:
Now, run the below command to check the available version of the Ubuntu package:
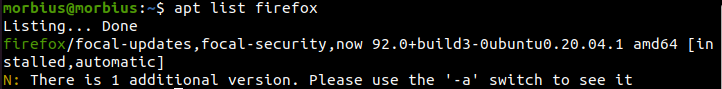
Here, we want to check the available version of firefox using apt-get list available packages. That’s why we have executed the below command:
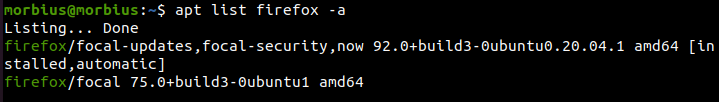
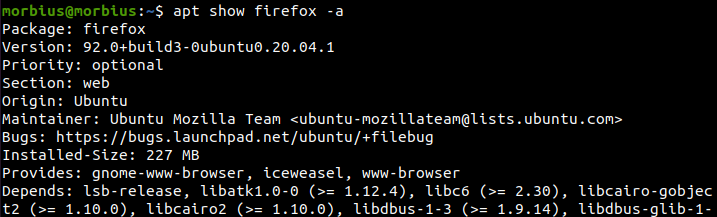
As the above result suggests, we can use ‘-a’ to get the additional version-related information. So we have executed the following command:
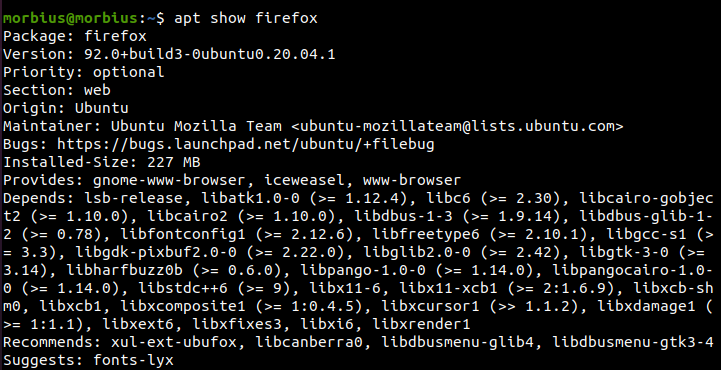
If you need more details about the available package, then use the following command:
Apt Cache Command
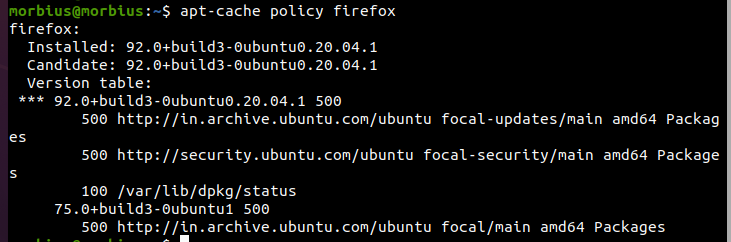
If you want to query the APT cache, then please use this command. Apt-cache command gives an operation to find and create appropriate output from the available package metadata. So, run the below command for it:
For example, we will find out all the available versions of the Firefox web browser from the Ubuntu repository. For this, we get the command run by writing “firefox” instead of “package name” in the above command.
After executing the above command, the system will provide brief details on the available version of the Firefox web browser. Along with this, this command also tells us from which repository this version is coming. The output also provides information on whether the package is installed.
In the above image, there are two words named candidate and install.
Installed
It shows us the version which is currently installed in the Ubuntu system.
Candidate
The candidate shows the package of that version in our Ubuntu system, which is to be installed. This example shows the version that we will install the Firefox browser from the Ubuntu repository using apt-get.
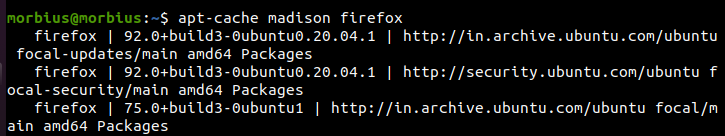
Through another command, we can display the package version from the Ubuntu repository. This command is something like this.
To display the version on the repository, we will run a command like this.
If we compare with the previous command, then this command displays the output in a clean format.
Aptitude Command
Ubuntu doesn’t offer aptitude, so please install it through this command:
Now, check the available version of Firefox using the command given below:
Bonus Tip
This method applies specifically to Ubuntu desktops. Visit the Ubuntu packages website using any web browser. Press the search button after entering the name of the package version.
That’s all we need to do. This will display the installation package version available in the Ubuntu repository.
Wrapping Up
This was a brief overview of how to check the available versions of a package in Ubuntu from the command line. We have used specific examples of the Firefox browser so that our readers can understand better. Please visit our official website to learn more new things about Linux.
About the author
Prateek Jangid
A passionate Linux user for personal and professional reasons, always exploring what is new in the world of Linux and sharing with my readers.
How can I check the version before installing a package using ‘apt-get’?
I’m thinking to install hylafax+ version 5.5.4 which was released last month on my Debian PC. I checked dpkg -l | grep «hylafax» and found out that the current version is 5.5.3. Then I checked apt-cache search hylafax and saw the packages are available, but I can’t see any version number. How can I find the version of packages available in the apt-get ?
11 Answers 11
apt-cache policy will show the version details.
It also shows which version is currently installed and which versions are available to install.
For example, apt-cache policy hylafax+
Can’t believe this isn’t shown in apt install , to give you a chance to review the versions before saying Y .
If we use apt install some packages (may not installed) get install straightaway. So I think for new Linux user its better to use apt policy .
$ apt-cache policy redis-server redis-server: Installed: (none) Candidate: 2:2.8.4-2 Version table: 2:2.8.4-2 0 500 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ trusty/universe amd64 Packages $ apt-get install -s redis-server NOTE: This is only a simulation! apt-get needs root privileges for real execution. Keep also in mind that locking is deactivated, so don't depend on the relevance to the real current situation! Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. Done The following extra packages will be installed: libjemalloc1 redis-tools The following NEW packages will be installed: libjemalloc1 redis-server redis-tools 0 upgraded, 3 newly installed, 0 to remove and 3 not upgraded. Inst libjemalloc1 (3.5.1-2 Ubuntu:14.04/trusty [amd64]) Inst redis-tools (2:2.8.4-2 Ubuntu:14.04/trusty [amd64]) Inst redis-server (2:2.8.4-2 Ubuntu:14.04/trusty [amd64]) Conf libjemalloc1 (3.5.1-2 Ubuntu:14.04/trusty [amd64]) Conf redis-tools (2:2.8.4-2 Ubuntu:14.04/trusty [amd64]) Conf redis-server (2:2.8.4-2 Ubuntu:14.04/trusty [amd64]) $ apt-cache show redis-server Package: redis-server Priority: optional Section: universe/misc Installed-Size: 744 Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers Original-Maintainer: Chris Lamb Architecture: amd64 Source: redis Version: 2:2.8.4-2 Depends: libc6 (>= 2.14), libjemalloc1 (>= 2.1.1), redis-tools (= 2:2.8.4-2), adduser Filename: pool/universe/r/redis/redis-server_2.8.4-2_amd64.deb Size: 267446 MD5sum: 066f3ce93331b876b691df69d11b7e36 SHA1: f7ffbf228cc10aa6ff23ecc16f8c744928d7782e SHA256: 2d273574f134dc0d8d10d41b5eab54114dfcf8b716bad4e6d04ad8452fe1627d Description-en: Persistent key-value database with network interface Redis is a key-value database in a similar vein to memcache but the dataset is non-volatile. Redis additionally provides native support for atomically manipulating and querying data structures such as lists and sets. . The dataset is stored entirely in memory and periodically flushed to disk. Description-md5: 9160ed1405585ab844f8750a9305d33f Homepage: http://redis.io/ Bugs: https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+filebug Origin: Ubunt $ dpkg -l nginx Desired=Unknown/Install/Remove/Purge/Hold | Status=Not/Inst/Conf-files/Unpacked/halF-conf/Half-inst/trig-aWait/Trig-pend |/ Err?=(none)/Reinst-required (Status,Err: uppercase=bad) ||/ Name Version Architecture Description +++-========================================-=========================-=========================-===================================================================================== ii nginx 1.6.2-1~trusty amd64 high performance web server How can I see all versions of a package that are available in the archive?
Is there a way I can see all the versions that are in the archives that I have configured in sources.list. I can see the last version of each archive with apt-get policy , but how can I see them all? Is there any way that this can also include PPA and anything in sources.list.d?
5 Answers 5
As far as I understand your requirements, the madison option for apt-cache does what you want:
madison /[ pkg(s) ]
apt-cache’s madison command attempts to mimic the output format and a subset of the functionality of the Debian archive management tool, madison. It displays available versions of a package in a tabular format. Unlike the original madison, it can only display information for the architecture for which APT has retrieved package lists (APT::Architecture).
$ apt-cache madison f-spot f-spot | 0.7.2-1~ppa~lucid0 | http://ppa.launchpad.net/f-spot/f-spot-ppa/ubuntu/ lucid/main Packages f-spot | 0.6.1.5-2ubuntu7 | http://ro.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ lucid-updates/main Packages f-spot | 0.6.1.5-2ubuntu6 | http://ro.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ lucid/main Packages f-spot | 0.6.1.5-2ubuntu6 | http://ro.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ lucid/main Sources f-spot | 0.6.1.5-2ubuntu7 | http://ro.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ lucid-updates/main Sources I hope this is what you need. It also includes the ppas.
The command apt list -a
Ancient Unix lingo really needs to die. In the modern day, we should be focused on user experience. The concept of a geeky «sysadmin» is antiquated and no longer relevant.
is the equivalent of madison.
Can second, I like the output this command produces. I just want to know the version numbers available to me, I don’t need all the additional information and warnings and messaging.
The rmadison program from the devscripts package will remotely query the Ubuntu archive and give you the status of a package in all supported releases, not only those you have locally insatlled. This is slightly more than what you want, but should get the job done easily.
lfaraone@stone:~$ rmadison sudo sudo | 1.6.8p12-1ubuntu6 | dapper | source, amd64, i386, powerpc sudo | 1.6.8p12-1ubuntu6.3 | dapper-security | source, amd64, i386, powerpc sudo | 1.6.8p12-1ubuntu6.3 | dapper-updates | source, amd64, i386, powerpc sudo | 1.6.9p10-1ubuntu3 | hardy | source, amd64, i386 sudo | 1.6.9p10-1ubuntu3.8 | hardy-security | source, amd64, i386 sudo | 1.6.9p10-1ubuntu3.8 | hardy-updates | source, amd64, i386 sudo | 1.6.9p17-1ubuntu3 | jaunty | source, amd64, i386 sudo | 1.6.9p17-1ubuntu3.3 | jaunty-security | source, amd64, i386 sudo | 1.6.9p17-1ubuntu3.3 | jaunty-updates | source, amd64, i386 sudo | 1.7.0-1ubuntu2 | karmic | source, amd64, i386 sudo | 1.7.0-1ubuntu2.4 | karmic-security | source, amd64, i386 sudo | 1.7.0-1ubuntu2.4 | karmic-updates | source, amd64, i386 sudo | 1.7.2p1-1ubuntu5 | lucid | source, amd64, i386 sudo | 1.7.2p1-1ubuntu5.1 | lucid-security | source, amd64, i386 sudo | 1.7.2p1-1ubuntu5.1 | lucid-updates | source, amd64, i386 sudo | 1.7.2p7-1ubuntu1 | maverick | source, amd64, i386 before you can use rmadison you must install the devscripts package:
sudo apt-get install devscripts Very nice! But it also doesn’t show unsupported packages, which are still available at old-releases.ubuntu.com I’ve asked about that at Information on package versions from old releases? — Ask Ubuntu — Stack Exchange
rmadison ffmpeg currently shows 14 lines of results, including «7:4.1.3-0ubuntu1», which is what I’m interested in ( launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/ffmpeg/7:4.1.3-0ubuntu1 ) But then sudo apt install ffmpeg=7:4.1.3-0ubuntu1 results in: «Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. Done E: Version ‘7:4.1.3-0ubuntu1’ for ‘ffmpeg’ was not found»
I don’t know how (or why) you said apt-cache policy doesn’t show all versions! I’m using this for several years now and It always showed all versions including the priority number.
Output of apt-cache policy nautilus
nautilus: Installed: 1:3.18.5-0ubuntu1~xenial1 Candidate: 1:3.18.5-0ubuntu1~xenial1 Version table: *** 1:3.18.5-0ubuntu1~xenial1 500 500 file:/media/Linux/apt-repo/xenial1 Packages 500 http://ppa.launchpad.net/budgie-remix/ppa/ubuntu xenial/main amd64 Packages 500 http://ppa.launchpad.net/gnome3-team/gnome3/ubuntu xenial/main amd64 Packages 100 /var/lib/dpkg/status 1:3.18.4.is.3.14.3-0ubuntu5 500 500 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-updates/main amd64 Packages 1:3.18.4.is.3.14.3-0ubuntu4 500 500 file:/media/Linux/apt-repo/xenial1 Packages 500 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial/main amd64 Packages 1:3.14.2-0ubuntu13 500 500 file:/media/Linux/apt-repo/wily Packages Output of apt-cache madison nautilus
nautilus | 1:3.18.5-0ubuntu1~xenial1 | file:/media/Linux/apt-repo/xenial1 Packages nautilus | 1:3.18.5-0ubuntu1~xenial1 | http://ppa.launchpad.net/budgie-remix/ppa/ubuntu xenial/main amd64 Packages nautilus | 1:3.18.5-0ubuntu1~xenial1 | http://ppa.launchpad.net/gnome3-team/gnome3/ubuntu xenial/main amd64 Packages nautilus | 1:3.18.4.is.3.14.3-0ubuntu5 | http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-updates/main amd64 Packages nautilus | 1:3.18.4.is.3.14.3-0ubuntu4 | file:/media/Linux/apt-repo/xenial1 Packages nautilus | 1:3.18.4.is.3.14.3-0ubuntu4 | http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial/main amd64 Packages nautilus | 1:3.14.2-0ubuntu13 | file:/media/Linux/apt-repo/wily Packages Only difference is that madison took some more time than policy and shorter version. But, policy is more useful to see which version get installed, which version is next candidate to be installed.
That’s why I’d suggest always using apt-cache policy instead.
Note about output: I have some local repository setup and both of the command shows those as well.
Note 2 Newer apt comes with policy integrated into them. So, you can use apt instead of apt-cache directly.