- How to Install netstat Command in Linux
- How to Install netstat Command in Linux
- How to Use netstat Command in Linux
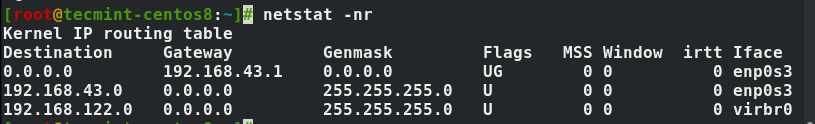
- 1. Viewing the Network Routing Table
- 2. Display Network Interface Statistics
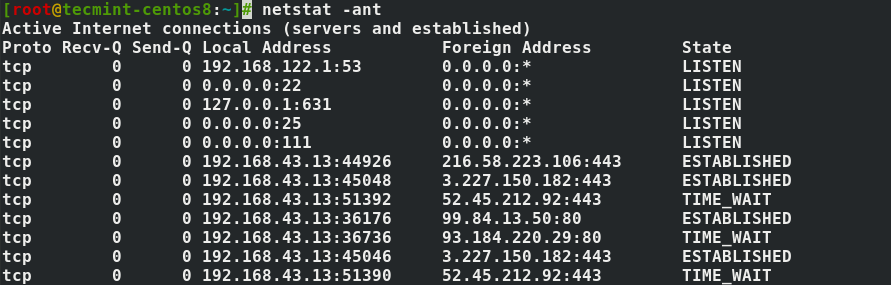
- 3. Show Network Connections
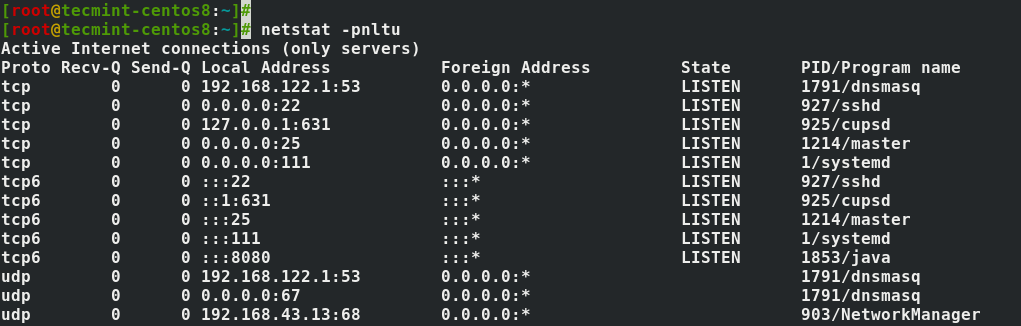
- 4. Show Network Services
- How to Install and Use Netstat on Linux (CentOS/RHEL, Debian/Ubuntu, OpenSuse & Arch Linux)
- Why Use Netstat?
- How to Install Netstat on Linux (CentOS/RHEL, Debian/Ubuntu, OpenSuse)
- How to Install Netstat on CentOS/RHEL
- How to Install Netstat on Debian/Ubuntu
- How to Install Netstat on OpenSuse
- How to Install Netstat on Arch Linux
- How to Use Netstat
- Common Netstat Commands
- Conclusion
- Install netstat on Debian 11
- Symptom:
How to Install netstat Command in Linux
Netstat – derived from the words network and statistics – is a command-line utility used by system administrators for analyzing network statistics. It displays a whole manner of statistics such as open ports and corresponding addresses on the host system, routing table, and masquerade connections.
In this article, we will walk you through how you can install the netstat command in different Linux distributions.
How to Install netstat Command in Linux
The package that contains netstat is called net-tools. On modern systems, the netstat utility comes pre-installed and there’s no need to install it.
On older systems, however, you are likely to bump into an error when you run the netstat command. Therefore, to install netstat on Linux distributions, run the command.
# yum install net-tools [On CentOS/RHEL] # apt install net-tools [On Debian/Ubuntu] # zypper install net-tools [On OpenSuse] # pacman -S net-tools [On Arch Linux]
Once installed, run the command below to check the version of netstat installed.
How to Use netstat Command in Linux
You can invoke the netstat command on any of the Linux distributions to get different statistics on your network.
1. Viewing the Network Routing Table
You use the -r flag to show the network routing table to get something similar to the output below.
The -n option forces netstat to print addresses separated by dots instead of using symbolic network names. The option is useful for avoiding address lookups over a network.
2. Display Network Interface Statistics
Use the -i flag to get an output of statistics of a network interface that is configured. The -a option prints all present interfaces in the kernel.
3. Show Network Connections
The netstat command utility supports options that display active or passive sockets using the options -t , -n , and -a . The flags show RAW, UDP, TCP, or UNIX connection sockets. Adding the -a option, it will sow sockets ready for connection.
4. Show Network Services
To list services, their current state, and their corresponding ports, run the command.
In this article, we shed light on how you can install netstat command and how it is used to checking a wide array of network statistics. It’s also important to point out that netstat has been deprecated and instead ss utility has taken its place in displaying more refined network statistics.
How to Install and Use Netstat on Linux (CentOS/RHEL, Debian/Ubuntu, OpenSuse & Arch Linux)
This article provides a tutorial on how to install and use Netstat, a command-line network tool, on Linux.
Netstat is a command-line utility that can be used to view network connections, routing tables, and a variety of other network-related information on Linux systems. While Netstat is typically used to troubleshoot network issues, it can also be used for tasks such as monitoring server traffic or checking which ports are open on a system.
Why Use Netstat?
Netstat is a network monitoring tool that can be used to view detailed information about network connections and statistics. This information can be useful for troubleshooting network problems, or for simply understanding what your system is doing. Netstat can be installed on most Linux distributions using the package manager. Once installed, it can be invoked from the command line with the “netstat” command.
How to Install Netstat on Linux (CentOS/RHEL, Debian/Ubuntu, OpenSuse)
How to Install Netstat on CentOS/RHEL
- 1. To install Netstat on a CentOS or RHEL system, first ensure that the EPEL repository is enabled. You can do this by running the following command:
How to Install Netstat on Debian/Ubuntu
sudo apt install net-tools -y
How to Install Netstat on OpenSuse
sudo zypper in net-tools -y
How to Install Netstat on Arch Linux
Once the installation is complete, you can verify that Netstat is working by running the ‘netstat’ command
How to Use Netstat
Netstat is a powerful command line tool that can be used to view all of the network connections on a computer. The netstat command can also be used to view summary statistics, monitor network traffic in real time, and more.
The syntax for the netstat command is as follows:
Some of the most common options for the netstat command are listed below:
- -a : Shows all active connections and listening ports.
- -n : Displays information using numerical IP addresses instead of hostnames. This can be useful for troubleshooting DNS issues.
- -r : Displays the kernel routing table.
- -s : Shows summary statistics by protocol type.
Common Netstat Commands
The most common use for netstat is to view all open network connections and listening ports. This can be done with the following command:
This will display all active internet connections as well as any open ports that are being listened to.
Netstat can also be used to view specific network protocol statistics. This can be done with the following command:
This will show statistics for each of the different protocols that are being used on the machine. This can be helpful in troubleshooting network issues.
The netstat command can also be used to view routing table information. This can be done with the following command:
This will show the route that packets will take when traveling to different destinations. This can be helpful in troubleshooting networking issues or determining the best route for traffic.
Conclusion
Netstat is a powerful tool that can be used to troubleshoot network issues on your Linux server. In this article, we’ve shown you how to install and use Netstat on Linux. We hope you find this tool helpful in your work.
Install netstat on Debian 11
Like all packages belonging to the net-tools collection, the command netstat isn’t included in new Linux distributions such as Debian 11. This tutorial explains how to add the netstat command on Debian 11, its predecessors, and based Linux distributions such as Ubuntu.
Symptom:
When trying to run netstat, you get the error shown in the screenshot below.
bash: / usr / bin / netstat: No such file or directory
Now you are able to run netstat, as shown in the screenshot below.
As you can see now, the output shows the IP of remote devices instead of their hostnames.
The following example shows how to display only TCP connections by adding the -t flag.
Running netstat with the -p flag, you will see a new column named PID/Program name. Under this column, you can see the processes or programs establishing connections.
The -s flag is used to print summary statistics for each protocol, as shown in the screenshot below.
And you can combine the -s flag with -u for statistics on UDP connections, as shown below.
Finally, to end this tutorial, you can print IPv6 information using the -g flag, as shown in the image below.